1, ELK overview
1. ELK introduction
ELK platform is a complete set of centralized log processing solution, which combines ElasticSearch, Logstash and Kiabana to meet more powerful user requirements for log query, sorting and statistics.
2. ELK composition
(1)ElasticSearch
• it is a distributed storage retrieval engine based on Lucene (a full-text retrieval engine architecture), which is used to store all kinds of logs
• Elasticsearch is developed in Java and allows users to communicate with Elasticsearch through a browser through a RESTful Web interface
• Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analysis engine. Its advantage is that it can store, search and analyze large amounts of data in near real time
• Elasticsearch can be divided into three types: master node, data node and client node
1,master Master node: elasticsearch.yml: node.master:true node.data:false Main functions: maintain metadata and manage cluster node status; Not responsible for data writing and query Configuration points: the memory can be relatively small, but the machine must be stable, preferably an exclusive machine 2,data Data node elasticsearch.yml: node.master:false node.data:true Main functions: responsible for data writing and query, high pressure Configuration points: large memory, preferably an exclusive machine 3,client Client node elasticsearch.yml: node.master:true node.data:true Main functions: integrate the functions of the above three nodes. Configuration points: large memory, preferably an exclusive machine. Special note: this configuration is not recommended, and the node is easy to hang up 4,The master node is generally configured with 3 servers, and the configuration ratio of data node and client node is generally 3:1 Left and right, adjust according to the actual situation
(2)Logstash
• as a data collection engine. It supports dynamic data collection from various data sources, filtering, analyzing, enriching and unifying the data, and then storing it to the location specified by the user, which is generally sent to Elasticsearch
• logstash is written in JRuby language and runs on the Java virtual machine (JVM). It is a powerful data processing tool that can realize data transmission, format processing and formatted output. Logstash has powerful plug-in functions and is commonly used for log processing
(3)Kibana
It is based on node The display tool developed by. JS can provide a graphical log analysis Web interface display for Logstash and ElasticSearch, and can summarize, analyze and search important data logs
(4)Filebeat
Lightweight open source log file data collector. Usually, install filebeat on the client that needs to collect data and specify the directory and log format. Filebeat can quickly collect data and send it to logstash for parsing, or directly send it to Elasticsearch for storage. In terms of performance, it has obvious advantages over loqstash running on JVM and is a substitute for it
3. Why use ELK
(1) Logs mainly include system logs, application logs and security logs. System operation and maintenance personnel and developers can understand the server software and hardware information, check the errors in the configuration process and the causes of errors through logs. Regular analysis of logs can understand the server load, performance and security, so as to take timely measures to correct errors
(2) Often, we can basically analyze the logs of a single machine by using grep, awk and other tools, but when the logs are scattered and stored on different devices. If you manage dozens or hundreds of servers, you still use the traditional method of logging in to each machine in turn to check the logs. This feels cumbersome and inefficient
