FastDFS distributed file system
Link to Baidu online disk of the same version: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1a6XgywCoAyM3CiVS-rrVAA
Extraction code: qq13
1, Introduction to FastDFS (Fast Distribution File System)
FastDFS is an open source distributed file system. Its functions mainly include: file storage, file synchronization, file access (file upload, file download), etc., which solves the problems of large-capacity file storage and high-performance access. FastDFS is especially suitable for online services based on files, such as pictures, videos, documents and so on.
FastDFS server has two roles: tracker and storage node. The tracker is mainly used for scheduling
Access plays a role of load balancing. The storage node stores files and completes all the functions of file management: storage, synchronization and providing access interface.
FastDFS also manages the meta data of files. The so-called meta data of a file is the related attributes of the file, which are represented by key value pairs
value pair), for example: width=1024, where key is width and value is 1024. The file meta data belongs to the file
Sex list, which can contain multiple key value pairs.
The FastDFS system structure is shown in the following figure:
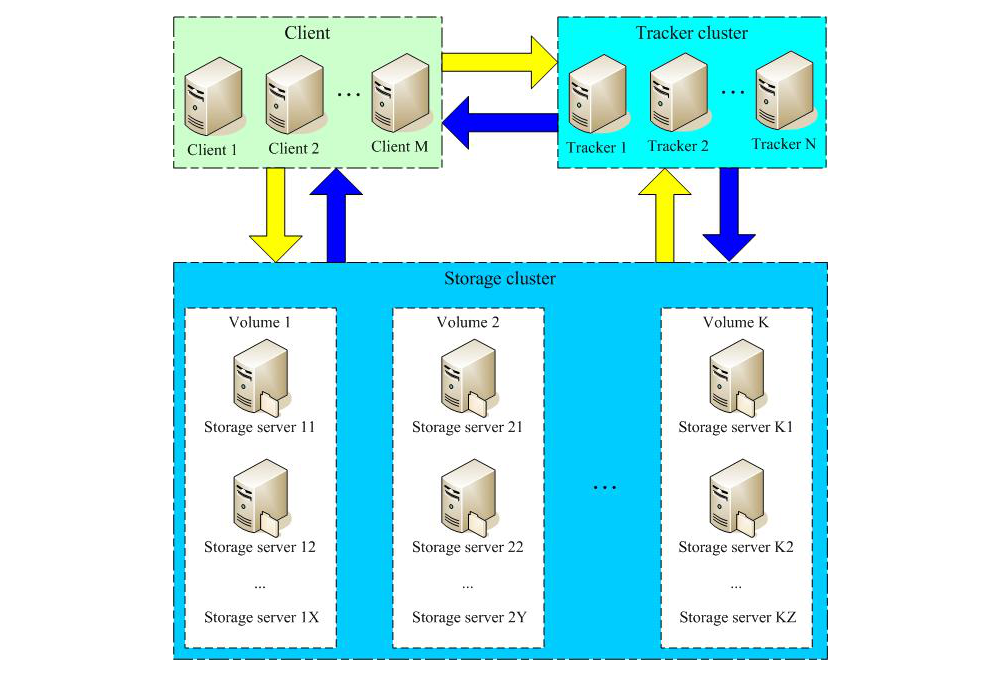
Both the tracker and the storage node can consist of one or more servers.
Servers in the tracker and storage nodes can be added or offline at any time without affecting online services. All servers in the tracker are peer-to-peer, which can be increased or decreased at any time according to the pressure of the server.
In order to support large capacity, storage nodes (servers) adopt the organization mode of volume (or grouping).
The storage system consists of one or more volumes. The files between volumes are independent of each other. The file capacity of all volumes is the file capacity of the whole storage system.
A volume can be composed of one or more storage servers. The files in the storage servers under a volume are the same. Multiple storage servers in the volume play the role of redundant backup and load balancing.
When the system automatically switches the newly added file to the existing server after the synchronization is completed.
When the storage space is insufficient or running out, you can add volumes dynamically. Just add one or more servers and configure them as a new volume, which expands the capacity of the storage system.
