Basic operation example
1. LED
There are four LEDs in pyBoard, namely LED (1) - led (4). The constructor and calling method of LED are as follows: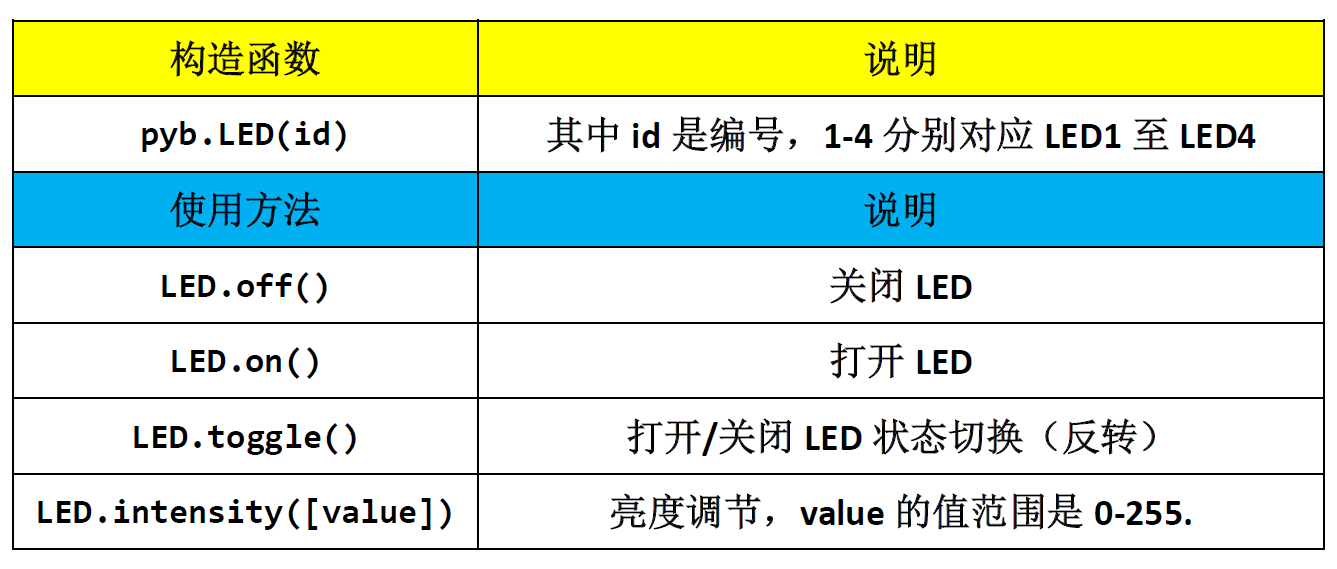
Example code to illuminate LED(4):
from pyb import LED LED(4).on()
2. button
There are two keys on pyBoard, one is reset key: RST, and the other is USER key. The constructor and calling method of key in MicroPython are as follows: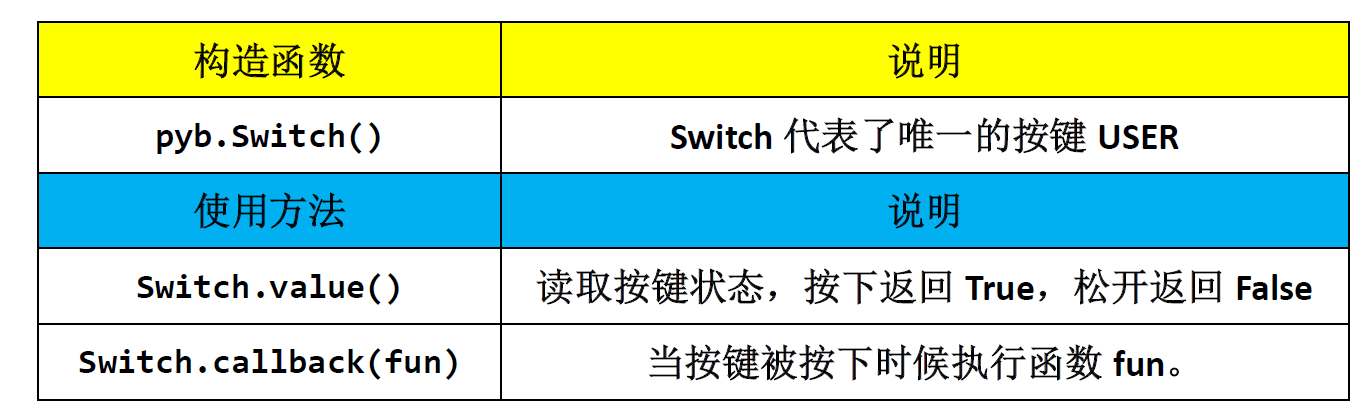
Press the key to call the sample code (press USER to light the LED):
