preface
Recently, I chose the elective course of Linux kernel principle. Although the class is relatively short, the content involved can only cover a small part of Linux knowledge, the teacher's level is really high and the knowledge is very in-depth. The small assignment this time is to write C language program under Linux platform to realize the following functions:
Imitate and realize some functions of readelf tool under Linux, and be able to simply analyze ELF executable files. (at least support the - h, - s and - s command options of readelf tool)
About the principle part, I think I don't have the ability to speak as thoroughly and clearly as the bosses, so the reference article link is posted at the end of the article, and I will understand it after reading it.
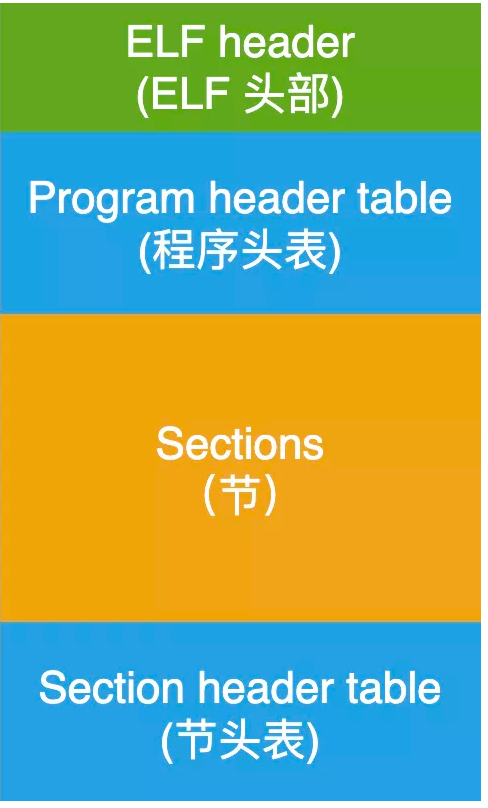
1.ELF document introduction
In Linux system, an ELF file is mainly used to represent three types of files:
- Executable file: it is read from the hard disk by the loader in the operating system and loaded into the memory for execution;
- Target file: read by the linker to generate an executable file or shared library file;
- Shared library files: during dynamic link, LD Linux So to read;
2.readelf command
-a : --all Show all information,Equivalent to -h -l -S -s -r -d -V -A -I -h : --file-header display elf Header information at the beginning of the file. -l : --program-headers ;--segments Display program header (segment header) information(If any). -S : --section-headers ;--sections Display section header information(If any). -g : --section-groups Display section group information(If any). -t : --section-details Show section details(-S of). -s : --syms ;--symbols Displays the items in the symbol table segment, if any. -e : --headers Display all header information, equivalent to: -h -l -S -n : --notes display note Section (kernel comment). -r : --relocs Displays information about relocatable segments. -u : --unwind display unwind Segment information. Currently only supported IA64 ELF of unwind Segment information. -d : --dynamic Displays information about the dynamic segment. -V : --version-info Displays information about the version segment. -A : --arch-specific display CPU Architecture information. -D : --use-dynamic Use the symbol table in the dynamic segment to display symbols instead of using symbol segments. -x <number or name> : --hex-dump=<number or name> Displays the contents of the specified segment in hexadecimal mode. number Specifies the index of the segment in the segment table,Or string to specify the segment name in the file. -w[liaprmfFsoR]perhaps -debugdump[=line,=info,=abbrev,=pubnames,=aranges, =macro,=frames,=frames-interp,=str,=loc,=Ranges] Displays the contents specified in the debugging section. -I : --histogram When the symbol is displayed, the bucket list Histogram of length. -v : --version display readelf Version information for. -H : --help display readelf Supported command line options. -W : --wide Wide line output.