(3) It is urgent that we use centralized log management, such as the open source syslog, to collect and summarize the logs on all servers. After centralized log management, log statistics and retrieval become a more troublesome thing. Generally, we can use grep, awk, wc and other Linux commands to achieve retrieval and statistics, but for more demanding queries, sorting and statistics The demand and the huge number of machines still use this method, which is inevitably a little inadequate
(4) Generally, a large-scale system is a distributed deployment architecture. Different service modules are deployed on different servers. When a problem occurs, it is necessary to locate the specific server and service module according to the key information exposed by the problem, and build a centralized log system, which can improve the efficiency of locating the problem
4. Basic characteristics of complete log system
(1) Collection: it can collect log data from multiple sources
(2) Transmission: it can analyze, filter and transmit the log data to the storage system stably
(3) Store: store log data
(4) Analysis: support UI analysis
(5) Warning: it can provide error reporting and monitoring mechanism
5. How ELK works
(1) Deploy Logstash on all servers that need to collect logs, or centrally manage logs on the log server and deploy Logstash on the log server.
(2) Logstash collects logs, formats them and outputs them to the Elasticsearch cluster.
(3) Elasticsearch indexes and stores formatted data.
(4) Kibana queries the data from the ES cluster, generates charts, and displays the front-end data.
2, ELK Elasticsearch cluster deployment (operate on Node1 and Node2 nodes)
1. Environmental preparation
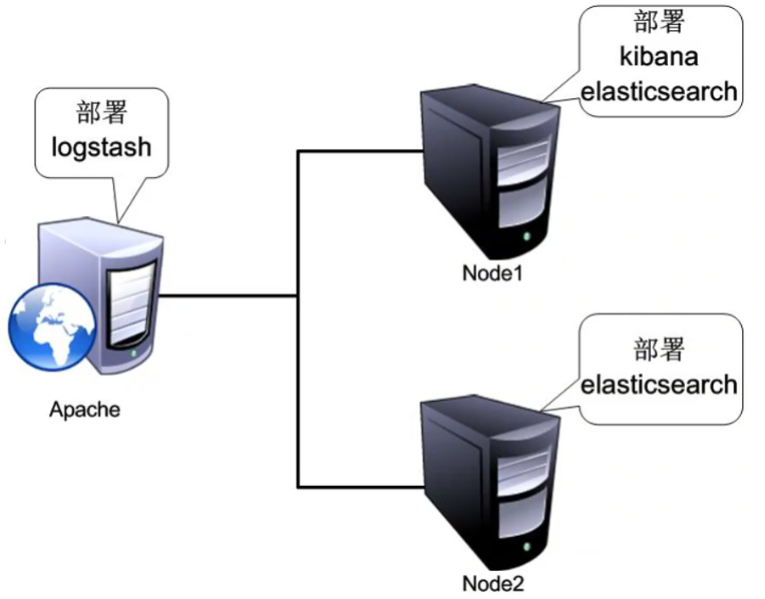
Node1 node (2C/4G): node1/192.168.142.3 Elasticsearch Kibana
Node2 node (2C/4G): node2/192.168.142.4 Elasticsearch
Apache node: Apache 192.168 142.5 Logstash Apache
(1) Turn off strong fire protection and safety functions
systemctl stop firewalld.service setenforce 0

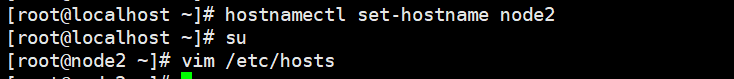
(2) Change host name
Node1 Node: hostnamectl set-hostname node1 Node2 Node: hostnamectl set-hostname node2

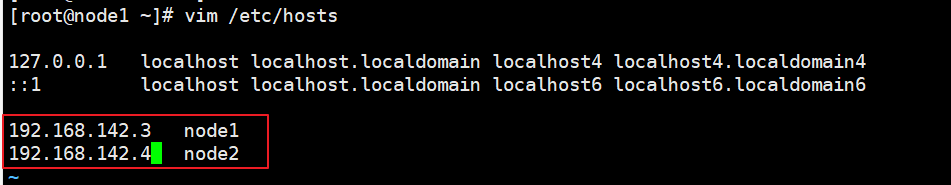
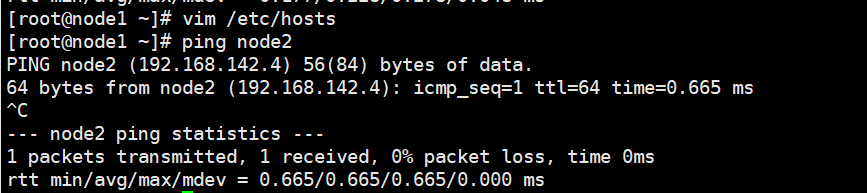
(3) Configure domain name resolution
vim /etc/hosts 192.168.142.3 node1 192.168.142.4 node2ping node22
(4) View java environment
java -version #If not installed, yum -y install java openjdk version "1.8.0_131" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_131-b12) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.131-b12, mixed mode
2. Deploy Elasticsearch software
(1) Install elasticsearch - rpm package
#Upload elasticsearch-5.5 0.rpm to / opt directory cd /opt rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm
(2) Load system services
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
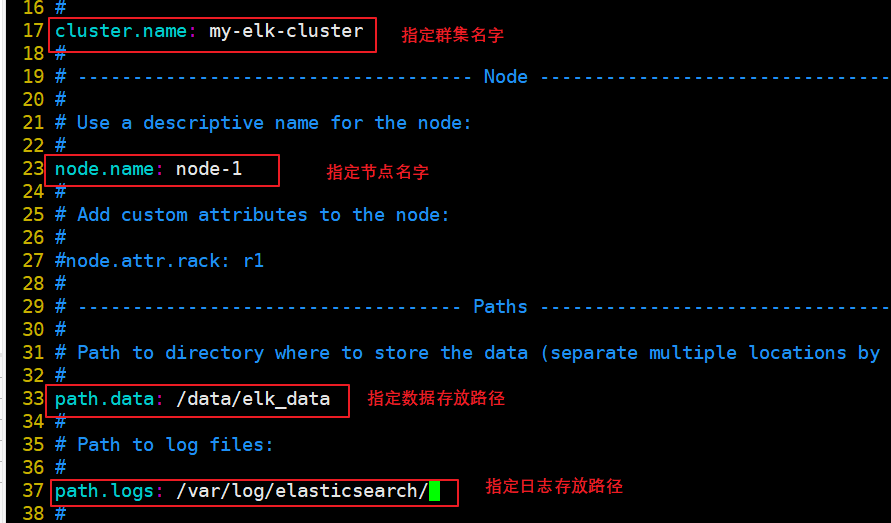
(3) Modify the elasticsearch main configuration file
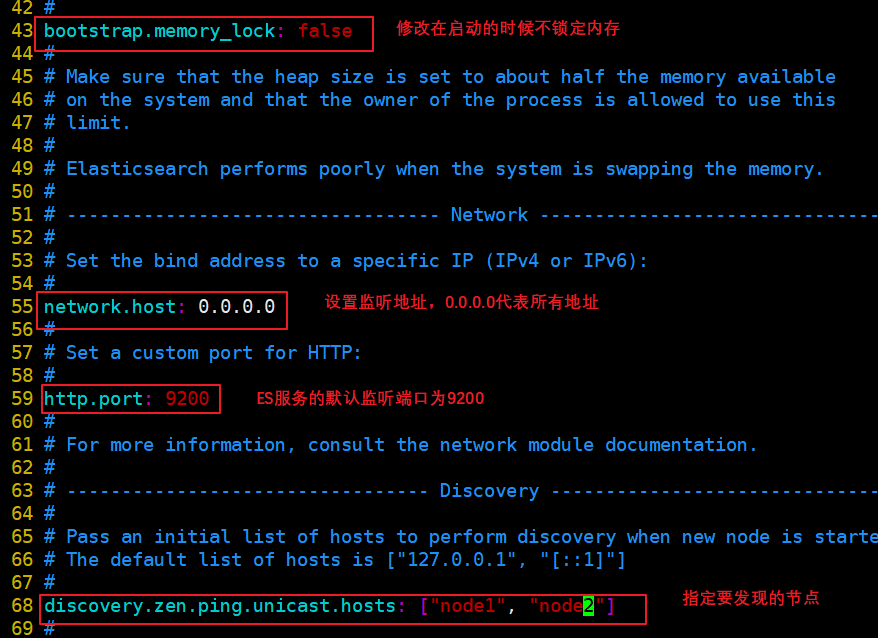
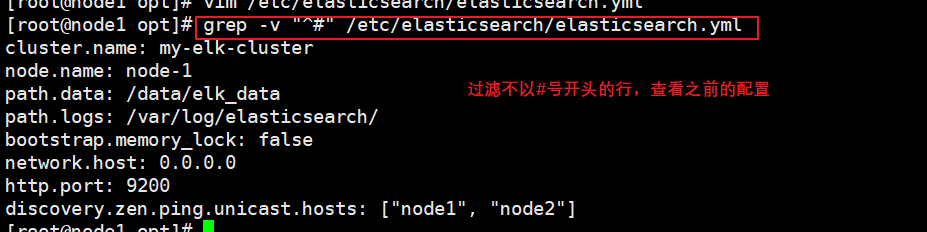
cp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.bak vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml --17--Uncomment and specify the cluster name cluster.name: my-elk-cluster --23--Uncomment and specify the node name: Node1 Node is node1,Node2 Node is node2 node.name: node1 --33--Uncomment and specify the data storage path path.data: /data/elk_data --37--Uncomment and specify the log storage path path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/ --43--Uncomment and change to not lock the memory at startup bootstrap.memory_lock: false --55--Uncomment, set listening address, 0.0.0.0 Represents all addresses network.host: 0.0.0.0 --59--Uncomment, ES The default listening port of the service is 9200 http.port: 9200 --68--Uncomment. Cluster discovery is implemented through unicast. Specify the nodes to be discovered node1,node2 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1", "node2"] grep -v "^#" /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml

