preface
The purpose of this article is to record my content about GitHub. It explains every step from registration, download to successful setting. Some screenshots or code come from the network.
Both GitHub and code cloud are based on Git, so their operation methods are basically the same. You only need to learn one of them.
Both GitHub and code cloud provide free code warehouses.
GitHub free version can only create public projects, and private projects need to be paid. As of the publication of this article, the service fee is $7.00;
Code cloud free version supports organizations with less than 5 people and can create private projects.
Code cloud: https://gitee.com/
GitHub: https://github.com
Because GitHub is an all English interface, the learning cost is a little high for an English blind, so I start from code cloud.
Text
1. Account registration:
Whether GitHub or code cloud (hereinafter referred to as Gitee), to use them, we need to register an account first. Those with existing accounts can skip this step.
|

|
| Gitee | GitHub |
2. Create warehouse:
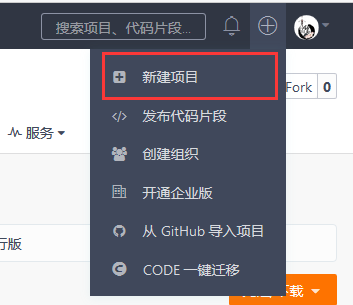
a. Create remote warehouse
After logging in to Gitee, click the "+" plus sign -- > next to the avatar to create a new project
The operation mode of GitHub is similar to that of Gitee. There is no screenshot comparison here
After filling in the basic information of the project, directly click create, so that a remote warehouse has been created.
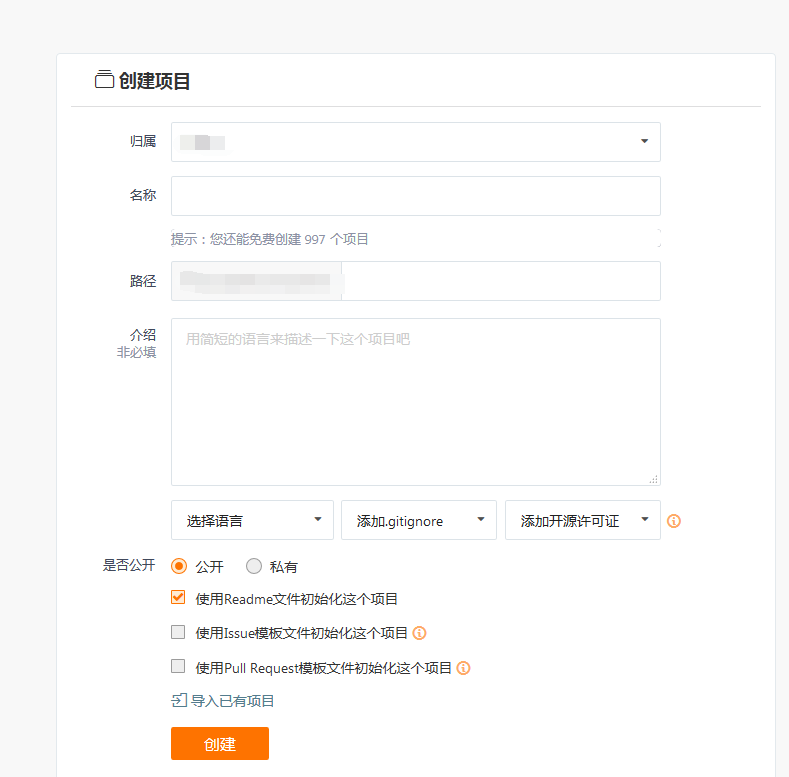
b. initialize local warehouse
1)Git Bash installation
The initialization of the local warehouse needs to be completed with the help of the software Git Bash. Click to go to Git official website
Download the Git version applicable to your computer, run the installation program after downloading, and use the default option in the process. If you need to modify the installation path, ensure that the installation path is in English.