3. Code implementation
Kakaluoto/ELFReader (github.com)
This time I divided it into five file headers h ; main. cpp ; readelf_ symbol. cpp ; readelf_ Section. cpp ; readelf_ header. cpp
Header file header h
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #include <elf.h> #ifndef ELFREADER_HEADER_H #define ELFREADER_HEADER_H using namespace std; void readelf_h(const char* filename); void readelf_S(const char* filename); void readelf_s(const char* filename); #endif //ELFREADER_HEADER_H
Main function main cpp
#include "header.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) { exit(0); }
//argv[0] is the current executable path
//arv[1] is a parameter, and the parameter is separated by a space
//argv[2] is the resolved executable name
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-h") == 0)
readelf_h(argv[2]);
else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-S") == 0)
readelf_S(argv[2]);
else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0)
readelf_s(argv[2]);
else
printf("invalid argument!\n");
return 0;
}
Imitate the implementation of readelf -h_ header. cpp
#include "header.h"
void readelf_h(const char* filename) {
FILE* fp;//Definition file pointer
Elf64_Ehdr elf_header;//Define elf header to store
fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL) { exit(0); }
fread(&elf_header, sizeof(Elf64_Ehdr), 1, fp);//Read header
if (elf_header.e_ident[0] != 0x7f || elf_header.e_ident[1] != 'E') { exit(0); }//Determine whether it is an elf file
printf("ELF Header:\n");
printf(" Magic:\t");
for (unsigned char i : elf_header.e_ident) {
printf("%02x ", i);
}
printf("\n");
printf(" Class:\t\t\t\t");
switch (elf_header.e_ident[EI_CLASS]) {
case 1:
printf("ELF%d\n", 32);
break;
case 2:
printf("ELF%d\n", 64);
break;
default:
printf("Error!\n");
}
printf(" Data:\t\t\t\t\t");
switch (elf_header.e_ident[EI_DATA]) {
case 1:
printf("2's complement, little endian\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("2's complement, big endian\n");
break;
default:
printf("Error!\n");
}
printf(" Version:\t\t\t\t%d (current)\n", elf_header.e_ident[EI_VERSION]);
printf(" OS/ABI:\t\t\t\t");
switch (elf_header.e_ident[EI_OSABI]) {
case ELFOSABI_NONE:
printf("UNIX System V ABI\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_HPUX:
printf("HP-UX\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_NETBSD:
printf("NetBSD.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_GNU:
printf("Object uses GNU ELF extensions.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_SOLARIS:
printf("Sun Solaris.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_AIX:
printf("IBM AIX.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_IRIX:
printf("SGI Irix.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_FREEBSD:
printf("FreeBSD.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_TRU64:
printf("Compaq TRU64 UNIX.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_MODESTO:
printf("Novell Modesto.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_OPENBSD:
printf("OpenBSD.\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_ARM_AEABI:
printf("ARM EABI\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_ARM:
printf("ARM\n");
break;
case ELFOSABI_STANDALONE:
printf("Standalone (embedded) application\n");
break;
default:
printf("Error!\n");
}
printf(" ABI Version:\t\t\t\t%d\n", elf_header.e_ident[EI_ABIVERSION]);
printf(" Type:\t\t\t\t\t");
switch (elf_header.e_type) {
case ET_REL:
printf("REL (Relocatable file)\n");
break;
case ET_EXEC:
printf("EXEC (Executable file)\n");
break;
case ET_DYN:
printf("DYN (Shared object file)\n");
break;
default:
printf("Error!\n");
}
printf(" Machine:\t\t\t\t");
switch (elf_header.e_machine) {
case EM_NONE:
printf("No Machine!\n");
break;
case EM_386:
printf("Intel 80386\n");
break;
case EM_860:
printf("Intel 80860\n");
break;
case EM_ARM:
printf("ARM\n");
break;
case EM_X86_64:
printf("AMD x86-64 architecture\n");
break;
case EM_AVR:
printf("Atmel AVR 8-bit microcontroller\n");
break;
case EM_MSP430:
printf("Texas Instruments msp430\n");
break;
case EM_ALTERA_NIOS2:
printf("Altera Nios II\n");
break;
case EM_MICROBLAZE:
printf("Xilinx MicroBlaze\n");
break;
case EM_8051:
printf("Intel 8051 and variants\n");
break;
case EM_STM8:
printf("STMicroelectronics STM8\n");
break;
case EM_CUDA:
printf("NVIDIA CUDA\n");
break;
case EM_AMDGPU:
printf("AMD GPU\n");
break;
case EM_RISCV:
printf("RISC-V\n");
break;
case EM_BPF:
printf("Linux BPF -- in-kernel virtual machine\n");
break;
default:
printf("Unknown Machine!\n");