(4) Create data storage path and authorize
mkdir -p /data/elk_data chown elasticsearch:elasticsearch /data/elk_data/

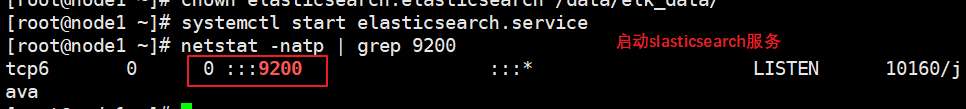
(5) Start elasticsearch successfully
systemctl start elasticsearch.service netstat -antp | grep 9200
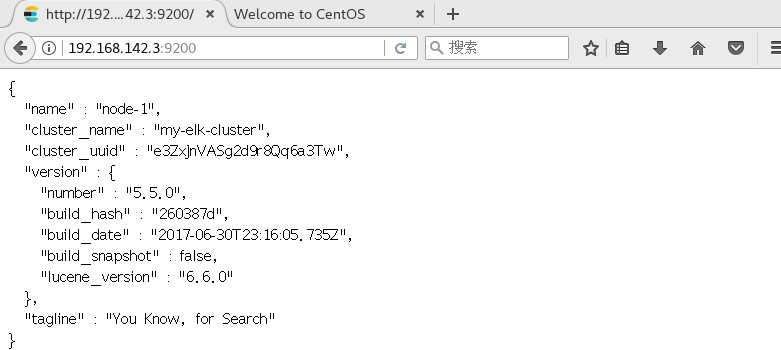
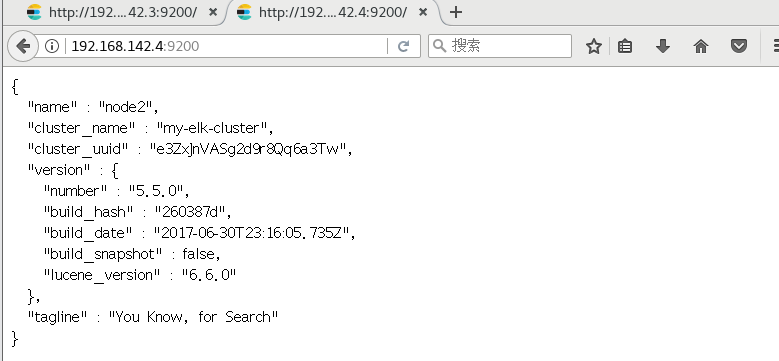
(6) View node information
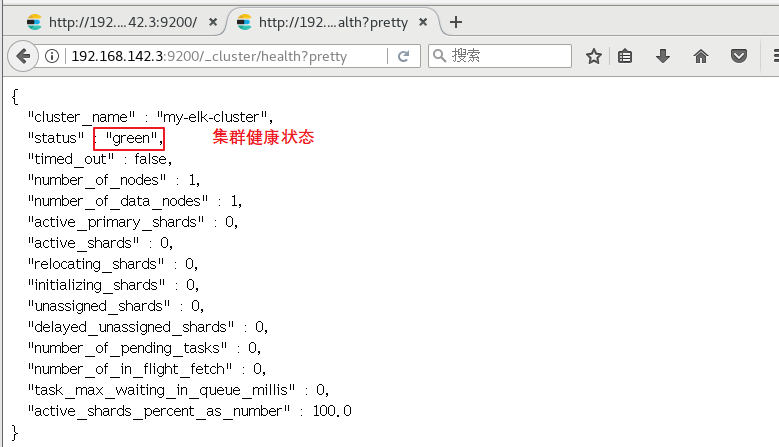
Browser access http://192.168. 142.3:9200 , http://192.168.142.3:9200 View the information of nodes Node1 and Node2. Browser access http://192.168.142.3:9200/_cluster/health?pretty , http://192.168.142.4:9200/_cluster/health?pretty Check the health of the cluster. You can see that the status value is green, indicating that the node is running healthily. Browser access http://192.168.142.4:9200/_cluster/state?pretty checks the cluster state information. #Viewing the status of the cluster in the above way is not user-friendly. You can more easily manage the cluster by installing the elasticsearch head plug-in.
3. Install elasticsearch head plug-in
After Elasticsearch version 5.0, Elasticsearch head plug-in needs to be installed as an independent service, and it needs to be installed using npm tool (package management tool of NodeJS).
To install elastic search head, you need to install the dependent software node and phantom JS in advance.
node: it is a JavaScript running environment based on Chrome V8 engine.
phantomjs: it is a JavaScript API based on webkit, which can be understood as an invisible browser. It can do anything based on webkit browser.
(1) Compile and install node
#Upload the software package node-v8 2.1. tar. GZ to / opt yum install gcc gcc-c++ make -y cd /opt tar zxvf node-v8.2.1.tar.gz cd node-v8.2.1/ ./configure make && make install
(2) Install phantomjs
#Upload software package phantomjs-2.1 1-linux-x86_ 64.tar. Bz2 to cd /opt tar jxvf phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2 -C /usr/local/src/ cd /usr/local/src/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin cp phantomjs /usr/local/bin
(3) Install elasticsearch head data visualization tool
#Upload the software package elasticsearch head tar. GZ to / opt cd /opt tar zxvf elasticsearch-head.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/ cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/ npm install
(4) Modify Elasticsearch main configuration file
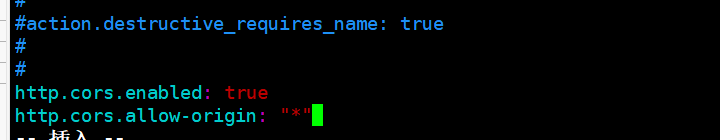
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml ...... --Add the following at the end-- http.cors.enabled: true #Enable cross domain access support. The default value is false http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #Specify that the domain names and addresses allowed for cross domain access are all systemctl restart elasticsearch

(5) Start the elasticsearch head service
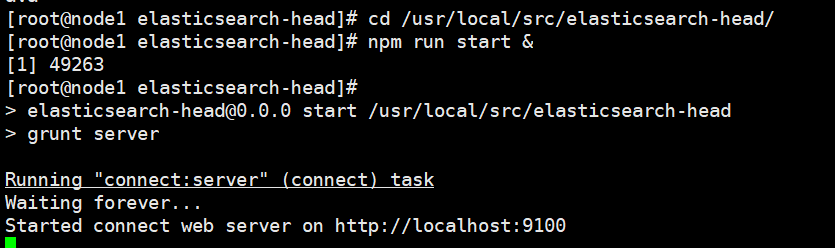
#The service must be started in the extracted elasticsearch head directory, and the process will read the gruntfile JS file, otherwise it may fail to start. cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/ npm run start & > elasticsearch-head@0.0.0 start /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head > grunt server Running "connect:server" (connect) task Waiting forever... Started connect web server on http://localhost:9100 #The port monitored by elastic search head is 9100 netstat -natp |grep 9100
(6) Browser access
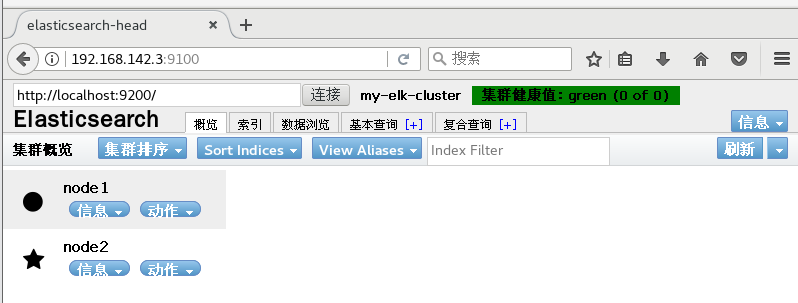
http://192.168. 142.3:9100 / address and connect to the cluster. If you see that the cluster health value is green, it means that the cluster is very healthy.
