📢📢📢📣📣📣
Hello! Hello, everyone. I'm [one heart classmate], a highly motivated [Java domain blogger]! 😜😜😜
✨ Writing style of [one heart students]: I like to explain every knowledge point in [easy to understand] writing, rather than using [tall and tall] official statement.
✨ The field of the blog is the learning of back-end technology, and more back-end technology and learning experience will be continuously updated in the future.
✨ If there is [xiaocute] who is interested in [back-end technology], please pay attention to [one heart students] 💞💞💞
❤️❤️❤️ Thank you, big and small! ❤️❤️❤️
catalogue
3, Basic operation of documents
Second: Post_ Update (recommended)
4.9.2 environmental preparation
4.10 exact query of multi value matching
🚀 Customize highlighted styles
1, What is the Rest style?
Rest style is a software architecture style, not a standard, but provides a set of design principles and constraints. It is mainly used for client and server interaction software. The software designed based on this style can be more concise, more hierarchical, and easier to implement caching and other mechanisms.
Basic Rest command:
| method | url address | describe |
|---|---|---|
| PUT (create, modify) | localhost:9200 / index name / type name / document id | Create document (specify document id) |
| POST (create) | localhost:9200 / index name / type name | Create document (random document id) |
| POST (modify) | Index type / localid / host: 9200/_ update | Modify document |
| DELETE | localhost:9200 / index name / type name / document id | remove document |
| GET (query) | localhost:9200 / index name / type name / document id | Query document ID |
| POST (query) | localhost:9200 / index name / type name / document id/_search | Query all data |
2, Basic operation of index
2.1 create index and add data
Syntax:
PUT /Index name/Type name/file id
{
Request body
}code:
PUT /yixin/user/1
{
"name":"Wholeheartedly",
"age":18
}result:
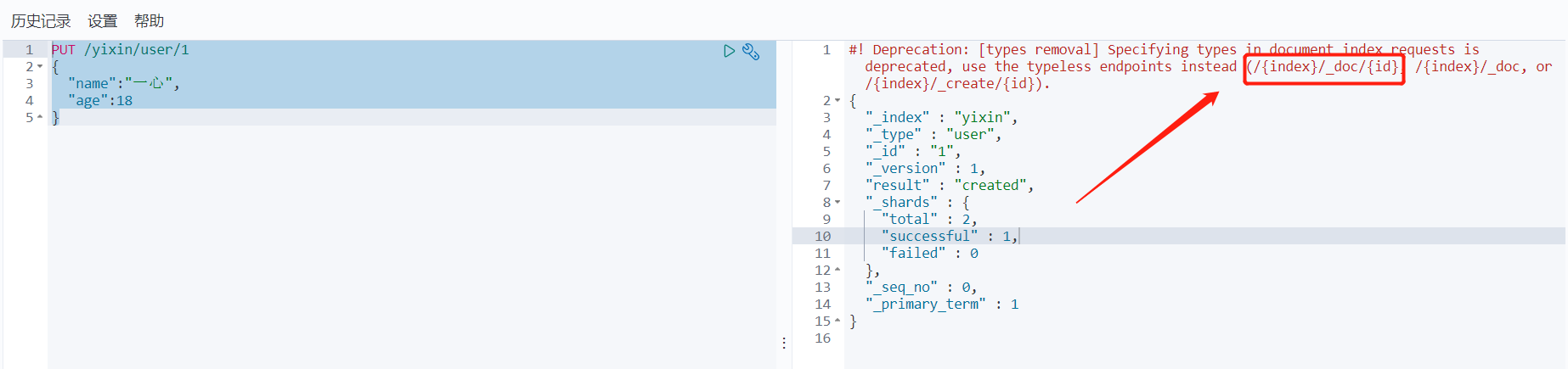
This is successful, but the prompt tells us that type will be gradually discarded in future versions, so a default type is generated_ doc.
2.2 acquisition rules
Function: through GET, you can request specific information and view our index information.
Syntax:
GET Index name
Input:
GET yixin
result:
It can be found that if we do not specify the field type when creating the index, it will assign the type to our field by default.