}
printf(" Version:\t\t\t\t%x\n", elf_header.e_ident[EI_VERSION]);
printf(" Entry point address:\t\t\t0x%016lx\n", elf_header.e_entry);
printf(" Start of program headers:\t\t%ld (bytes into file)\n", elf_header.e_phoff);
printf(" Start of section headers:\t\t%ld (bytes into file)\n", elf_header.e_shoff);
printf(" Flags:\t\t\t\t0x%x\n", elf_header.e_flags);
printf(" Size of this header:\t\t\t%d (bytes)\n", elf_header.e_ehsize);
printf(" Size of program headers:\t\t%d (bytes)\n", elf_header.e_phentsize);
printf(" Number of program headers:\t\t%d\n", elf_header.e_phnum);
printf(" Size of section headers:\t\t%d (bytes)\n", elf_header.e_shentsize);
printf(" Number of section headers:\t\t%d\n", elf_header.e_shnum);
printf(" Section header string table index:\t%d\n", elf_header.e_shstrndx);
}
Imitate the implementation of readelf -S_ Section. cpp
#include "header.h"
void readelf_S(const char* filename) {
FILE* fp;
Elf64_Ehdr elf_header;
fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL) { exit(0); }
fread(&elf_header, sizeof(Elf64_Ehdr), 1, fp);
if (elf_header.e_ident[0] != 0x7f || elf_header.e_ident[1] != 'E') { exit(0); }
//The definition array is used to store each section in the segment table_ Header, number of segments: elf_header.e_shnum
Elf64_Shdr* sec_headers = new Elf64_Shdr[elf_header.e_shnum];
//Move the pointer to the starting address of the segment table, and the starting address of the segment elf_header.e_shoff is the offset relative to the entire ELF file, SEEK_SET offset from the beginning of the file
fseek(fp, elf_header.e_shoff, SEEK_SET);
//Read section_header. The size of each header is sizeof(Elf64_Shdr), and elf is read in total_ header. e_ Shnum header segments
fread(sec_headers, sizeof(Elf64_Shdr), elf_header.e_shnum, fp);
printf("There are %d section headers, starting at offset 0x%lx\n\n", elf_header.e_shnum, elf_header.e_shoff);
printf("Section Headers:\n");
int str_tab_ind = elf_header.e_shstrndx;//Gets the index elf of the string table in the segment table_ header. e_ Shstrndx, which is used to read the segment name
fseek(fp, sec_headers[str_tab_ind].sh_offset, SEEK_SET);//Move pointer to string table
char* string_table = new char[sec_headers[str_tab_ind].sh_size];//Construct a character array to store the characters in the string table
fread(string_table, 1, sec_headers[str_tab_ind].sh_size, fp);//Read out all the characters in the string table
//Get the type of section segment, enter the value corresponding to the type, and return the type name of string type
auto get_sh_type = [](int sh_type, string& sec_header_name) {
switch (sh_type) {
case SHT_NULL:
sec_header_name = "NULL";
break;
case SHT_PROGBITS:
sec_header_name = "PROGBITS";
break;
case SHT_SYMTAB:
sec_header_name = "SYMTAB";
break;
case SHT_STRTAB:
sec_header_name = "STRTAB";
break;
case SHT_RELA:
sec_header_name = "RELA";
break;
case SHT_HASH:
sec_header_name = "HASH";
break;
case SHT_DYNAMIC:
sec_header_name = "DYNAMIC";
break;
case SHT_NOTE:
sec_header_name = "NOTE";
break;
case SHT_NOBITS:
sec_header_name = "NOBITS";
break;
case SHT_REL:
sec_header_name = "REL";
break;
case SHT_SHLIB:
sec_header_name = "SHLIB";
break;
case SHT_DYNSYM:
sec_header_name = "DYNSYM";
break;
case SHT_INIT_ARRAY:
sec_header_name = "INIT_ARRAY";
break;
case SHT_FINI_ARRAY:
sec_header_name = "FINI_ARRAY";
break;
case SHT_PREINIT_ARRAY:
sec_header_name = "PREINIT_ARRAY";
break;
case SHT_GROUP:
sec_header_name = "GROUP";
break;
case SHT_SYMTAB_SHNDX:
sec_header_name = "SYMTAB_SHNDX";
break;
case SHT_NUM:
sec_header_name = "NUM";
break;
case SHT_GNU_HASH:
sec_header_name = "GNU_HASH";
break;
case SHT_GNU_versym:
sec_header_name = "VERSYM";
break;
case SHT_GNU_verneed:
sec_header_name = "VERNEED";
break;
default:
sec_header_name = "UnknownType";
}
};
//Get the flag flag of the section section, enter the value corresponding to the type, and return the string flag
//Because multiple flags may be satisfied at the same time, judge whether the corresponding flag is satisfied according to whether the corresponding bit is 1. If yes, piece up the flag string
auto get_sh_flags = [](unsigned int sh_flags, string& sec_header_name) {
if ((sh_flags & SHF_WRITE) >> 0)
sec_header_name += "W";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_ALLOC) >> 1)
sec_header_name += "A";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_EXECINSTR) >> 2)
sec_header_name += "X";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_MERGE) >> 4)
sec_header_name += "M";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_STRINGS) >> 5)
