8, TableAPI and FlinkSQL
brief introduction
- Flink provides a unified upper API for batch and stream processing
- Table API is a set of query APIs embedded in Java and Scala languages. It allows you to combine queries from some relational operators in a very intuitive way
- Flink's SQL support is based on Apache compute, which implements the SQL standard
simple example
package day7
import com.atguigu.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.api._
import org.apache.flink.table.api.scala._
object TableExample_study1 {
def main(args:Array[String]):Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
//Read data and create dataStream
val inputStream : DataStream[String] = env.readTextFile("D:\\Flink\\20-Flink[www.hoh0.com]\\FlinkTutorial\\src\\main\\resources\\sensor.txt")
val dataStream : DataStream[SensorReading] = inputStream
.map(data => {
val dataArray = data.split(",")
SensorReading(dataArray(0),dataArray(1).toLong,dataArray(2).toDouble)
})
//Create table execution environment
val tableEnv : StreamTableEnvironment = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env)
//Based on the data flow, it is converted into a table and then operated
val dataTable : Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream)
//Call the TableAPI to get the conversion result
val resultTable : Table = dataTable
.select("id,temperature")
.filter("id=='sensor_1'")
//Or write sql directly to get the result
val resultSqltable : Table = tableEnv
.sqlQuery("select id, temperature from "+dataTable + " where id = 'sensor_1'")
//Convert to data stream and print out
//val resultStream : DataStream[(String,Double)] = resultTable.toAppendStream
val resultStream : DataStream[(String,Double)] = resultSqltable.toAppendStream[(String,Double)]
resultStream.print("result")
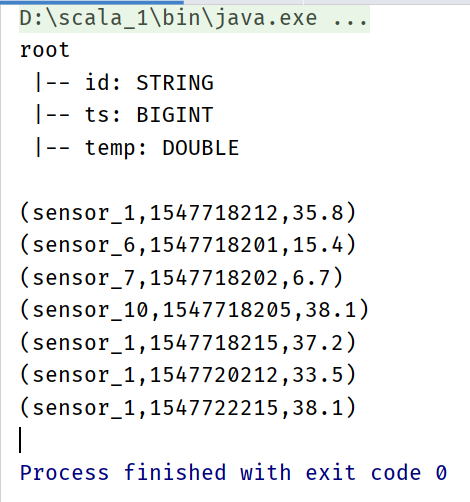
resultTable.printSchema()
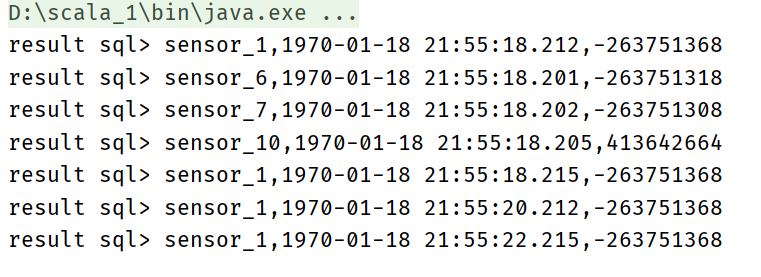
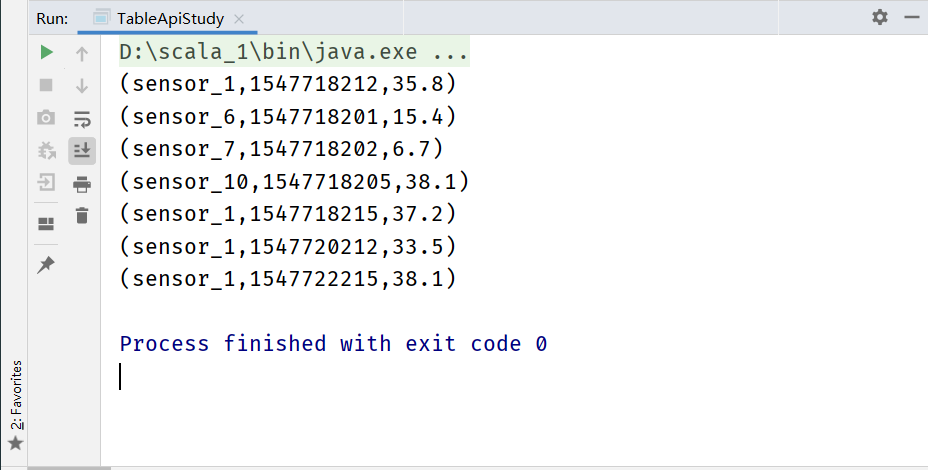
/*Output results
root
|-- id: STRING
|-- temperature: DOUBLE
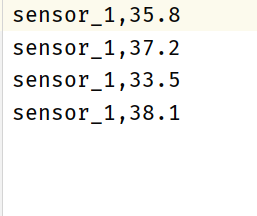
result> (sensor_1,35.8)
result> (sensor_1,37.2)
result> (sensor_1,33.5)
result> (sensor_1,38.1)
*/
env.execute("table api test")
}
}
Create tableenvironment
//1 create table environment //Create an old version of the stream query environment val settings : EnvironmentSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance() .useOldPlanner() .inStreamingMode() .build() val tableEnv:StreamTableEnvironment = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