from pyb import LED,Switch def fun1(): LED(4).toggle() sw = Switch() #Define the key object name as sw sw.callback(fun1) #When the key is pressed, the function fun1() is executed, i.e. the LED(4) status is reversed
The use of callback functions can also be replaced by the following:
from pyb import LED,Switch sw = Switch() #Define the key object name as sw sw.callback(lambda:LED(4).toggle()) #When the key is pressed, the LED(4) status reverses
3. GPIO
Almost all IO on pyBoard can be configured with GPIO. Its constructor and calling method are as follows: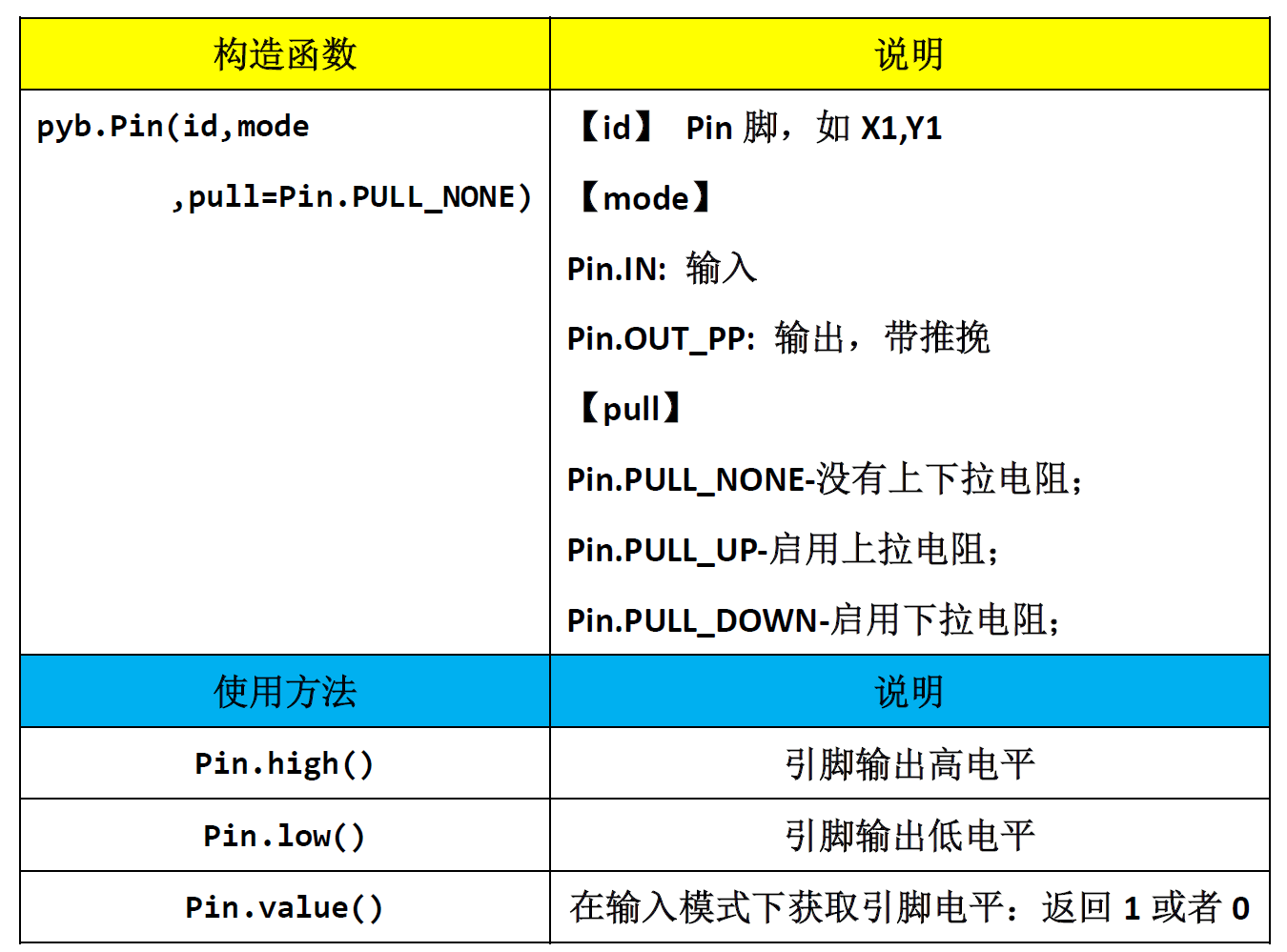
GPIO sample code:
