Fundamentals of software testing
Software Foundation
1: Definition of software
Software testing (English): Software Testing),
Describes a process used to promote the verification of software correctness, integrity, safety and quality.
In other words, software testing is a review or comparison process between actual output and expected output.
2: Application scenarios of software
Game testing, e-commerce testing, financial software, embedded testing, etc
3: Software architecture classification
B/S architecture software
Client is browser:Baidu, good 123
C/S architecture software
The client needs to install special software, such as QQ Wechat, etc
Definition and principle of software testing
1: Why software testing
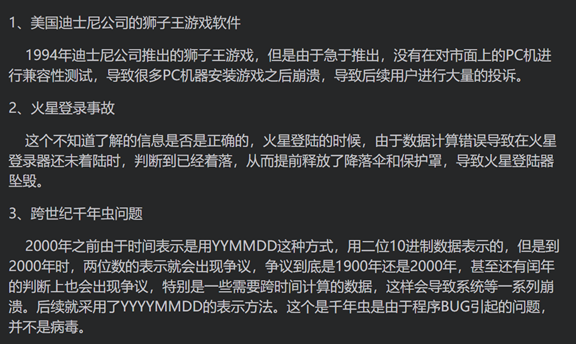
2: Definition of software testing
The process of verifying whether the actual results of software are consistent with user requirements manually or automatically
3: Principles of software testing
Principle 1: enter software testing as soon as possible Principle 2: exhaustive testing is not feasible Principle 3: programmers should avoid checking their own programs Principle 4: pay full attention to the clustering of defects in the test Principle 5: strictly implement the test plan and eliminate the randomness of the test Principle 6: every test result should be comprehensively checked Principle 7: properly save the test plan, test cases, error statistics and final analysis report to facilitate maintenance Principle 8: when designing test cases, it should include reasonable input data and unreasonable input data Principle 9: test cases should be composed of test data and corresponding expected output results
Software testing process
| Stage name | job content | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Test preparation stage | Project initiation, demand analysis and demand review | Requirements document, product PRD |
| Test plan phase | Prepare test plan and plan review | test plan |
| Test design phase | Extract test points, write test cases and review test cases | test case |
| Test execution phase | Smoke test, execute test cases, raise bug s, regression test | Defect report |
| Test completion phase | Acceptance test, preparation of test report and project launch | Test report |
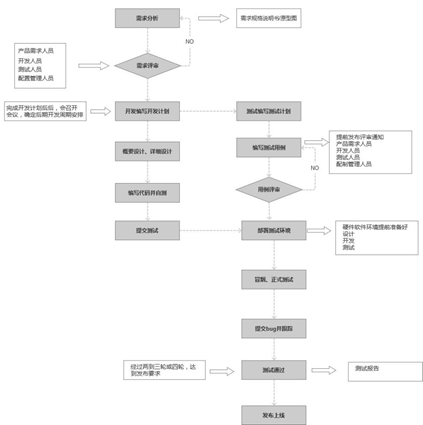
| Requirements review | Test plan development | Test plan execution | Release and test report summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| From the point of view of design, whether there are defects, whether it can provide suggestions from the point of view of user experience, whether there are defects in the design, and whether it can analyze whether there are other functions from the point of view of design | 1 test case design 2 test time estimation 3 personnel arrangement 4 test resource application 5 risk assessment | 1 use case execution 2 Bug repair verification and promotion of version progress 3 performance monitoring, stress test and compatibility test | 1. Whether there are problems in version release and online quality monitoring and user feedback |
| Follow up the demand change in the whole process and communicate seamlessly with the product. If there is a demand change in the testing stage, understand the scope of the change at the first time. If it affects the quality of the version, explain the risk, and evaluate whether the demand must be changed and whether it affects the timeline of the release and launch of the version | Plan the proportion of development and testing required by the test project, plan the time required for the whole test process, and reserve a buffer for dealing with emergencies | Execute and coordinate test resources, deploy test environment, urge development and products to provide all required test tools and test data, promote version progress, conduct bug verification every day, identify the priority of bug resolution and the time point of submitting test, and provide the product quality report of the day every day | After the project is released and launched, actively cooperate with the on-site operation and maintenance personnel to follow up and reproduce the bug s in the later stage of the project and communicate with the development |
Classification of software testing
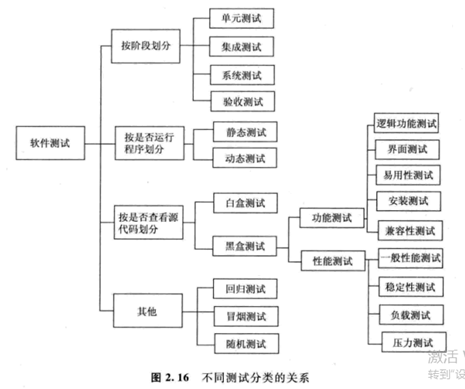
1. By technology:
Black box test, white box test, gray box test Black box test: a test method that does not need to know the source code of the program and verifies whether the program meets the requirements by using the whole software function White box test: it is a test method to design test data and complete the test according to the internal logic structure and coding structure of the program Gray box test: a test method that designs test data based on the external performance of the program while combining the internal structure of the program
2. By stage
Unit test, integration test, system test and acceptance test Unit test: a test method to verify the correctness of a module, function or class Integration test: after unit test, the individual modules are assembled into subsystems or systems according to the design requirements and tested as a whole System test: after the integration test, take the hardware and software as a whole,Overall test of system function and performance Acceptance test: after system test, user test is the main test method, or testers participate in the test of software quality
3. By content
Function test, performance test and compatibility test
Function test:
Interface test, smoke test, regression test, business logic test and usability test Function test: a test method to test whether the characteristics and operable behavior of a product meet the needs of users according to the product operation description and requirements documents Interface test: test whether the layout of the functional modules of the user interface conforms to the customer's usage habits, and test the convenience of interface operation and simple and understandable navigation Smoke test: a test method to verify whether the core functions of the system can operate normally Regression test: refers to a test method that re tests after modifying the old code to confirm that the modification does not introduce new errors or lead to errors in other codes Business logic test: on the basis that the basic function points have passed, prepare a variety of test data to drive the business process under various constraints and determine whether the final output results meet the expected test Usability test: refers to the test of whether users feel convenient when using the software
Performance test:
Stress test, load test, concurrent test Performance test: a test method to verify various performance indexes of the system by simulating various normal, peak and abnormal load conditions through automatic test tools Stress test: test the change of system performance by gradually increasing the system load, and determine under what conditions the system performance is in failure state Load test: test the change of system performance by gradually increasing the system load, and test the maximum load that the system can bear under the condition of meeting the performance index Concurrency test: it is a process of load test and stress test, that is, gradually increase the number of concurrent users until the bottleneck of the system, and determine the concurrency performance of the system by analyzing resource monitoring indicators
Compatibility test:
Different versions and resolutions of the tour Mobile phone model, different versions, resolution
4. By other
Smoke test, random test, safety test, regression test Alpha Testing Beta test Random test: random test is mainly a test method to spot check the function and performance of software without test cases according to the experience of testers Security test: a test method to verify the security of programs, networks and databases through different test methods Alpha Test: commonly known as internal test,αTesting. Testing in internal environment; Developers or testers on site Beta Test: commonly known as external test and public test,βTesting. Testing in production environment; Neither developers nor testers were present
5: Test case (demand: 500ml water cup)

Write the test points of the water cup (function, performance, interface, safety and easy to use)
commonsense knowledge
1: Organizational structure of testing department
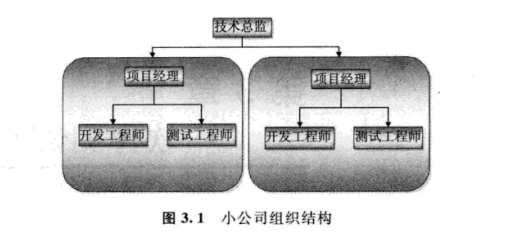
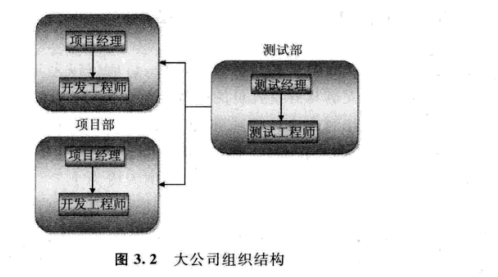
PRD Product Requirement Document
PM product manager RD:Research and development personnel FE Front end developer QA test OP Operation and maintenance UE User experience case test case https://blog.csdn.net/springlovejava/article/details/78757838
2: Daily / weekly
Nail nail/Enterprise wechat, etc
3: oa office software
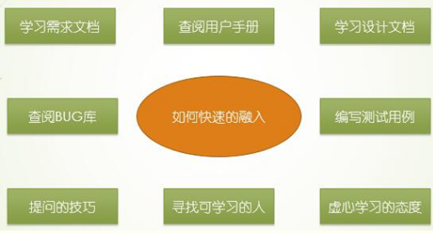
4: How do newcomers integrate into a project team