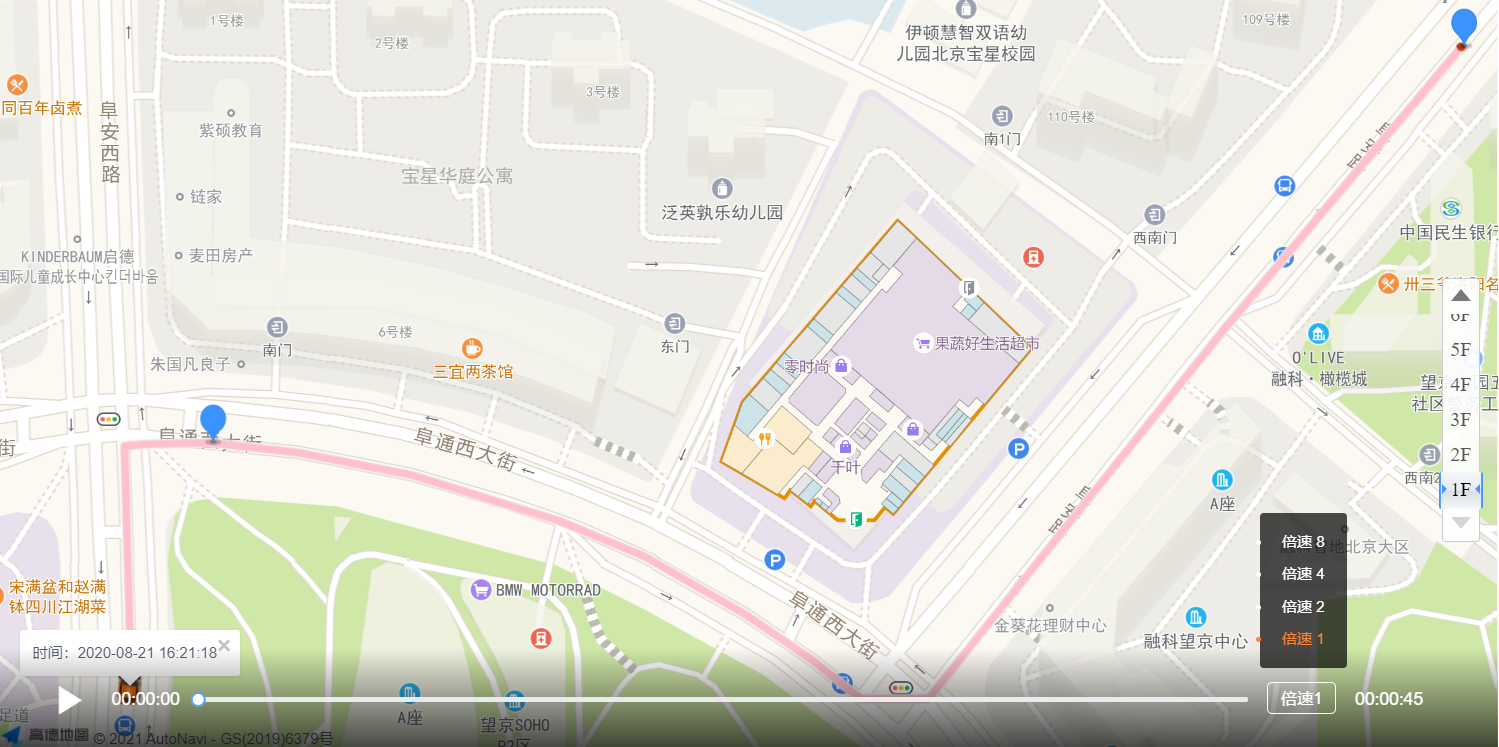
Gaode map path playback
Create Gaode map
- Install our Vue amap dependencies
- Official website https://github.com/ElemeFE/vue-amap It has detailed teaching
- Visual panel installation (I recommend a super favorite method)
- npm install -S vue-amap
- Configure on main.js
// Import AMap import AMap from 'vue-amap' // register Vue.use(AMap) // load AMap.initAMapApiLoader({ // Golde's key key: 'You're cute key', // Plug in collection plugin: ['AMapManager', 'AMap.Autocomplete', 'AMap.PlaceSearch', 'AMap.Scale', 'AMap.OverView', 'AMap.ToolBar', 'AMap.MapType', 'AMap.PolyEditor', 'AMap.CircleEditor', 'Geocoder', 'Geolocation', 'AMap.MarkerClusterer', 'AMap.PolyEditor', 'AMap.CircleEditor', 'AMap.MouseTool', 'AMap.Driving', 'AMap.CitySearch', 'AMap.InfoWindow', 'AMap.LngLat', 'AMap.DistrictSearch', 'AMap.TileLayer.Traffic', 'AMap.Heatmap', 'AMap.Autocomplete', 'AMap.PlaceSearch'], // Gaode sdk version, the default is 1.4.4 v: '1.4.4' }) - If AMap's is not defined, try the following method
- Configure in. eslintrc.js
globals: { AMap: true, AMapUI: true, }, - Configure in index.html
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://Webapi. Amap. COM / maps? V = 1.4.15 & key = your lovely key "> </script> <script src="//webapi.amap.com/ui/1.1/main.js?v=1.1.1"></script>
- Configure in. eslintrc.js
- Set the container for storing the map (the set div size of the map is not shown)
<!-- Map --> <div id="container"></div>
- Set up map
mounted() { // Setting up the map is basically configured const param = { // Are map container size changes monitored resizeEnable: true, // Initial map level zoom: 15 } this.map = new AMap.Map('container', param) },
If you do this, the map can be displayed
Create alignment
Style of alignment: https://lbs.amap.com/api/amap-ui/reference-amap-ui/mass-data/pathsimplifier/
-
Data transferred from the background (it can be lost in data or imported into js)
// Route from background linePath: [ { latitude: 39.997761, longitude: 116.478935, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:18' }, { latitude: 39.997825, longitude: 116.478939, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:21' }, { latitude: 39.998549, longitude: 116.478912, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:24' }, { latitude: 39.998555, longitude: 116.478998, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:27' }, { latitude: 39.99856, longitude: 116.479282, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:30' }, { latitude: 39.998528, longitude: 116.479658, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:33' }, { latitude: 39.998453, longitude: 116.480151, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:36' }, { latitude: 39.998302, longitude: 116.480784, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:39' }, { latitude: 39.998184, longitude: 116.481149, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:42' }, { latitude: 39.997997, longitude: 116.481573, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:45' }, { latitude: 39.997846, longitude: 