from pyb import Pin #Configure LED(4)-"B4" to push-pull output mode p_out=Pin('B4',Pin.OUT_PP) #Configure USR key - "X17" as input mode p_in = Pin('X17', Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) while True: if p_in.value()==0: #USR pressed to ground p_out.high() #Turn on LED (4) blue light else: p_out.low() #Turn off LED (4) blue light
'B4' and 'X17' in the example are pins corresponding to LED(4) and USR: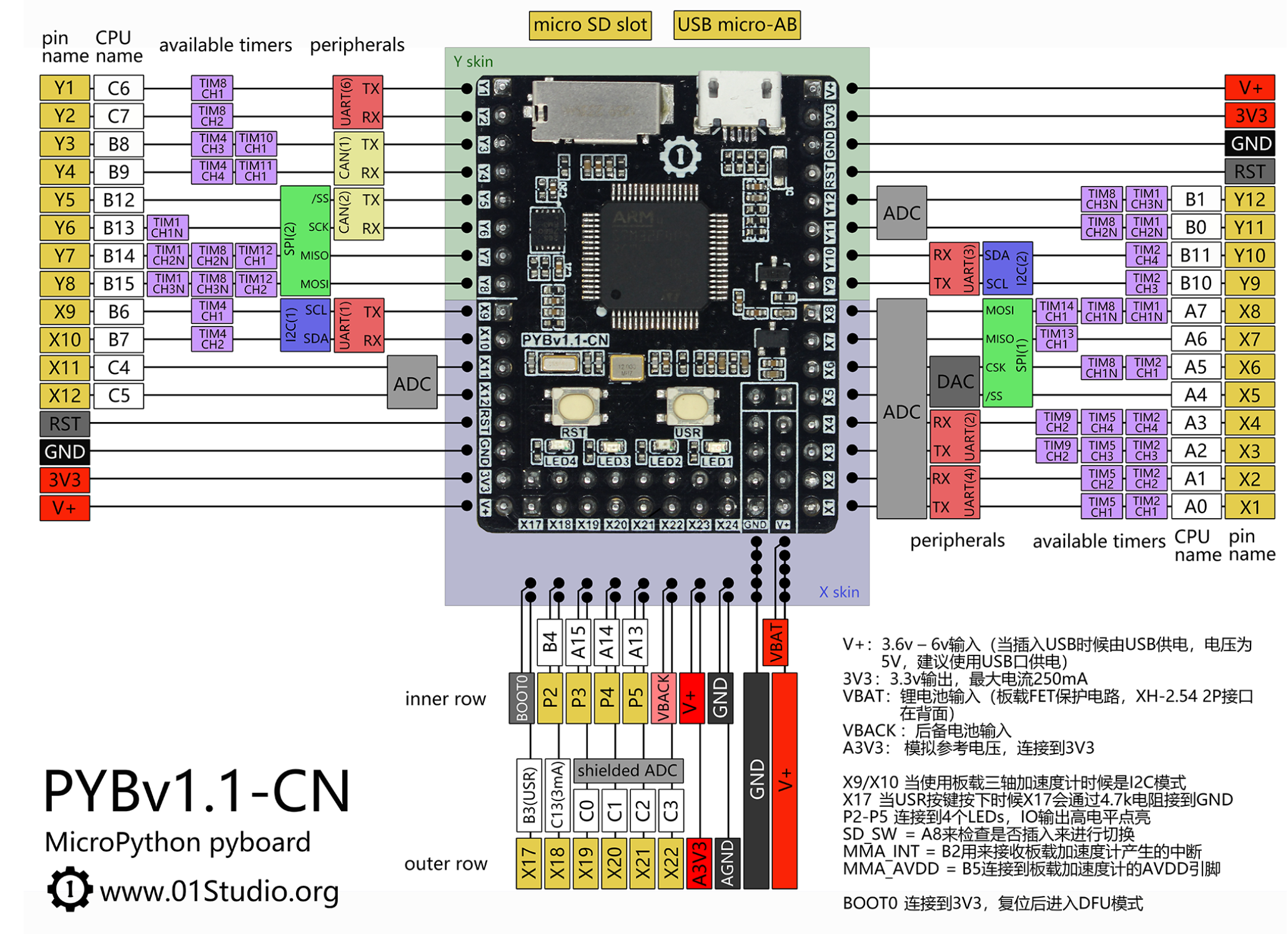
4. External interruption
The external interrupt is completed by GPIO. Every IO on pyBoard has the function of external