Since most SIP registry server writings on the web are C/C++/python, post this post and share the JAVA implementation
GB28181 defines the SIP-based video monitoring interconnection specification. For most private protocol-implemented monitoring systems, if they want to access the SIP architecture, they need to use the gateway. GB28181 specifies the interconnection between SIP monitoring domain and non-SIP monitoring domain.
The following are some of the questions that I have summarized in my practical use:
1. When the client connects for the first time, the client will continue to send REGISTER messages to the Server until the Server replies to "200 OK";
2. The registration process of GB28181 involves user certification, so it is relatively complex, but it is also a highlight of security communication security;
Its registration process is as follows:
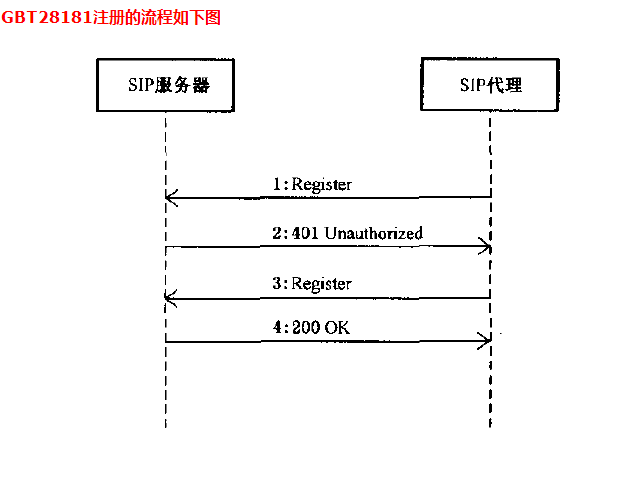
With the package capture tool, as shown in the following figure
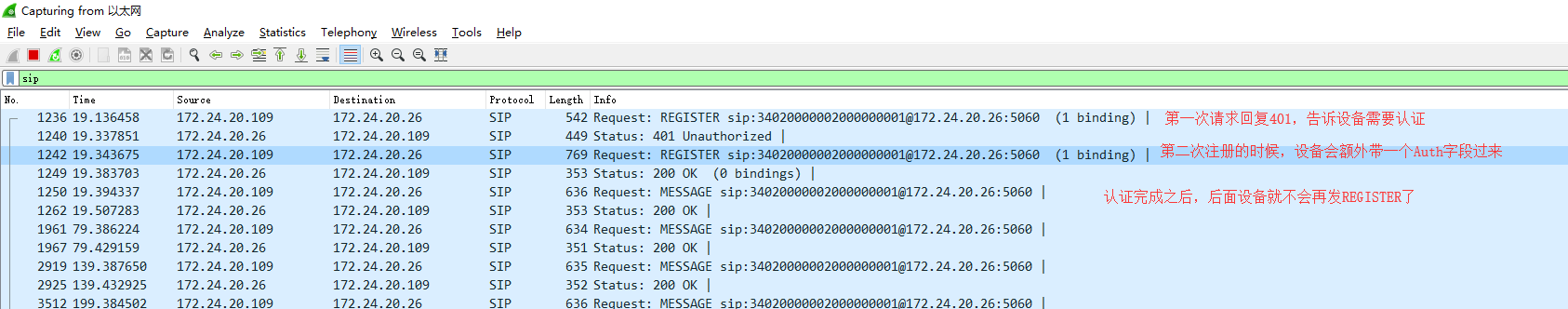
Registration process:
1. Clients send Register messages to the server indefinitely:
Here the Reister message sent by the client at the beginning is the simplest message
2. When the server receives a message, it sends back a 401 message "Unauthorized" and adds the following fields to the message header:
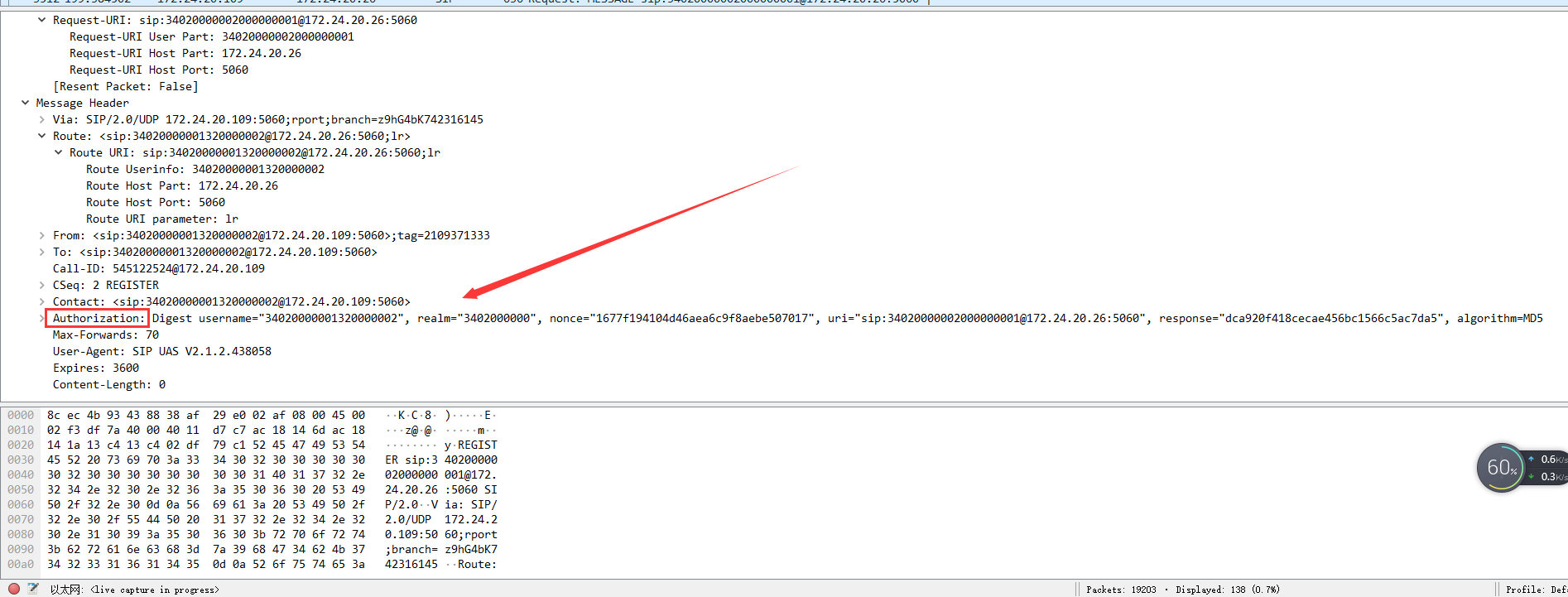
As shown below, this is the REGISTER message sent again by the client after receiving 401-Unauthorized with the Auth field that was not present in the first REGISTER message:
The full 401 reply is as follows (captured by the package grabber Wireshark):
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 172.24.20.109:5060;rport=5060;received=172.24.20.109;branch=z9hG4bK352707374 From: <sip:34020000001320000002@172.24.20.109:5060>;tag=2109371333 To: <sip:34020000001320000002@172.24.20.109:5060>;tag=888 Call-ID: 545122524@172.24.20.109 CSeq: 1 REGISTER WWW-Authenticate: Digest realm="3402000000",nonce="1677f194104d46aea6c9f8aebe507017" Content-Length: 0
The second REGISTER, the report with the Auth field attached:
ìKC8¯)à¯Eóßz@@×Ǭm¬ÄÄßyÁREGISTER sip:34020000002000000001@172.24.20.26:5060 SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 172.24.20.109:5060;rport;branch=z9hG4bK742316145 Route: <sip:34020000001320000002@172.24.20.26:5060;lr> From: <sip:34020000001320000002@172.24.20.109:5060>;tag=2109371333 To: <sip:34020000001320000002@172.24.20.109:5060> Call-ID: 545122524@172.24.20.109 CSeq: 2 REGISTER Contact: <sip:34020000001320000002@172.24.20.109:5060> Authorization: Digest username="34020000001320000002", realm="3402000000", nonce="1677f194104d46aea6c9f8aebe507017", uri="sip:34020000002000000001@172.24.20.26:5060", response="dca920f418cecae456bc1566c5ac7da5", algorithm=MD5 Max-Forwards: 70 User-Agent: SIP UAS V2.1.2.438058 Expires: 3600 Content-Length: 0
The validation algorithm is as follows:
HA1=MD5 (username:realm:passwd)#username and realm can be found in the field "Authorization". Passwd is a password negotiated between client and server. Usually UAC stores a password that UAS also knows.