//1.2 create an old version of batch query environment val batchEnv:ExecutionEnvironment = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment val batchTableEnv : BatchTableEnvironment = BatchTableEnvironment.create(batchEnv)
//1.3 create a blink version of the stream query environment val bsSettings =EnvironmentSettings.newInstance() .useBlinkPlanner() .inStreamingMode() .build() val bsTableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,bsSettings)
//1.4 create a blink version batch query environment val bbSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance() .useBlinkPlanner() .inBatchMode() .build() val bbTableEnv = TableEnvironment.create(bbSettings)
Table
- TableEnvironment can register Catalog and can be based on Catalog registry
- A Table is specified by an identifier and consists of three parts: Catalog name, database name and object name
- Tables can be regular or virtual (View)
- General tables can generally be used to describe external data, such as files, database tables or message queue data, or can be directly converted from DataStream
- A View can be created from an existing table, usually a table API or a result set of an SQL query
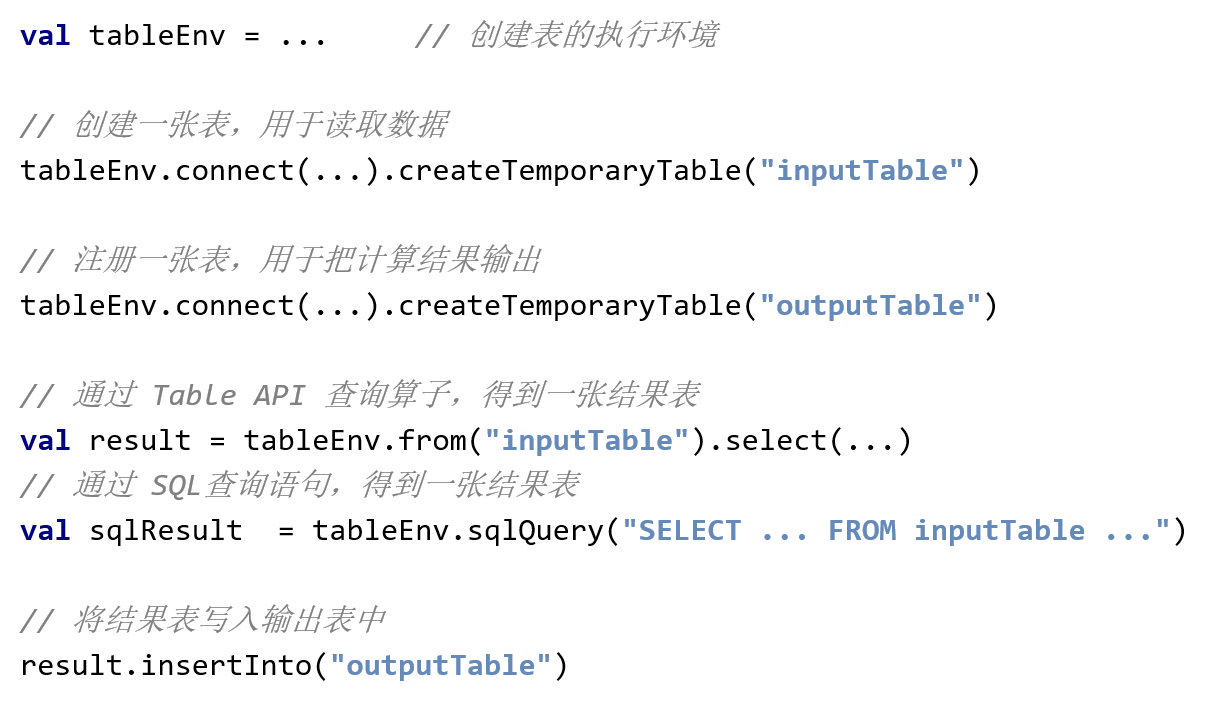
Read data from file
//2.1 connect to file system (Csv)
val filePath = "D:\\Flink\\20-Flink[www.hoh0.com]\\FlinkTutorial\\src\\main\\resources\\sensor.txt"
tableEnv.connect(new FileSystem().path(filePath))
.withFormat(new OldCsv())//Defines the formatting method after reading the data
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id",DataTypes.STRING())
.field("timestamp",DataTypes.BIGINT())
.field("temperature",DataTypes.DOUBLE())
) //Define table structure
.createTemporaryTable("inputTable")//Register a form
//switch to stream and print
val sensorTable : Table = tableEnv.from("inputTable")
sensorTable.toAppendStream[(String,Long,Double)].print()
Read data from kafka
tableEnv.connect(new Kafka()
.version("0.11")
.topic("sensor")
.property("bootstrap.servers","hadoop103:9092")
.property("zookeeper.connect","hadoop103:2181")
)
.withFormat(new Csv() )
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id",DataTypes.STRING())
.field("timestamp",DataTypes.BIGINT())
.field("temp",DataTypes.DOUBLE()))
.createTemporaryTable("kafkatable")
//switch to stream and print
val sensorTable : Table = tableEnv.from("kafkatable")
sensorTable.toAppendStream[(String,Long,Double)].print()