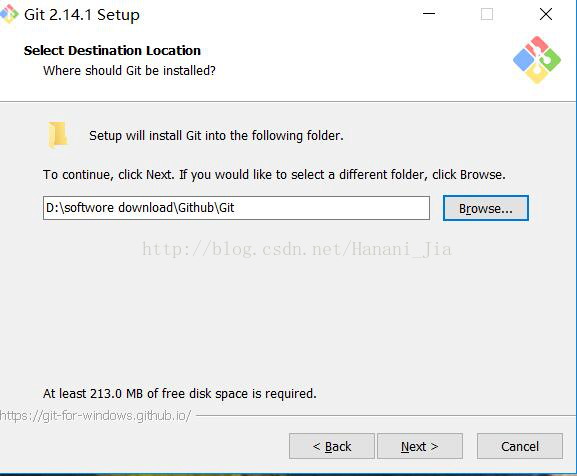
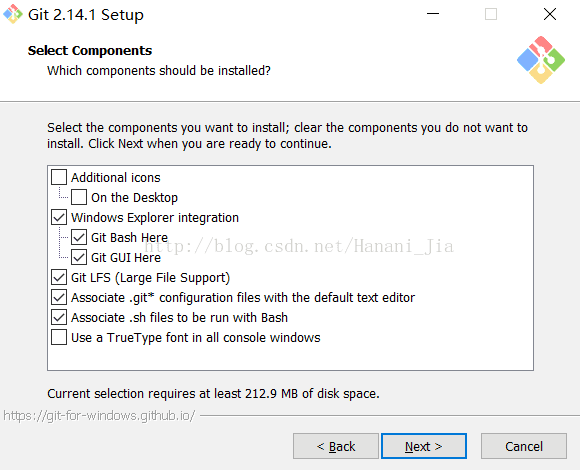
After installation, run Git Bash and the following command line window will appear,
Hanani@LAPTOP -What does afp6hies mingw64 ~ mean,
@The former is the computer user name,
@Followed by the computer name,
MINGW64 indicates the information of the running Git Bash
~Indicates the root directory. By default, it is C:\Users\Administrator. Here, it is C:\Users\Hanani
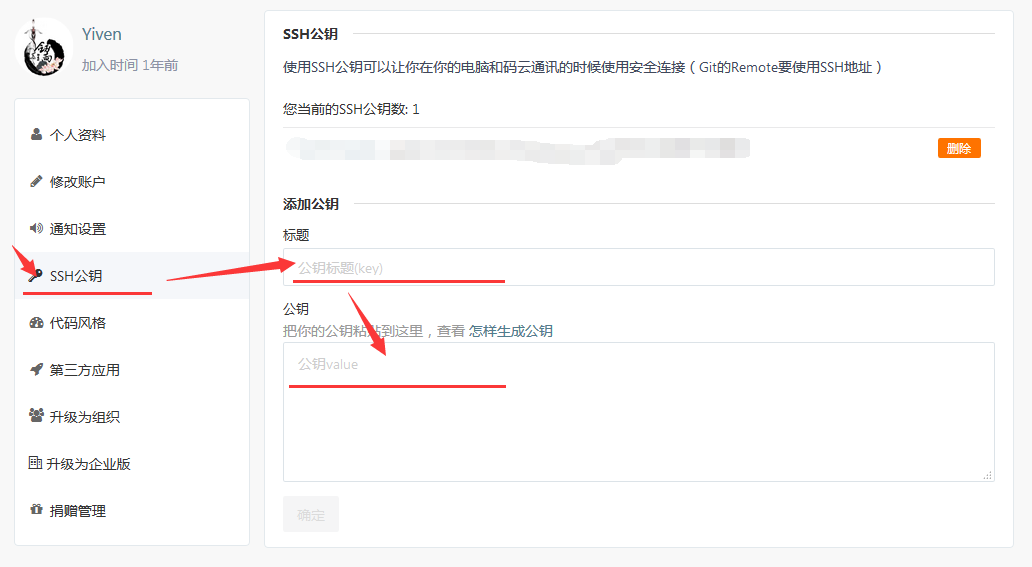
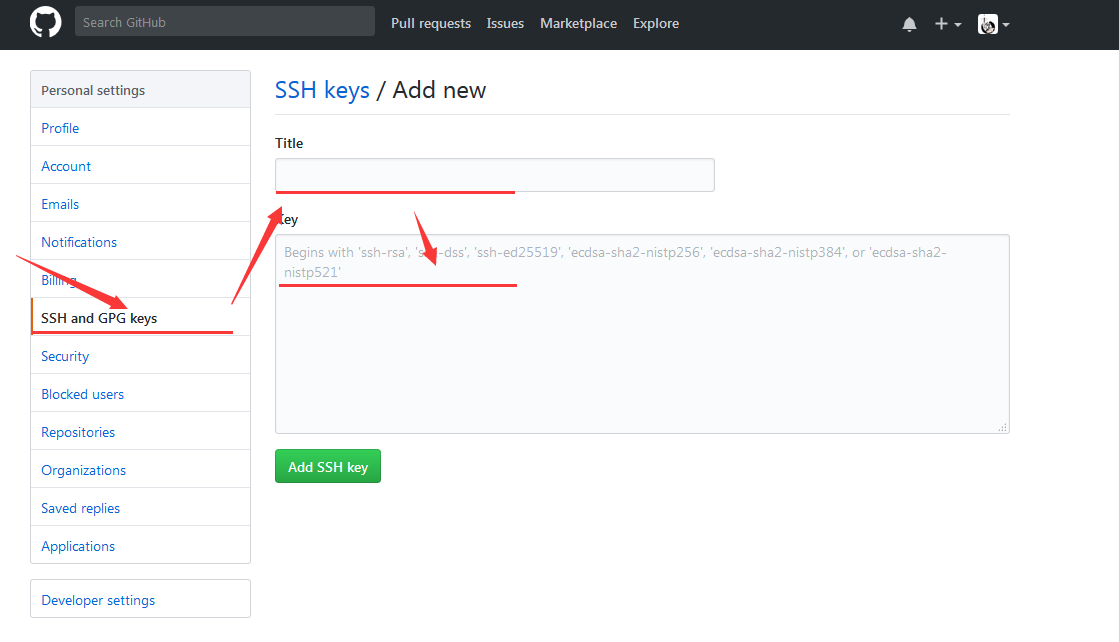
2) Get SSHKey
First, create an ssh key locally. The purpose of this is that you now need to obtain a key on your computer.