116.481863, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:48' }, { latitude: 39.997718, longitude: 116.482072, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:51' }, { latitude: 39.997718, longitude: 116.482362, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:54' }, { latitude: 39.998935, longitude: 116.483633, time: '2020-08-21 16:21:57' }, { latitude: 39.998968, longitude: 116.48367, time: '2020-08-21 16:22:00' }, { latitude: 39.999861, longitude: 116.484648, time: '2020-08-21 16:22:03' } ] -
We need to convert the json passed in the background into an array
// initialization init() { // The data passed in the background is json, so we change it to array // trajectory // Line route let linePath = this.linePath linePath.forEach(item => { // Convert json to array this.pathList.push([item.longitude, item.latitude]) }) // Set route this.setPath() }, -
Set route
// Set route setPath() { let that = this AMapUI.load(['ui/misc/PathSimplifier', 'lib/$'], function( PathSimplifier ) { if (!PathSimplifier.supportCanvas) { console.log('The current environment does not support Canvas!') return } function onload() { that.pathSimplifierIns.renderLater() } function onerror() { console.log('Picture loading failed!') } // Historical track cruiser that.pathSimplifierIns = new PathSimplifier({ zIndex: 100, map: that.map, // Map instance to which getPath: function(pathData) { // The pathData here saves the route return pathData.path }, // Auto set view autoSetFitView: true, // Cruise style renderOptions: { // Path navigation style pathNavigatorStyle: { // Rotation angle of trolley at the beginning initRotateDegree: 0, // Width of trolley width: 20, // Height of trolley height: 32, // Automatic rotation autoRotate: true, // Polyline inflection point connection style lineJoin: 'round', // PathSimplifier provides a shortcut to create content (function) of picture content: // Picture address // The picture is loaded successfully. Redraw the onload method again // Picture loading failed. onerror method content: PathSimplifier.Render.Canvas.getImageContent( 'https://webapi.amap.com/images/car.png', onload, onerror ), // This position reminds us that we can't see the effect because we use pictures // To see the effect, delete the content above // It's a triangle. Here's how to set the border color and internal color // Fill color fillStyle: null, // Stroke color strokeStyle: null, // Width of edge lineWidth: 1, // The style of the path the cruiser passes through pathLinePassedStyle: { lineWidth: 6, strokeStyle: 'skyblue' } }, // Line style pathLineStyle: { lineWidth: 6, strokeStyle: 'pink' }, // The style of the line after the mouse is moved in pathLineHoverStyle: { lineWidth: 0, borderWidth: 0 }, // The style of the line after the mouse click pathLineSelectedStyle: { lineWidth: 6, borderWidth: 0, strokeStyle: 'blue' }, pathTolerance: 0, keyPointTolerance: -1, renderAllPointsIfNumberBelow: 0 // Draw the route node, which can be set to - 1 if not required } }) // Historical track cruiser setting data here is the data of pathData above that.pathSimplifierIns.setData([ { name: 'trajectory', path: that.pathList } ]) }) }
