4. DQL query data (the most important)
4.1 DQL
(date query language: Data Query Language)
- All query operations use it, select
- Simple queries and complex queries are available
- The core language and the most important statement in the database
- Most frequently used statements
select[ALL | DISTINCT]
{ * | TABLE.* | [table.field1[as alias1][,table.field2[as alias2]][,...]]}
from table_name [as table_alias]
[left | right | inner join table_name2] -- Joint query
[where...] -- Specify the conditions to be met
[group by ...] -- Specify which fields the results need to be grouped by
[having] -- Secondary conditions that must be met to filter grouped records
[order by ...] -- Specifies that query records are sorted by one or more criteria
[limit {[offset,]row_count | row_countOFFSET offset}]; -- Specify which records to query from
4.2 specify a field to query
-- Query all students select field from Table name
select * from student
-- Query specified fields
select `studentNo`,`studentName` from student
-- Alias, give the result a name AS
-- You can alias fields or tables
SELECT `name` AS full name,`gender` AS Gender FROM student
-- function concat(a,b)
SELECT CONCAT('name:',`name`) AS New name FROM student
Syntax: select field... from table
Sometimes, column names are not so well-known, and can be aliased (AS)
Field name as alias, table name as alias
Remove duplicate distinct: remove the duplicate data in the select query result, and only one duplicate data is displayed
-- Find out which students took the exam and got good grades SELECT * FROM result -- Query all test scores SELECT `studentNo` FROM result -- Check which students took the exam SELECT DISTINCT `StudentNo` FROM result -- Duplicate data found, de duplication
Database columns (expressions)
-- Query System Version (function) SELECT VERSION() -- Used to evaluate (an expression) SELECT 100*3-6 AS Calculation results -- Query self increasing step size (variable) SELECT @@auto_increment_increment -- Student examination results+1 Sub view SELECT `studentNo`,`studentResult`+1 AS 'After scoring' FROM result
4.3 where conditional clause
Function: retrieve qualified values in data
Logical operator
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| and && | a and b a&&b | And |
| or || | a or b a||b | or |
| not ! | not a !a | wrong |
-- =========== where ==================== -- The query test score is 95~100 Between points SELECT `studentNo`,`StudentResult` FROM result WHERE StudentResult>=95 AND StudentResult<=100 SELECT `studentNo`,`StudentResult` FROM result WHERE StudentResult>=95 && StudentResult<=100 -- Fuzzy query (interval) SELECT `studentNo`,`StudentResult` FROM result WHERE StudentResult BETWEEN 95 AND 100 -- Grades of departments other than student 1000 SELECT `studentNo`, `StudentResult` FROM result WHERE studentNo!=1000; SELECT `studentNo`, `StudentResult` FROM result WHERE NOT studentNo=1000;
Fuzzy queries: comparison operators
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| IS NULL | a is null | The operator is null and the result is true |
| IS NOT NULL | a is not null | The operator is not empty and the result is true |
| between | a between b and c | Between a and b and c, the result is true |
| like | a like b | sql matches. If a matches b, the result is true |
| in | a in(a1,a2,a3...) | If a is one of a1, a2, a3... The result is true |
-- ================ Fuzzy query ========================
-- Inquire about students surnamed Liu
-- like combination %(Represents 0 to any character) _(1 (characters)
SELECT `name`, `major` FROM student
WHERE `name` LIKE 'Liu%'
-- Query students surnamed Liu. There is only one word after their surname
SELECT `name`, `major` FROM student
WHERE `name` LIKE 'Liu_'
-- Query students surnamed Liu. There are only two words after their surname
SELECT `name`, `major` FROM student
WHERE `name` LIKE 'Liu__'
-- Check the students with strange names in the middle,%odd%
SELECT `name`, `major` FROM student
WHERE `name` LIKE '%odd%'
-- Query 15,18,24 Student No
SELECT `id`,`name` FROM student
WHERE `id` IN (15,18,24)