env.execute("table api test")
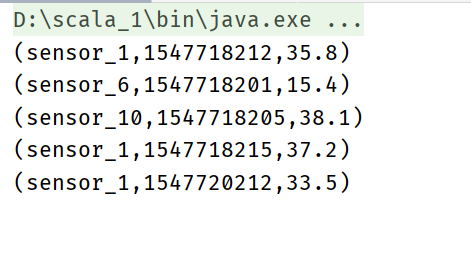
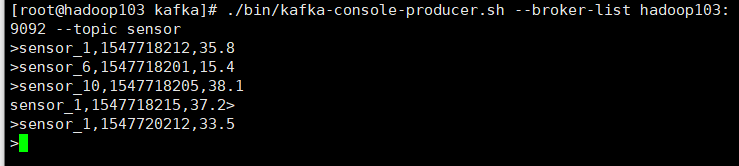
Table query (Table API)
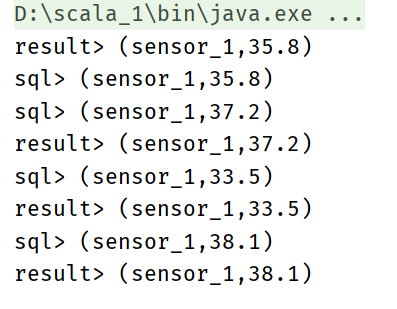
Simple query
val sensorTable: Table = tableEnv.from("inputTable")
val resultTable: Table = sensorTable
.select('id, 'temperature)
.filter('id === "sensor_1")
SQL simple query
val resultSqlTable: Table = tableEnv.sqlQuery(
"""
|select id,temperature
|from inputTable
|where id = 'sensor_1'
""".stripMargin
)
resultTable.toAppendStream[(String, Double)].print("result")
resultSqlTable.toAppendStream[(String,Double)].print("sql")
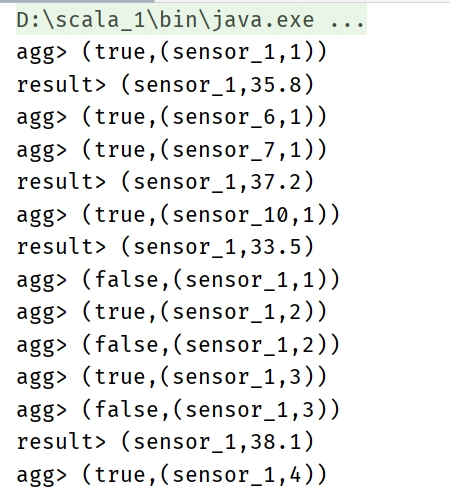
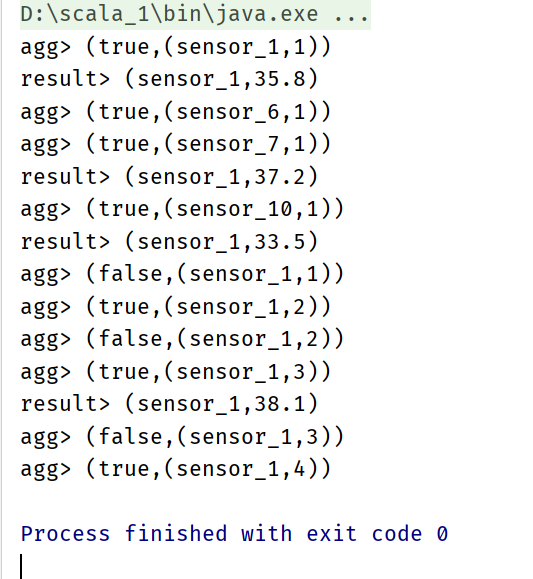
Simple aggregation, statistics of the temperature of each sensor
val aggResultTable: Table = sensorTable.groupBy('id)
.select('id, 'id.count as 'count)
resultTable.toAppendStream[(String, Double)].print("result")
aggResultTable.toRetractStream[(String,Long)].print("agg")
Simple aggregation with SQL
val aggResultSqlTable: Table = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select id,count(id) as cnt from inputTable group by id")
resultTable.toAppendStream[(String, Double)].print("result")
aggResultSqlTable.toRetractStream[(String, Long)].print("agg")
Conversion of tables and streams
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
// TODO change DataStream to Table
val sensorTable : Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,'id,'timestamp as 'ts,'temperature as 'temp)
sensorTable.printSchema()
sensorTable.toAppendStream[(String,Long,Double)].print()
Import data into a file
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
// TODO change DataStream to Table
val sensorTable : Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,'id,'timestamp as 'ts,'temperature as 'temp)
//TODO change table , get the result_table
val resultTable : Table = sensorTable
.select('id,'temp)
.filter('id==="sensor_1")
//TODO define a output_table ,that the Tablesink be written data
tableEnv.connect(new FileSystem().path("D:\\Flink\\20-Flink[www.hoh0.com]\\FlinkTutorial\\src\\main\\resources\\out.txt"))
.withFormat(new Csv())
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id",DataTypes.STRING())
.field("temperature",DataTypes.DOUBLE())
)
.createTemporaryTable("outputTable")
//write the result_table to table sink
resultTable.insertInto("outputTable")
Update mode
