catalogue
0. Links to related articles
1. union and connect operators
2. split, select and Side Outputs
0. Links to related articles
1. union and connect operators
API:
- Union: the union operator can merge multiple data streams of the same type and generate data streams of the same type, that is, multiple DataStream[T] can be merged into a new DataStream[T]. The data will be merged according to the First In First Out mode without de duplication.

- connect:
-
Connect provides a function similar to that of union, which is used to connect two data streams. The difference between connect and union is that connect can only connect two data streams, and union can connect multiple data streams.
-
The data types of the two data streams connected by connect can be inconsistent, and the data types of the two data streams connected by union must be consistent.
-
Two datastreams are converted into ConnectedStreams after being connected. ConnectedStreams will apply different processing methods to the data of the two streams, and the state can be shared between the two streams.
-
Examples of requirements:
union two streams of String type
connect a stream of String type and a stream of Long type
Code implementation:
import org.apache.flink.api.common.RuntimeExecutionMode;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.ConnectedStreams;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.co.CoMapFunction;
/**
* Author itcast
* Desc
*/
public class TransformationDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.env
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setRuntimeMode(RuntimeExecutionMode.AUTOMATIC);
//2.Source
DataStream<String> ds1 = env.fromElements("hadoop", "spark", "flink");
DataStream<String> ds2 = env.fromElements("hadoop", "spark", "flink");
DataStream<Long> ds3 = env.fromElements(1L, 2L, 3L);
//3.Transformation
DataStream<String> result1 = ds1.union(ds2);//Merge without redoing https://blog.csdn.net/valada/article/details/104367378
ConnectedStreams<String, Long> tempResult = ds1.connect(ds3);
//interface CoMapFunction<IN1, IN2, OUT>
DataStream<String> result2 = tempResult.map(new CoMapFunction<String, Long, String>() {
@Override
public String map1(String value) throws Exception {
return "String->String:" + value;
}
@Override
public String map2(Long value) throws Exception {
return "Long->String:" + value.toString();
}
});
//4.Sink
result1.print();
result2.print();
//5.execute
env.execute();
}
}2. split, select and Side Outputs
API:
- Split is to divide a stream into multiple streams. Note: the split function has expired and is removed
- Select is to obtain the corresponding data after shunting
- Side Outputs: you can use the process method to process the data in the stream and collect the data into different outputtags according to different processing results
Examples of requirements:
The data in the convection is shunted according to odd and even numbers, and the shunted data is obtained
Code implementation:
import org.apache.flink.api.common.RuntimeExecutionMode;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.ProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
import org.apache.flink.util.OutputTag;
/**
* Author itcast
* Desc
*/
public class TransformationDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.env
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setRuntimeMode(RuntimeExecutionMode.AUTOMATIC);
//2.Source
DataStreamSource<Integer> ds = env.fromElements(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
//3.Transformation
/*SplitStream<Integer> splitResult = ds.split(new OutputSelector<Integer>() {
@Override
public Iterable<String> select(Integer value) {
//value It's the number coming in
if (value % 2 == 0) {
//even numbers
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Even ");
return list;
} else {
//Odd number
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Odd ");
return list;
}
}
});
DataStream<Integer> evenResult = splitResult.select("Even ");
DataStream<Integer> oddResult = splitResult.select("Odd ");*/
//Define two output labels
OutputTag<Integer> tag_even = new OutputTag<Integer>("even numbers", TypeInformation.of(Integer.class));
OutputTag<Integer> tag_odd = new OutputTag<Integer>("Odd number"){};
//Process the data in ds
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Integer> tagResult = ds.process(new ProcessFunction<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public void processElement(Integer value, Context ctx, Collector<Integer> out) throws Exception {
if (value % 2 == 0) {
//even numbers
ctx.output(tag_even, value);
} else {
//Odd number
ctx.output(tag_odd, value);
}
}
});
//Take out the marked data
DataStream<Integer> evenResult = tagResult.getSideOutput(tag_even);
DataStream<Integer> oddResult = tagResult.getSideOutput(tag_odd);
//4.Sink
evenResult.print("even numbers");
oddResult.print("Odd number");
//5.execute
env.execute();
}
}3. rebalance partition
Function overview:
- Similar to repartition in Spark, but more powerful, it can directly solve data skew.
- Flink also has data skew. For example, at present, there are about 1 billion pieces of data to be processed. In the process of processing, the situation shown in the figure may occur. In case of data skew, the other three machines have to wait for the execution of machine 1 before the overall task is completed.