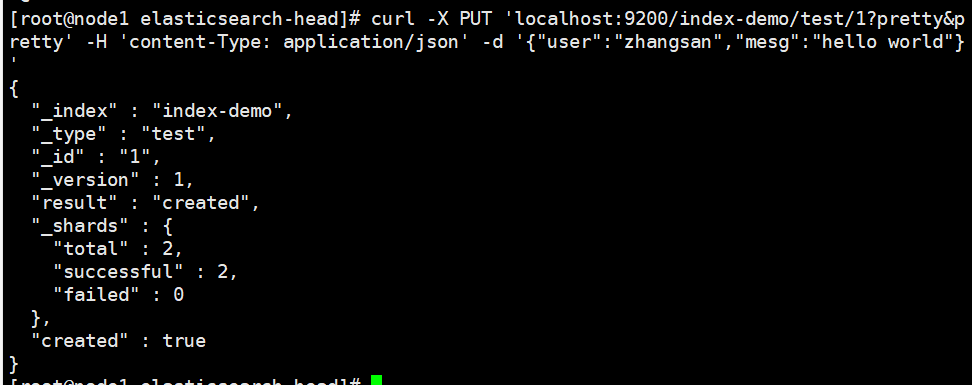
(7) Insert Index
#Insert a test index through the command. The index is index demo and the type is test.
curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty' -H 'content-Type: application/json' -d '{"user":"zhangsan","mesg":"hello world"}'
//The output results are as follows:
{
"_index" : "index-demo",
"_type" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"created" : true
}
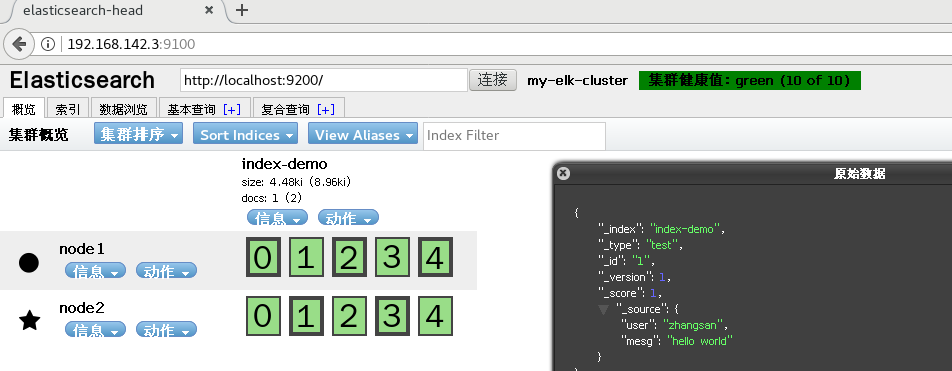
Browser access http://192.168. 80.10:9100/ check the index information. You can see that the index is divided into 5 by default, and there is a copy.
Click "data browsing" and you will find node1 The index created on is index-demo,Type is test Information about.
4. ELK Logstash deployment (operating on Apache nodes)
(1) Change host name
hostnamectl set-hostname apache
(2) Install Apahce service (httpd)
yum -y install httpd systemctl start httpd
(3) Installing the Java environment
yum -y install java java -version
(4) Install logstash
#Upload the software package logstash-5.5 1. Rpm to / opt directory cd /opt rpm -ivh logstash-5.5.1.rpm systemctl start logstash.service systemctl enable logstash.service ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/local/bin/
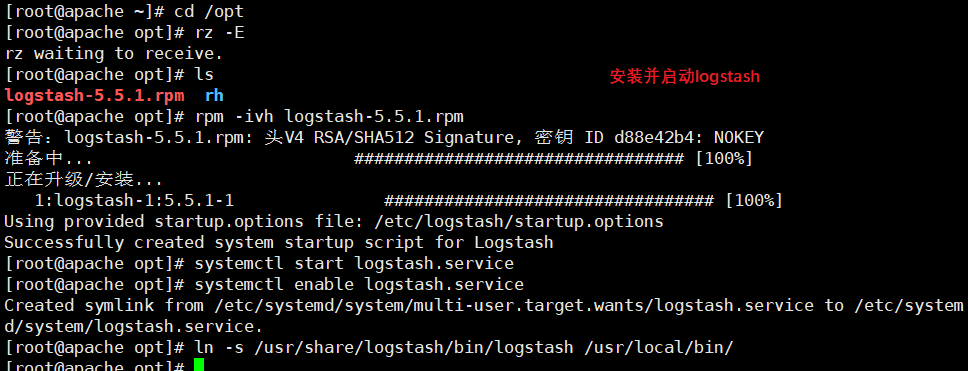
(5) Test Logstash
| Logstash command options | explain |
|---|---|
| -f | With this option, you can specify the configuration file of Logstash, and configure the input and output streams of Logstash according to the configuration file |
| -e | From the command line, the input and output are followed by a string, which can be used as the configuration of Logstash (if it is empty, stdin is used as the input and stdout as the output by default) |
| -t | Test that the configuration file is correct and exit |
Define input and output streams:
1,#The input adopts standard input and the output adopts standard output (similar to pipeline)
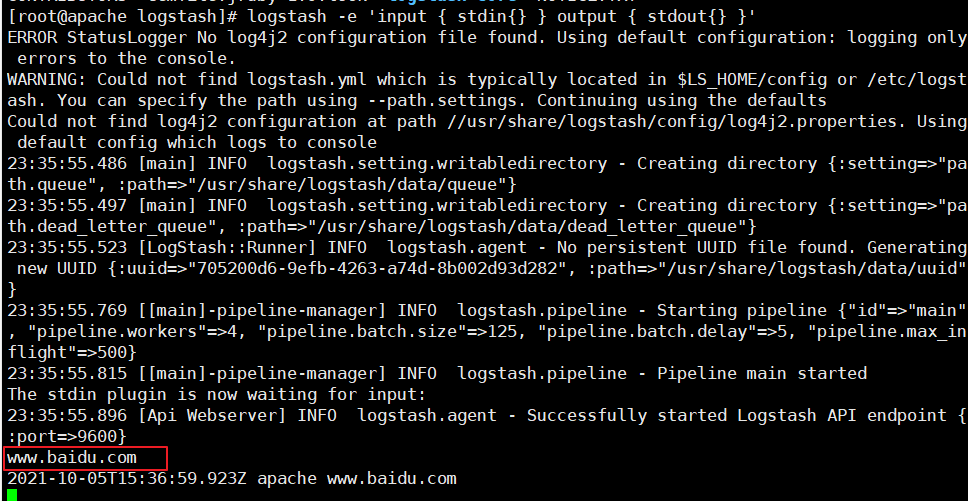
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }'
......