- For streaming queries, you need to declare how to perform transformations between tables and external connectors
- The type of message exchanged with the external system, specified by the Update Mode
Append mode
– tables only perform Insert operations, and only exchange Insert messages with external connectors
Retract mode
– tables and external connectors exchange Add and Retract messages
– Insert is encoded as Add message; Delete the message encoded as Retract; The Update code is the Retract message of the previous item and the Add message of the next item
Update insert mode
Both update and insert are encoded as Upsert messages; Delete message encoded as delete
Input data to kafka
package day7
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.api.{DataTypes, EnvironmentSettings, Table}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.descriptors.{Csv, Kafka, Schema}
object kafkaTableStudy {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//Create environment
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
//Connect kafka and register the input table
tableEnv.connect(new Kafka()
.version("0.11")
.topic("sensor")
.property("bootstrap.servers","hadoop103:9092")
.property("cookeeper.connect","hadoop103:2181")
)
.withFormat(new Csv())
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id",DataTypes.STRING())
.field("timestamp",DataTypes.BIGINT())
.field("temperature",DataTypes.DOUBLE()))
.createTemporaryTable("kafkaInputTable")
//Convert the input table to the result table
val resultStream = tableEnv.from("kafkaInputTable")
.select('id,'temperature)
.filter('id ==="sensor_1")
//Connect kafka and register the output table
tableEnv.connect(new Kafka()
.version("0.11")
.topic("sinkTest")
.property("bootstrap.servers","hadoop103:9092")
.property("zookeeper.connect","hadoop103:2181")
)
.withFormat(new Csv())
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id",DataTypes.STRING())
.field("temperature",DataTypes.DOUBLE())
)
.createTemporaryTable("kafkaOutputTable")
//Enter the result table into the output table
resultStream.insertInto("kafkaOutputTable")
env.execute("kafka job")
}
}
Time Attributes
- For time-based operations (such as window operations in Table API and SQL), you need to define relevant time semantics and time data source information
- Table can provide a logical time field to indicate the time and access the corresponding timestamp in the table handler
