Introduction: Drawing a 3D surface of a two-dimensional function can help us better understand the rules contained in the function. Axes3D is a drawing function in matplotlib. surface, countour,countourf, and so on can be used to display function 3D content very well.
Keywords: Axes3D, surface, contour, II
_01 Draw a surface
_Many times it is necessary to draw three-dimensional surface, such as drawing two-dimensional function values, optimizing the slice projection of the problem on two-dimensional, and so on. adopt Drawing meshgrid functions in classification interfaces and performance surfaces Or two-dimensional grid points can be calculated to draw three-dimensional surfaces and contours using surface, contour, and other functions.
1. Drawing Examples
1. Test Code
from headm import * #
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
x = arange(-4, 4, 0.1)
y = arange(-4, 4, 0.1)
x,y = meshgrid(x, y)
r = sqrt(x**2+y**2)
z = sin(r)
printt(z.shape\)
ax = Axes3D(plt.figure(figsize=(12,8)))
ax.plot_surface(x,y,z,rstride=1, cstride=2, cmap=plt.cm.hot)
ax.contour(x,y,z,
zdir='z',
offset=-2,
cmap=plt.cm.hot)
ax.set_zlim(-2,2)
plt.show()
2. Test results
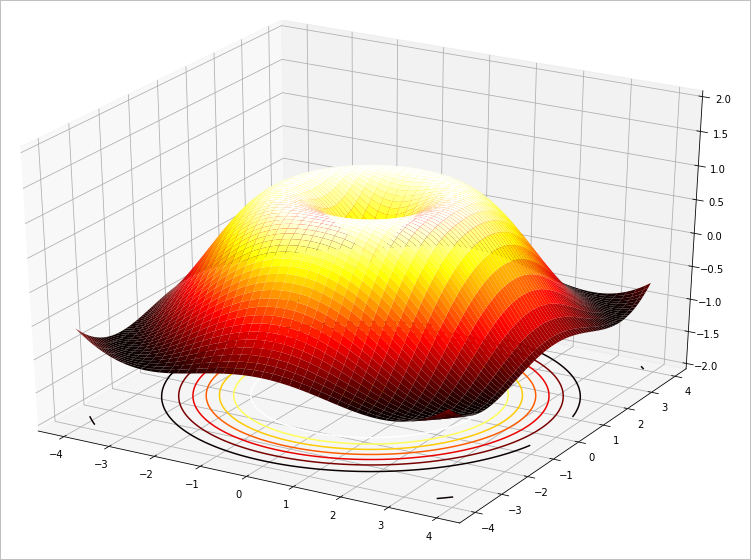
z.shape:(80, 80)
2. Color parameters
stay Python Visualization | matplotlib07 - Colormap with its own color bar (3) The various combinations of CMAPs are given.
