catalogue
1.2. Judge whether the folder exists
1.4. Obtain common directories
5. Standard message dialog box
1, Document management
1. Directory operation
The directory operations in qt mainly use two classes: QDir and QFileInfo. The following focuses on these two classes
1.1 QDir and QFileInfo
QDir:
QDir class has the ability to access directory structure and content. It can operate directories, access directory or file information, operate the underlying file system, and access Qt resource files.
To determine whether a directory exists, you can use exists(), and the attributes of the directory can be obtained using isReadable(), isAbsolute (), isRelative(), and isRoot().
There are many entries in the directory, including files, directories and symbolic connections,
The total number of entries can be counted using count().
entryList() returns a string linked list of all entries in the directory.
The file can be deleted using the remove() function,
Delete the directory with rmdir(),
Rename with rename().
Filters are generally used to filter the files in the directory.
QFileInfo:
QFilelnfo class provides system independent file information, including file name, location (path) in the file system, file access permission, whether it is a directory or symbolic link, etc. QFilelnfo can also obtain the file size and the last modification / reading time, as well as the relevant information of Qt resources.
The file pointed to by QFilelnfo can be set when the QFileinfo object is built, or set later using setFile(). You can use exists() to see if the file exists, and size() to get the size of the file.
1.2. Judge whether the folder exists
QDir dir("D:/qtmode");//The absolute path, or relative path, is where the project's build directory begins
qDebug()<<dir.exists();//Return false if none, return true if none
1.3. Create directory
QDir dir("D:/test");
if(!dir.exists())
{
dir.mkdir("D:/test");
qDebug()<<"A new folder was created";
}
else
{
qDebug()<<"Folder exists";
}
1.4. Obtain common directories
Code:
QDir dir;
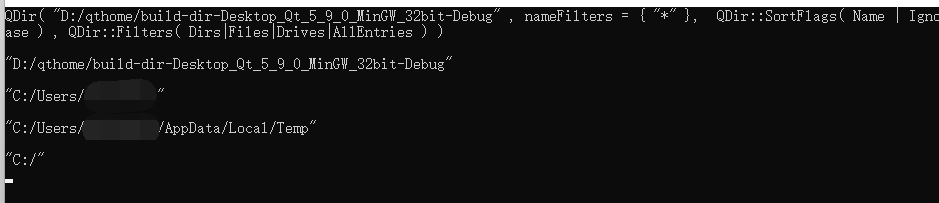
qDebug()<<dir.current()<<endl;
qDebug()<<dir.currentPath()<<endl;
qDebug()<<dir.homePath()<<endl;
qDebug()<<dir.tempPath()<<endl;
qDebug()<<dir.rootPath();Demonstration effect:
1.5. Switching path
QDir dir("D:/text");
qDebug()<<dir.dirName();//The name of the current folder
qDebug()<<dir.absolutePath();//The absolute path of the current folder
dir.cd("C:/");//Switch to drive C
qDebug()<<dir.absolutePath();1.6. Traversing files
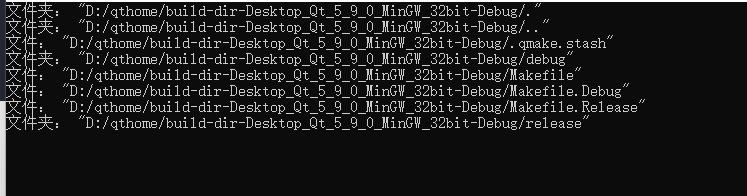
QDir dir(dir.current());
foreach(QFileInfo item,dir.entryInfoList())
{
if(item.isDir())
{
qDebug()<<"folder:"<<item.filePath(); //fileName only has the name of the file (folder)
}else if(item.isFile()){
qDebug()<<"File:"<<item.filePath();
}
}Effect display:
1.7 file filtering
QDir dir(dir.current()); QStringList listters; listters<<"*.txt"<<"*.exe";//< - here is the fi lt er criteria, which depends on the type of item dir.setNameFilters(listters); qDebug()<<dir.entryList(listters,QDir::Files);
2. File operation
2.1,QFile
QFile class provides an interface for reading / writing files. It can be used to read / write text files, binary files and I/0 devices of Qt resources.
Generally, the file name is specified when building the QFile object. Of course, it can also be set by using setFileName(). You can use exists () to check if a file exists and remove () to delete a file.