If you do this, the route can be displayed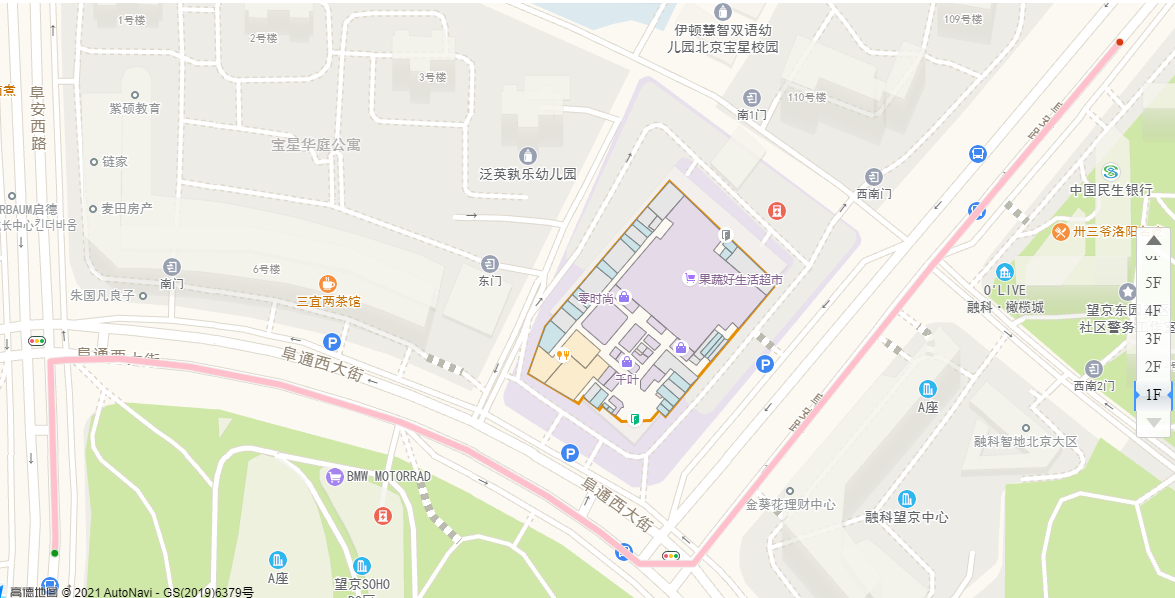
Create small icons
-
Data transferred from the background (it can be lost in data or imported into js)
// icon on the map passed from the background inco: [ { latitude: 39.997761, longitude: 116.478935 }, { latitude: 39.99856, longitude: 116.479282 }, { latitude: 39.999861, longitude: 116.484648 } ] -
Traverse to create icon
// initial init() { // Create start and pass icon s this.icon.forEach(item => { this.addIcon(item) }) }, addIcon(item) { // Set the content of each icon const marker = new AMap.Marker({ // picture icon: '//a.amap.com/jsapi_demos/static/demo-center/icons/poi-marker-default.png', // position position: [item.longitude, item.latitude], //Set base point offset offset: new AMap.Pixel(-13, -30) }) // Put the icon on the map marker.setMap(this.map) } -
Modify the style (if the icon is too large, you can modify the image f12 to check. If the setting fails, you need to consider a deeper scope)
// Set icon size /deep/.amap-icon img { width: 25px; height: 34px; }
After this step, the icon can be displayed
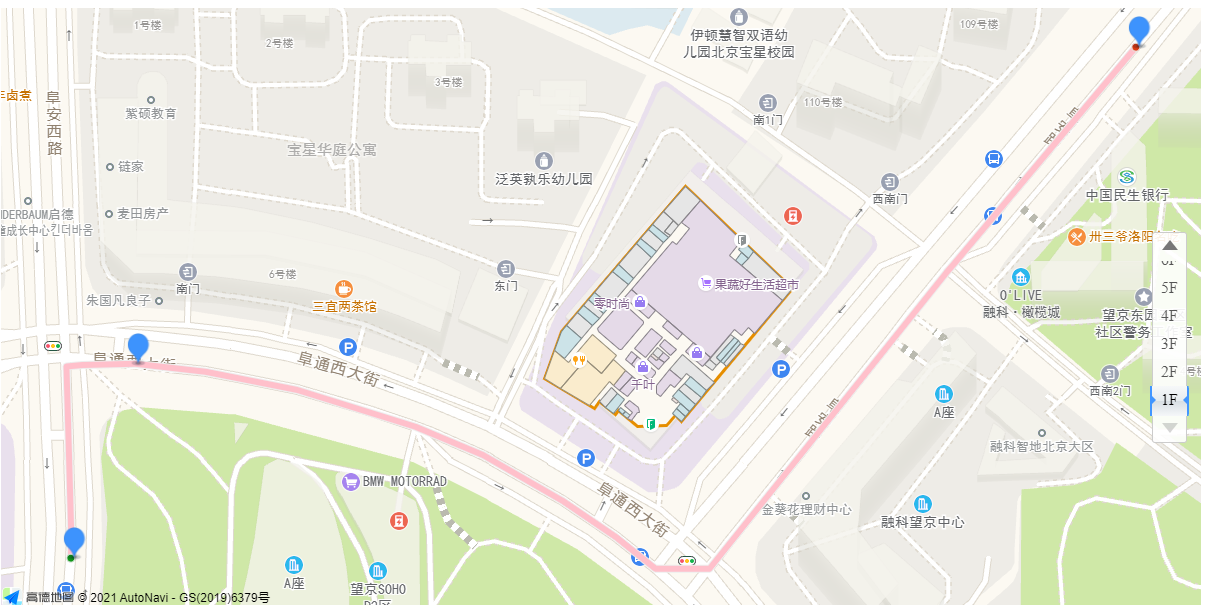
Create Cruise
Let's create a cruiser first, then study it, and then move it
- Set a cruise control in the data
// Cruiser navgtr: null
- setPath
// Turn on Center adaptation that.pathSimplifierIns.setFitView(-1) // Create a cruiser for the first line (i.e. index 0) that.navgtr = that.pathSimplifierIns.createPathNavigator(0, { loop: false // Loop Playback })
After this step, the car can be displayed
Add import progress bar
-
You can use iview here in any framework
- Installation dependency
- Import (main.js)
// Import Vue amap import AMap from 'vue-amap' // Import iview import iView from 'iview' // Register iview Vue.use(iView)
-
Code part
<!-- progress bar --> <div class="map-control"> <!-- Start button --> <Icon v-if="!start" class="play-icon" type="ios-play" @click="navgControl"/> <!-- Pause button --> <Icon v-else class="play-icon" type="ios-pause" @click="navgControl"/> <!-- start time --> <span class="passed-time">00:00:00</span> <Slider class="map-slider"></Slider> <!-- multiple --> <div class="map-times" @mouseenter="isTimesChoose=true" @mouseleave="isTimesChoose=false"> <div class="times-show">Double speed{{times}}</div> <div class="choose-box"> <!-- <ul v-show="isTimesChoose"> --> <ul v-show="isTimesChoose"> <li v-for="item in speedList" :key="item" :class="{active:times==item}" @click="changeSpeed(1)">Double speed {{item}}</li> </ul> </div> </div>> <!-- end --> <span class="passed-time">00:00:00</span> </div>// Set icon size /deep/.amap-icon img { width: 25px; height: 34px; } // Set circulator style .map-control { // Absolute positioning position: absolute; bottom: 0; left: 0; width: 1200px; height: 80px; line-height: 80px; color: #fff; background-image: linear-gradient(to top, rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7), transparent); padding: 0 40px; z-index: 1000; // Set button size .play-icon { font-size: 36px; } // Set time style .passed-time { // Relative positioning position: relative; // Convert to