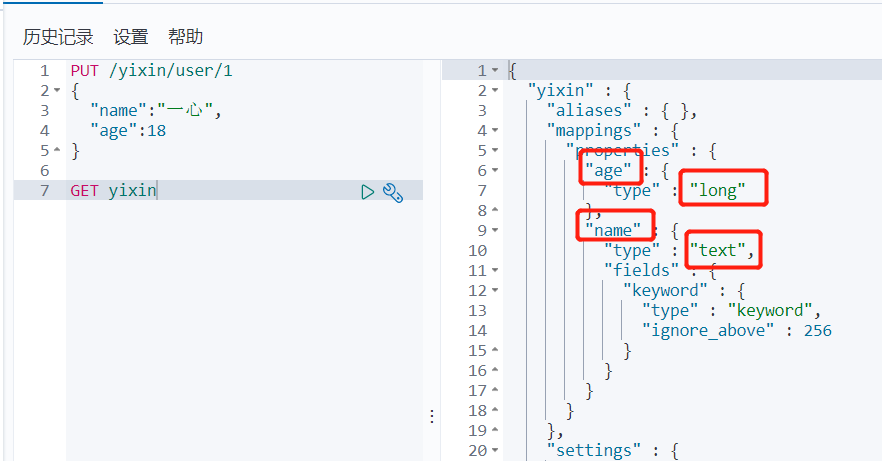
2.3 specifying field types
Function: it is used to create rules, which is similar to building a database (establishing indexes and corresponding types of fields), and can also be regarded as the establishment of rules.
Common field data types:
| type | attribute |
| String type | Text: supports word segmentation, full-text retrieval, fuzzy and accurate query, and does not support aggregation and sorting operations; The maximum supported character length of text type is unlimited, which is suitable for large field storage; Keyword: no word segmentation, direct index, fuzzy, accurate matching, aggregation and sorting. The maximum supported length of keyword type is 32766 UTF-8 characters. You can set ignore_above specifies the length of the self-contained character. The data exceeding the given length will not be indexed and the returned results cannot be accurately matched and retrieved through term. |
| Numerical type | long,Integer,short,byte,double,float,half float,scaled float |
| Date type | date |
| Boolean type | boolean |
| Binary type | binary |
code:
PUT /test1
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name":{
"type": "text"
},
"age":{
"type": "long"
},
"birthday":{
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}Get rules:
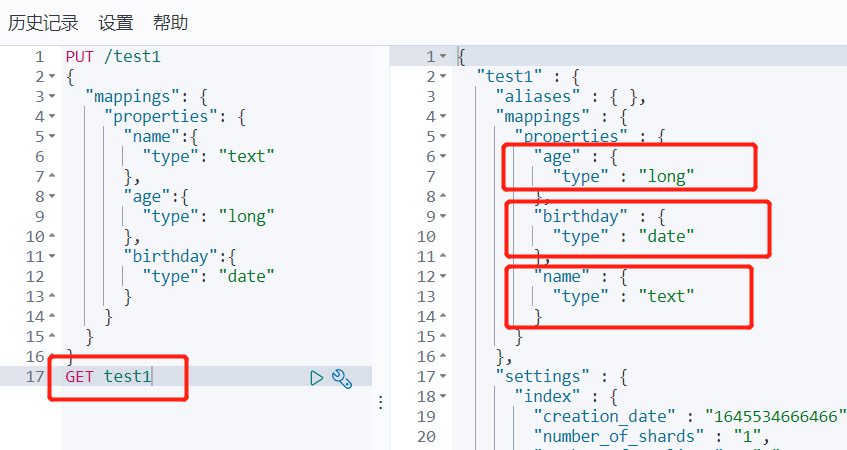
Now we just need to insert data according to the corresponding type:
PUT /test1/_doc/1
{
"name":"Wholeheartedly",
"age":18,
"birthday":"2000-01-01"
}2.4 delete index
Syntax:
DELETE /Index name
Input:
DELETE /test1
Note: if you only want to delete a document, it is DELETE /test1/_doc/1.