- Time attribute, which can be part of each table schema. Once the time attribute is defined, it can be referenced as a field and can be used in time-based operations
- The behavior of the time attribute is similar to a regular timestamp, which can be accessed and calculated
Define Processing Time
val resultTable : Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,'id,'timestamp,'temperature ,'pt.proctime) resultTable.printSchema() resultTable.toAppendStream[Row].print()
- Under the processing time semantics, the table handler is allowed to generate results according to the local time of the machine. It is the simplest concept of time. It does not need to extract time stamps or generate watermark s
- Specified when converting from DataStream to table
- During Schema definition, you can use Procime, which specifies the field name and defines the processing time field
- This procime attribute can only extend the physical schema by attaching logical fields. Therefore, it can only be defined at the end of the schema definition
Define Event Time
package day7
import com.atguigu.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.timestamps.BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time
import org.apache.flink.table.api._
import org.apache.flink.table.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.types.Row
object TimeAndWindowStudy {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
val inputStream : DataStream[String] = env.readTextFile("D:\\Flink\\20-Flink[www.hoh0.com]\\FlinkTutorial\\src\\main\\resources\\sensor.txt")
val dataStream : DataStream[SensorReading] = inputStream.map(
data => {
val dataArray = data.split(",")
SensorReading(dataArray(0),dataArray(1).toLong,dataArray(2).toDouble)
}
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor[SensorReading](Time.seconds(1)) {
override def extractTimestamp(element: SensorReading): Long = element.timestamp*1000L
})
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
//val resultTable : Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,'id,'timestamp,'temperature ,'pt.proctime)
val resultTable : Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,'id,'timestamp.rowtime,'temperature)
resultTable.printSchema()
resultTable.toAppendStream[Row].print()
env.execute("time test")
}
}
- Event time semantics that allow table handlers to generate results based on the time contained in each record. In this way, correct results can be obtained even when there are out of order events or delayed events.