sec_header_name += "S";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_INFO_LINK) >> 6)
sec_header_name += "I";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_LINK_ORDER) >> 7)
sec_header_name += "L";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_OS_NONCONFORMING) >> 8)
sec_header_name += "O";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_GROUP) >> 9)
sec_header_name += "G";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_TLS) >> 10)
sec_header_name += "T";
if ((sh_flags & SHF_COMPRESSED) >> 11)
sec_header_name += "C";
//Special flags can be processed separately because the corresponding bits do not overlap with the corresponding bits of the above flag
switch (sh_flags) {
case SHF_MASKOS:
sec_header_name = "o";
break;
case SHF_MASKPROC:
sec_header_name = "p";
break;
case SHF_EXCLUDE:
sec_header_name = "E";
break;
}
};
printf(" [Nr]\tName\t\t\tType\t\tAddr\t\tOffset\t\tSize\t\t"
"EntSize\t\tFlags\tLink\tInfo\tAlign\n");
//Traverse section_ For each section in the headers section table, the corresponding information is output
for (int i = 0; i < elf_header.e_shnum; i++) {
printf(" [%2d]\t", i);
printf("%-24s", &string_table[sec_headers[i].sh_name]);
string sh_type;
get_sh_type(sec_headers[i].sh_type, sh_type);
printf("%-16s", sh_type.data());
printf("0x%08lx\t", sec_headers[i].sh_addr);
printf("0x%08lx\t", sec_headers[i].sh_offset);
printf("0x%08lx\t", sec_headers[i].sh_size);
printf("0x%08lx\t", sec_headers[i].sh_entsize);
string sh_flags;
get_sh_flags(sec_headers[i].sh_flags, sh_flags);
printf("%-8s", sh_flags.data());
printf("%-8d", sec_headers[i].sh_link);
printf("%-8d", sec_headers[i].sh_info);
printf("%-8ld", sec_headers[i].sh_addralign);
printf("\n");
}
printf("Key to Flags:\n"
"\tW (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),\n"
"\tL (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),\n"
"\tC (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),\n"
"\tl (large), p (processor specific)\n");
//Free heap memory
delete[] string_table;
delete[] sec_headers;
fclose(fp);
}
Imitate the implementation of readelf -s_ symbol. cpp
#include "header.h"
void readelf_s(const char* filename) {
FILE* fp;
Elf64_Ehdr elf_header;
fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL) { exit(0); }
fread(&elf_header, sizeof(Elf64_Ehdr), 1, fp);
if (elf_header.e_ident[0] != 0x7f || elf_header.e_ident[1] != 'E') { exit(0); }
Elf64_Shdr* sec_headers = new Elf64_Shdr[elf_header.e_shnum];//Store each section_ Array of headers
fseek(fp, elf_header.e_shoff, SEEK_SET);//Move the pointer to the offset address corresponding to the segment table
fread(sec_headers, sizeof(Elf64_Shdr), elf_header.e_shnum, fp);//Read segment table data into the opened array sec_ In headers
int str_tab_ind = elf_header.e_shstrndx;//Get string table Index of shstrtab in segment table
fseek(fp, sec_headers[str_tab_ind].sh_offset, SEEK_SET);//Move pointer to string table Offset address corresponding to shstrtab
char* string_table = new char[sec_headers[str_tab_ind].sh_size];//Open up heap memory to store string tables shstrtab
fread(string_table, 1, sec_headers[str_tab_ind].sh_size, fp);//String table The data at the corresponding address of shstrtab is read into the string array
int dynsym_ind = -1;//Default dynsym symbol table index is - 1
int symtab_ind = -1;//Default symtab symbol table index is - 1
int dynstr_ind = -1;//Default dynstr string table index is - 1
int strtab_ind = -1;//Default strtab string index is - 1
//Traversal segment table section_headers gets the symbol table dynsym;. symtab;. dynstr;. Index of four strtab tables in segment table
for (int i = 0; i < elf_header.e_shnum; i++) {
if (sec_headers[i].sh_type == SHT_DYNSYM)//Yes dynsym symbol table
dynsym_ind = i;
else if (sec_headers[i].sh_type == SHT_SYMTAB)//Yes symtab symbol table
symtab_ind = i;
if (strcmp(&string_table[sec_headers[i].sh_name], ".strtab") == 0)//Yes strtab string table
strtab_ind = i;
else if (strcmp(&string_table[sec_headers[i].sh_name], ".dynstr") == 0)//Yes dynstr string table
dynstr_ind = i;
}
//Get the st corresponding to the symbol table entry_ Info section, which is used to calculate symbol type and binding information
auto get_st_info = [](unsigned int st_info, string& symbol_type, string& symbol_binding) {
unsigned char st_type = st_info & 0x0000000f;//The lower 4 bits indicate the symbol type
unsigned char st_binding = (st_info & (~0x0000000f)) >> 4;//The upper 28 bits represent symbol binding information