3, Basic operation of documents
3.1 adding data
code:
PUT /yixin/user/1
{
"name":"yixin",
"age":18
}To view indexed data:
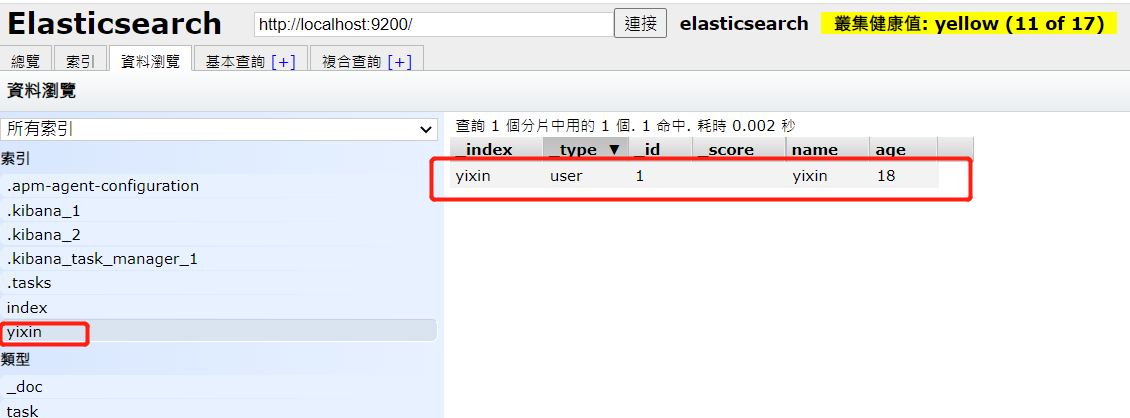
3.2 data acquisition
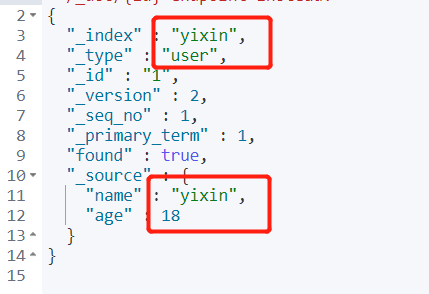
code:
GET yixin/user/1
result:
3.3 update data
First: use PUT
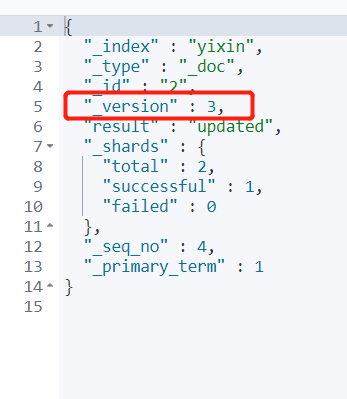
code:
PUT /yixin/user/2
{
"name":"One heart classmate",
"age":18
}Output:
Analysis: "version" represents the number of times this data has been changed. Each time PUT is executed, whether it is changed or not, the verson value will increase, and if the document attribute of PUT does not pass a value, it will be overwritten.
Second: Post_ Update (recommended)
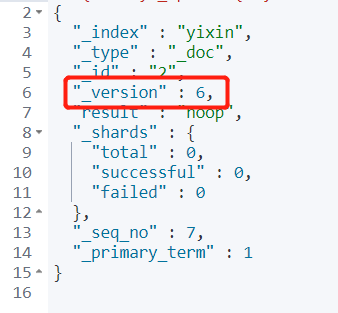
code:
POST yixin/user/2/_update
{
"doc":{
"name":"One heart"
}
}Output:
Analysis: "verson" also refers to the number of changes. If POST is executed multiple times without modification, the verson value remains unchanged, and our field has no set value and will not be overwritten, so it has high flexibility!
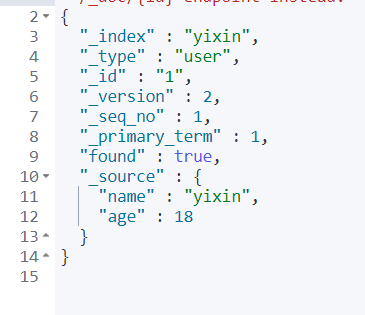
3.4 simple query
Demand: query a piece of data.