www.baidu.com #Type (standard input)
2020-12-22T03:58:47.799Z node1 www.baidu.com #Output result (standard output)
www.sina.com.cn #Type (standard input)
2017-12-22T03:59:02.908Z node1 www.sina.com.cn #Output result (standard output)
//Execute ctrl+c to exit
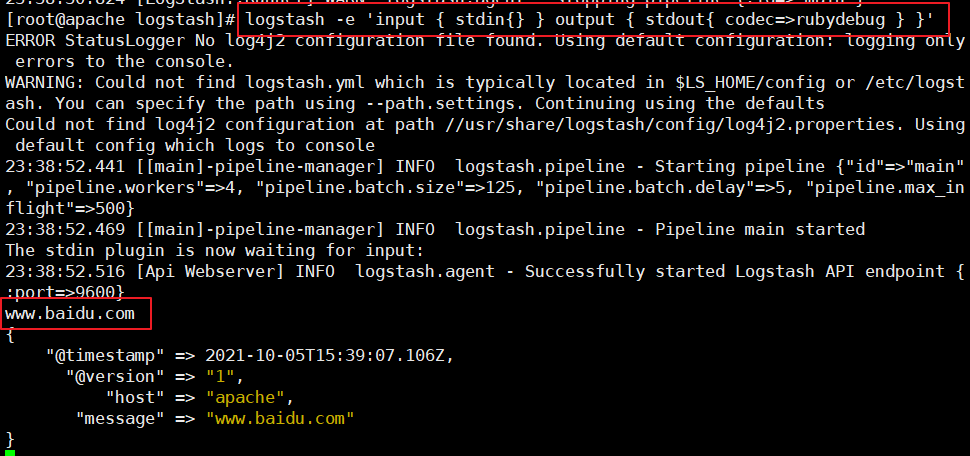
2,#Using rubydebug output detailed format display, codec is a codec
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=>rubydebug } }'
......
www.baidu.com #Type (standard input)
{
"@timestamp" => 2020-12-22T02:15:39.136Z, #Output results (processed results)
"@version" => "1",
"host" => "apache",
"message" => "www.baidu.com"
}
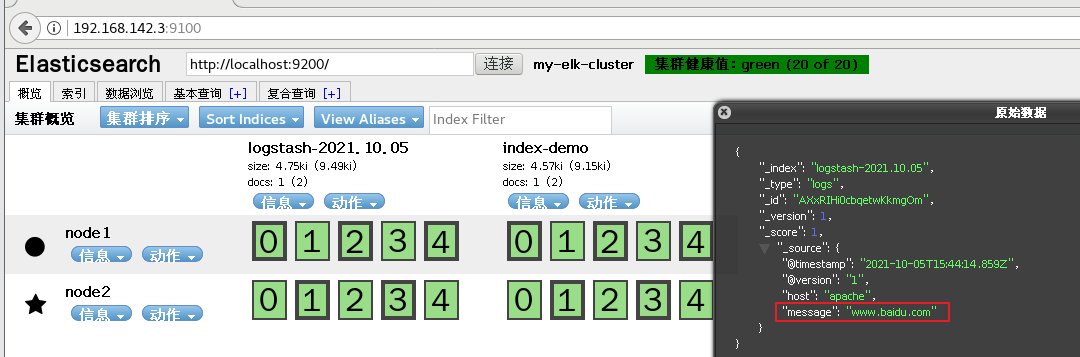
3,#Use Logstash to write information to Elasticsearch
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.142.3:9200"] } }'
input output Docking
......
www.baidu.com #Type (standard input)
www.sina.com.cn #Type (standard input)
www.google.com #Type (standard input)
//The results are not displayed in the standard output, but are sent to Elasticsearch, which can be accessed by the browser http://192.168.80.10:9100/ View index information and data browsing.
(6) Define logstash configuration file
Logstash The configuration file basically consists of three parts: input,output as well as filter(Optional, use as needed).
#The format is as follows:
input {...}
filter {...}
output {...}
#In each section, you can also specify multiple access methods. For example, to specify two log source files, the format is as follows:
input {
file { path =>"/var/log/messages" type =>"syslog"}
file { path =>"/var/log/httpd/access.log" type =>"apache"}
}
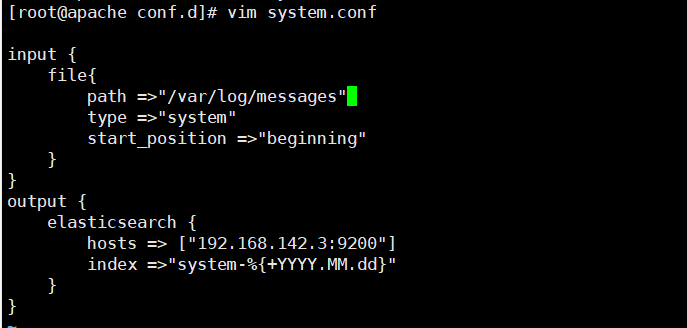
#Modify the Logstash configuration file to collect the system log / var/log/messages and output it to elasticsearch.