interrupt. The constructor and calling method of external interrupt are as follows: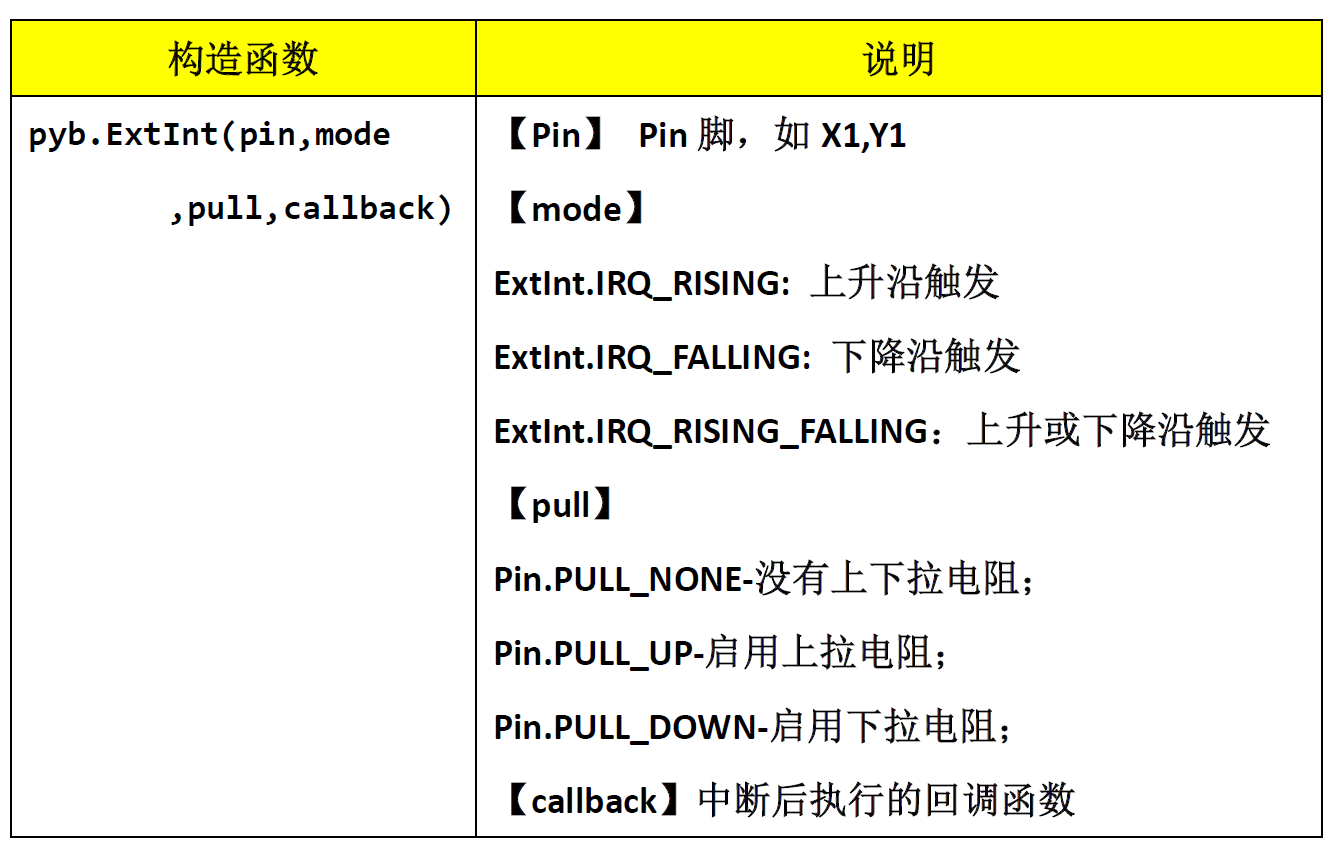
External interrupt example method:
from pyb import Pin,ExtInt,LED callback = lambda e: LED(4).toggle() #Falling edge trigger, turn on pull-up resistance ext = ExtInt(Pin('Y1'), ExtInt.IRQ_FALLING, Pin.PULL_UP, callback)
5. I2C bus
Taking I2C communication of OLED and pyBoard as an example, the pins connecting OLED are Y8(SDA) and Y6(SCL), respectively. This routine uses the Machine module of MicroPython to define the Pin port and I2C initialization.