- In order to deal with disorderly events and separate punctual and late events in the diversion; Flink needs to extract time stamps from event data and use them to promote the progress of event time
- There are also three methods to define event time:
- Specified when converting from DataStream to table
- Specified when defining Table Schema
- Defined in the DDL where the table was created
Window operation
Group Windows
package day8
import java.sql.Timestamp
import com.atguigu.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.timestamps.BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time
import org.apache.flink.table.api.{EnvironmentSettings, Over, Table, Tumble}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.types.Row
object WindowStudy {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
val inputStream = env.readTextFile("D:\\Flink\\20-Flink[www.hoh0.com]\\FlinkTutorial\\src\\main\\resources\\sensor.txt")
val dataStream : DataStream[SensorReading] = inputStream.map(
data => {
val dataArray = data.split(",")
SensorReading(dataArray(0),dataArray(1).toLong,dataArray(2).toDouble)
}
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor[SensorReading](Time.seconds(1)) {
override def extractTimestamp(element: SensorReading): Long = element.timestamp * 1000L
}
)
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
val sensorTable: Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream, 'id, 'timestamp.rowtime as 'ts, 'temperature)
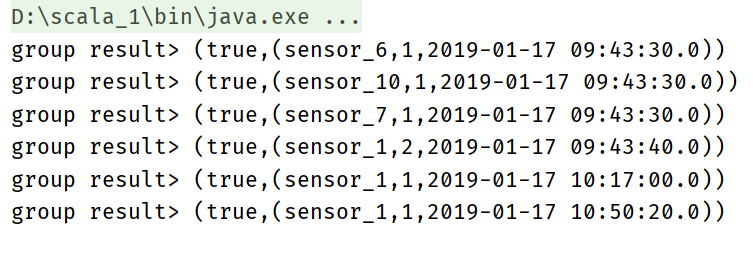
val groupResultTable: Table = sensorTable
.window( Tumble over 10.seconds on 'ts as 'tw )
.groupBy('id, 'tw)
.select('id, 'id.count, 'tw.end)
groupResultTable.toRetractStream[(String, Long, Timestamp)].print("group result")
env.execute("window_job")
}
}
Implement group window through sql
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor",sensorTable)
val groupResultTableSql : Table = tableEnv.sqlQuery(
"""
|select id,
|count(id),
|tumble_end(ts,interval '10' second)
|from sensor
|group by
|id,
|tumble(ts, interval '10' second)
""".stripMargin
)
//groupResultTable.toRetractStream[(String, Long, Timestamp)].print("group result")
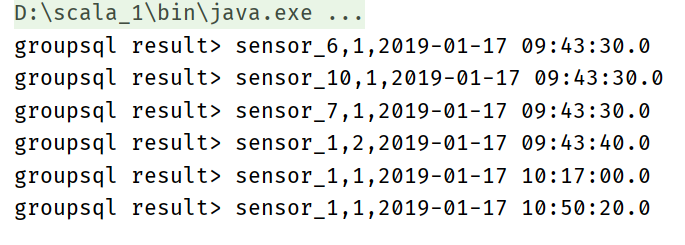
groupResultTableSql.toAppendStream[Row].print("groupsql result")
env.execute("window_job")
- The scrolling window should be defined with the Tumble class

- The sliding window should be defined with the Slide class

- The Session window should be defined with the Session class

Over Windows
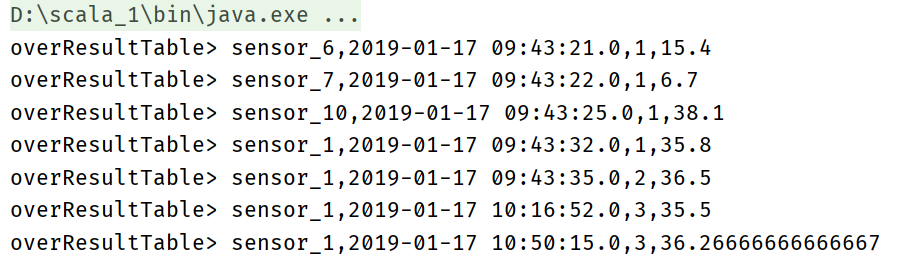
val overResultTable : Table = sensorTable
.window(Over partitionBy 'id orderBy 'ts preceding 2.rows as 'w)
.select('id,'ts,'id.count over 'w ,'temperature.avg over 'w)
overResultTable.toAppendStream[Row].print("overResultTable")
Implementing over window with sql
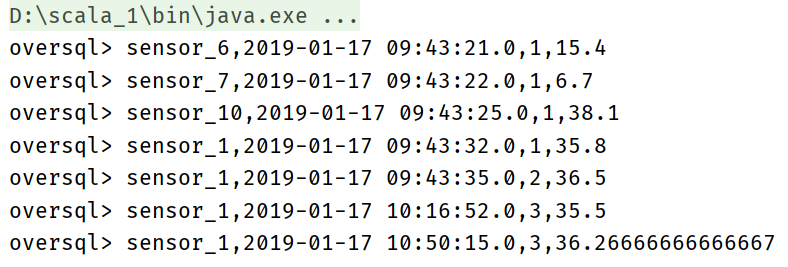
val overResultTableSql = tableEnv.sqlQuery(
"""
|select id, ts,
| count(id) over w,
| avg(temperature) over w
|from sensor
|window w as (
| partition by id
| order by ts
| rows between 2 preceding and current row
|)
|""".stripMargin
)
overResultTableSql.toAppendStream[Row].print("oversql")
- Over window aggregation is an existing (over clause) in standard SQL and can be defined in the SELECT clause of the query