GET yixin/user/1
Output:
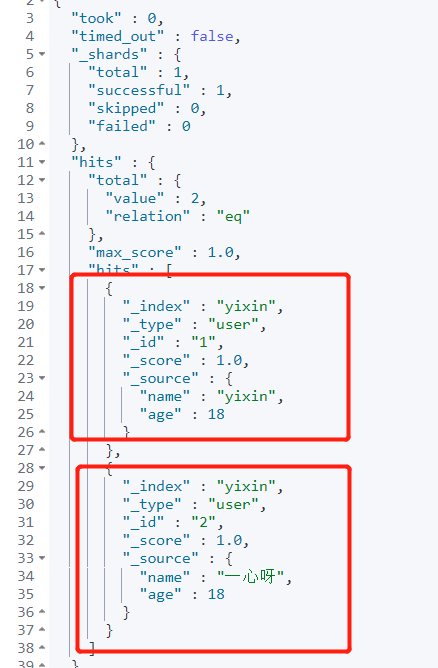
Requirement: query all data.
GET yixin/user/_search
Output:
4, search query operation
4.1} condition query
Requirements: query users whose name has "one heart" and age is 18 years old.
GET yixin/user/_search?q=name:"Wholeheartedly",age:18
Output:
4.2 fuzzy query
Keywords: match
Requirement: query hits users with "one heart".
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
}
}Output:

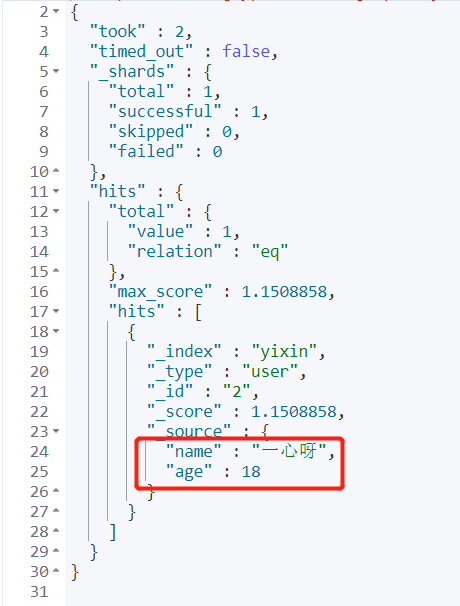
4.3 result filtering
Keyword: source
Function: if we don't want to show so much information, we can use_ source to filter the results.
Requirement: only name is displayed in the output field.
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
},
"_source": ["name"]
}Output:
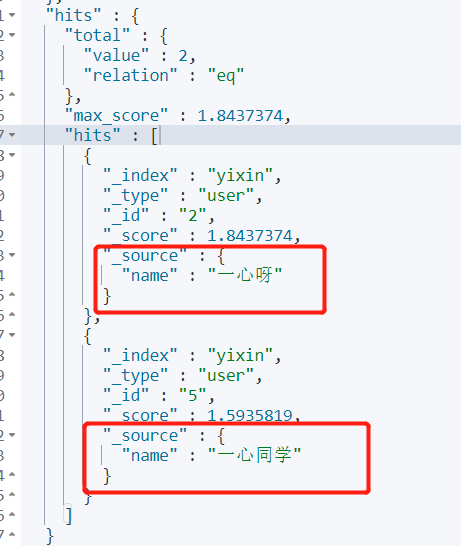
4.4 sorting
Keywords: sort
- Descending order: desc
- Ascending: asc
Requirements: match names with "one heart" and rank them in descending order according to age.
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}Output:
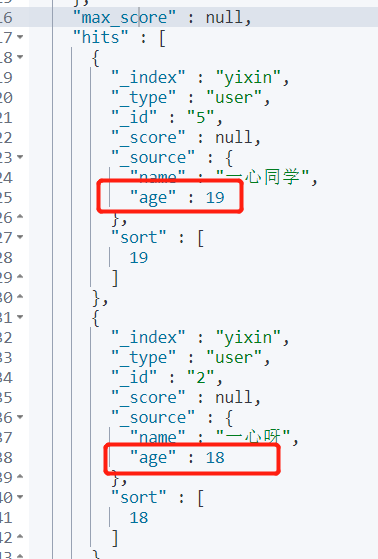
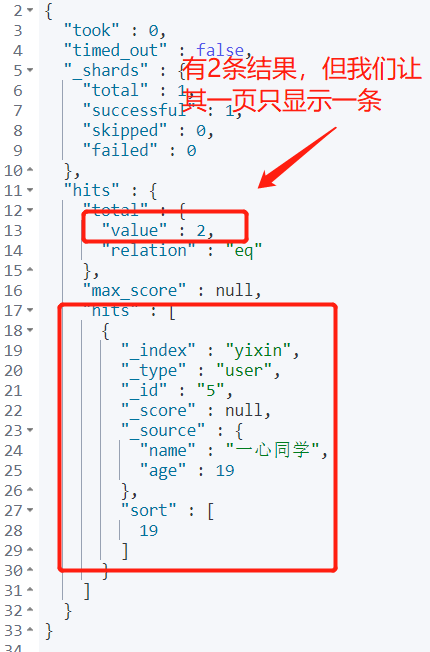
4.5 paging
key word:
From: start from the first data, and the subscript starts from 0.