chmod +r /var/log/messages #Allow Logstash to read logs
vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf
input {
file{
path =>"/var/log/messages" #Specify the location of the logs to collect
type =>"system" #Custom log type ID
start_position =>"beginning" #Indicates collection from the beginning
}
}
output {
elasticsearch { #Output to elasticsearch
hosts => ["192.168.142.3:9200"] #Specify the address and port of the elasticsearch server
index =>"system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" #Specifies the index format to output to elasticsearch
}
}
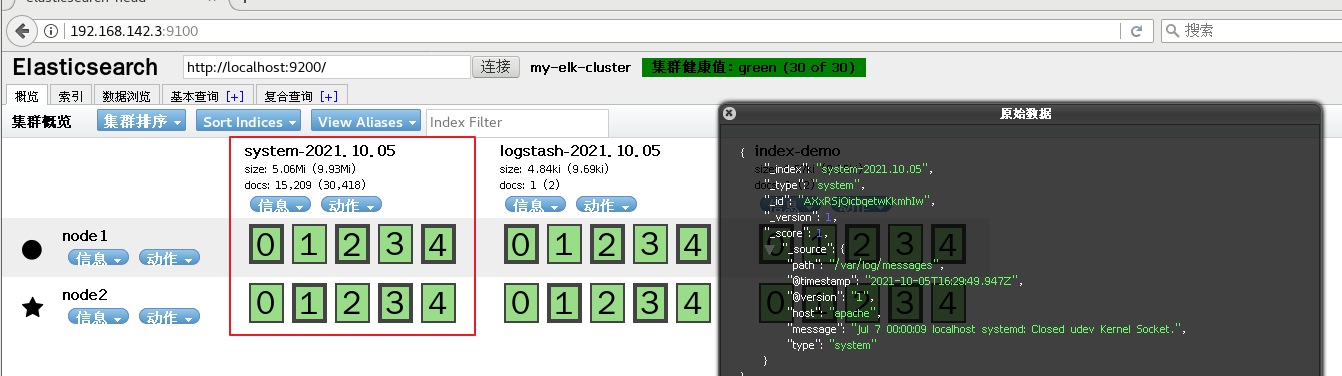
systemctl restart logstash
Browser access http://192.168. 80.10:9100/ view index information
5. ELK Kiabana deployment (operating on Node1 node)
(1) Install Kiabana
#Upload software package kibana-5.5 1-x86_ 64.rpm to / opt directory cd /opt rpm -ivh kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm
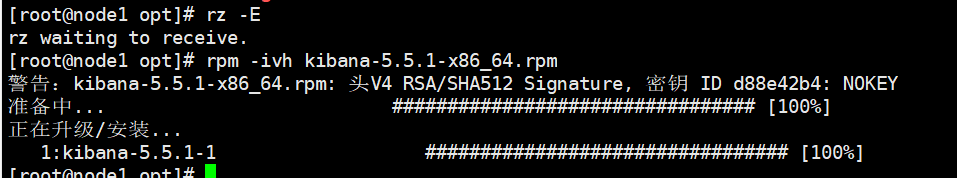
(2) Set up Kibana's master profile
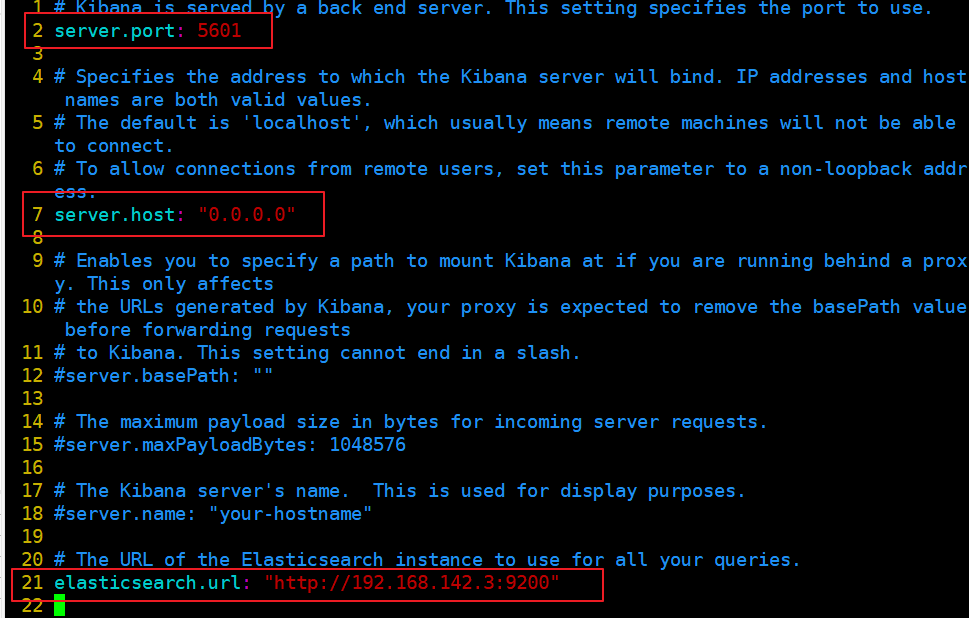
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml --2--Uncomment, Kiabana The default listening port of the service is 5601 server.port: 5601 --7--Uncomment, set Kiabana Listening address, 0.0.0.0 Represents all addresses server.host: "0.0.0.0" --21--Uncomment, set, and Elasticsearch Address and port for establishing connection elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.80.10:9200" --30--Uncomment, set in elasticsearch Add in.kibana Indexes kibana.index: ".kibana"

(3) Start Kibana service
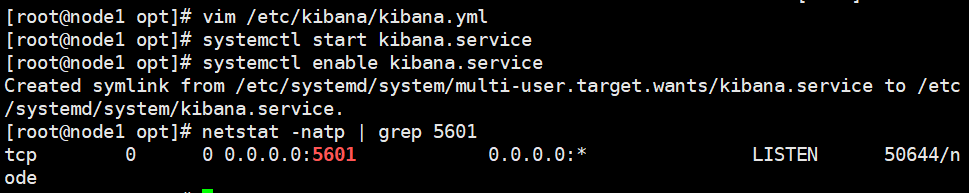
systemctl start kibana.service systemctl enable kibana.service netstat -natp | grep 5601
(4) Verify Kibana
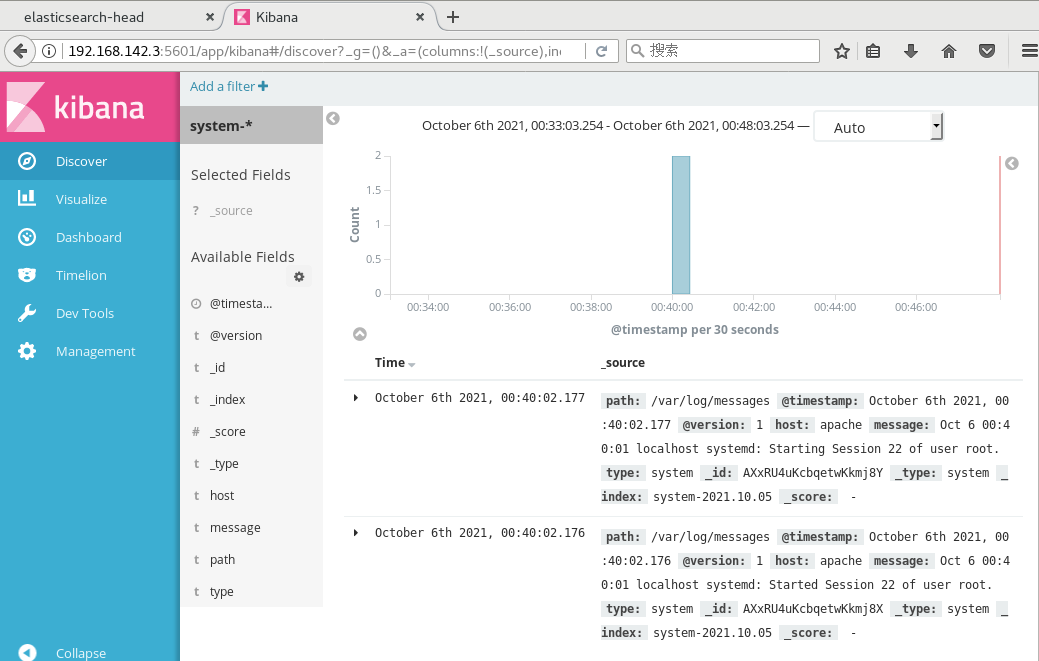