switch (st_binding) {
case STB_LOCAL:
symbol_binding = "LOCAL";
break;
case STB_GLOBAL:
symbol_binding = "GLOBAL";
break;
case STB_WEAK:
symbol_binding = "WEAK";
break;
case STB_NUM:
symbol_binding = "NUM";
break;
case STB_LOOS:
symbol_binding = "LOOS";
break;
case STB_HIOS:
symbol_binding = "HIOS";
break;
case STB_LOPROC:
symbol_binding = "LOPROC";
break;
case STB_HIPROC:
symbol_binding = "HIPROC";
break;
default:
symbol_binding = "UnknownType";
}
switch (st_type) {
case STT_NOTYPE:
symbol_type = "NOTYPE";
break;
case STT_OBJECT:
symbol_type = "OBJECT";
break;
case STT_FUNC:
symbol_type = "FUNC";
break;
case STT_SECTION:
symbol_type = "SECTION";
break;
case STT_FILE:
symbol_type = "FILE";
break;
case STT_COMMON:
symbol_type = "COMMON";
break;
case STT_TLS:
symbol_type = "TLS";
break;
case STT_NUM:
symbol_type = "NUM";
break;
case STT_LOOS:
symbol_type = "LOOS";
break;
case STT_HIOS:
symbol_type = "HIOS";
break;
case STT_LOPROC:
symbol_type = "LOPROC";
break;
case STT_HIPROC:
symbol_type = "HIPROC";
break;
default:
symbol_type = "UnknownBinding";
}
};
//Get the index of the segment in which the symbol is located in the segment table, and handle special symbols
auto get_st_shndx = [](unsigned int st_shndx, string& Ndx) {
switch (st_shndx) {
case SHN_UNDEF:
Ndx = "UNDEF";break;
case SHN_COMMON:
Ndx = "COMMON";break;
case SHN_ABS:
Ndx = "ABS";break;
default:
Ndx = to_string(st_shndx);
}
};
//Output the symbol table information and input the index sym of the symbol table in the segment table_ Ind, number of symbol table entries_ Num, string table corresponding to symbol table_ table
auto show_symbol_table = [&](int sym_ind, unsigned long entry_num, char* string_table) {
fseek(fp, sec_headers[sym_ind].sh_offset, SEEK_SET);//Move the pointer to the offset address corresponding to the symbol table
Elf64_Sym* sym_entries = new Elf64_Sym[entry_num];//Heap memory is used to store all entries in the symbol table
fread(sym_entries, sizeof(Elf64_Sym), entry_num, fp);//Read symbol table
printf(" Num:\t\tValue\t\tSize\tType\tBind\tVis\t"
"Ndx\t\tName\n");
//Traverse each entry in the symbol table and output the information of the entry
for (int i = 0; i < entry_num; i++) {
printf(" %3d:\t", i);
printf("0x%016lx:\t", sym_entries[i].st_value);
printf("%4ld\t", sym_entries[i].st_size);
string symbol_type;
string symbol_binding;
get_st_info(sym_entries[i].st_info, symbol_type, symbol_binding);
printf("%s\t", symbol_type.data());
printf("%s\t", symbol_binding.data());
printf("DEFAULT\t");
string Ndx;
get_st_shndx(sym_entries[i].st_shndx, Ndx);
printf("%4s\t", Ndx.data());
//According to the st of entry_ The name attribute finds the name of the entry in the string table corresponding to the symbol table
printf("%s", &string_table[sym_entries[i].st_name]);
printf("\n");
}
//Free heap memory
delete[] sym_entries;
};
//If dynsym segment exists and dynstr exists
if ((dynsym_ind != -1) && (dynstr_ind != -1)) {
//Symbol table size sec_headers[dynsym_ind].sh_size each entry size sec_headers[dynsym_ind].sh_entsize
// Calculate the number of entries_ num
unsigned long entry_num = sec_headers[dynsym_ind].sh_size / sec_headers[dynsym_ind].sh_entsize;
printf("Symbol table '.dynsym' contains %ld entries\n", entry_num);
fseek(fp, sec_headers[dynstr_ind].sh_offset, SEEK_SET);//Move the pointer to The offset address corresponding to the dynstr string table
//Heap memory is used to store string tables
char* dynstr_string_table = new char[sec_headers[dynstr_ind].sh_size];
//Read data into string table
fread(dynstr_string_table, 1, sec_headers[dynstr_ind].sh_size, fp);
show_symbol_table(dynsym_ind, entry_num, dynstr_string_table);
//Release string table
delete[] dynstr_string_table;
} else {
printf("No Dynamic linker symbol table!\n");
}
printf("\n");
//If symtab segment exists and strtab exists
if ((symtab_ind != -1) && (strtab_ind != -1)) {
unsigned long entry_num = sec_headers[symtab_ind].sh_size / sec_headers[symtab_ind].sh_entsize;
printf("Symbol table '.symtab' contains %ld entries\n", entry_num);
fseek(fp, sec_headers[strtab_ind].sh_offset, SEEK_SET);
char* strtab_string_table = new char[sec_headers[strtab_ind].sh_size];
fread(strtab_string_table, 1, sec_headers[strtab_ind].sh_size, fp);
show_symbol_table(symtab_ind, entry_num, strtab_string_table);
delete[] strtab_string_table;
} else {
printf("No symbol table!\n");
}
//release
delete[] string_table;
delete[] sec_headers;
fclose(fp);
}
4. Compile and execute with cmake make
Enter the directory where elfront is located and execute the following command
