Today's learning capacity is somewhat large, here it is necessary to comb what you have learned today.
Catalog
First, the first choice statement
2. First Identity Circular Sentences
First, the first choice statement
There are many choices in life, no matter right or wrong, you should not regret the choices you made.
Select the statement as follows
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int input = 0;
printf("Do you want to study hard?(1/0)");
scanf("%d", &input);
if(input==1)
{
printf("good offer");
}
else
{
printf("Sell sweet potatoes\n");
}
return 0;
}Whether we get a good offer or not, we should continue to expand our knowledge reserve or we may only be able to "sell sweet potatoes". 😆
2. First Identity Circular Sentences
Some things have to be done all the time, and they go on and on, like learning
In C, loop statements are the while statement
for statement
Do... While statement
Since the title of this article is "First-time C Language", we will introduce the while cycle first today and then the other two later periods.
There are the following codes
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int line = 0;
while (line < 30000)
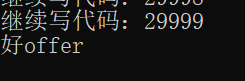
{
printf("Continue writing code:%d\n", line);
line++;//line=line+1 can also be used here
}
if (line == 30000)
printf("good offer\n");
return 0;
}When certain conditions are met, the loop stops
3. Functions
C language, some independent functions can also be encapsulated into a function
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int sum = 0;
printf("Enter two operands");
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
sum = num1 + num2;
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
The code above is written as a function as follows:
#include <stdio.h>
int Add(int x, int y)
{
int z = x+y;
return z;
}
int main()
{
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int sum = 0;
printf("Enter two operands:>");
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
sum = Add(num1, num2);
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
The code above shows the first as a normal sum and the second as a function sum.
Where the function must be defined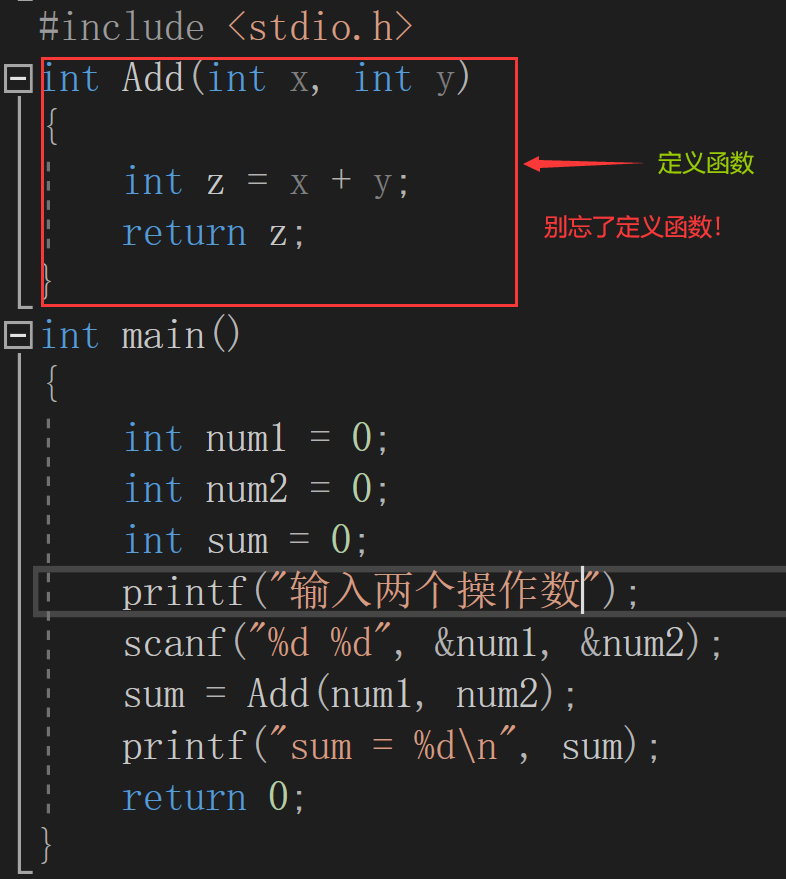

4. Arrays
How do I store 1-10 numbers?
Arrays are defined in C: a set of elements of the same type
int arr[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};// Define an integer array with up to 10 elements
Subscript of array
Language C specifies that each element of an array has a subscript, which starts with 0. Arrays can be accessed through subscripts.
such as
int arr[10] = {0}; // If the array has 10 elements, the subscript range is 0-9
| int arr [10] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subscript | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
Use of arrays
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int i = 0;//Use i to generate Subscripts
while (i < 10)
{
printf("%d", arr[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
} If you want to print an array
Character Array
char ch[5]={'a','b','c'};This is not fully initialized, the remaining two elements default to 0
char ch[6]={"hello"}So much for arrays.
