brief introduction
JDBC (Java database connectivity) is a Java API used to execute SQL statements. It can provide unified access to a variety of relational databases. It consists of a group of classes and interfaces written in Java language. JDBC provides a benchmark by which more advanced tools and interfaces can be built, enabling database developers to write database applications
Note: the above is quoted from Baidu Encyclopedia JDBC
Environmental preparation
Eclipse+JDK8+Mysql
Project directory
In this paper, the author uses java application to build a simple jdbc project
jar package used
Database connection configuration
- Load JDBC configuration file (jdbc.properties)
/**
* Instantiate Properties
*/
private static Properties properties = new Properties();
static {
/**
* Absolute path to load configuration file (1) class: class. Class. Getclass(). Getresource ("/). Getpath ()
*/
try {
properties.load(JDBCTemplate.class.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}-
Set link configuration
private static Connection connection = null; private static PreparedStatement preparedstatement = null; private static ResultSet resultSet = null; /** * <p> * Title: precompile * </p> * <p> * Description: * </p> * * @param sql * @throws ClassNotFoundException * @throws SQLException */ private static void precompile(String sql) throws Exception { /** * Specify connection driver */ Class.forName(properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver")); /** * Get database connection */ connection = DriverManager.getConnection(properties.getProperty("jdbc.url"), properties.getProperty("jdbc.user"), properties.getProperty("jdbc.password")); /** * Precompiled sql */ preparedstatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); } /** * <p> * Title: close * </p> * <p> * Description: Close connection * </p> */ private static void close() { try { connection.close(); preparedstatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } -
Execute SQL operation (in this paper, I add, delete, and check mixed encapsulation, and suggest that I check separately encapsulation)
/** * Execute sql * <p> * Title: executeQuery * </p> * <p> * Description: operation: Operation ①: JdbcMode.QUERY.operation() query * ②: JdbcMode.INSERT.operation()Insert ③: JdbcMode.UPDATE.operation() update * ④: JdbcMode.DELETE.operation()Delete claszz: Specifies the return value type (add, delete, change to nullable), and the query operation returns list < T >. * </p> * * @param sql * Execute sql * @param operation * operation * @param claszz * return type * @param params * Set the value of placeholder (note the order of parameters) (no placeholder can be null) * @return Object * @throws Exception */ public static <T> Object execute(String sql, List<Object> params, String operation, Class<T> claszz) throws Exception { /** * Precompiled sql */ precompile(sql); /** * Set the value of placeholder (note the order of parameters) */ if (params != null && params.size() > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < params.size(); i++) { preparedstatement.setObject(i + 1, params.get(i)); } } switch (JdbcMode.getByValue(operation)) { case UPDATE: /** * Perform modification */ int countu = preparedstatement.executeUpdate(); close(); return countu; case INSERT: /** * Perform insert operation */ int counti = preparedstatement.executeUpdate(); close(); return counti; case DELETE: /** * Perform delete operation */ int countd = preparedstatement.executeUpdate(); close(); return countd; case QUERY: /** * Execute query to get result set */ resultSet = preparedstatement.executeQuery(); List<T> listT = getModel(resultSet, claszz); close(); return listT; default: break; } /** * Close connection */ close(); return null; }PS: for the use of enumeration constants, please refer to the author Constants for ENUM usage in Java Bowen
-
Convert the result set of the query to the specified object
/** * <p> * Title: getModel * </p> * <p> * Description: Replace data in result set with object * </p> * * @param resultSet * @param t * @return * @throws Exception */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private static <T> List<T> getModel(ResultSet resultSet, Class<T> claszz) throws Exception { ResultSetMetaData metadata = resultSet.getMetaData(); List<T> listT = new ArrayList<>(); while (resultSet.next()) { int columncount = metadata.getColumnCount(); if (columncount == 1) { listT.add((T) resultSet.getObject(1)); } else { Map<String, Object> mapdata = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= columncount; i++) { // Gets the column name of the specified column String columnName = metadata.getColumnName(i); // Gets the column value of the specified column Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i); mapdata.put(columnName, columnValue); } T obj = claszz.newInstance(); BeanUtils.populate(obj, mapdata); listT.add(obj); } } return listT; }
JDBC configuration file
#Database connection
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://...../databasename?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
#Database driven
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#user name
jdbc.user=user
#Password
jdbc.password=pwdRun tests
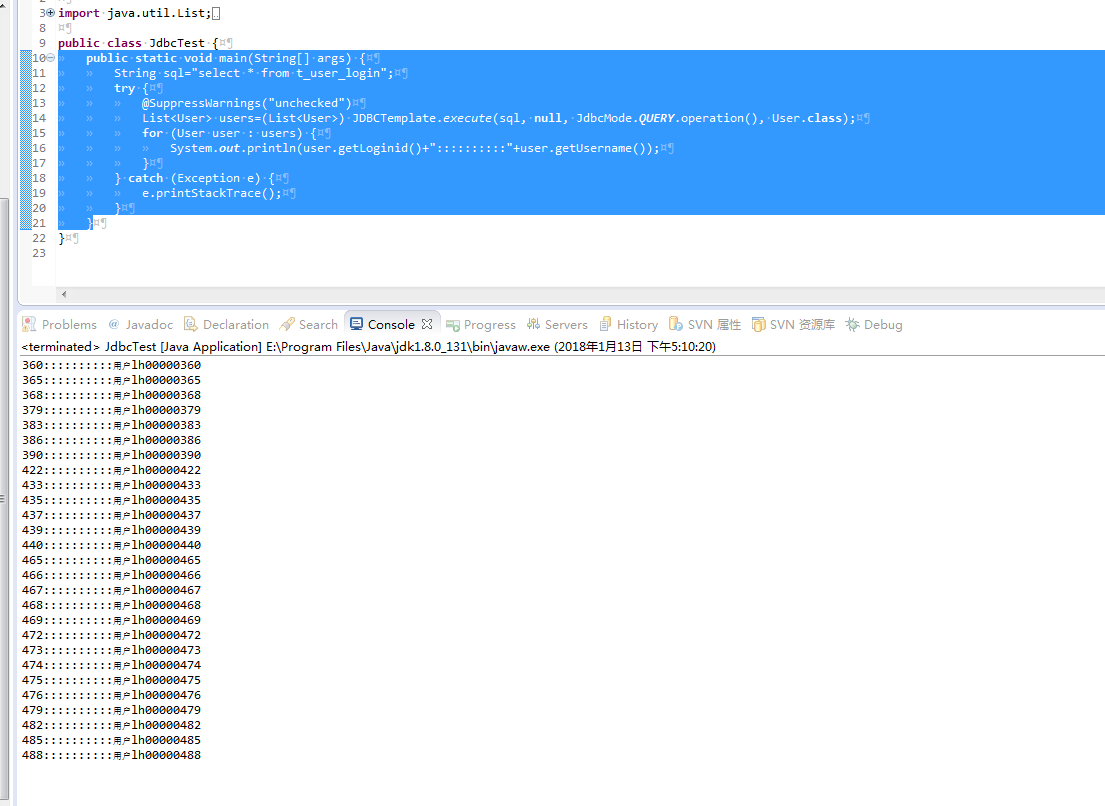
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sql="select * from t_user_login";
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<User> users=(List<User>) JDBCTemplate.execute(sql, null, JdbcMode.QUERY.operation(), User.class);
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user.getLoginid()+"::::::::::"+user.getUsername());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}