-
Therefore, in the actual work, the better solution to this situation is rebalance (the internal round robin method is used to evenly disperse the data).

Code demonstration:
import org.apache.flink.api.common.RuntimeExecutionMode;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FilterFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
/**
* Author itcast
* Desc
*/
public class TransformationDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.env
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setRuntimeMode(RuntimeExecutionMode.AUTOMATIC).setParallelism(3);
//2.source
DataStream<Long> longDS = env.fromSequence(0, 100);
//3.Transformation
//The following operations are equivalent to randomly distributing the data. There may be data skew
DataStream<Long> filterDS = longDS.filter(new FilterFunction<Long>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(Long num) throws Exception {
return num > 10;
}
});
//Next, use the map operation to convert the data to (partition number / subtask number, data)
//Rich means multi-functional. There are more API s than MapFunction for us to use
DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, Integer>> result1 = filterDS
.map(new RichMapFunction<Long, Tuple2<Integer, Integer>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<Integer, Integer> map(Long value) throws Exception {
//Get partition number / subtask number
int id = getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask();
return Tuple2.of(id, 1);
}
}).keyBy(t -> t.f0).sum(1);
DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, Integer>> result2 = filterDS.rebalance()
.map(new RichMapFunction<Long, Tuple2<Integer, Integer>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<Integer, Integer> map(Long value) throws Exception {
//Get partition number / subtask number
int id = getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask();
return Tuple2.of(id, 1);
}
}).keyBy(t -> t.f0).sum(1);
//4.sink
//result1.print();// Data skew is possible
result2.print();//rebalance repartition balance is performed before output to solve the problem of data skew
//5.execute
env.execute();
}
}4. Other partition operators
API:
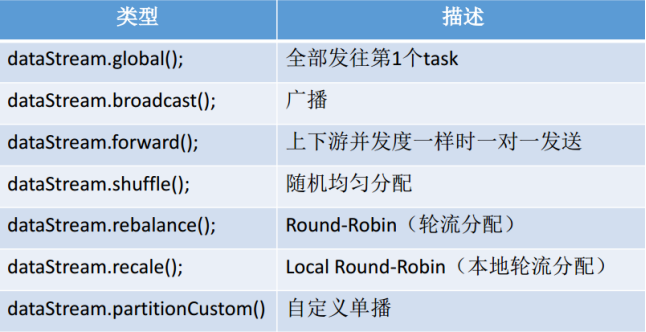
Description:
recale partition. Based on the parallelism of upstream and downstream operators, records are output to each instance of downstream operators in a circular manner.
give an example:
If the upstream parallelism is 2 and the downstream parallelism is 4, one upstream parallelism outputs the record to the two downstream parallelism in a circular manner; The other parallel degree upstream outputs the record to the other two parallel degrees downstream in a circular manner. If the upstream parallelism is 4 and the downstream parallelism is 2, the two upstream parallelism will output the record to one downstream parallelism; The other two parallel degrees upstream output the record to another parallel degree downstream.
Code demonstration:
import org.apache.flink.api.common.RuntimeExecutionMode;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.Partitioner;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
/**
* Author itcast
* Desc
*/
public class TransformationDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.env
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setRuntimeMode(RuntimeExecutionMode.AUTOMATIC);
//2.Source
DataStream<String> linesDS = env.readTextFile("data/input/words.txt");
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> tupleDS = linesDS.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) throws Exception {
String[] words = value.split(" ");
for (String word : words) {
out.collect(Tuple2.of(word, 1));
}
}
});
//3.Transformation
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result1 = tupleDS.global();
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result2 = tupleDS.broadcast();
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result3 = tupleDS.forward();
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result4 = tupleDS.shuffle();
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result5 = tupleDS.rebalance();
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result6 = tupleDS.rescale();
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> result7 = tupleDS.partitionCustom(new Partitioner<String>() {
@Override
public int partition(String key, int numPartitions) {
return key.equals("hello") ? 0 : 1;
}
}, t -> t.f0);
//4.sink
//result1.print();
//result2.print();
//result3.print();
//result4.print();
//result5.print();
//result6.print();
result7.print();
//5.execute
env.execute();
}
}This blog is adapted from the 2020 New Year video of a horse: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1oX4y1K7kM