JDBC
1: Database driven
For example: sound card, graphics card, driver, etc;
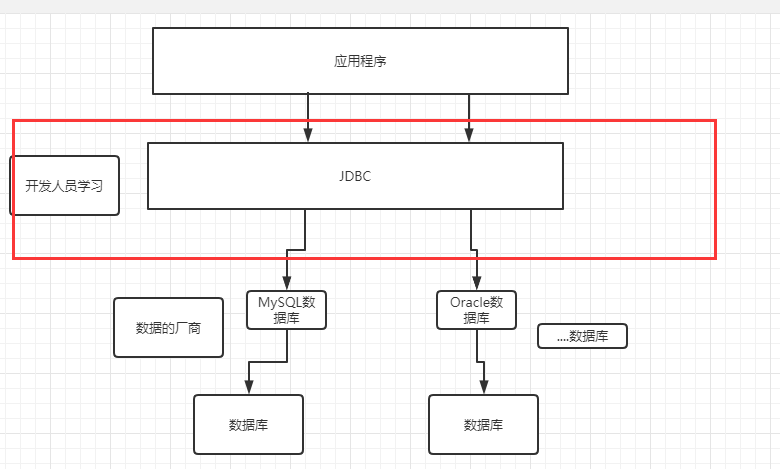
2: JDBC
In order to simplify the (unified database) operation of developers, SUN company provides a (Java database operation) specification, commonly known as JDBC. The implementation of these specifications is done by specific manufacturers.
For developers, we only need to master the operation of JDBC interface!
3: First JDBC program
Create database
CREATE DATABASE jdbcStudy CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; USE jdbcStudy; CREATE TABLE `users`( id INT PRIMARY KEY, NAME VARCHAR(40), PASSWORD VARCHAR(40), email VARCHAR(60), birthday DATE ); INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday) VALUES(1,'zhansan','123456','zs@sina.com','1980-12-04'), (2,'lisi','123456','lisi@sina.com','1981-12-04'), (3,'wangwu','123456','wangwu@sina.com','1979-12-04')
1: Create a normal project;
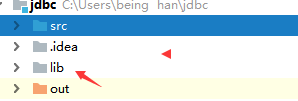
2: Import the driver of the database and add the jar
-mysql-connector-java-5.1.47.jar
Create lib in the IDEA and add the package to the lib directory
3: Write test code
import java.sql.*;
//My first jdbc program
public class jdbcfristDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1. Load driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//Fixed writing
//2. User information and url
//useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
//3. The connection is successful, and the database object;
//The connection represents the database
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4. The object to execute sql; statement object to execute sql
//createStatement creates a Statement object to send SQL statements to the database
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5. The object to execute sql; Execute sql statements; There may be results. Check the returned results
String sql = "SELECT *FROM users";
//Returned result set; The result set encapsulates all our query results
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("id=" + resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("name=" + resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println("password=" + resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("email=" + resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("birthday=" + resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("====================================");
}
//6. Release link;
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Writing steps:
1. Load the driver.
2. Connect to database DriverManager
3. Get the Statement object that executes SQL
4. Get the returned result set
5. Release resources
How does JDBC work? What does it mean
DriverManager
//DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver()); Original writing
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//Fixed writing method (view Driver bottom layer)
//The connection represents the database
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//connection represents the database
//Transaction auto commit
//Transaction commit
//Transaction rollback
connection.commit();
connection.rollback();
connection.setAutoCommit();
URL
Note here: mysql8+ For the above version of, do you want to set the configuration of a time zone? serverTimezone=UTC String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true"; //mysql --3306 //Protocol: / / host address: port number / database name? Parameter 1 & parameter 2 & parameter 3 // oralce -- 1521 //jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
statement object executing SQL prepareStatement() object executing SQL
The statement object in Jdbc is used to send SQL statements to the database. To complete the addition, deletion, modification and query of the database, you only need to send the addition, deletion, modification and query statements to the database through this object.
The executeUpdate method of the Statement object is used to send sql statements of addition, deletion and modification to the database. After executeUpdate is executed, an integer will be returned (that is, the addition, deletion and modification statements cause several rows of data in the database to change).
Statement. The executeQuery method is used to send query statements to the database. The executeQuery method returns the ResultSet object representing the query results,
statement implement sql Object of statement.executeUpdate();//Insert, delete and update all use this to return the number of affected rows; statement.execute(); //Execute arbitrary SQL statement.executeQuery();//Query operation returns resultSet ResultSet The result set encapsulates all our query results resultSet.getObject();//Use without knowing //If you know the properties of the column, use the specified type resultSet.getString(); resultSet.getInt(); resultSet.getBoolean(); .... resultSet.beforeFirst();//Move to the front resultSet.afterLast();//Move to the back resultSet.next();//Move to next data resultSet.previous();//Move to previous line resultSet.absolute(row);//Move to specified row
Release company
//6. Release link; resultSet.close(); statement.close(); connection.close();
Encapsulating JDBC:
Most of the steps of our JDBC program are the same
1. Load the driver.
2. Connect to database DriverManager
3. Get the Statement object that executes SQL
4. Get the returned result set
5. Release resources
The SQL executed is different. In this way, we can encapsulate it into a tool class; Convenient for our operation.
1: Create a toolkit: encapsulate JDBC
public class jdbcUtils {
private static String driver = null;
private static String url = null;
private static String username = null;
private static String password = null;
static {
try {
//Obtain the class loader and load resources;
//Here is to obtain the reflection object through the class, then obtain the class loader of the reflection object, and call the method of obtaining resources of the class loader. Step by step
InputStream in = jdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
//Read the stream into properties
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
//The driver can only be loaded once
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
}
//Release connection resources
public static void release(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet){
if (resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
All additions, deletions and modifications are made with executeUpdate
Add:
public class TestInsert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stat = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
conn = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//Get sql object
stat = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "INSERT INTO users(id,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,email,birthday)" +
"VALUES(4,'kuangshen','123456','123456@qq.com','2021-01-01')";
int i = stat.executeUpdate(sql);//The result set is returned after the addition, deletion and modification are completed
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("Insert successful!!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
jdbcUtils.release(conn, stat, res);
}
}
Delete
public class TestDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet re = null;
try {
conn = jdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection to database
st = conn.createStatement(); //Get the execution object of sql
// Execute specific sql statements
String sql = "DELETE FROM USERS WHERE ID = 4";
int i = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if (i > 0){
System.out.println("Deletion succeeded.");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(conn,st,re);
}
}
change
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet re = null;
try {
conn = jdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection to database
st = conn.createStatement(); //Get the execution object of sql
// Execute specific sql statements
String sql = "update users set name = 'kuangshen',email = '123456@qq.com' where id = 1";
int i = st.executeUpdate(sql);//Result set returned after execution
if (i > 0){
System.out.println("Insert succeeded.");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(conn,st,re);
}
}
check
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection coon = null;
Statement stat = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
coon = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
stat = coon.createStatement();
//Execute sql statement
String sql = "Select * from users where id = 1";
res = stat.executeQuery(sql);//Result set returned after execution
//If there is only one piece of data (if), use (while) if there are multiple pieces of data
while (res.next()) {
System.out.println(res.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
jdbcUtils.release(coon, stat, res);
}
}
Summary:
1: We can see that encapsulating a class can reduce our code, reduce our code redundancy and improve the reusability of the program.
2: Add, delete and modify, executeUpdate. Query: executeQuery
3: Be sure to turn off resources and remember.