Related concepts
Stand alone & cluster
When a single Elasticsearch server provides services, it often has the maximum load capacity. If it exceeds this threshold, the server performance will be greatly reduced or even unavailable. Therefore, in the production environment, it usually runs in the specified server cluster.
In addition to load capacity, single point servers also have other problems:
- Limited storage capacity of a single machine
- Single server is prone to single point of failure and cannot achieve high availability
- The concurrent processing capability of single service is limited
When configuring a server cluster, there is no limit on the number of nodes in the cluster. If there are more than or equal to 2 nodes, it can be regarded as a cluster. Generally, considering high performance and high availability, the number of nodes in the cluster is more than 3.
Cluster cluster
A cluster is organized by one or more server nodes to jointly hold the whole data and provide indexing and search functions together. An elasticsearch cluster has a unique name ID, which is "elasticsearch" by default. This name is important because a node can only join a cluster by specifying the name of the cluster
Node node
The cluster contains many servers, and a node is one of them. As a part of the cluster, it stores data and participates in the indexing and search functions of the cluster.
A node is also identified by a name. By default, this name is the name of a random Marvel comic character, which will be given to the node at startup. This name is very important for management, because in this management process, you will determine which servers in the network correspond to which nodes in the Elasticsearch cluster.
A node can join a specified cluster by configuring the cluster name. By default, each node is scheduled to join a cluster called "elasticsearch", which means that if you start several nodes in your network and assume that they can find each other, they will automatically form and join a cluster called "elasticsearch".
In a cluster, you can have as many nodes as you want. Moreover, if there is no elasticsearch node running in your network, start a node at this time, and a cluster called "elasticsearch" will be created and joined by default.
colony
Deployment cluster
Create the elasticsearch cluster folder and copy three elasticsearch services internally
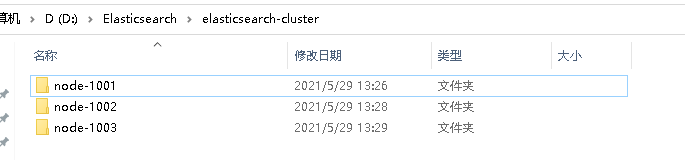
Modify config / elasticsearch. For each node in the cluster file directory YML profile
node-1001 node
#Configuration information of node 1: #Cluster name and nodes should be consistent cluster.name: my-elasticsearch #The node name should be unique in the cluster node.name: node-1001 node.master: true node.data: true #ip address network.host: localhost #http port http.port: 1001 #tcp listening port transport.tcp.port: 9301 #discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost:9301", "localhost:9302","localhost:9303"] #discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m #discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5 #List of nodes in the cluster that can be selected as the master node #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2","node-3"] #Cross domain configuration #action.destructive_requires_name: true http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
node-1002 node