5. Operators
1. Arithmetic Operators
+ - * / %
Here are the main descriptions/and%
/:divide
An example: 9/2=4
The reason is that both sides of'/'are integers, dividing by integers, whether int or float, results in 4
Solution: 9/2.0 or 9.0/2 Results 4.500000
2. Shift Operators
>> <<
Here's an example of moving left
The result is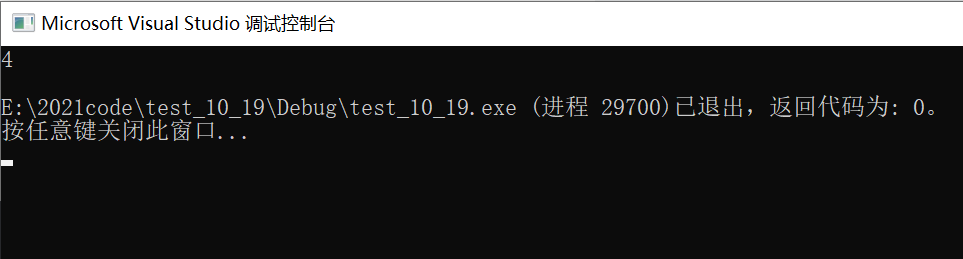
Reason: 
By 1*2^1=2 Change to 1*2^2=4
3. Bit Operators
& ^ |
Bitwise and (0 for binary bits, 1 for all)
| Bitwise or (11 for all 0)
^ Bitwise XOR (same 0, dissimilar 1)
Here's an ex amp le
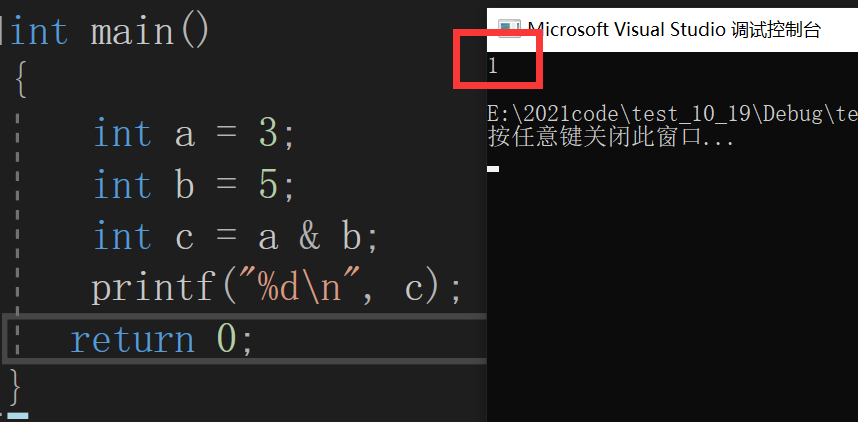
So why is the result 1?
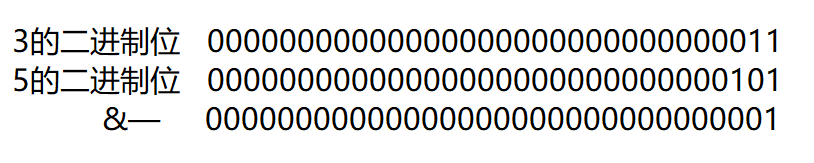
4. Assignment Operators
= += -= *= /= &= ^= |= >>= <<=
5. Monocular Operators
a+b has two operands, so + is a binocular operator
! Logical Inverse Operation
- negative
+ Positive
& Take Address
sizeof Type length of operand in bytes
~ Bitwise negation of a number
-- Front and rear --
++. Front and rear ++
* Indirect access operator (dereference operator)
(type) Mandatory Type Conversion
(1)-- Front and rear --
++ Front and rear ++
The first is to use++ first, the second is to use++.
