/Software / command / script that will not be used when usr/sbin Linux system starts up
/Under usr/bin are all executable programs pre installed by the system, and the system upgrade may be overwritten
/The usr/local/bin directory is where users can place their own executable programs
/fdfs file under usr/bin /
fdfs_append_file
fdfs_appender_test
fdfs_appender_test1
fdfs_crc32
fdfs_delete_file
fdfs_download_file
fdfs_file_info
fdfs_monitor
fdfs_storaged
fdfs_test fdfs_test1
fdfs_trackerd
fdfs_upload_appender
fdfs_upload_file
method: fdfs_upload_file <config_file> <local_filename> For example:/usr/bin/fdfs_upload_file /etc/fdfs/client.conf a.txt
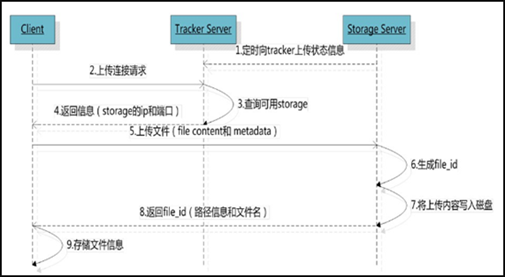
When there is more than one tracker server in the cluster, because the relationship between trackers is completely equal, the client can choose any trackcer when upload ing files. (2) Select storage group
When the tracker receives the request to upload a file, it will assign a group to the file that can store the file. The following rules for selecting a group are supported: 1 Round robin, polling between all groups 2 Specified group: specify a certain group 3 Load balance, more remaining storage space is preferred (3) Select storage server
When a group is selected, the tracker will select a storage server in the group for the client. The following rules for selecting storage are supported: 1 Round robin, poll 2.0% of all storage in the group First server ordered by ip, sorted by ip 3 First server ordered by priority (priority is configured on storage) (4) Select storage path
After the storage server is allocated, the client will send a file write request to storage, and storage will allocate a data storage directory for the file. The following rules are supported: 1 Round robin, polling among multiple storage directories 2 The one with the most remaining storage space is preferred (5) Generate Fileid
After selecting the storage directory, storage will generate a Fileid for the file, which is generated by storage server ip, file creation time, file size, file crc32 and a random number are spliced, and then the binary string is base64 encoded and converted into a printable string. (6) Select two-level directory
After selecting the storage directory, storage will assign a fileid to the file. There are two levels of 256 * 256 subdirectories under each storage directory. Storage will hash (guess) twice according to the file fileid, route to one of the subdirectories, and then store the file in the subdirectory with fileid as the file name. (7) Generate file name
When the file is stored in a subdirectory, it is considered that the file is successfully stored. Next, a file name will be generated for the file. The file name is spliced by group, storage directory, two-level subdirectory, fileid and file suffix (specified by the client and mainly used to distinguish file types). 2,fdfs_download_file Use "fdfs_download_file" to download files. The command is:
method: fdfs_download_file <config_file> <path> For example:/usr/bin/fdfs_download_file /etc/fdfs/client.conf group1/M00/00/21/rBABl2IgEJ2AXTIxAAC5ERGBk_A734.png
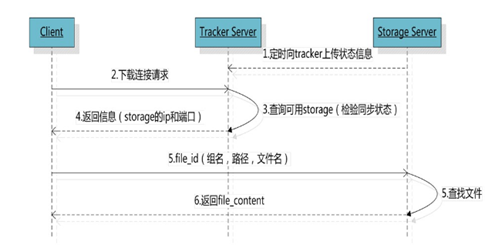
Command:
4,fdfs_delete_file Using fdfs_delete_file to delete a file, command:method: fdfs_file_info <config_file> <path> For example: /usr/bin/fdfs_file_info /etc/fdfs/client.conf group1/M00/00/1F/rBABtGIfljmACwDjAAC5ERGBk_A347.png
5, fdfs_upload_appender/fdfs_append_file Use "fdfs_upload_appender" to upload a file that can be appended, followed by the configuration file of the client and the path of the file to be uploaded:method: fdfs_delete_file <config_file> <path> For example: /usr/bin/fdfs_delete_file /etc/fdfs/client.conf group1/M00/00/1F/rBABtGIfljmACwDjAAC5ERGBk_A347.png