A file can be operated as follows:
open() open close()close flush()Refresh File reading and writing can be used read(), readLine(), readAll()and write () size()Function to get the size of the file seek()To navigate to any location in the file pos()To get the current location atEnd()To determine whether the end of the file has been reached
You can also use the following learned FILE and fstream to operate files.
2.2. Open and write files
File operation flow open > write / read > close
Before accessing a device, you need to use the open() function to open the device, and you must specify the correct opening mode. Different opening modes can be used simultaneously with the "|" symbol.
After the device is turned on, you can use write() or putChar() to write, use the seek function to move the file pointer (if any), use read(), readLine() or readAll() to read, and finally use close() to close the device.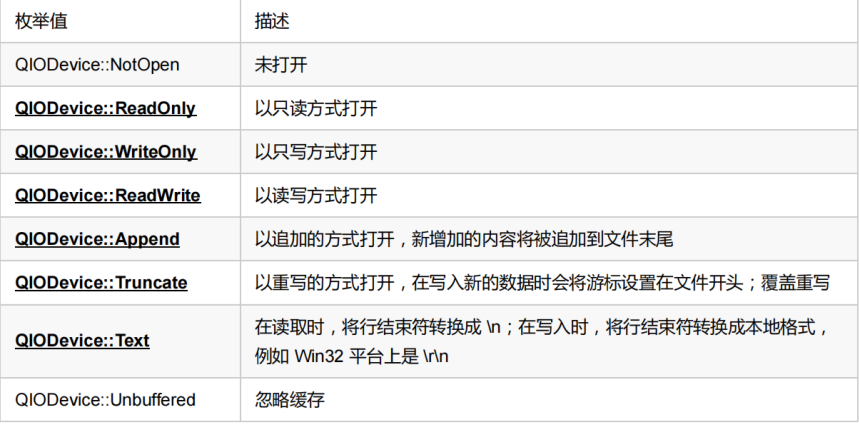
Demo:
QFile file("demonstration.txt");
if (!file.open(QIODevice::WriteOnly | QIODevice::Text)) //If the file does not exist, the file will be created
{
qDebug() << file.errorString();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "Open successfully!";
}
file.write("ABBA ABBA ABBA");
file.close();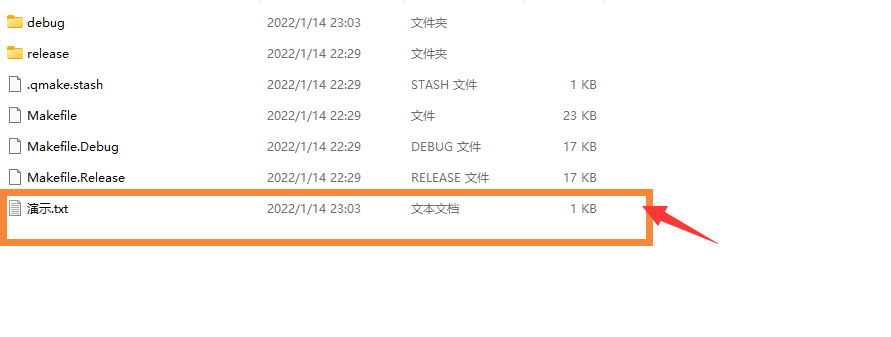

2.3. Read all contents
QFile file("demonstration.txt");
if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text)) //If the file does not exist, the file will be created
{
qDebug() << file.errorString();
}
else
{
qDebug() << "Open successfully!";
}
while(!file.atEnd())
{
QByteArray line=file.readLine();
qDebug()<<line;
}
file.close();
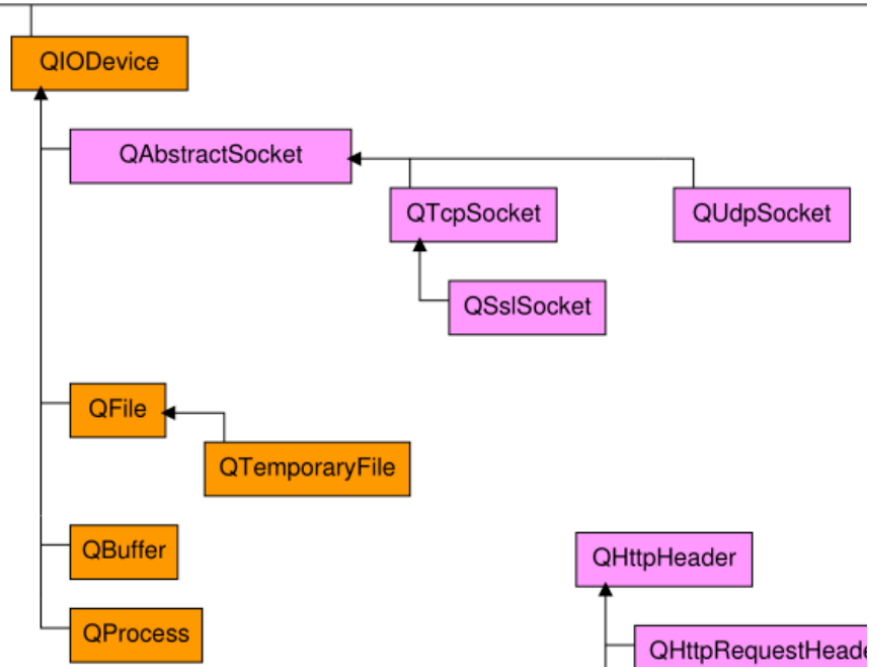
2.4. QIOdevice class
QIODevice class is the basic class of all I/O devices in Qt. It provides an abstract interface for QFIle and other classes
The inheritance diagram is as follows:
2, Standard dialog box
1. Standard input dialog box
#include <QInputDialog>
bool ok;
There are the following:
//Numbers in spinxbox
int i= QInputDialog::getInt(this,"Tips"," Get number",
15,//Default value
0,//minimum value
100,//Maximum
1,//step
&ok);//Used to determine if ok is clicked
//Number in spinxbox (decimal)
int i= QInputDialog::getDouble(this,"Tips"," Get number",
15.34,//Default value
0,//minimum value
100,//Maximum
3,//Display decimal places
&ok);//Used to determine if ok is clicked
QStringList items;
//Displays the string in the QStringList
items<<"String 1"<<"String 2"<<"String 3"<<"String 4"<<"String 5";
bool ok;