size: how many pieces of data are returned on a single page.
Requirements: match the names with "one heart" and in descending order by age. Only one piece of data is displayed on each page and the first page is returned.
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"from": 0,
"size": 1
}
Output:
4.6 multi criteria query
key word:
bool: Boolean query
Must (and): all conditions must meet where id=1 and name = xxx
should (or): all conditions must meet where id=1 or name = xxx
must_not (not): non-conforming conditions
🌴 must
Requirements: query users whose name is "one heart" and age is 19.
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
},
{
"match": {
"age": "19"
}
}
]
}
}
}Output:

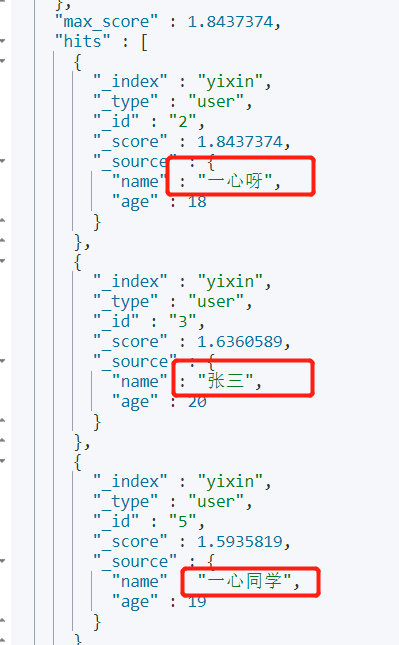
🌴 should
Requirement: query users with "one heart" or "Zhang".
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
},
{
"match": {
"name": "Zhang"
}
}
]
}
}
}Output:
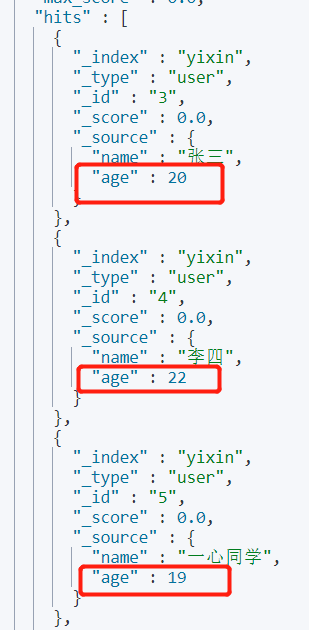
🌴 must_not(not)
Requirements: query users who are not 18 years old.
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
}
]
}
}
}Output:
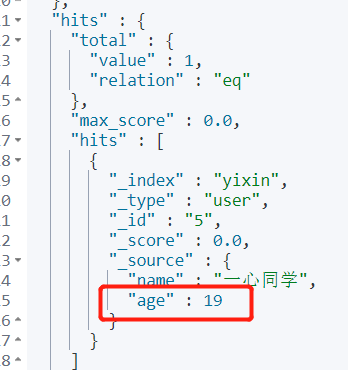
4.7 filter
Keywords: filter
- gt greater than
- gte is greater than or equal to
- lt less than
- lte less than or equal to
Requirement 1: query users younger than 20 years old, but not equal to 18 years old.
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"lt": 20
}
}
}
}
}
}Output:
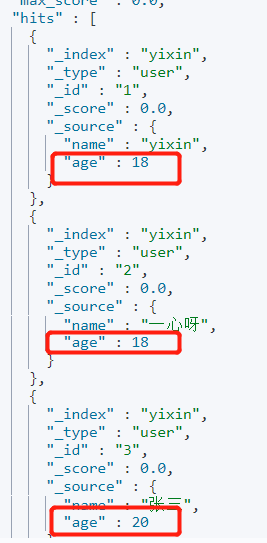
Requirement 2: query users aged 15-20.