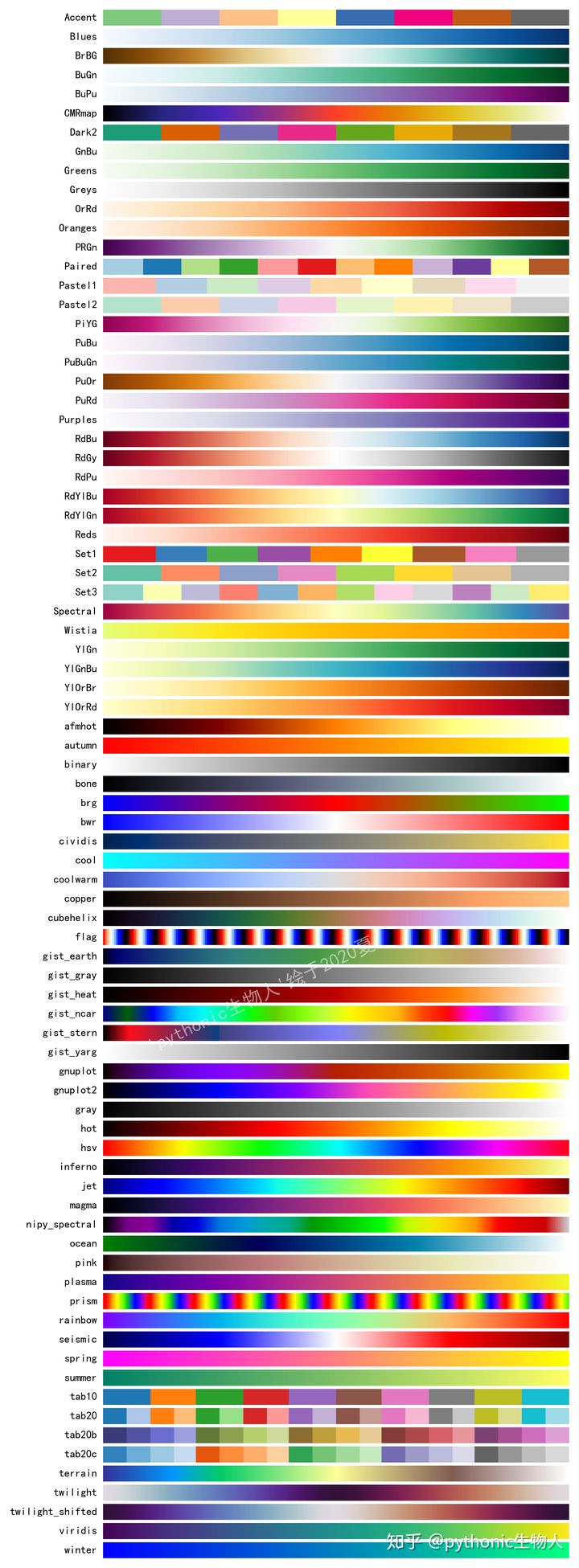
1. Color Name
['Accent', 'Blues', 'BrBG', 'BuGn', 'BuPu', 'CMRmap', 'Dark2', 'GnBu', 'Greens', 'Greys', 'OrRd', 'Oranges', 'PRGn', 'Paired', 'Pastel1', 'Pastel2', 'PiYG', 'PuBu', 'PuBuGn', 'PuOr', 'PuRd', 'Purples', 'RdBu', 'RdGy', 'RdPu', 'RdYlBu', 'RdYlGn', 'Reds', 'Set1', 'Set2', 'Set3', 'Spectral', 'Wistia', 'YlGn', 'YlGnBu', 'YlOrBr', 'YlOrRd', 'afmhot', 'autumn', 'binary', 'bone', 'brg', 'bwr', 'cividis', 'cool', 'coolwarm', 'copper', 'cubehelix', 'flag', 'gist_earth', 'gist_gray', 'gist_heat', 'gist_ncar', 'gist_stern', 'gist_yarg', 'gnuplot', 'gnuplot2', 'gray', 'hot', 'hsv', 'inferno', 'jet', 'magma', 'nipy_spectral', 'ocean', 'pink', 'plasma', 'prism', 'rainbow', 'seismic', 'spring', 'summer', 'tab10', 'tab20', 'tab20b', 'tab20c', 'terrain', 'twilight', 'twilight_shifted', 'viridis', 'winter']
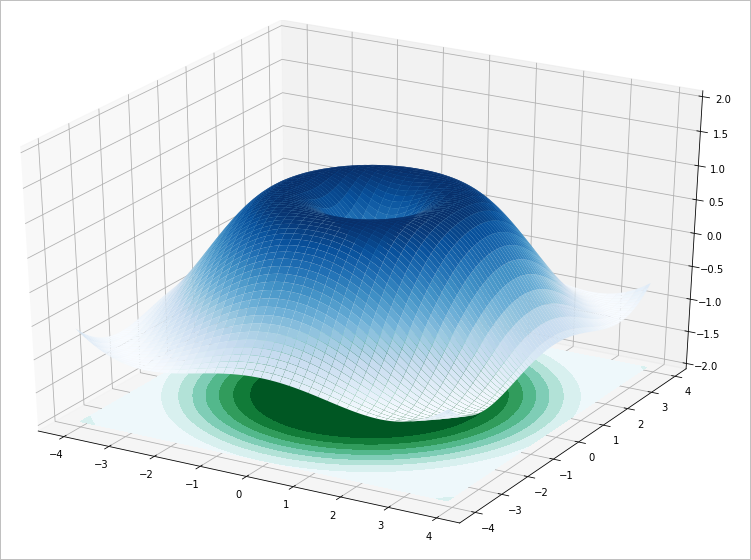
2. Change color
ax.plot_surface(x,y,z,rstride=1, cstride=2, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
ax.contourf(x,y,z,
zdir='z',
offset=-2,
cmap=plt.cm.BuGn)
_02 More examples
1. Combination of resistors
_In Read multiple buttons through one port When searching for multiple resistor parallel switches, the corresponding maximum voltage interval. You can see that the peaks are very complex. The following searches for a combination of two resistors to draw a performance surface.