# echo "upload_appende 2022-3-3" >a.txt # echo "upload_appender2 2022-3-3" >b.txt #/usr/bin/fdfs_upload_appender /etc/fdfs/client.conf a.txt # cat rBABl2IgHTaENYMrAAAAADBEg7A330.txt upload_appender 2022-3-3 // Additional content # /usr/bin/fdfs_append_file /etc/fdfs/client.conf group1/M09/00/21/rBABl2IgHTaENYMrAAAAADBEg7A330.txt b.txt # cat rBABl2IgHTaENYMrAAAAADBEg7A330.txt upload_appender 2022-3-3 upload_appender2 2022-3-3

//Delete storage node usr/bin/fdfs_monitor /etc/fdfs/storage.conf delete group3 172.16.1.180 //Add Storage nodes (automatically join through configuration). //Status of the node # FDFS_STORAGE_STATUS: INIT: initialization. The source server that has not been synchronized with the existing data # FDFS_STORAGE_STATUS: WAIT_SYNC: wait for synchronization and get the source server that has synchronized the existing data # FDFS_STORAGE_STATUS: synchronizing # FDFS_STORAGE_STATUS: DELETED: DELETED. The server is removed from this group # FDFS_STORAGE_STATUS: OFFLINE # FDFS_STORAGE_STATUS: ONLINE: ONLINE, unable to provide service # FDFS_STORAGE_STATUS: ACTIVE: online, can provide services # group_name: group name # ip_addr: IP address # version: # sync_src_ip_addr: the source server that synchronizes the existing data files to the storage server # sync_until_timestamp: deadline for synchronizing existing data files (UNIX timestamp) # Total storage: total storage # free storage # Upload priority: upload priority # store_path_count: number of paths # subdir_count_per_path: number of folders per level # storage_port # storage_http_port # current_write_path: current write path # Source storage id: source storage id # if_trunk_server: whether to use trunk # connection.alloc_count # connection.current_count # connection.max_count: maximum number of concurrent connections # total_upload_count: number of file uploads # success_upload_count: number of successful file uploads # total_append_count: number of times to append files # success_append_count: the number of times the file was successfully appended # total_modify_count: total modification times # success_modify_count: number of successfully modified # total_truncate_count: total truncation count times # success_truncate_count: number of successful truncations # total_set_meta_count: number of times to change meta data # success_set_meta_count: the number of successful changes to meta data # total_delete_count: number of times to delete files # success_delete_count: the number of times the file was successfully deleted # total_download_count: number of file downloads # success_download_count: number of successful file downloads # total_get_meta_count: number of times to obtain meta data # success_get_meta_count: the number of times meta data was successfully obtained # total_create_link_count: number of links created # success_create_link_count: number of successful Link Creation # total_delete_link_count: number of deleted links # success_delete_link_count: number of successfully deleted links # total_upload_bytes: total number of uploaded bytes # success_upload_bytes: the total number of bytes uploaded successfully # total_append_bytes: append # success_append_bytes # total_modify_bytes # success_modify_bytes # stotal_download_bytes # success_download_bytes # total_sync_in_bytes: synchronous bytes # success_sync_in_bytes # total_sync_out_bytes # success_sync_out_bytes # total_file_open_count # success_file_open_count # total_file_read_count # success_file_read_count # total_file_write_count: number of file writes # success_file_write_count: the number of files successfully written # last_heart_beat_time: the last time the storage sent a heartbeat to the tracker # last_source_update: the latest source update time (the update operation comes from the client) # last_sync_update: the latest synchronization update time (the update operation is from the synchronization of other storage server s) # last_synced_timestamp: timestamp of last synchronization
7. Start command
service fdfs_storaged restart service fdfs_trackerd restart docker Container startup service: fdfs_storaged /etc/fdfs/storage.conf start fdfs_trackerd /etc/fdfs/tracker.conf start /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload curl -i 127.0.0.1:8888 //View nginx version