Constructor and usage of Pin in Mchine: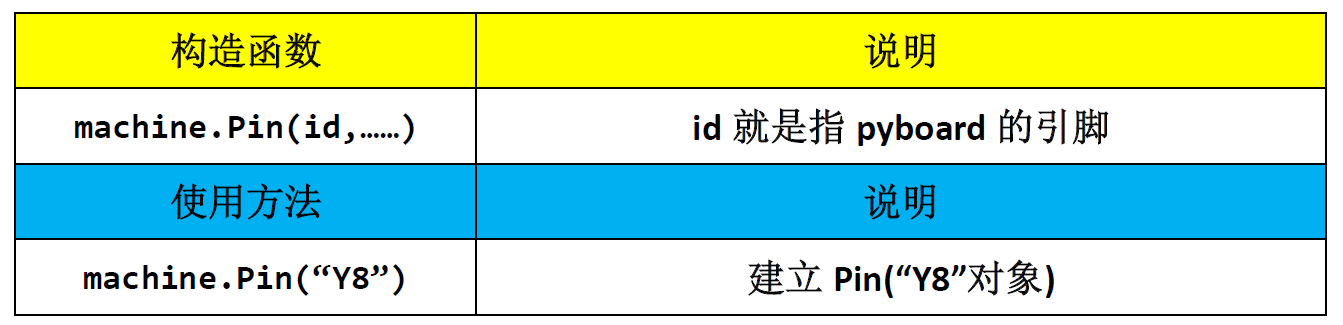
Constructor and usage of I2C in Machine: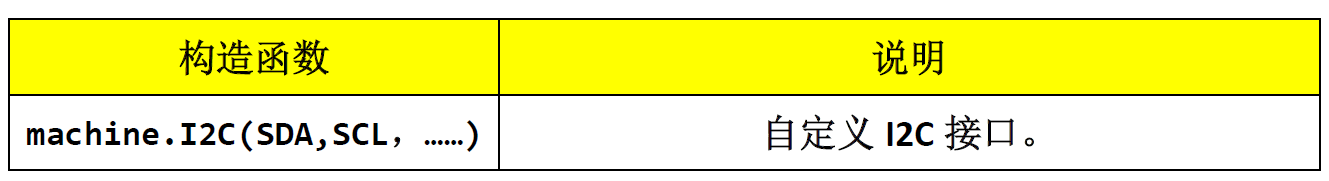

The sample code is as follows:
from machine import I2C,Pin #Import I2C and Pin submodules from machine module from ssd1306 import SSD1306_I2C #Import ssd1306 ﹣ I2C submodule from ssd1306 module i2c = I2C(sda=Pin("Y8"), scl=Pin("Y6")) #pyBoard I2C initialization: SDA -- > Y8, SCL -- > y6 oled = SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c, addr=0x3c) #OLED display initialization: 128 * 64 resolution, the I2C address of OLED is 0x3c oled.text("Hello World!", 0, 0) #Write line 1 oled.text("MicroPython", 0, 20) #Write line 2 oled.text("By 01Studio", 0, 50) #Write line 3 oled.show() #OLED execution display