./ELFReader -h filename
./ELFReader -S filename
./ELFReader -s filename
Where filename is the path of the elf file being parsed.
Example:
Execute cmake... And then make in the build folder. Finally, the project directory structure is as follows. Elfront is the elf file parser, libmylib The so shared library and helloworld executable are the test files to be parsed
.
├── build
│ ├── bin
│ │ ├── ELFReader
│ │ ├── helloworld
│ │ └── libMylib.so
......
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── readme.md
└── src
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── header.h
├── main.cpp
├── readefl_h.cpp
├── readelf_s.cpp
└── readelf_S.cpp
Root directory cmakelists txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10) project(ELFReader) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11) ADD_SUBDIRECTORY(./src)
Cmakelists. In the src directory txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
SET(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/bin)
AUX_SOURCE_DIRECTORY(./ DIR_SRCS)
ADD_EXECUTABLE(ELFReader ${DIR_SRCS})
Enter the bin directory and execute
cd build/bin/ ./ELFReader -h helloworld
Output:
ELF Header: Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 Class: ELF64 Data: 2's complement, little endian Version: 1 (current) OS/ABI: UNIX System V ABI ABI Version: 0 Type: DYN (Shared object file) Machine: AMD x86-64 architecture Version: 1 Entry point address: 0x00000000000010c0 Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file) Start of section headers: 36440 (bytes into file) Flags: 0x0 Size of this header: 64 (bytes) Size of program headers: 56 (bytes) Number of program headers: 13 Size of section headers: 64 (bytes) Number of section headers: 36 Section header string table index: 35
Execute - S command
./ELFReader -S helloworld
Output:
There are 36 section headers, starting at offset 0x8e58 Section Headers: [Nr] Name Type Addr Offset Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align [ 0] NULL 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0 0 0 [ 1] .interp PROGBITS 0x00000318 0x00000318 0x0000001c 0x00000000 A 0 0 1 [ 2] .note.gnu.property NOTE 0x00000338 0x00000338 0x00000020 0x00000000 A 0 0 8 [ 3] .note.gnu.build-id NOTE 0x00000358 0x00000358 0x00000024 0x00000000 A 0 0 4 [ 4] .note.ABI-tag NOTE 0x0000037c 0x0000037c 0x00000020 0x00000000 A 0 0 4 [ 5] .gnu.hash GNU_HASH 0x000003a0 0x000003a0 0x00000028 0x00000000 A 6 0 8 [ 6] .dynsym DYNSYM 0x000003c8 0x000003c8 0x00000138 0x00000018 A 7 1 8 [ 7] .dynstr STRTAB 0x00000500 0x00000500 0x00000163 0x00000000 A 0 0 1 [ 8] .gnu.version VERSYM 0x00000664 0x00000664 0x0000001a 0x00000002 A 6 0 2 [ 9] .gnu.version_r VERNEED 0x00000680 0x00000680 0x00000040 0x00000000 A 7 2 8 [10] .rela.dyn RELA 0x000006c0 0x000006c0 0x00000120 0x00000018 A 6 0 8 [11] .rela.plt RELA 0x000007e0 0x000007e0 0x00000060 0x00000018 AI 6 24 8 [12] .init PROGBITS 0x00001000 0x00001000 0x0000001b 0x00000000 AX 0 0 4 [13] .plt PROGBITS 0x00001020 0x00001020 0x00000050 0x00000010 AX 0 0 16 [14] .plt.got PROGBITS 0x00001070 0x00001070 0x00000010 0x00000010 AX 0 0 16 [15] .plt.sec PROGBITS 0x00001080 0x00001080 0x00000040 0x00000010 AX 0 0 16 [16] .text PROGBITS 0x000010c0 0x000010c0 0x00000205 0x00000000 AX 0 0 16 [17] .fini PROGBITS 0x000012c8 0x000012c8 0x0000000d 0x00000000 AX 0 0 4 [18] .rodata PROGBITS 0x00002000 0x00002000 0x00000013 0x00000000 A 0 0 4 [19] .eh_frame_hdr PROGBITS 0x00002014 0x00002014 0x00000054 0x00000000 A 0 0 4 [20] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0x00002068 0x00002068 0x00000148 0x00000000 A 0 0 8 [21] .init_array INIT_ARRAY 0x00003d78 0x00002d78 0x00000010 0x00000008 WA 0 0 8 [22] .fini_array FINI_ARRAY 0x00003d88 0x00002d88 0x00000008 0x00000008 WA 0 0 8 [23] .dynamic DYNAMIC 0x00003d90 0x00002d90 0x00000200 0x00000010 WA 7 0 8 [24] .got PROGBITS 0x00003f90 0x00002f90 0x00000070 0x00000008 WA 0 0 8 [25] .data PROGBITS 0x00004000 0x00003000 0x00000010 0x00000000 WA 0 0 8 [26] .bss NOBITS 0x00004040 0x00003010 0x00000118 0x00000000 WA 0 0 64 [27] .comment PROGBITS 0x00000000 0x00003010 0x0000002a 0x00000001 MS 0 0 1 [28] .debug_aranges PROGBITS 0x00000000 0x0000303a 0x00000030 0x00000000 0 0 1 [29] .debug_info PROGBITS 0x00000000 0x0000306a 0x00002c34 0x00000000 0 0 1 [30] .debug_abbrev PROGBITS 0x00000000 0x00005c9e 0x00000649 0x00000000 0 0 1 [31] .debug_line PROGBITS 0x00000000 0x000062e7 0x00000406 0x00000000 0 0 1 [32] .debug_str PROGBITS 0x00000000 0x000066ed 0x00001b08 0x00000001 MS 0 0 1 [33] .symtab SYMTAB 0x00000000 0x000081f8 0x00000780 0x00000018 34 55 8 [34] .strtab STRTAB 0x00000000 0x00008978 0x00000381 0x00000000 0 0 1 [35] .shstrtab STRTAB 0x00000000 0x00008cf9 0x0000015a 0x00000000 0 0 1 Key to Flags: W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info), L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS), C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude), l (large), p (processor specific)