QString item=QInputDialog::getItem(this,"Tips","Get string",
items,//QStringList type
0,//Selected by default
true,//Can the content be changed
&ok);
//Get the input string, one line
QString text=QInputDialog::getText(this,"Tips","Input string",
QLineEdit::Normal,"Default display content",&ok);
//Get the input string, multiple lines
QString text=QInputDialog::getMultiLineText(this,"Tips","Enter multiline string","Default display content",&ok);
2. Standard font dialog box
#include <QColorDialog>
QColor color=QColorDialog::getColor(Qt::red,//Default selection color
this,"get colors");
if(color.isValid())
{
ui->lineEdit_4->setText(color.name());
QPalette pa=ui->lineEdit_4->palette(); //Get palette of lineEdit
pa.setColor(QPalette::Base,color); //Set to get color
ui->lineEdit_4->setPalette(pa); //Override settings back
}3. Standard color dialog box
#include <QFontDialog>
bool ok;
QFont font=QFontDialog::getFont(&ok,
QFont("Blackbody")//default font
,this,"Select font");
if(ok)
{
ui->lineEdit_5->setText(font.key());//Font name
ui->lineEdit_5->setFont(font); //Set font
}4. Standard file dialog box
#include <QFileDialog>
QString path=QFileDialog::getExistingDirectory(this,"Select file",
"D:\\");//Starting path
//Select only a single file
QString fileName=QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this,"Select file","D:\\",//Starting path
"All Files (*);;Text Files(*.txt)");//Screening conditions
//Path to open multiple files
QStringList fileName=QFileDialog::getOpenFileNames(this,"Select file","D:\\",
"All Files (*);;Text Files (*.txt)");
//It is used to save files, but it will not create files. You need to create files and write contents through file operation
QString fileName=QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this,"Save file","D:\\",
"All Files (*);;Text Files (*.txt)");
5. Standard message dialog box
QMessageBox::information(this," title","text"); QMessageBox::warning(this,"title","text"); QMessageBox::critical(this,"title","text"); QMessageBox::question(this,"title","text"); The return value is the selected button. Of course, the buttons specified by the 4th, 5th and 6th counselors have default values, which can be left blank. Note that this is the first parent class The parent class in must be a window object and cannot die before the window is processed,The buttons can be the following: QMessageBox::NoButton QMessageBox::Ok QMessageBox::Cancel QMessageBox::Yes QMessageBox::No QMessageBox::Abort QMessageBox::Retry QMessageBox::Ignore QMessageBox::YesAll QMessageBox::NoAll