6. ADC
The built-in ADC's constructor and calling method in pyBoard are: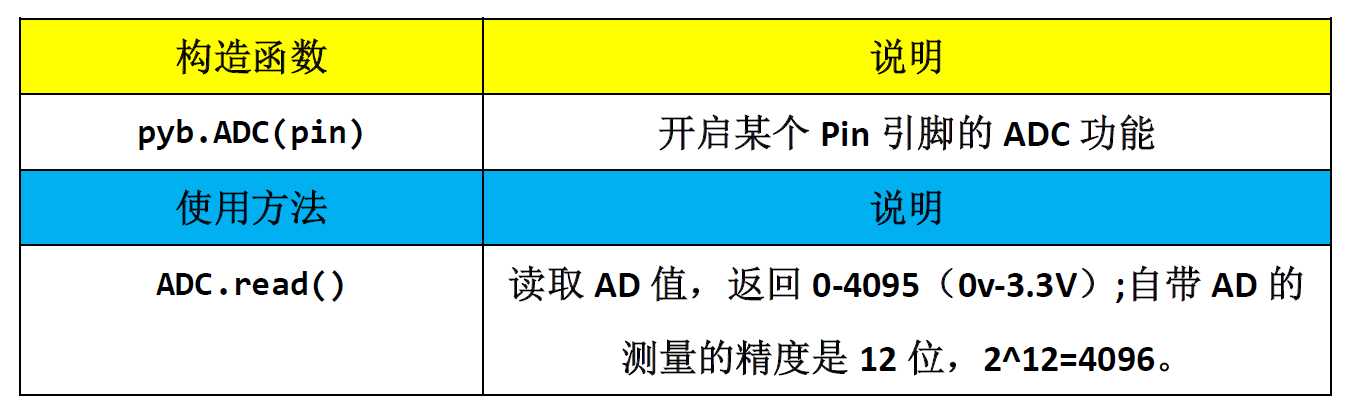
Example code:
#Import related modules import pyb from machine import Pin,I2C #Initialize related modules i2c = I2C(sda=Pin("Y8"), scl=Pin("Y6")) adc = pyb.ADC('X7') #Pin='X7'
7. DAC
The constructors and calling methods of the DAC built in pyBoard are:
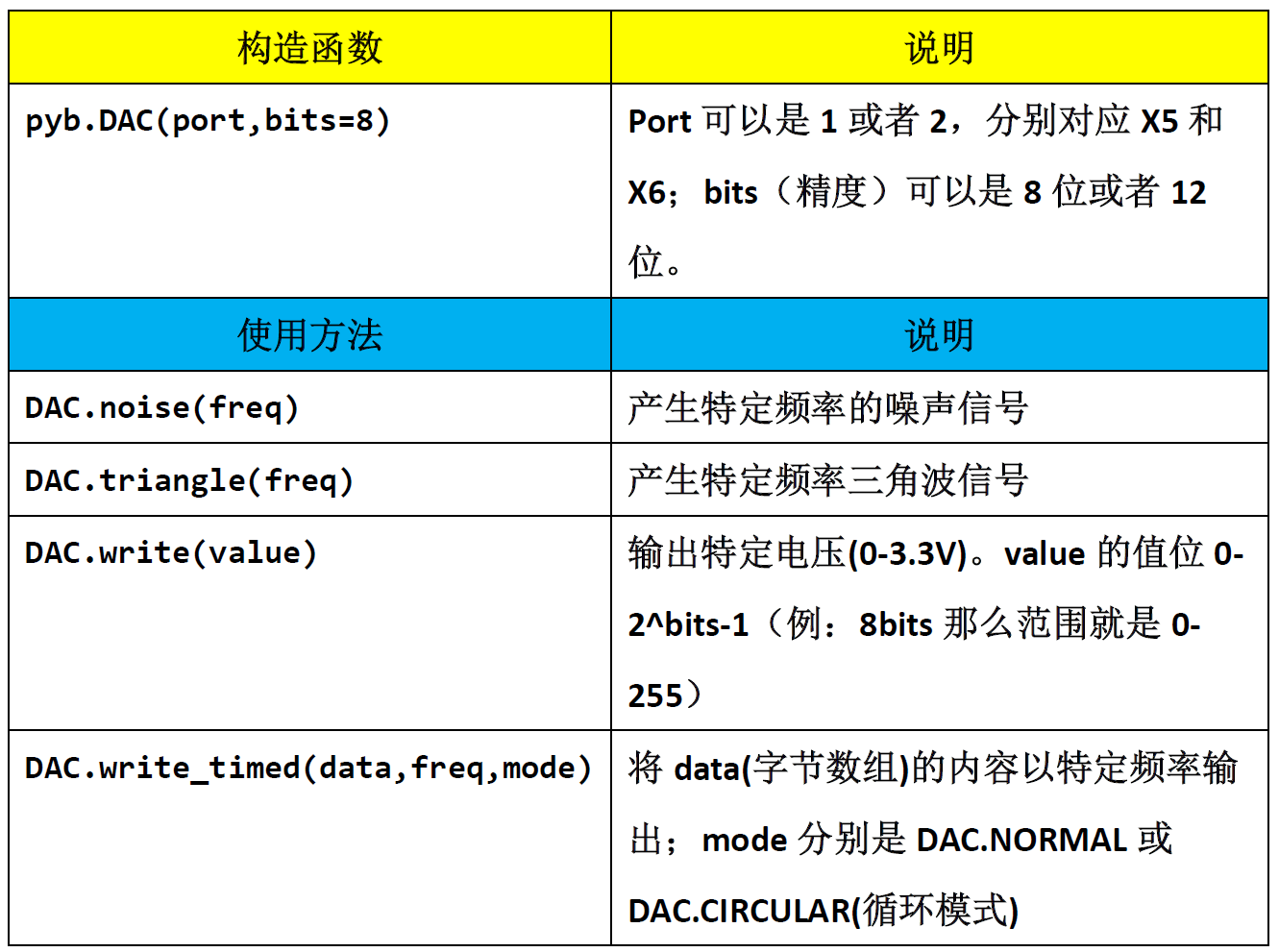
Example code:
from pyb import DAC,Switch from machine import Pin,I2C #Initialize related modules i2c = I2C(sda=Pin("Y8"), scl=Pin("Y6")) sw = Switch() #Define the key object name as sw dac = DAC(1) #Define DAC object name as DAC and output pin as X5 #Define 