int main()
{
int a=10;
intb=a++
printf ("%d %d",a,b);
return 0;
}Results: 11,10
(2) (type) Mandatory Type Conversion
int main()
{
int n=3.14;
int n=(int)3.14
return 0;
}6. Relational Operators
>
>=
<
<=
!= Used to test "inequality"
== Used to test equality
7. Logical Operators
&& Logical and
|| Logical or
&& Logical and (and)
|| Logical or (or)
8. Conditional Operators (Trinomial Operators)
exp1 ? exp2 : exp3
Function: Simplify if statement
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int max = 0;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(a>b)
max=a;
else
max=b;
printf("%d\n", max);
return 0;
}
//Use Conditional Operators
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int max = 0;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
max=(a>b?a;b;);
printf("%d\n", max);
return 0;
}exp1 ? exp2 : exp3
Expression 1 turns true, expression 2 does not count 3, and expression 2 turns out to be
Expression 1 results in false, expression 3 calculates 2 does not, and expression 3 results in false
9. Comma expression (calculated from left to right, but the result of the whole expression is the result of the last expression)
exp1, exp2, exp3, ...expN
int main()
{
int a = 3;
int b = 5;
int c = 10;
int d = (a + 2, b = a - 3, c = b + 4);
printf("%d\n", d);
return 0;
} 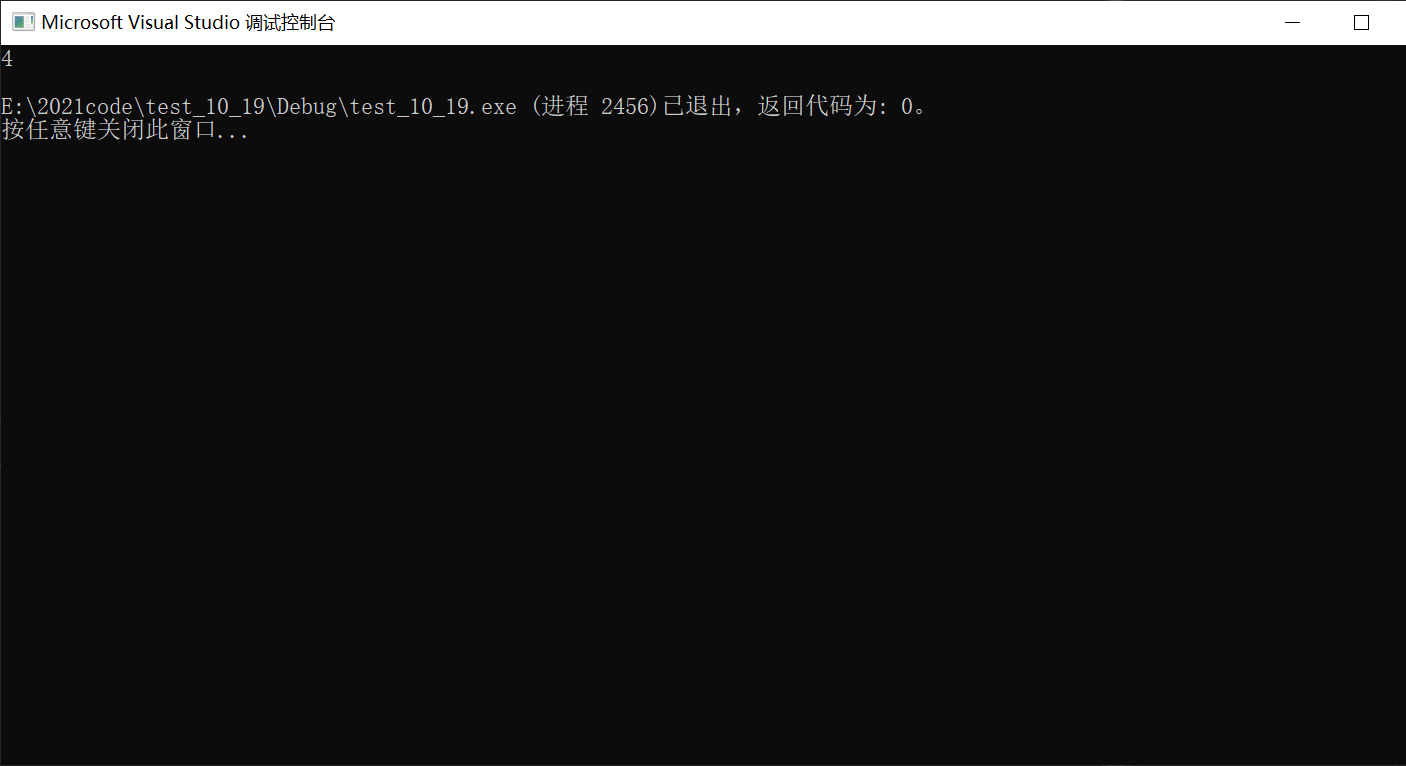
(b=0,c=4) -> d=0+4=4
10. Subscript references, function calls, and structure members
[] () . ->
6. Keyword
auto break case char const continue default do double else enum extern float for goto if int long register return short signed sizeof static struct switch typedef union unsigned void volatile while
Auto-auto-define automatic variable
const-Modify constant variable, Modify pointer

Keyword typedef
typedef, as its name implies, is a type definition, which should be understood here as type renaming
//Rename unsigned int to uint_32, so uint_32 is also a type name
typedef unsigned int uint_32;
int main()
{
//Looking at num1 and num2, the two variables are of the same type
unsigned int num1 = 0;
uint_32 num2 = 0;
return 0;
}
It's 0:48 on October 20th. After more than two hours, I finally finished this blog and am ready to sleep. Good night!! ✨✨