1. Search Code
R0 = 1e3
U0 = 3.3
def minVoltage(r1,r2):
rdim = [10e10, r1, r2,
1/(1/r1 + 1/r2)]
vdim = sorted([r/(r+R0)*U0 for r in rdim])
vdiff = [b-a for a,b in zip(vdim[:-1], vdim[1:])]
vdiff.append(vdim[0])
return min(vdiff)
STEP_NUM = 50
x = arange(100, 10000, STEP_NUM)
y = arange(100, 10000, STEP_NUM)
x,y = meshgrid(x, y)
z = array([minVoltage(x,y) for x,y in zip(x.flatten(), y.flatten())]).reshape(x.shape)
2. Search results
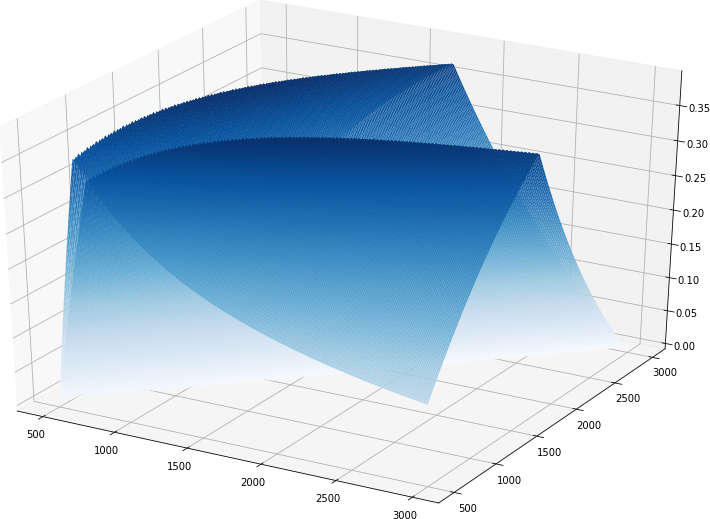
(1) Search scope: 100:10000:50
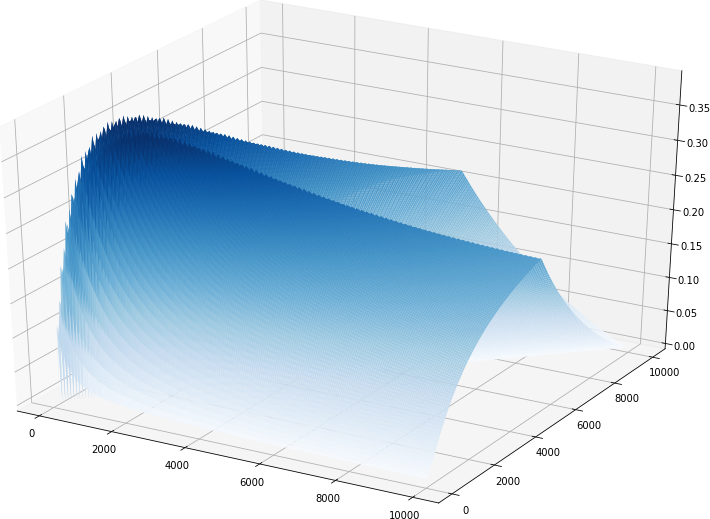
(2) Search range: 500:3000:10
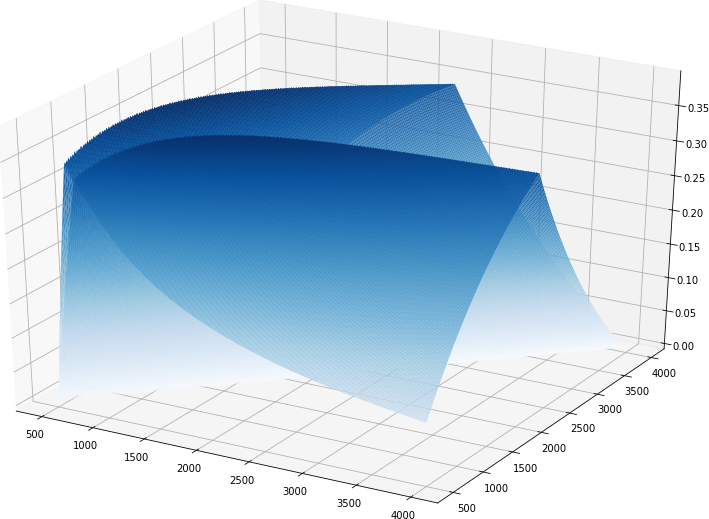
(3) Search range: 500:4000:10
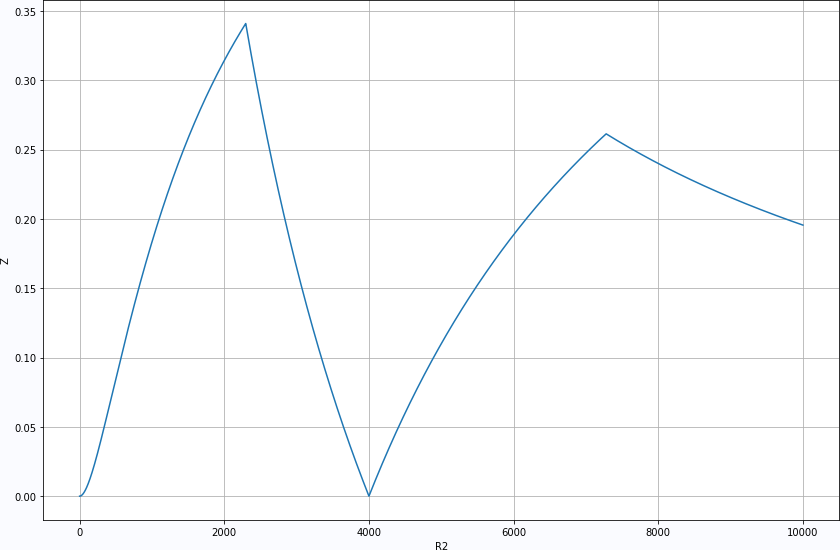
3. Slice to one dimension
R1 = 4e3
R2 = linspace(0, 10000, 10000)
z = [minVoltage(R1, r2) for r2 in R2]