4 groups of frequency values: 1Hz, 200Hz, 1000Hz, 5000Hz freq=[1,200,1000,5000] # Define the value of square wave with 8-bit precision. 0 and 255 respectively correspond to output 0V and 3.3V. Need to be defined as a byte array. buf = bytearray(2) buf[0]=0 buf[1]=255 key_node = 0 #Key flag bit i = 0 #Used to select frequency array # Keys and their callback functions def key(): global key_node key_node = 1 sw.callback(key) #When the key is pressed, execute the function key() while True: if key_node==1: #Key pressed i = i+1 if i == 4: i = 0 key_node = 0 #Clear key flag #DAC output specified frequency dac.write_timed(buf, freq[i]*len(buf), mode=DAC.CIRCULAR)
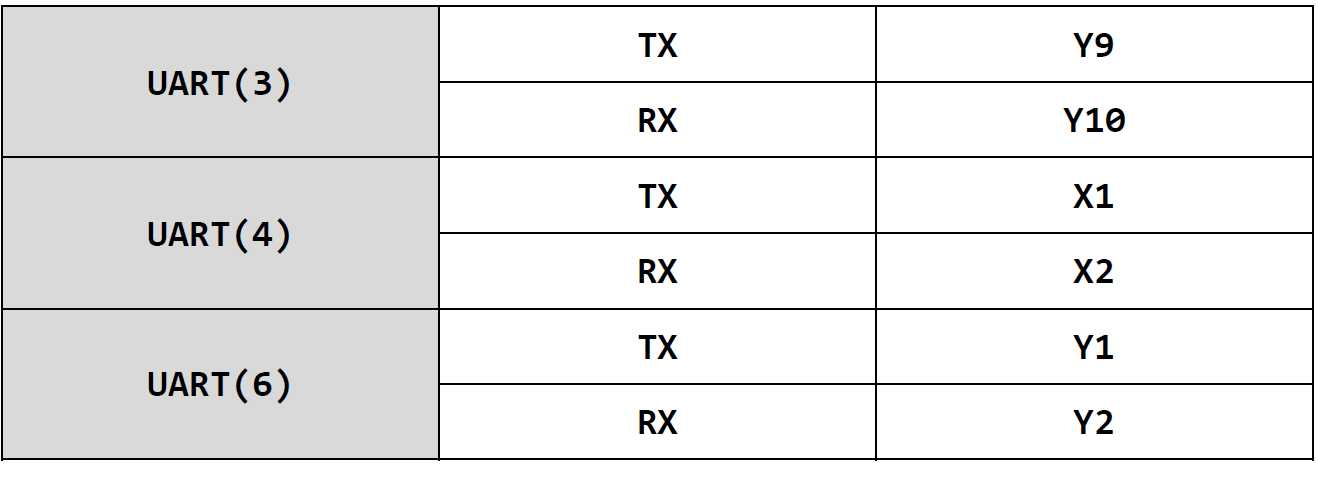
8. UART