Browser access http://192.168.142.3:5601 You need to add one for the first login Elasticsearch Indexes: Index name or pattern //Input: System - * # enter the previously configured Output prefix "system" in the index name Click“ create" Button to create, click“ Discover" Button to view chart information and log information. Data display can be classified and displayed in“ Available Fields"Medium“ host",Then click“ add"Button, you can see“ host"Filtered results
(5) Add the Apache server logs (accessed, incorrect) to Elasticsearch and display them through Kibana
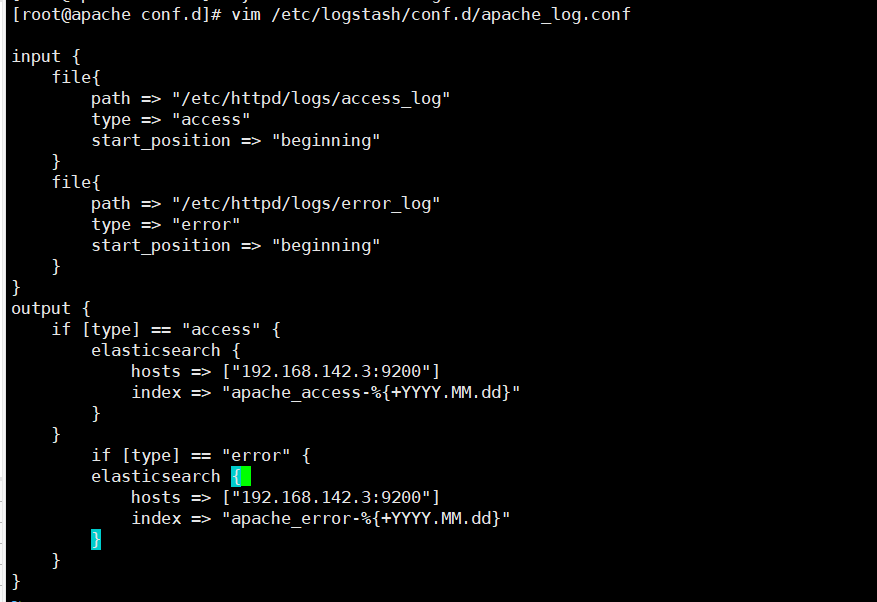
vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/apache_log.conf
input {
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/access_log"
type => "access"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/error_log"
type => "error"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "access" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.142.3:9200"]
index => "apache_access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.142.3:9200"]
index => "apache_error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/
/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f apache_log.conf
Browser access http://192.168. 142.3:9100 check whether the index is created
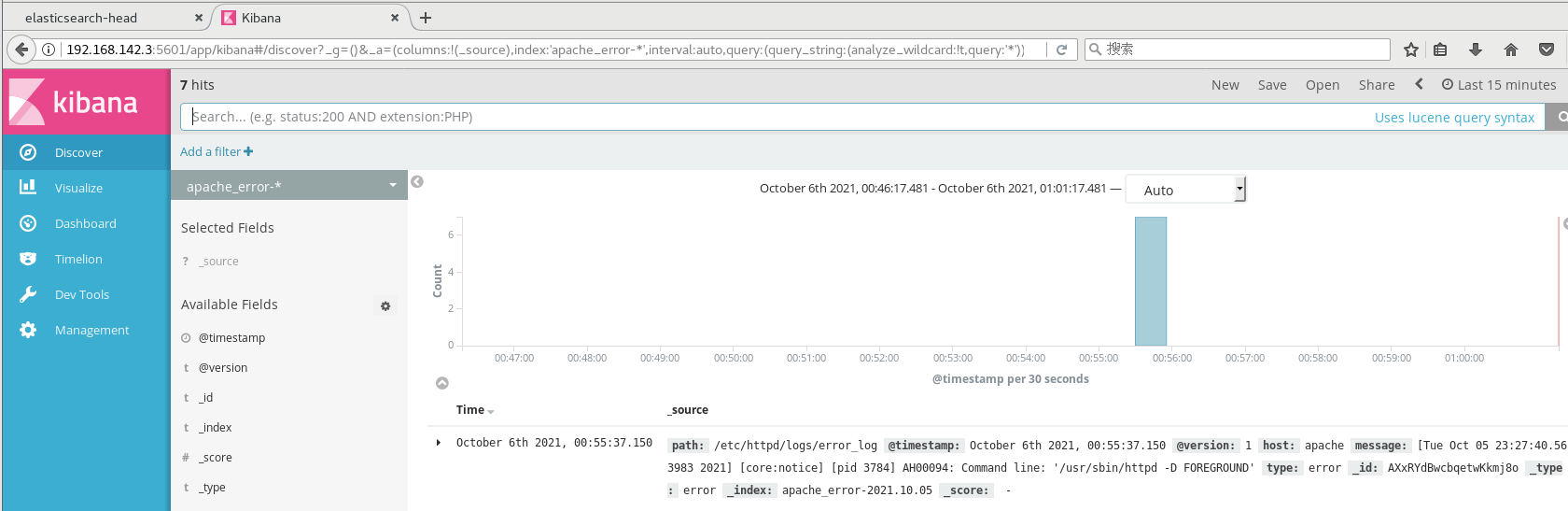
Browser access http://192.168. 142.3:5601 log in to Kibana, click the "Create Index Pattern" button to add an index, and enter the previously configured Output prefix Apache in the index name_ Access - *, and click the Create button. Add Apache in the same way_ Error - * index.
Choose“ Discover"Tab, select the newly added in the middle drop-down list apache_access-* ,apache_error-* Index, you can view the corresponding chart and log information.