GET yixin/user/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 15,
"lte": 20
}
}
}
}
}
}Output:
4.8 multi criteria query
🌵 Environmental preparation
PUT /yixin2/user/1
{
"name":"One heart classmate",
"age":18,
"tags":["technology","motion","social contact"]
}
PUT /yixin2/user/2
{
"name":"Zhang San",
"age":20,
"tags":["game","motion","Drink coffee"]
}
PUT /yixin2/user/3
{
"name":"Li Si",
"age":21,
"tags":["skiing","technology"]
}🌵 query
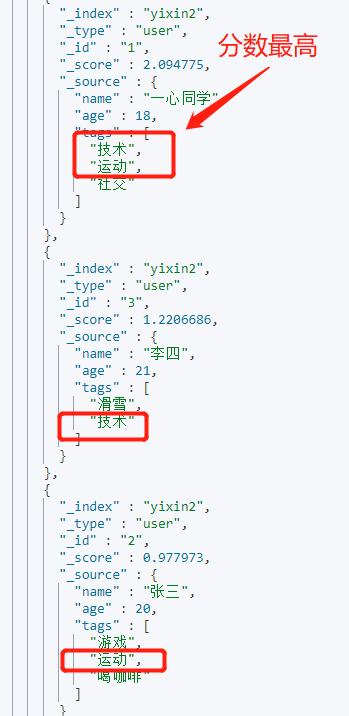
Requirements: query users with "technology" or "Sports" in the tag.
GET yixin2/user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"tags": "Technical movement"
}
}
}Output:
4.9 precise query
Key words: term
term: precise query. The value of the query is not divided into words. It is directly entered into the inverted index to match.
match; Fuzzy query, the value of the query word segmentation, word segmentation results one by one into the inverted index to match
4.9.1 text and keyword
text: when writing, the written values are segmented and then inserted into the inverted index one by one.
keyword: when writing, insert the whole value into the inverted index without word segmentation.
Query keyword:
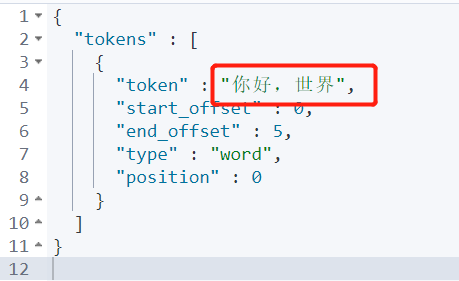
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "keyword",
"text": "Hello, world"
}Output:
It can be found that words will not be split!
Query common types:
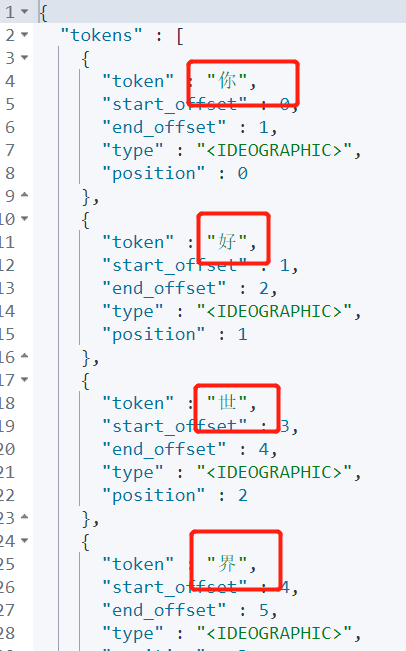
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "Hello, world"
}Output:
4.9.2 environmental preparation
PUT /yixin3
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"age":{
"type": "long"
},
"desc":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
PUT /yixin3/_doc/1
{
"name":"One heart classmate",
"age":18,
"desc":"Focus on Java"
}
4.9.3 query
Keyword segmentation
Let's segment "one heart classmate". Since name belongs to keyword, we use keyword to segment words:
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "keyword",
"text": "One heart classmate"
}Output:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "One heart classmate",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}
In other words, for accurate query, we can only query "one heart students" to show success!
Non keyword segmentation
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "Focus on java"
}Output:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "expert",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "notes",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "to",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "java",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
}
]
}
In other words, for accurate query, we can query successfully as long as we input any words after word segmentation!