HA2=MD5(Method:Uri) #Method generally has INVITE, ACK, OPTIONS, BYE, CANCEL, REGISTER; Uri can be found in the field "Authorization"
response = MD5(HA1:nonce:HA2)
Source of algorithm: http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2069 [Page 6]
JAVA implementation of key authentication algorithms (note that colons are required):
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String ha1 = md5("34020000001320000002" + ":" + "3402000000" + ":" + "admin123", ""); //HA1=MD5(username:realm:passwd) String ha2 = md5("REGISTER" + ":" + "sip:34020000002000000001@172.24.20.26:5060", ""); //HA2=MD5(Method:Uri) String response = ha1 + ":" + "326d59f91b6e448fa461fcacd9161abe" + ":" + ha2; System.out.println("MD5 The encrypted string is:encodeStr="+md5(response, "")); }
MD5 Tool Class
import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.DigestUtils; public class MD5Utils { /** * MD5 Method * * @param text Clear text * @param key secret key * @return ciphertext * @throws Exception */ public static String md5(String text, String key) { //Encrypted string String encodeStr=DigestUtils.md5Hex(text + key); return encodeStr; } /** * MD5 Validation Method * * @param text Clear text * @param key secret key * @param md5 ciphertext * @return true/false * @throws Exception */ public static boolean verify(String text, String key, String md5) throws Exception { //Verify against the incoming key String md5Text = md5(text, key); if(md5Text.equalsIgnoreCase(md5)) { System.out.println("MD5 Verification Passed"); return true; } return false; } }
The final run process is as follows:

Register Server Core Code:
import java.text.ParseException; import java.util.TooManyListenersException; import javax.sip.InvalidArgumentException; import javax.sip.ObjectInUseException; import javax.sip.PeerUnavailableException; import javax.sip.SipException; import javax.sip.TransportNotSupportedException; import org.apache.commons.lang.exception.ExceptionUtils; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; public class SIPMain { protected Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SIPMain.class); public void run() { //User name, IP address, port try { int port = 5060; SipLayer sipLayer = new SipLayer("admin" , "172.24.20.26" , port); //local //SipLayer sipLayer = new SipLayer("admin","xx.xx.xx.xx",port); //IP VECS01532 on Ali cloud sipLayer.setMessageProcessor(new MessageProcessorImpl()); System.out.println("Service Start Completed, Already in"+port+"Port Listening Messages\n\n"); } catch (PeerUnavailableException e) { e.printStackTrace(); logger.error(ExceptionUtils.getFullStackTrace(e)); } catch (TransportNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); logger.error(ExceptionUtils.getFullStackTrace(e)); } catch (ObjectInUseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); logger.error(ExceptionUtils.getFullStackTrace(e)); } catch (InvalidArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); logger.error(ExceptionUtils.getFullStackTrace(e)); } catch (TooManyListenersException e) { e.printStackTrace(); logger.error(ExceptionUtils.getFullStackTrace(e)); } } /** * This method is temporarily unavailable and currently there is no business scenario where the system needs to actively send messages to SIP terminal devices * @throws InvalidArgumentException * @throws TooManyListenersException * @throws ParseException * @throws SipException */ public void sendMsg() throws InvalidArgumentException, TooManyListenersException, ParseException, SipException{ SipLayer sipLayer = new SipLayer("admin","127.0.0.1",5060); sipLayer.sendMessage(sipLayer.getUsername(), sipLayer.getHost(), "test message"); } }
SipLayer.java code:
import java.text.ParseException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.TooManyListenersException; import javax.sip.DialogTerminatedEvent; import javax.sip.IOExceptionEvent; import javax.sip.InvalidArgumentException; import javax.sip.ListeningPoint; import javax.sip.ObjectInUseException; import javax.sip.PeerUnavailableException; import javax.sip.RequestEvent; import javax.sip.ResponseEvent; import javax.sip.SipException; import javax.sip.SipFactory; import javax.sip.SipListener; import javax.sip.SipProvider; import javax.sip.SipStack; import javax.sip.TimeoutEvent; import javax.sip.TransactionTerminatedEvent; import javax.sip.TransportNotSupportedException; import javax.sip.address.Address; import javax.sip.address.AddressFactory; import javax.sip.address.SipURI; import javax.sip.header.CSeqHeader; import javax.sip.header.CallIdHeader; import javax.sip.header.ContactHeader; import javax.sip.header.ContentTypeHeader; import javax.sip.header.FromHeader; import javax.sip.header.HeaderFactory; import javax.sip.header.MaxForwardsHeader; import javax.sip.header.ToHeader; import javax.sip.header.ViaHeader; import javax.sip.message.MessageFactory; import javax.sip.message.Request; import javax.sip.message.Response; public class SipLayer implements SipListener { private MessageProcessor messageProcessor; private String username; private SipStack sipStack; private SipFactory sipFactory; private AddressFactory addressFactory; private HeaderFactory headerFactory; private MessageFactory messageFactory; private SipProvider sipProvider; /** Here we initialize the SIP stack. */ @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public SipLayer(String username, String ip, int port) throws PeerUnavailableException, TransportNotSupportedException, InvalidArgumentException, ObjectInUseException, TooManyListenersException { setUsername(username); sipFactory = SipFactory.getInstance(); sipFactory.setPathName("gov.nist"); Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty("javax.sip.STACK_NAME", "cameraReg"); properties.setProperty("javax.sip.IP_ADDRESS", ip); /** * sip_server_log.log And sip_debug_log.log * public static final int TRACE_NONE = 0; public static final int TRACE_MESSAGES = 16; public static final int TRACE_EXCEPTION = 17; public static final int TRACE_DEBUG = 32; */ properties.setProperty("gov.nist.javax.sip.TRACE_LEVEL", "16"); properties.setProperty("gov.nist.javax.sip.SERVER_LOG", "sip_server_log"); properties.setProperty("gov.nist.javax.sip.DEBUG_LOG", "sip_debug_log"); sipStack = sipFactory.createSipStack(properties); headerFactory = sipFactory.createHeaderFactory(); addressFactory = sipFactory.createAddressFactory(); messageFactory = sipFactory.createMessageFactory(); ListeningPoint tcp = sipStack.createListeningPoint(port, "tcp"); ListeningPoint udp = sipStack.createListeningPoint(port, "udp"); sipProvider = sipStack.createSipProvider(tcp); sipProvider.addSipListener(this); sipProvider = sipStack.createSipProvider(udp); sipProvider.addSipListener(this); } /** * This method uses the SIP stack to send a message. First parameter: User name Second parameter: IP address * Third parameter: message content */ public void sendMessage(String username, String address, String message) throws ParseException, InvalidArgumentException, SipException { SipURI from = addressFactory.createSipURI(getUsername(), getHost() + ":" + getPort()); Address fromNameAddress = addressFactory.createAddress(from); fromNameAddress.setDisplayName(getUsername()); FromHeader fromHeader = headerFactory.createFromHeader(fromNameAddress, "cameraReg1.0"); SipURI toAddress = addressFactory.createSipURI(username, address); Address toNameAddress = addressFactory.createAddress(toAddress); toNameAddress.setDisplayName(username); ToHeader toHeader = headerFactory.createToHeader(toNameAddress, null); SipURI requestURI = addressFactory.createSipURI(username, address); requestURI.setTransportParam("udp"); ArrayList<ViaHeader> viaHeaders = new ArrayList<ViaHeader>(); ViaHeader viaHeader = headerFactory.createViaHeader(getHost(), getPort(), "udp", "branch1"); viaHeaders.add(viaHeader); CallIdHeader