plt.clf()
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.plot(R2, z)
plt.xlabel("R2")
plt.ylabel("Z")
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
2. 2-D Nonlinear Functions
f = 10 4 x 1 2 − 2.1 x 1 4 + 1 3 x 1 6 + x 1 x 2 − 4 x 2 2 + 4 x 2 2 + 2 f = {{10} \over {4x_1^2 - 2.1x_1^4 + {1 \over 3}x_1^6 + x_1 x_2 - 4x_2^2 + 4x_2^2 + 2}} f=4x12−2.1x14+31x16+x1x2−4x22+4x22+210
x = arange(-4, 4, 0.1)
y = arange(-2, 2, 0.1)
x,y = meshgrid(x,y)
z = 10/(4*x**2 - 2.1*x**4 + x**6/3 + x*y - 4*y**2+4*y**4 + 2)
print(z.shape)
ax = Axes3D(plt.figure(figsize=(12,8)))
ax.plot_surface(x,y,z,
rstride=1,
cstride=1,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.show()
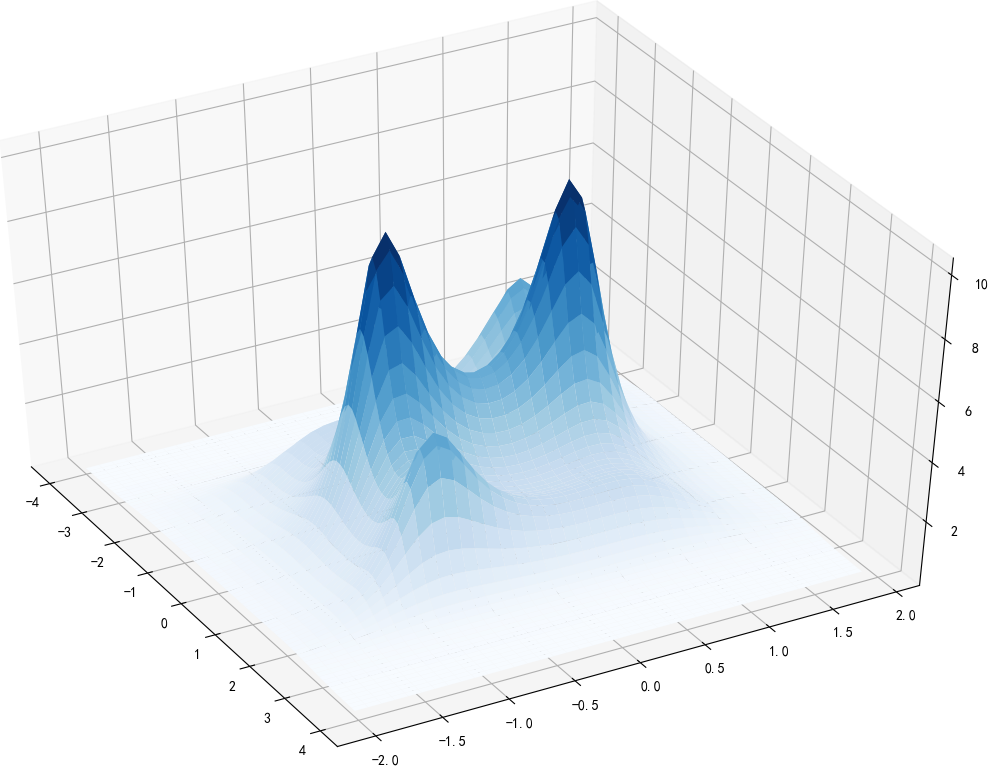
_total_knot_
_Drawing a 3D surface of a two-dimensional function can help us better understand the rules contained in the function. Axes3D is a drawing function in matplotlib. surface, countour,countourf, and so on can be used to display function 3D content very well.
Links to related literature:
- Drawing meshgrid functions in classification interfaces and performance surfaces
- Python Visualization | matplotlib07 - Colormap with its own color bar (3)
- Read multiple buttons through one port
Related chart links:
- Figure 1.1.1 depicts the z-dimensional function
- Figure 1.2.1 colormap
- Figure 1.2.2 Altitude after color change
- Figure 2.1.1 Search performance curves for R1,R2
- Figure 2.1.2 Searches for R1,R2 performance curves
- Figure 2.1.3 Searches for R1,R2 performance curves
- Figure 2.1.4 R2 corresponding maximum voltage
- Figure 2.2.1 Drawn 3D Image