There are six serial ports in pyBoard, among which serial port 5 is used for REPL debugging. The serial ports and corresponding pins available for us are as follows: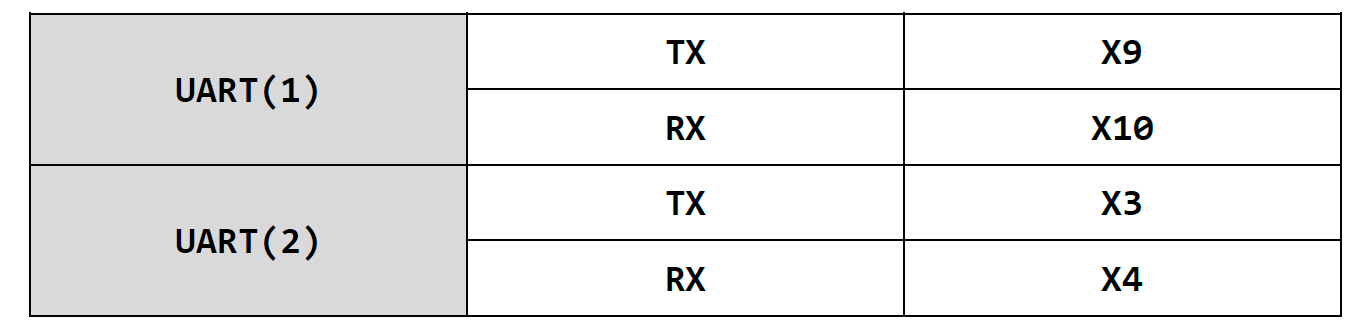
The constructor and usage of UART in pyb are as follows: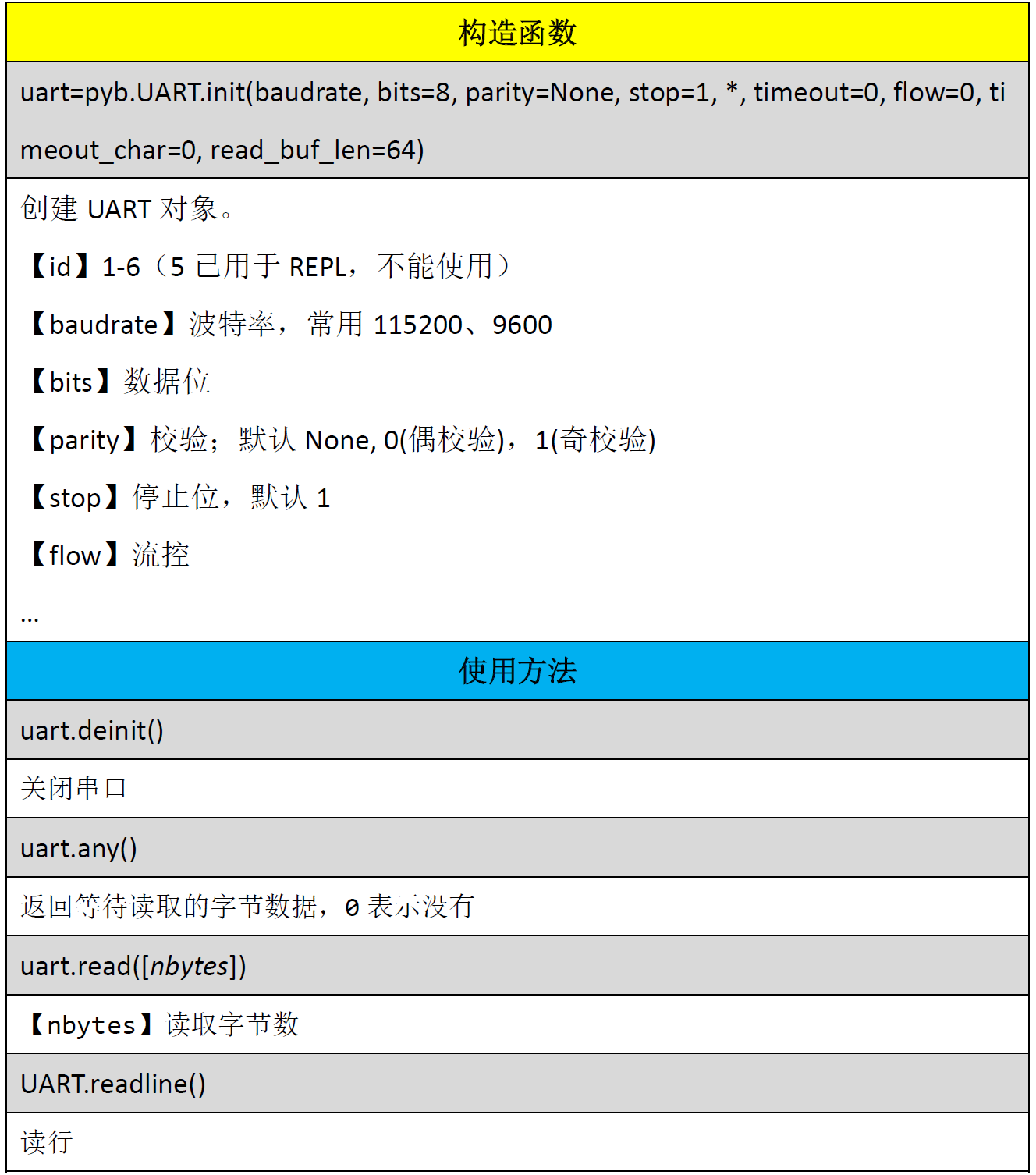
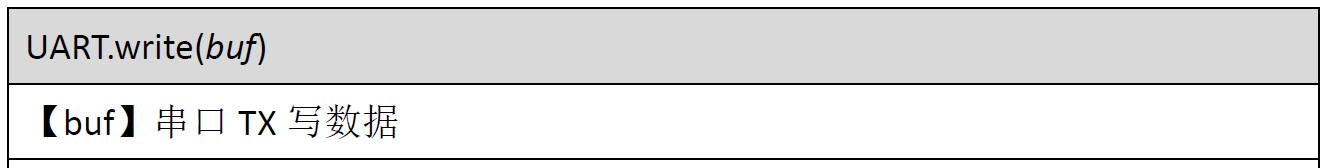
UART code example:
#Import serial port module from pyb import UART uart=UART(3,115200) #Set serial port number 3 and baud rate, tx-y9, rx-y10 uart.write('Hello 01Studio!')#Send a piece of data while True: #Judge whether information is received if uart.any(): text=uart.read(64) #Default single receive up to 64 bytes print(text) #Print the data received through the REPL serial port 3