- Over window aggregation will calculate the aggregation within the range of adjacent rows for each input row
- Over windows is defined using the window (W: over windows *) clause and is referenced by an alias in the select () method

Unbounded Over Windows
- Over windows can be defined within the event time or processing time, and within the range specified as time interval, or row count
- The unbounded over window is specified using a constant

Bounded Over Windows
- The bounded over window is specified by the size of the interval

9, Function
TableFunction (table function)
- User defined table functions can also take 0, 1 or multiple scalar values as input parameters; Unlike scalar functions, it can return any number of rows as output instead of a single value
- In order to define a table function, you must extend org apache. flink. table. The base class TableFunction in functions and implements one or more evaluation methods
- The behavior of a table function is determined by its evaluation method, which must be public and named eval

UDF instance
package day8
import com.atguigu.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.timestamps._
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time
import org.apache.flink.table.api.EnvironmentSettings
import org.apache.flink.table.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.TableFunction
import org.apache.flink.types.Row
object TableFunctionStudy {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
val inputStream = env.readTextFile("D:\\Flink\\20-Flink[www.hoh0.com]\\FlinkTutorial\\src\\main\\resources\\sensor.txt")
val dataStream : DataStream[SensorReading] = inputStream
.map(data => {
val dataArray = data.split(",")
SensorReading(dataArray(0),dataArray(1).toLong,dataArray(2).toDouble)
})
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor[SensorReading](Time.seconds(1)) {
override def extractTimestamp(element: SensorReading): Long = element.timestamp*1000L
})
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
val sensorTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,'id,'timestamp.rowtime as 'ts,'temperature )
val split = new SplitStudy("_")
val resultTable = sensorTable
.joinLateral(split('id) as ('word,'length))//Pass in the id, which is divided into word and word Length, as word and length respectively
.select('id,'ts,'word,'length)
resultTable.toAppendStream[Row].print("result")
env.execute("job")
}
}
class SplitStudy(seperatore:String) extends TableFunction[(String,Int)] {
def eval(str : String) : Unit ={
str.split(seperatore).foreach(
word => collect((word,word.length))
)
}
}
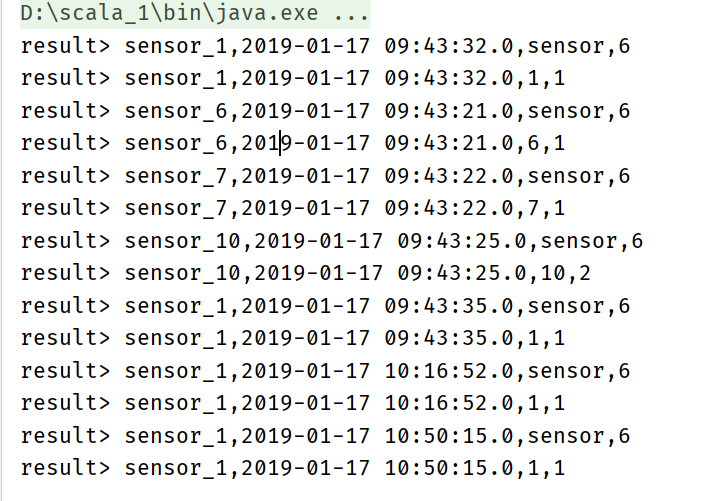
Implemented with SQL
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor",sensorTable)
tableEnv.registerFunction("split",split)
val resultTableSql = tableEnv.sqlQuery(
"""
|select id,ts,word,length
|from
|sensor,lateral table(split(id)) as splitid(word,length)
|
|""".stripMargin
)
resultTableSql.toAppendStream[Row].print("result sql")

Differences between functions in Table API and SQL
Comparison function
SQL
value1 = value2 value1 > value2
Table API
ANY1 === ANY2 ANY1 > ANY2
Logic function
SQL
boolean1 OR boolean2 boolean IS FALSE NOT boolean
Table API