inline element display: inline-block; top: 1px; margin-left: 15px; font-size: 14px; } // Progress bar style .map-slider { // Convert to inline element display: inline-block; width: 75%; margin-left: 15px; position: relative; top: 14px; } // Modify the default progress bar style .choose-box { // Relative positioning position: absolute; top: -135px; left: -6px; height: 162px; // filter transition: all 0.5s linear; } // multiple .map-times { display: inline-block; position: relative; margin-left: 15px; // Double speed style .times-show { padding: 0 10px; line-height: 24px; font-size: 13px; border: 1px solid #fff; border-radius: 4px; // Set the mouse to the default style cursor: default; } // multiple ul { background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7); padding: 10px; width: 70px; text-align: center; border-radius: 3px; li { height: 26px; line-height: 26px; cursor: pointer; } li.active { color: #ff8533; } li:hover { font-size: 13px; } } } }// Pause and play buttons navgControl() { this.start = !this.start }, // progress bar changeSpeed(item) { this.times = item }

Calculate speed and playback time
-
We need to convert the time passed to us by the background into a timestamp
-
2020-08-21 16:21:18 — 1597998078000
-
Continue coding in init
linePath.forEach(item => { // Convert json to array this.pathList.push([item.longitude, item.latitude]) // Current timestamp item.stampTime = new Date(item.time).getTime() })
-
-
We need to calculate the speed of each distance. Here, let's assume that the length of the array is x, and there are a, b, c
-
We need to calculate the speed, time and distance of a-b, and so on
-
The time and distance have given us, but the speed is poor. This primary school problem is not explained. Go to the code
-
Calculate the direct distance of 2 points, which is inconvenient to extract in for
// Calculate the distance between two coordinate points distanceFun(point1, point2) { // That array is converted to latitude and longitude let p1 = new AMap.LngLat(point1[0], point1[1]) let p2 = new AMap.LngLat(point2[0], point2[1]) // Calculate the direct distance distance of 2 points. This function continues. You can learn about it let distance = Math.round(p1.distance(p2)) return distance } -
Calculate the 2-point direct velocity
- Calculate how many s the next journey takes,
- intervalTime interval seconds
- nextDistance: next distance: m,
- nextDistance: next section speed: km/h
linePath.forEach((item, i) => { // Get to the next location let next = linePath[i + 1] // Determine if there is another one if (next) { // Calculate the interval per second item.intervalTime = (next.stampTime - item.stampTime) / 1000 // Calculate the next station item.nextDistance = this.distanceFun( [item.longitude, item.latitude], [next.longitude, next.latitude] ) // Find the specific speed item.nextSpeed = item.nextDistance / 1000 / (item.intervalTime / 60 / 60) } }) -
Calculate the total time (because it's too simple, let's just say it here)