Generate sshkey with the following command:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "youremail@youremail.com" # Generating public/private rsa key pair...# Press enter three times to generate ssh key
Check your public key,
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub# ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2E... youremail@youremail.com
And add it to Gitee (gitee.com SSHKey add address )Or GitHub (github.com SSHKey add address)
|
|
|
| Gitee | GitHub |
After adding, enter in the terminal
#Gitee$ ssh -T git@gitee.com#GitHub$ ssh -T git@github.com
When Binding for the first time, you will be prompted whether to continue after entering the above code. After entering yes, the program will automatically connect. If login is required, you can directly enter the login information.
Execute the above command again to check whether the connection is successful. If the following information is returned, it indicates that the addition is successful
1 2 3 4 5 #Gitee Welcome to Gitee.com, YourName! #GitHub You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not provide shell access.
3) Set basic information
Next, you need to set up some simple things.
$ git config --global user.name "yourname"$ git config --global user.email "youremail@youremail.com"
name should be consistent with the code cloud or GitHub as much as possible, but the email must be the email used when the code cloud or GitHub is registered. Commands are not sequential.
4) Initialize local library
Then clone your remote warehouse locally, or you can initialize a project locally and then bind to the cloud.
clone
#Gitee$ git clone https://gitee.com/yourname/repository#Github$ git clone https://github.com/yourname/repository.git#yourname You are in code cloud or github Registered user name#Repository is the name of the remote repository you created
Local initialization
#Gitee$ cd d:/test //First create a project folder in the file system, and then Git in cd To this project directory$ git init //Initialize local project$ git remote add origin <Remote warehouse address> //Bind remote warehouse#notes:The address form is https://gitee.com/yourname/test.git or git@gitee.com:yourname/test.git#Github$ cd d:/test$ git init$ git remote add origin <Remote warehouse address>
#Note: the address form is https://github.com/yourname/test.git
c. Update to remote warehouse
After editing locally, update to the remote warehouse
git add . //Specify what to update . Indicates all updates, test.txt Indicates that the specified file is updatedgit commit -m "Some notes" //Add update descriptiongit push origin master //Perform update operation
During the update operation, the program responds slowly because it needs to verify the user information of the remote warehouse. Don't think Git Bash is dead
If it is the first update, the following window may pop up, enter your user name and password, and click login.
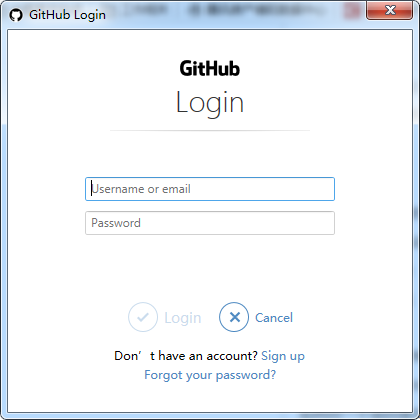
If this happens during subsequent update operations, it means that the login failed. You need to re record your user information and enter your user name and password again to log in
Logon failed, use ctrl+c to cancel basic credential prompt.Username for 'https://githun.com'
Two more words at the end
How to synchronize the latest version from the remote warehouse to the local
$ cd d:/test$ git pull origin master
How to clear the screen
$ clear
reference resources:
Code cloud platform help document http://git.mydoc.io/
---------------------
Author: Yiven
Source: CNBLOGS
Original text: https://www.cnblogs.com/yiven/p/8465054.html
Copyright notice: This article is the author's original article. Please attach the blog link for reprint!