File identification in FastDFS is divided into two parts: volume name and file name, both of which are indispensable.
2, Related terms
Tracker Server: a tracking server, which is mainly used for scheduling and load balancing in access. Record the status of the storage server, which is the hub connecting the Client and the storage server.
Storage Server: Storage Server. Files and meta data are saved to the Storage Server
Group: a group, also known as a volume. The files on the servers in the same group are identical
File identification: includes two parts: group name and file name (including path)
meta data: file related attributes, Key Value Pair method, such as width = 1024, height = 768
3, Synchronization mechanism
- Storage servers in the same group are peer-to-peer, and file upload, deletion and other operations can be carried out on any storage server;
- File synchronization is only conducted between storage server s in the same group. push mode is adopted, that is, the source server is synchronized to the target server;
- Only the source data needs to be synchronized, and the backup data does not need to be synchronized again, otherwise it will form a loop;
- An exception to the second rule above is that when a new storage server is added, the existing storage server synchronizes all the existing data (including source data and backup data) to the new server.
4, FastDFS upload file interaction process
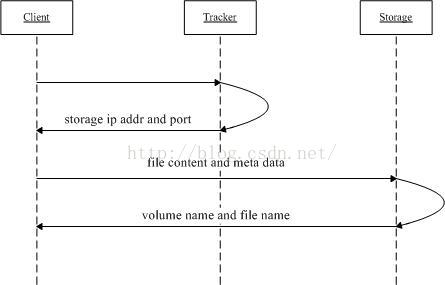
-
The client asks about the storage uploaded by the tracker, and no additional parameters are required;
-
The tracker returns an available storage;
-
client communicates directly with storage to complete file upload.
The client initiates the file transfer action of FastDFS by connecting to the designated end of a Tracker Server
The Tracker Server decides which Storage Server to choose according to the information it has so far, and then
The address and other information of the Storage Server are returned to the client, and then the client connects to the Storage Server through these information,
Transfer the file to be uploaded to the Storage Server.
5, FastDFS download file interaction process
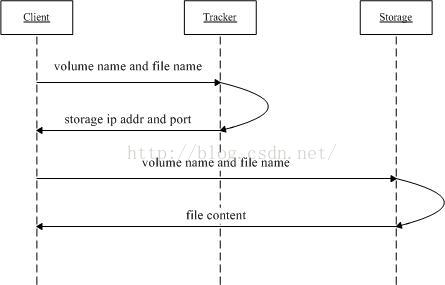
-
The client asks the tracker to download the storage of the file. The parameter is the file ID (volume name and file name);
-
The tracker returns an available storage;
-
client communicates directly with storage to complete file download.
6, Runtime directory structure
6.1. Tracker server

6.2 Storage server

7, Official website resources
FastDFS Forum: http://bbs.chinaunix.net/forum-240-1.html
8, Single point installation mode
The Tracker server and the Storage server perform the same operation
8.1. Dependent environment required for compilation and installation