// Calculate the total time. hh:mm:ss because the calculated time is time, format it this.totalTime = this.getTime( (endPoint.stampTime - startPoint.stampTime) / 1000 ) // Format time (not explained) getTime(sTime) { let ss let mm = '00' let hh = '00' if (sTime > 60) { let s = sTime % 60 ss = s > 9 ? s : '0' + s let mTime = parseInt(sTime / 60) if (mTime > 60) { let m = mTime % 60 mm = m > 9 ? m : '0' + m hh = parseInt(mTime / 60) } else { mm = mTime > 9 ? mTime : '0' + mTime } } else { ss = sTime > 9 ? sTime : '0' + sTime } return hh + ':' + mm + ':' + ss }- Add in date
// Total time totalTime: '00:00:00',
- Total time to modify pages
<span class="passed-time">{{totalTime}}</span>
- Add in date
-
Slider change event
Bind sliding event to sliding bar
<Slider class="map-slider" @on-input="sliderChange"></Slider>
// Slider change event
sliderChange(val) {
// Calculate start distance
let num = parseInt((val / 100) * this.pathList.length)
// Distance to end of calculation
let decimal =
String((val / 100) * this.pathList.length).split('.')[1] || 0
// Mobile trolley
this.navgtr.moveToPoint(num, Number('0.' + decimal))
// Redraw
this.pathSimplifierIns.renderLater()
},
After completion, move the slider to change the trolley position
Set the status in the move
-
We need to get an open speed, two ways
- Calculate the initial speed
- Get the speed of array 0 directly
-
We adopt scheme 2. First, set the previously traversed data into data
// Add this line to the init method // Modify global alignment data this.linePath = linePath
-
Write it in setPath to obtain the starting speed and set the starting speed for the cruiser
// Get initial speed // Set the default to 0.1 let startSpeed = 0.1 if (that.linePath.length !== 0) { // Get the initial speed and judge whether it is 0. If it is not 0, return to 0 directly to give an initial speed startSpeed = that.linePath[0].nextSpeed === 0 ? 0.1 : that.linePath[0].nextSpeed } // Create a cruiser for the first line (i.e. index 0) that.navgtr = that.pathSimplifierIns.createPathNavigator(0, { loop: false, // Loop Playback // speed × Double speed speed: startSpeed * that.times }) -
Calculate the start time and end time. The original presentation is written in setPath
let linePath = that.linePath let len = linePath.length let startPoint = linePath[0] let endPoint = linePath[len - 1]
-
Write move status
-
Modify the style of the slider and start time
<!-- The start time is set to 00 as the elapsed time, which can no longer be fixed--> <span class="passed-time">{{passedTime}}</span> <!-- Slider modified 2 places step step tip-forma prompt box --> <Slider class="map-slider" @on-input="sliderChange" :step="0.0001" :tip-format="hideFormat"></Slider>// Tips for slider hideFormat() { return this.passedTime } -
Move status