#Configuration information of node 2: #Cluster name and nodes should be consistent cluster.name: my-elasticsearch #The node name should be unique in the cluster node.name: node-1002 node.master: true node.data: true #ip address network.host: localhost #http port http.port: 1002 #tcp listening port transport.tcp.port: 9302 discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost:9301"] discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5 #List of nodes in the cluster that can be selected as the master node #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2","node-3"] #Cross domain configuration #action.destructive_requires_name: true http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
node-1003 node
#Configuration information of node 3: #Cluster name and nodes should be consistent cluster.name: my-elasticsearch #The node name should be unique in the cluster node.name: node-1003 node.master: true node.data: true #ip address network.host: localhost #http port http.port: 1003 #tcp listening port transport.tcp.port: 9303 #The address of the candidate master node can be selected as the master node after the service is started discovery.seed_hosts: ["localhost:9301", "localhost:9302"] discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5 #List of nodes in the cluster that can be selected as the master node #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2","node-3"] #Cross domain configuration #action.destructive_requires_name: true http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
Start cluster
1. Delete all contents (if any) in the data directory and logs directory of each node before startup
2. Double click to execute bin / elasticsearch Bat, start the node server. After starting, it will automatically join the cluster with the specified name
Test cluster
View cluster status
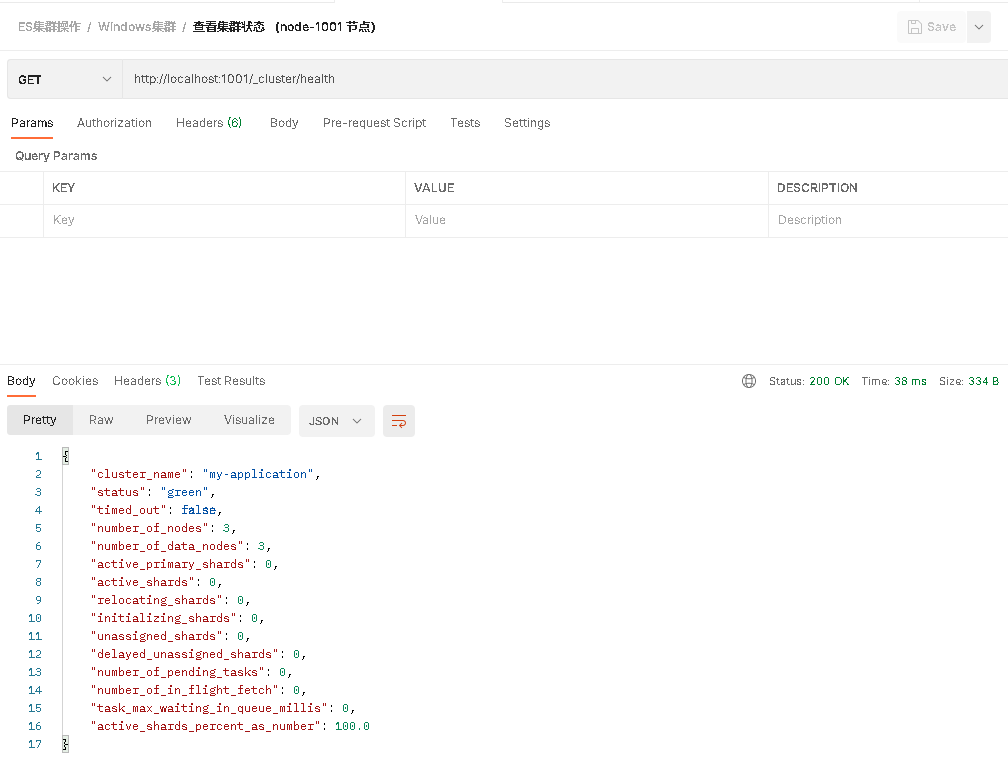
node-1001 node
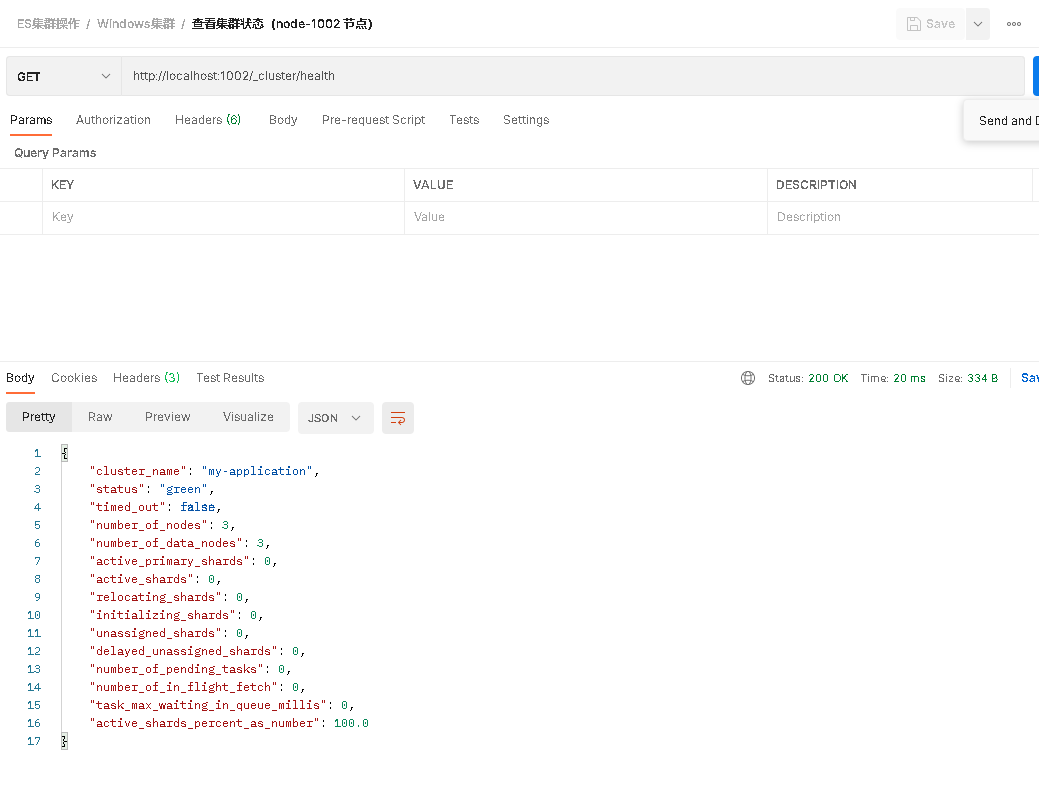
node-1002 node
node - 1003 nodes
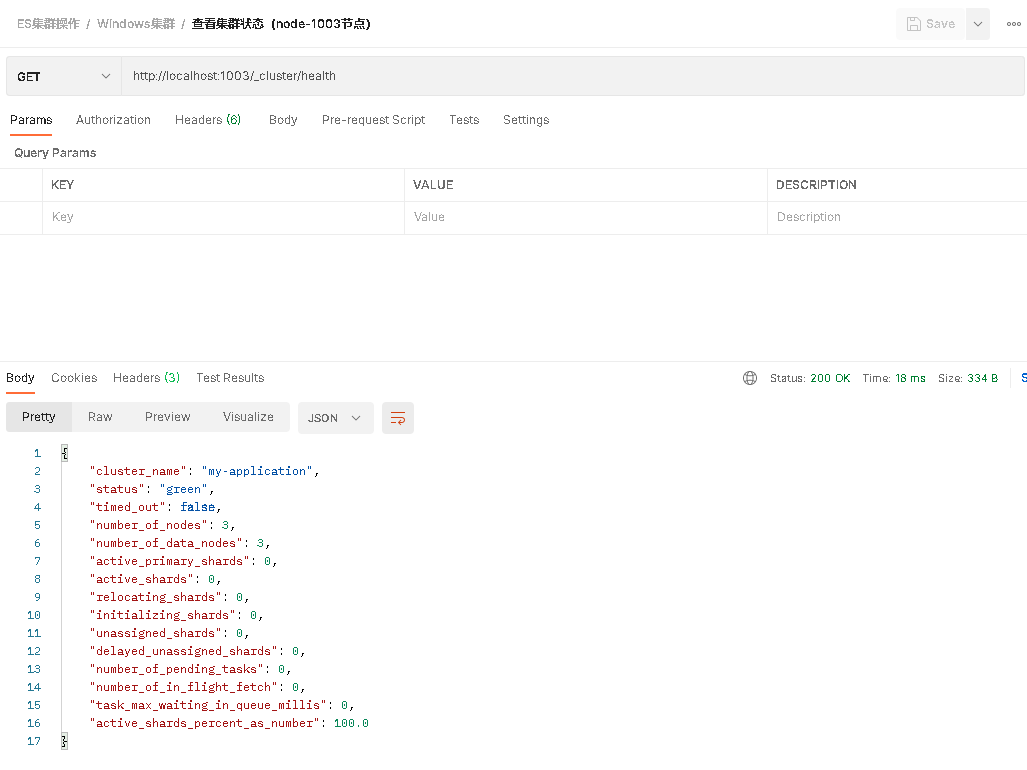
The status field in the second line is parsed