Execute the - s command
./ELFReader -s helloworld
Output:
Symbol table '.dynsym' contains 13 entries
Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name
0: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UNDEF
1: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZSt4endlIcSt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_ostreamIT_T0_ES6_
2: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF __cxa_atexit
3: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZStlsISt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_ostreamIcT_ES5_PKc
4: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZNSolsEPFRSoS_E
5: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZNSt8ios_base4InitC1Ev
6: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF _ITM_deregisterTMCloneTable
7: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF __libc_start_main
8: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF __gmon_start__
9: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF _ITM_registerTMCloneTable
10: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZNSt8ios_base4InitD1Ev
11: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF __cxa_finalize
12: 0x0000000000004040: 272 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 26 _ZSt4cout
Symbol table '.symtab' contains 80 entries
Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name
0: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UNDEF
1: 0x0000000000000318: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 1
2: 0x0000000000000338: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 2
3: 0x0000000000000358: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 3
4: 0x000000000000037c: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 4
5: 0x00000000000003a0: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 5
6: 0x00000000000003c8: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 6
7: 0x0000000000000500: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 7
8: 0x0000000000000664: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 8
9: 0x0000000000000680: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 9
10: 0x00000000000006c0: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 10
11: 0x00000000000007e0: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 11
12: 0x0000000000001000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 12
13: 0x0000000000001020: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 13
14: 0x0000000000001070: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 14
15: 0x0000000000001080: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 15
16: 0x00000000000010c0: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 16
17: 0x00000000000012c8: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 17
18: 0x0000000000002000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 18
19: 0x0000000000002014: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 19
20: 0x0000000000002068: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 20
21: 0x0000000000003d78: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 21
22: 0x0000000000003d88: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 22
23: 0x0000000000003d90: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 23
24: 0x0000000000003f90: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 24
25: 0x0000000000004000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 25
26: 0x0000000000004040: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 26
27: 0x0000000000000000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 27
28: 0x0000000000000000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 28
29: 0x0000000000000000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 29
30: 0x0000000000000000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 30
31: 0x0000000000000000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 31
32: 0x0000000000000000: 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 32
33: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS crtstuff.c
34: 0x00000000000010f0: 0 FUNC LOCAL DEFAULT 16 deregister_tm_clones