// During movement that.navgtr.on('move', function() { // What point did you reach let idx = this.getCursor().idx // Proportional position to next node let tail = this.getCursor().tail // Total distance let totalIdx = idx + tail // Calculate next distance speed let point = linePath[idx] if (idx < len - 1) { // Judge whether the speed is 0. If it is 0, give a speed of 0.1 point.nextSpeed === 0 && (point.nextSpeed = 0.1) // The speed here, remember × multiple that.navgtr.setSpeed(point.nextSpeed * that.times) } // The remaining kilometers are displayed on the form at any time // Determine whether there is another point and time point && point.time && infoWindow.setContent( `<p class="info-window">Time:<span>${point.time}` ) // Set prompt box infoWindow.open(that.map, that.navgtr.getPosition()) // Real time display of progress bar !that.isOnSlider && (that.sliderVal = (totalIdx / len) * 100) // Played time let sTime = parseInt( (((endPoint.stampTime - startPoint.stampTime) / 1000) * that.sliderVal) / 100 ) // Format time that.passedTime = that.getTime(sTime) // If it's over, go back to the initial state if (that.navgtr.isCursorAtPathEnd()) { // Set as pause button that.start = false that.passedTime = that.totalTime } })
-
Trolley movement
-
First of all, we can learn about the events of the car
- resume (colors that have passed will not be drawn)
- Pause pause
- start here will return to the original position
-
So according to this, we should have a clear idea
- If the start button is set to start, you will return to the original position when you restart
- Therefore, it is best to set resume during the move process
- Pause after pause, you can only use resume to continue
- So our idea is to set start after the journey
-
Modify start button
<!-- Start button --> <Icon v-if="!start" class="play-icon" type="ios-play" @click="navgControl(playIcon)"/>
-
Modify pause button
<!-- Pause button --> <Icon v-else class="play-icon" type="ios-pause" @click="navgControl('pause')"/> -
Set the initial data of playIcon
-
playIcon: 'start' //Start button is to restart or continue
-
-
Modify the end of the path code in setpath
// If it's over, go back to the initial state if (that.navgtr.isCursorAtPathEnd()) { // Set it to the start state to return the trolley to its original position that.playIcon = 'start' // Set icon status that.start = false // Set elapsed time that.passedTime = that.totalTime // Set slider status that.sliderVal = 100 } -
Pause start button
// Pause and play buttons navgControl(action) { if (action === 'start') { let that = this this.passedTime = '00:00:00' setTimeout(() => { that.navgtr[action]() }, 300) } else { this.navgtr[action]() } // Modify icon status this.start = !this.start }, -
Settings are also required during movement
// During movement that.navgtr.on('move', function() { that.playIcon = 'resume' //........................ -
Set slider (forgot to design before)
-
Bind data to slider v-model = "sliderVal"
<Slider class="map-slider" v-model="sliderVal" @on-input="sliderChange" :step="0.0001" :tip-format="hideFormat"></Slider> ```
-
-
Then I found that the speed of modification is not good...... It turned out that I passed 1 when I passed the value... (pay attention when setting the code)
-
changeSpeed(item) remember it's item here
<li v-for="item in speedList" :key="item" :class="{active:times==item}" @click="changeSpeed(item)">Double speed {{item}}</li> ``` -
Then I found... ul also forgot to set it to false
// Modification speed changeSpeed(item) { this.times = item this.isTimesChoose = false },
-