[root@localhost ~]# yum install make cmake gcc gcc-c++
8.2. Install libfastcommon
-
github official website download address: https://github.com/happyfish100/libfastcommon
-
Upload libfastcommon master Zip to / usr/local/src directory
-
decompression
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/src [root@localhost src]# unzip libfastcommon-master.zip [root@localhost src]# cd libfastcommon-master
-
Compile and install
[root@localhost libfastcommon-master]# ./make.sh [root@localhost libfastcommon-master]# ./make.sh install
libfastcommon is installed by default to:
/usr/lib64/libfastcommon.so
/usr/lib64/libfdfsclient.so
-
Because the Lib directory set by FastDFS main program is / usr/local/lib, you need to create a soft link
ln -s /usr/lib64/libfastcommon.so /usr/local/lib/libfastcommon.so ln -s /usr/lib64/libfastcommon.so /usr/lib/libfastcommon.so ln -s /usr/lib64/libfdfsclient.so /usr/local/lib/libfdfsclient.so ln -s /usr/lib64/libfdfsclient.so /usr/lib/libfdfsclient.so
8.3. Installing FastDFS
-
Download address: https://sourceforge.net/projects/fastdfs/
-
Upload the FastDFS source package to the / usr/local/src directory
-
decompression
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/src/ [root@localhost src]# tar -zxvf FastDFS_v5.05.tar.gz [root@localhost src]# cd FastDFS
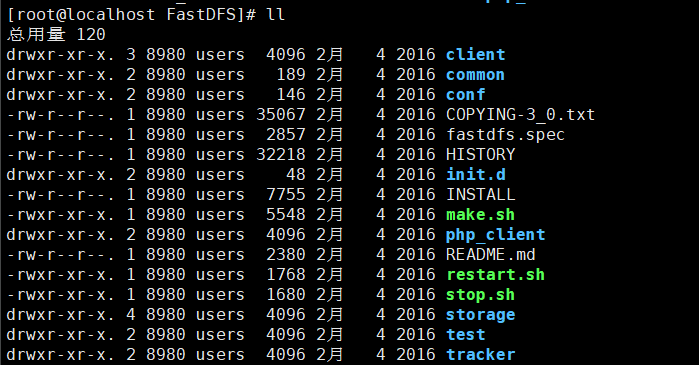
-
Compile and install (make sure libfastcommon is successfully installed before compiling)
[root@localhost FastDFS]# ./make.sh [root@localhost FastDFS]# ./make.sh install
The default installation method is adopted. The corresponding files and directories after installation are as follows:
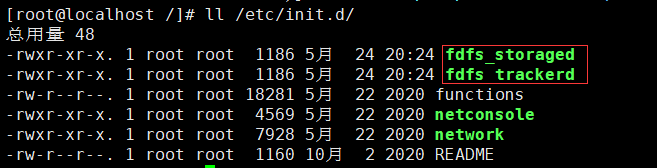
- Service script in:
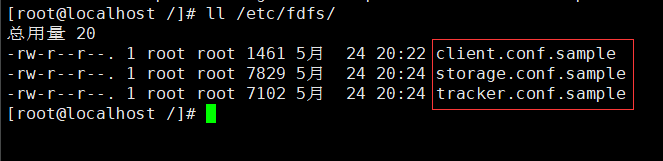
- (sample configuration file):
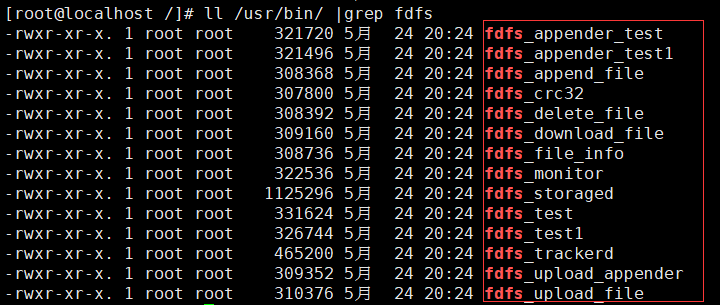
- With in / usr/bin / Directory:
-
Because the bin directory set by the FastDFS service script is / usr/local/bin, but the actual command is installed in / usr/bin, you need to modify the corresponding command path in the FastDFS service script, that is, / etc / init d/fdfs_ Stored and / etc / init d/fdfs_ / usr/local/bin in the two scripts of tracker is modified to / usr/bin:
[root@localhost /]# vim /etc/init.d/fdfs_trackerd [root@localhost /]# vim /etc/init.d/fdfs_storaged
Use the find replace command for unified modification (vi/vim command):
:%s+/usr/local/bin+/usr/bin
8.4. Configure tracker
-
Copy the FastDFS tracker sample configuration file and rename it
[root@localhost fdfs]# cd /etc/fdfs/ [root@localhost fdfs]# cp tracker.conf.sample tracker.conf
-
To edit a tracker profile:
[root@localhost fdfs]# vim tracker.conf
Amend the following:
disabled=false port=22122 base_path=/fastdfs/tracker
Other parameters remain the default configuration.
