1. RBAC authority design idea
-
Administrators assign roles to users
-
Then assign permission points to the role, and the administrator logs out
-
Role login displays the permissions you can use
two Permission application - control dynamic routing (navigation menu)
-
Get all menu IDS accessible to the current user
-
Get all the local dynamic routing lists
-
The two data are filtered together to obtain all the dynamic routing tables that can be accessed by the current user
-
Add the routing table to the routing system so that the route can be accessed
-
Add the routing table to the navigation menu and display it to the left
Start writing code:
1. Find the current user's personal information interface and return the personal information
The return of personal information is basically like this
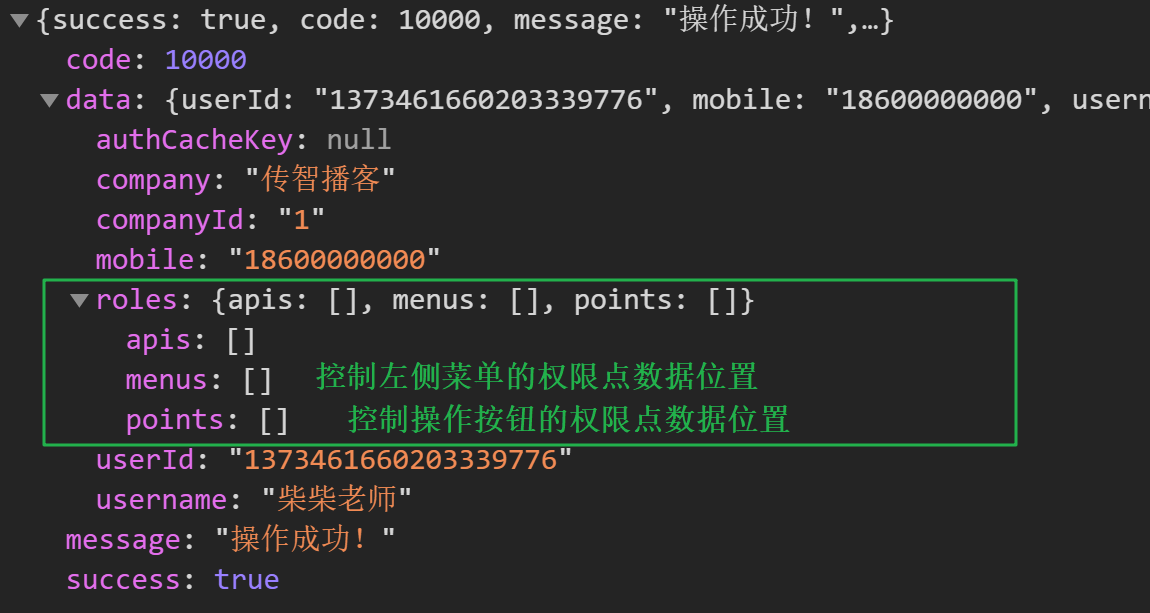
The code is as follows:
// I wrote this in vuex. See where I wrote it at that time
async getUserInfo(ctx) {
// Call the interface to get user information
const res = await getUserInfo()
// Get user Avatar
const info = await getUserDetailById(res.userId)
ctx.commit('setUserInfo', { ...res, ...info })
// Return personal permission data
return res.roles
}two Introduce all dynamic routing tables for filtering
Write in routing guard:
Note: the route. Addroutes () method adds dynamic routes to the application's routing system
import { asyncRoutes } from '@/router'
if (!store.getters.userId) {
// Get menu permission data
const roles = await store.dispatch('user/getUserInfo')
// Filter
// If the name attribute of the route can be found in the menu permission data, the representative can access it
let filterRoutes = []
// Filter filter
filterRoutes = asyncRoutes.filter(route => {
// includes filtering
return roles.menus.includes(item.children[0].name)
})
console.log('The routing table filtered according to permissions is:',filterRoutes)
// Add dynamic routing to the application's routing system
// router.addRoutes(filterRoutes)
// This setting does not work, because the 404 page runs to the middle, you have to take the 404
router.addRoutes([...filterRoutes, { path: '*', redirect: '/404', hidden: true }])
// The key code is here
next({
...to, // The purpose of next ({... To}) is to ensure that the route is added before entering the page (which can be understood as a re-entry)
replace: true // Overwrite last record
})
return
}Operation: manually enter the address of a dynamic route in the browser to see if the corresponding page can be rendered~
three Override menu generation logic
Data used in the current menu rendering: this.$router.options.routes
-
This data is dead and will not increase as you call the addRoutes method
-
This data is not responsive data. Even if there is data in it, it will not be reflected in the view
In other words, if we want to immediately reflect the routing data into the menu after calling the addRoutes method, we need to think like an additional method. Which technology can ensure that the responsive feature can be dynamically modified in vue development? vuex management
1. Define vuex management menu data menu.js
// Import static route
import { constantRoutes } from '@/router'
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
// First, the static routing table is used as the initial value of menu data
menuList: [...constantRoutes]
},
mutations: {
setMenuList(state, asyncRoutes) {
// Combining dynamic routing and static routing
state.menuList = [...constantRoutes, ...asyncRoutes]
}
}
}Return to the routing guard js page and call the setMenuList function
if (!store.getters.userId) {
await store.dispatch('user/getUserInfo')
// Add dynamic routing to the application's routing system
router.addRoutes(asyncRoutes)
// Give the dynamic routing data to the menu
store.commit('menu/setMenuList', asyncRoutes)
}The menu generation section rewrites the data in vuex
routes() {
// What you get is a complete data structure including static routing and dynamic routing
// return this.$router.options.routes
return this.$store.state.menu.menuList
}