6. Filebeat+ELK deployment
(1) Environmental preparation
Node1 Node (2) C/4G): node1/192.168.142.3 Elasticsearch Kibana Node2 Node (2) C/4G): node2/192.168.142.4 Elasticsearch Apache Node: apache/192.168.142.5 Logstash Apache Filebeat Node: filebeat/192.168.142.5 Filebeat
Operation on Node1 node
(2) Install Filebeat
#Upload software package filebeat-6.2 4-linux-x86_ 64.tar. GZ to / opt directory tar zxvf filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz mv filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64/ /usr/local/filebeat
(3) Set the main profile for filebeat
cd /usr/local/filebeat
vim filebeat.yml
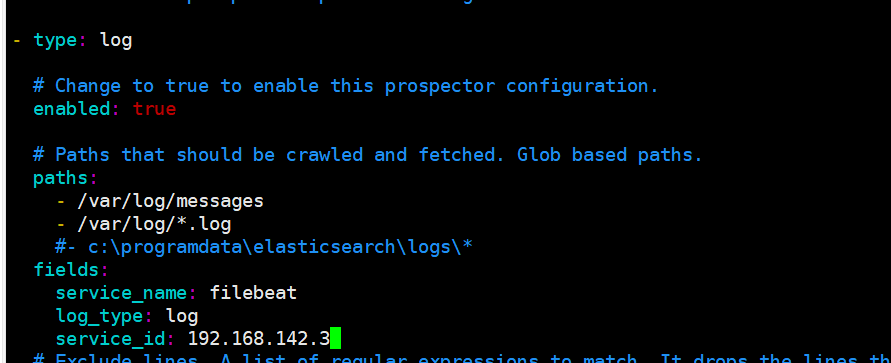
filebeat.prospectors:
- type: log #Specify the log type to read messages from the log file
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/messages #Specify the log file to monitor
- /var/log/*.log
fields: #You can use the fields configuration option to set some parameters and add fields to output
service_name: filebeat
log_type: log
service_id: 192.168.142.3
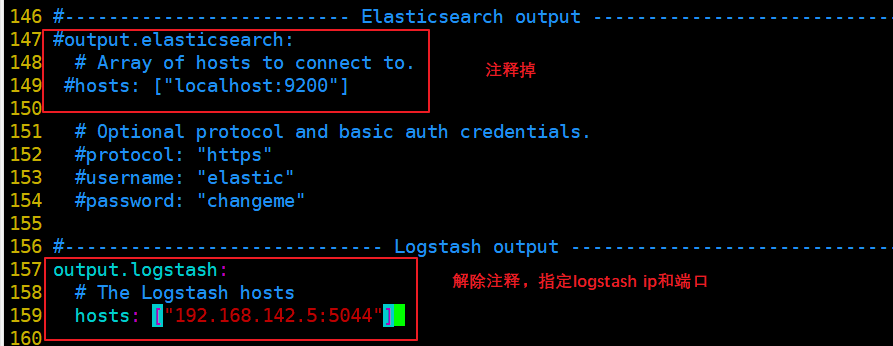
--------------Elasticsearch output-------------------
(Comment out all)
----------------Logstash output---------------------
output.logstash:
hosts: ["192.168.142.5:5044"] #Specify the IP and port of logstash
#Start filebeat
./filebeat -e -c filebeat.yml
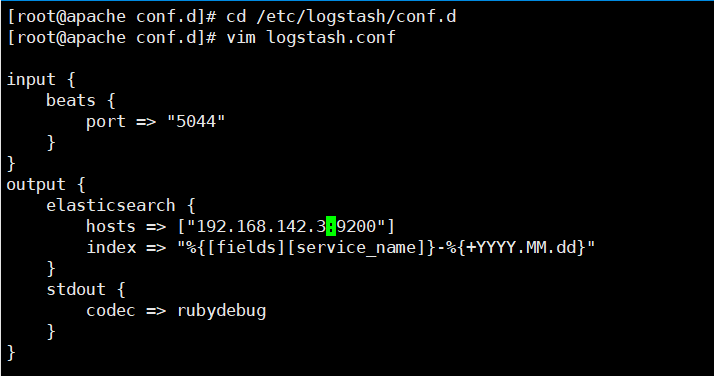
(4) Create a new Logstash configuration file on the node where the Logstash component is located
cd /etc/logstash/conf.d
vim logstash.conf
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.80.10:9200"]
index => "%{[fields][service_name]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
#Start logstash
logstash -f logstash.conf
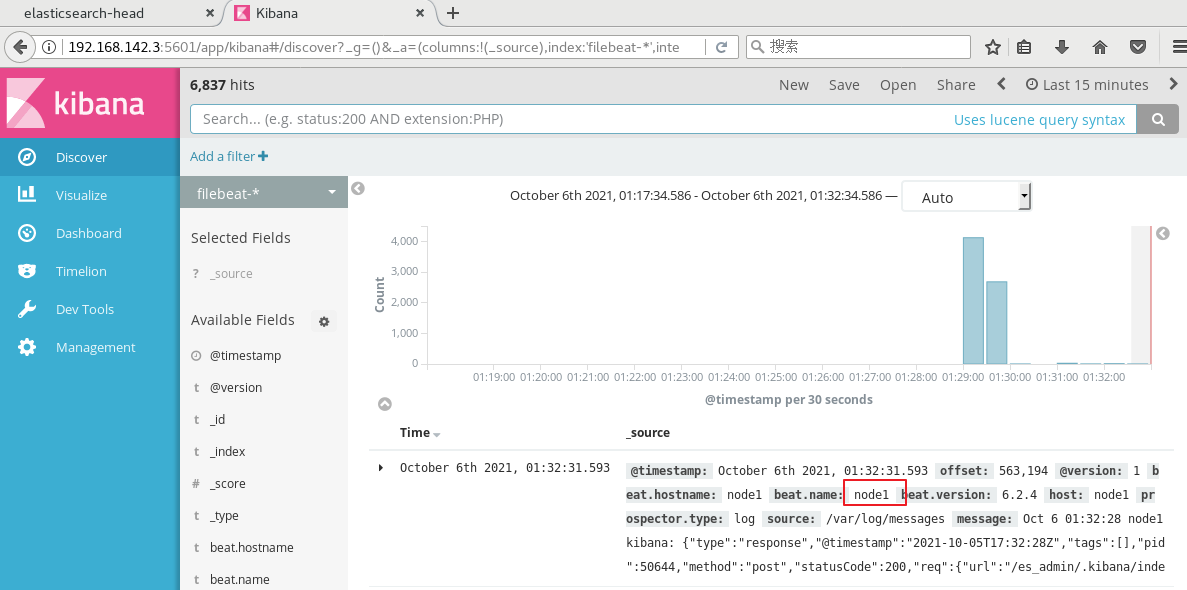
(5) Browser access test
http://192.168. 142.3:5601 log in to Kibana, click the "Create Index Pattern" button to add the index "filebeat - *", click the "create" button to create, and click the "Discover" button to view the chart information and log information.
4dU76Grb-1639897846802)]
[external chain picture transferring... (img-4pl5YhEm-1639897846802)]
(4) Create a new Logstash configuration file on the node where the Logstash component is located
cd /etc/logstash/conf.d
vim logstash.conf
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.80.10:9200"]
index => "%{[fields][service_name]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
#Start logstash
logstash -f logstash.conf
[external chain picture transferring... (img-2vxBUNjm-1639897846803)]
(5) Browser access test
http://192.168. 142.3:5601 log in to Kibana, click the "Create Index Pattern" button to add the index "filebeat - *", click the "create" button to create, and click the "Discover" button to view the chart information and log information.
[external chain picture transferring... (img-wT2rjvyO-1639897846803)]