-
Create basic data directory (refer to the configuration of basic directory base_path)
[root@localhost fdfs]# mkdir -p /fastdfs/tracker
-
Open the tracker port in the firewall (22122 set)
[root@localhost fdfs]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=22122/tcp --permanent success [root@localhost fdfs]# firewall-cmd --reload success [root@localhost fdfs]# firewall-cmd --list-ports #Check whether the port is opened successfully 22122/tcp
-
Start Tracker tracking server
[root@localhost fdfs]# /etc/init.d/fdfs_trackerd start Reloading systemd: [ determine ] Starting fdfs_trackerd (via systemctl): [ determine ]
After successful startup for the first time, data and logs directories will be created in / fastdfs/tracker directory
Check whether FastDFS Tracker has started successfully:
[root@localhost fdfs]# ps -ef | grep fdfs root 3484 1 0 21:12 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/fdfs_trackerd /etc/fdfs/tracker.conf root 3493 1290 0 21:13 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto fdfs
-
Turn off the Tracker tracking server
[root@localhost fdfs]# /etc/init.d/fdfs_trackerd stop Stopping fdfs_trackerd (via systemctl): [ determine ]
-
Set FastDFS tracker startup:
[root@localhost fdfs]# vim /etc/rc.d/rc.local
Add the following:
/etc/init.d/fdfs_trackerd start
8.5. Configuration memory
-
Copy the FastDFS storage sample configuration file and rename:
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/fdfs/ [root@localhost fdfs]# cp storage.conf.sample storage.conf
-
Edit storage sample configuration file
[root@localhost fdfs]# vim /etc/fdfs/storage.conf
Amend the following:
disabled=false port=23000 base_path=/fastdfs/storage store_path0=/fastdfs/storage tracker_server=192.168.4.121:22122 #Tracking server address and port (write your own configuration) http.server_port=8888 # Generally changed to 80
-
Create basic data directory (refer to basic directory base_path configuration)
[root@localhost fdfs]# mkdir -p /fastdfs/storage
-
Open storage port in firewall (23000 by default)
[root@localhost fdfs]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=23000/tcp --permanent success [root@localhost fdfs]# firewall-cmd --reload success [root@localhost fdfs]# firewall-cmd --list-ports #Check whether the port is opened successfully 22122/tcp 23000/tcp
-
Start the Storage server
[root@localhost fdfs]# /etc/init.d/fdfs_storaged start Starting fdfs_storaged (via systemctl): [ determine ]
After successful startup for the first time, data and logs directories will be created in / fastdfs/tracker directory
Check whether FastDFS Tracker has started successfully:
[root@localhost fdfs]# ps -ef | grep fdfs root 1387 1 0 21:34 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/fdfs_storaged /etc/fdfs/storage.conf root 1389 1279 0 21:35 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto fdfs
-
Shut down the Storage server
[root@localhost fdfs]# /etc/init.d/fdfs_storaged stop Stopping fdfs_storaged (via systemctl): [ determine ]
-
Set the FastDFS storage server to boot
[root@localhost fdfs]# vim /etc/rc.d/rc.local
Add the following line:
/etc/init.d/fdfs_storaged start
9, File upload test
-
Modify the client configuration file in the Tracker server
[root@localhost fdfs]# cp /etc/fdfs/client.conf.sample /etc/fdfs/client.conf [root@localhost fdfs]# vim /etc/fdfs/client.conf
base_path=/fastdfs/tracker tracker_server=192.168.4.121:22122 # Modify to your own IP
-
Execute the file upload command:
[root@localhost fdfs]# /usr/bin/fdfs_upload_file /etc/fdfs/client.conf /usr/local/src/FastDFS_v5.05.tar.gz
Return ID No.: group1 / M00 / 00 / 00 / wkgefvuynyeab7xfaavfol7fju4 tar. gz
If the above file ID can be returned, it indicates that the file has been uploaded successfully.