🚀 Query succeeded:
GET yixin3/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name":"One heart classmate"
}
}
}🚀 Query succeeded:
GET yixin3/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"desc":"expert"
}
}
}🚀 Query succeeded:
GET yixin3/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"desc":"java"
}
}
}🚀 Query failed:
GET yixin3/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name":"Wholeheartedly"
}
}
}🚀 Query failed:
GET yixin3/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"desc":"Focus on Java"
}
}
}The analysis shows that:
| Query type | Write type | result |
|---|---|---|
| term | text | nothing |
| term | keyword | have |
| match | text | have |
| match | keyword | have |
4.10 exact query of multi value matching
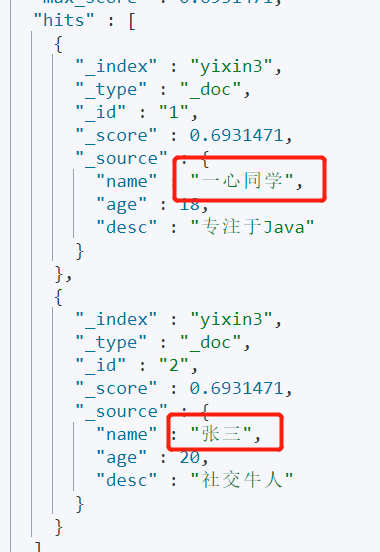
Demand: query users named "Zhang San" and "one heart classmate".
GET yixin3/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"name": "Zhang San"
}
},{
"term": {
"name": "One heart classmate"
}
}
]
}
}
}Output:
Highlight 11.4
Key words: highlight
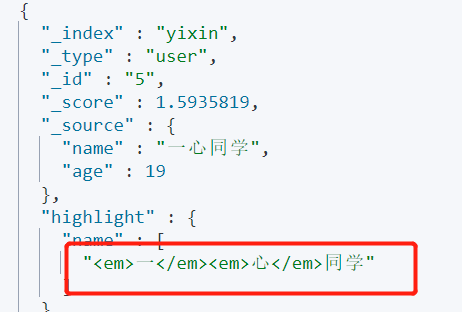
🚀 Default style
Requirement: highlight the search term.
GET yixin/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}Output:
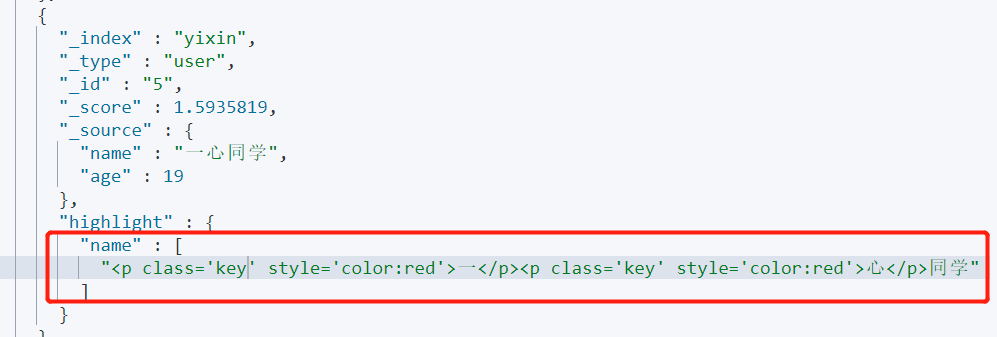
🚀 Customize highlighted styles
pre_tags: prefix
post_tags: suffix
code:
GET yixin/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "Wholeheartedly"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<p class='key' style='color:red'>",
"post_tags": "</p>",
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}Output:
Summary
The above is the basic operation of ElasticSearch compiled by "one heart student". For the above knowledge points, it is very important to [Master] the big housework. It is suggested to follow the idea of "one heart student" and knock it by yourself. I believe it will be mastered [faster]!
If this [article] is helpful to you, I hope I can praise [one heart classmate] 👍, It's not easy to create. Compared with the official statement, I prefer to use [easy to understand] to explain every knowledge point. If there are cute people who are interested in [back-end technology], they are also welcome to pay attention ❤️❤️❤️ [one heart students] ❤️❤️❤️, I will bring you great [harvest and surprise] 💕💕!