BOOLEAN1||BOOLEAN2 BOOLEAN.isFalse !BOOLEAN
arithmetic function
SQL
numeric1 + numeric2 POWER(numeric1,numeric2)
Table API
NUMERIC1 + NUMERIC2 NUMERIC1.power(NUMERIC2)
String function
SQL
string1||string2 UPPER(string) CHAR_LENGTH(string)
Table API
STRING1 + STRING2 STRING.upperCase() STRING.charLength()
Time function
SQL
DATE string TIMESTAMP string CURRENT_TIME INTERVAL string range
Table API
STRING.toData STRING.toTimestamp currentTime() NUMERIC.days NUMERIC.minutes
Aggregate function
SQL
COUNT(*) SUM(expression) RANK() ROW_NUMBER()
Table API
FIELD.count FIELD.sum()
User defined function (UDF)
- User defined functions (UDF s) are an important feature, which significantly expand the expressive ability of queries
- In most cases, user-defined functions must be registered before they can be used in queries
- The function is registered in the TableEnvironment by calling the * * registerFunction() * * method. When a user-defined function is registered, it is inserted into the function directory of the TableEnvironment so that the Table API or SQL parser can recognize and interpret it correctly
Scalar function
- A user-defined scalar function that maps 0, 1, or multiple scalar values to new scalar values
- In order to define scalar functions, you must apache. flink. table. Functions extends the base class Scalar Function and implements (one or more) evaluation (eval) methods
- The behavior of scalar functions is determined by the evaluation method, which must be publicly declared and named eval

UDF
package day8
import com.atguigu.apitest.SensorReading
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.timestamps.BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time
import org.apache.flink.table.api.{EnvironmentSettings, Table}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.ScalarFunction
import org.apache.flink.types.Row
object ScalarFunctionStudy {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
val inputStream = env.readTextFile("D:\\Flink\\20-Flink[www.hoh0.com]\\FlinkTutorial\\src\\main\\resources\\sensor.txt")
val dataStream : DataStream[SensorReading] = inputStream
.map(data => {
val dataArray = data.split(",")
SensorReading(dataArray(0),dataArray(1).toLong,dataArray(2).toDouble)
})
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor[SensorReading](Time.seconds(1)) {
override def extractTimestamp(element: SensorReading): Long = element.timestamp
})
val settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build()
val tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
val sensorTable : Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,'id,'timestamp.rowtime as 'ts,'temperature)
val hashCode = new hashCodeStudy(10)
val resultTable = sensorTable
.select('id,'ts,hashCode('id))
resultTable.toAppendStream[Row].print("result")
env.execute("job")
}
}
//Custom scalar function
class hashCodeStudy(factor : Int) extends ScalarFunction{
def eval(str :String) : Int ={
str.hashCode*factor
}
}
Implemented with SQL
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensor",sensorTable)
tableEnv.registerFunction("hashCode",hashCode)
val resultTableSql = tableEnv.sqlQuery(
"""
|select id,ts,hashCode(id) from sensor
|""".stripMargin
)
resultTableSql.toAppendStream[Row].print("result sql")