-- Inquire about students in Hougang
SELECT `id`,`name`,`address` FROM student
WHERE `address` IN ('Hougang town','Lishi town')
-- =========null , not null ====================
-- Query students with empty address null ''
SELECT `StudentNo`, `StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE address='' OR address IS NULL
-- Query students with birth date cannot be blank
SELECT `studentNo`, `studentName` FROM `student`
WHERE `BornDate` IS NOT NULL
-- It is blank to query students without birth date
SELECT `StudentNo`, `StudentName` FROM `student`
WHERE `BornDate` IS NULL
4.4 associated table query
JOIN comparison
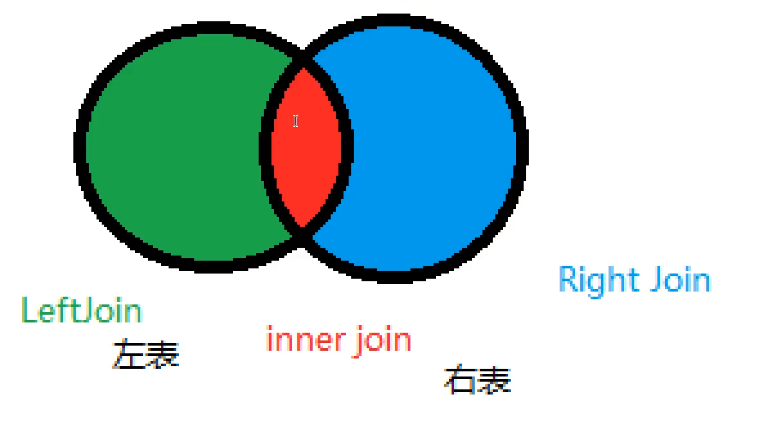
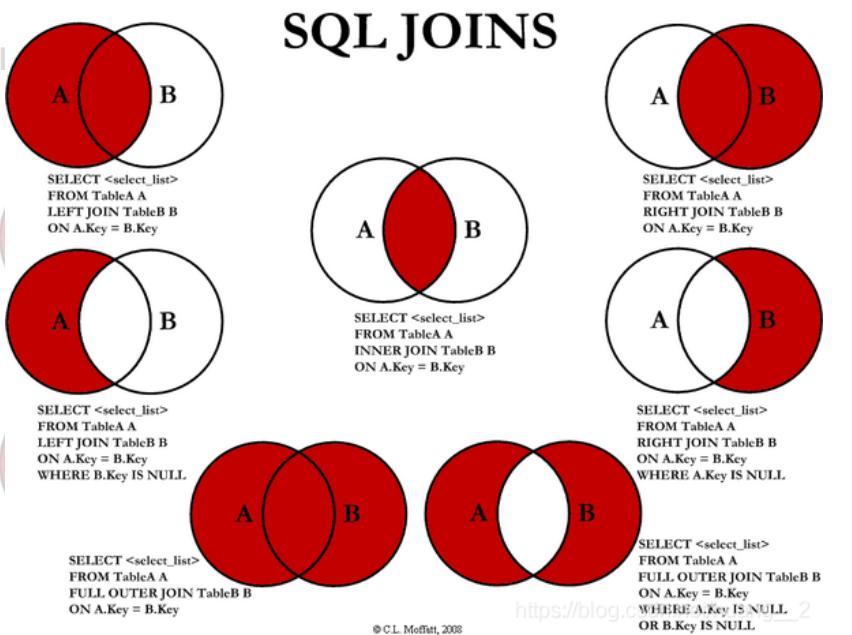
-- =================== Join table query join ================ -- Query the students who took the exam (student number, name, subject number, score)) SELECT * FROM student SELECT * FROM result /*thinking 1.Analyze the requirements, and analyze which tables the query fields come from (connection query) 2.Determine which connection query to use? 7 kinds Determine the intersection (which data is the same in the two tables) Conditions for judgment: studentNo in the student table = studentNo in the grade table */ -- JOIN (Connected tables) ON(Judged conditions) connection query -- where Equivalent query -- INNER JOIN SELECT s.studentNO , studentName , subjectNo,StudentResult FROM student AS s INNER JOIN result AS r ON s.studentNO = r.studentNO -- RIGHT JOIN // student is the left table and result is the right table SELECT s.studentNO , studentName , subjectNo,StudentResult FROM student AS s RIGHT JOIN result AS r ON s.studentNO = r.studentNO -- LEFT JOIN // student is the left table and result is the right table SELECT s.studentNO , studentName , subjectNo,StudentResult FROM student AS s LEFT JOIN result AS r ON s.studentNO = r.studentNO -- Query absent students SELECT s.studentNO , studentName , subjectNo,StudentResult FROM student AS s LEFT JOIN result AS r ON s.studentNO = r.studentNO WHERE StudentResult IS NULL
| operation | describe |
|---|---|
| inner join | If there is at least one match in the table, the row is returned |
| left join | All values will be returned from the left table, even if there is no match in the right table |
| right join | All values will be returned from the right table, even if there is no match in the left table |
-- Thinking questions (query the information of students participating in the exam):Student number, student name, subject name, score) /*thinking 1.Analyze the requirements, analyze which tables the query fields come from, student, result, subject (connection query) 2.Determine which connection query to use? 7 kinds Determine the intersection (which data is the same in both tables) > Conditions for judgment: studentNo in student table = studentNo in grade table */ SELECT s.studentNo,studentName,SubjectNo,`StudentResult` FROM student s RIGHT JOIN result r ON r.studentNo = s.studentNo INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.SubjectNo = sub.SubjectNo -- What data do I want to query select... -- Look it up from those tables from surface XXX JOIN Connected tables ON Cross condition -- Suppose there is a multi table query. Take your time. Query two tables first and then add them slowly -- FROM A LEFT JOIN B -- FROM A RIGHT JOIN B
Self connection: connect your own table with your own table. Core: split one table into two identical tables
[the external chain image transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the image and upload it directly (img-rrb0bzvv-1641611984843) (C: \ users \ Lenovo \ appdata \ roaming \ typora user images \ image-20220105211321715. PNG)]
Parent class:
| categoryid | categoryName |
|---|---|
| 2 | information technology |
| 3 | software development |
| 5 | Art design |
Subclass:
| categoryid | categoryName | pid |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | database | 3 |
| 8 | Office information | 2 |
| 6 | web development | 3 |
| 7 | ps Technology | 5 |
Operation: query the subclass relationship corresponding to the parent class