35: 0x0000000000001120: 0 FUNC LOCAL DEFAULT 16 register_tm_clones
36: 0x0000000000001160: 0 FUNC LOCAL DEFAULT 16 __do_global_dtors_aux
37: 0x0000000000004150: 1 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 26 completed.8060
38: 0x0000000000003d88: 0 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 22 __do_global_dtors_aux_fini_array_entry
39: 0x00000000000011a0: 0 FUNC LOCAL DEFAULT 16 frame_dummy
40: 0x0000000000003d78: 0 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 21 __frame_dummy_init_array_entry
41: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS main.cpp
42: 0x0000000000002004: 1 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 18 _ZStL19piecewise_construct
43: 0x0000000000004151: 1 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 26 _ZStL8__ioinit
44: 0x00000000000011e0: 77 FUNC LOCAL DEFAULT 16 _Z41__static_initialization_and_destruction_0ii
45: 0x000000000000122d: 25 FUNC LOCAL DEFAULT 16 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
46: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS crtstuff.c
47: 0x00000000000021ac: 0 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 20 __FRAME_END__
48: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS
49: 0x0000000000002014: 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT 19 __GNU_EH_FRAME_HDR
50: 0x0000000000001000: 0 FUNC LOCAL DEFAULT 12 _init
51: 0x0000000000003d90: 0 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 23 _DYNAMIC
52: 0x0000000000003d88: 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT 21 __init_array_end
53: 0x0000000000003d78: 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT 21 __init_array_start
54: 0x0000000000003f90: 0 OBJECT LOCAL DEFAULT 24 _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_
55: 0x0000000000004010: 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT 25 _edata
56: 0x0000000000004000: 0 NOTYPE WEAK DEFAULT 25 data_start
57: 0x0000000000002000: 4 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 18 _IO_stdin_used
58: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF __cxa_finalize@@GLIBC_2.2.5
59: 0x00000000000011a9: 55 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 16 main
60: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZSt4endlIcSt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_ostreamIT_T0_ES6_@@GLIBCXX_3.4
61: 0x0000000000004008: 0 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 25 __dso_handle
62: 0x00000000000012c8: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 17 _fini
63: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF __cxa_atexit@@GLIBC_2.2.5
64: 0x00000000000010c0: 47 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 16 _start
65: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZStlsISt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_ostreamIcT_ES5_PKc@@GLIBCXX_3.4
66: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZNSolsEPFRSoS_E@@GLIBCXX_3.4
67: 0x0000000000004010: 0 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 25 __TMC_END__
68: 0x0000000000004040: 272 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 26 _ZSt4cout@@GLIBCXX_3.4
69: 0x0000000000004000: 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT 25 __data_start
70: 0x0000000000004158: 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT 26 _end
71: 0x0000000000004010: 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT 26 __bss_start
72: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZNSt8ios_base4InitC1Ev@@GLIBCXX_3.4
73: 0x0000000000001250: 101 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 16 __libc_csu_init
74: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF _ITM_deregisterTMCloneTable
75: 0x00000000000012c0: 5 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 16 __libc_csu_fini
76: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF __libc_start_main@@GLIBC_2.2.5
77: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF __gmon_start__
78: 0x0000000000000000: 0 NOTYPE WEAK DEFAULT UNDEF _ITM_registerTMCloneTable
79: 0x0000000000000000: 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UNDEF _ZNSt8ios_base4InitD1Ev@@GLIBCXX_3.4
Reference articles
ELF file structure description - yooo - blog Park (cnblogs.com)
C/C + + implementation of ELF Structure Parsing tool - lysark - blog Garden (cnblogs.com)
Implementation of elf file parsing in C language_ Yuhan's blog - CSDN blog_ elf file reading
Self cultivation of programmers: linking, loading and library Yu Jiazi, Shi fan, pan Aimin