| Parent class | Subclass |
|---|---|
| information technology | Office information |
| software development | database |
| software development | web development |
| Art design | ps Technology |
4.5 paging and sorting
sort
-- ============ paging limit And sorting order by =============== -- Sorting: ascending ASC ,Descending order DESC -- Query results are sorted in descending order according to scores SELECT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`,`SubjectName`,`StudentResult` FROM student s INNER JOIN `result` r ON s.StudentNo = r.Student INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`SubjectNo` = sub.`SubjectNo` WHERE subjectName = 'data structure' ORDER BY StudentResult DESC -- Sort by grades in descending order ORDER BY StudentResult ASC -- Sort in ascending order according to grades
Pagination:
-- Why pagination? -- Ease the pressure of the database and give people a better experience, waterfall flow -- Pagination: only five pieces of data are displayed on each page -- Syntax: limit Starting value, page size -- Web application: current, total pages, page size -- limit 0,5 The first to fifth data are displayed -- limit 1,5 The second to sixth data are displayed SELECT s.`StudentNo`,`StudentName`,`SubjectName`,`StudentResult` FROM student s INNER JOIN `result` r ON s.StudentNo = r.Student INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`SubjectNo` = sub.`SubjectNo` WHERE subjectName = 'data structure' ORDER BY StudentResult DESC -- Sort by grades in descending order LIMIT 0,5 -- first page limit 0,5 (1-1)*5 -- Page 2 limit 5,5 (2-1)*5 -- Page 3 limit 10,5 (3-1)*5 -- The first n page limit (n-1)*5,5 (n-1)* pagesize , pagesize -- [pagesize: [page size] -- [(n-1)*pagesize: Starting value] -- [n: Current page] -- [Total data/Page size=Number of pages]
Syntax: limit starting subscript, page size
-- query JAVA Information of the students with the top ten course scores in the first academic year and a score greater than 80 (student number, name, course name, score) SELECT `studentNo`,`studentname`,`subjectname`,`subjectresult` FROM `student` s INNER JOIN `result` r ON s.studentNo = r.studentNo INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON sub.`subjectNo` = r.`subjectNo` WHERE subjectname = 'java First academic year' AND `subjectresult` >= 80 ORDER BY studentresult DESC LIMIT 0,10
4.6 sub query
where (this value is calculated)
Essence: nest a query statement within a where statement
where (select * from)
-- ====================== where ====================== -- 1.Query all test results (student number, subject number, score) in the database structure and arrange them in descending order -- Method 1: connection query SELECT `studentno`,`subjectname`,`studentresult` FROM `result` r INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`subjectno` = sub.`subjectno` WHERE `subjectname` = 'database structure ' ORDER BY sutdentresult DESC -- Method 2: sub query () SELECT `studentno`,`subjectname`,`studentresult` FROM `result` r WHERE studentno = ( SELECT studentno FROM `subject` WHERE `subjectname` = 'database structure ' ) ORDER BY `studentresult` DESC -- Query student numbers of all database structures SELECT studentno FROM `subject` WHERE `subjectname` = 'database structure ' -- Student number and name of students with a score of no less than 80 SELECT s.`studentNo`,`studentName` FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON r.studentNo = s.studentNo WHERE `studentResult`>=80 -- Query the student number and name of students whose course is advanced mathematics and whose score is not less than 80 SELECT DISTINCT s. `studentNo`, `studentName` FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON r.studentNo = s.studentNo WHERE `studentResult`>=80 AND `SubjectNo`= ( SELECT subjectNo FROM `subject` WHERE `subjectName`='Advanced mathematics' ) SELECT s.studentNo, studentName FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON s.studentNo = r.studentNo work NNERJOIN`subject` sub ON r.`subjectNo` = sub.`subjectNo` WHERE `subjectName`='Advanced mathematics' AND StudentResult>=80