callIdHeader = sipProvider.getNewCallId(); @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") CSeqHeader cSeqHeader = headerFactory.createCSeqHeader(1, Request.MESSAGE); MaxForwardsHeader maxForwards = headerFactory.createMaxForwardsHeader(70); Request request = messageFactory.createRequest(requestURI, Request.MESSAGE, callIdHeader, cSeqHeader, fromHeader, toHeader, viaHeaders, maxForwards); SipURI contactURI = addressFactory.createSipURI(getUsername(), getHost()); contactURI.setPort(getPort()); Address contactAddress = addressFactory.createAddress(contactURI); contactAddress.setDisplayName(getUsername()); ContactHeader contactHeader = headerFactory.createContactHeader(contactAddress); request.addHeader(contactHeader); ContentTypeHeader contentTypeHeader = headerFactory.createContentTypeHeader("text", "plain"); request.setContent(message, contentTypeHeader); sipProvider.sendRequest(request); } /** This method is called by the SIP stack when a response arrives. */ public void processResponse(ResponseEvent evt) { Response response = evt.getResponse(); int status = response.getStatusCode(); if ((status >= 200) && (status < 300)) { // Success! messageProcessor.processInfo("--Sent"); return; } messageProcessor.processError("Previous message not sent: " + status); } /** * SIP How the server receives messages * Content GBK encoding inside * This method is called by the SIP stack when a new request arrives. */ public void processRequest(RequestEvent evt) { Request req = evt.getRequest(); messageProcessor.processMessage(req,messageFactory,sipProvider); } /** * This method is called by the SIP stack when there's no answer to a * message. Note that this is treated differently from an error message. */ public void processTimeout(TimeoutEvent evt) { messageProcessor.processError("Previous message not sent: " + "timeout"); } /** * This method is called by the SIP stack when there's an asynchronous * message transmission error. */ public void processIOException(IOExceptionEvent evt) { messageProcessor.processError("Previous message not sent: " + "I/O Exception"); } /** * This method is called by the SIP stack when a dialog (session) ends. */ public void processDialogTerminated(DialogTerminatedEvent evt) { } /** * This method is called by the SIP stack when a transaction ends. */ public void processTransactionTerminated(TransactionTerminatedEvent evt) { } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public String getHost() { String host = sipStack.getIPAddress(); return host; } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public int getPort() { int port = sipProvider.getListeningPoint().getPort(); return port; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String newUsername) { username = newUsername; } public MessageProcessor getMessageProcessor() { return messageProcessor; } public void setMessageProcessor(MessageProcessor newMessageProcessor) { messageProcessor = newMessageProcessor; } }
MessageProcessor interface:
import javax.sip.SipProvider; import javax.sip.message.MessageFactory; import javax.sip.message.Request; /** * Message Processing Callback Function Interface */ public interface MessageProcessor { /** * Callback function generated when receiving SIP protocol messages from IPCamera */ public void processMessage(Request req,MessageFactory messageFactory, SipProvider sipProvider); public void processError(String errorMessage); public void processInfo(String infoMessage); }
The MessageProcessor implementation class is not given here because it contains many of the company's SIP registration details
One thing to note is that you need to install a decompile tool to read the properties and methods in the Request source code to get the contents of the SIP message
For example, get the sender and method fields that I want to get
FromHeader fromHeader = (FromHeader) req.getHeader("From"); String sender = fromHeader.getAddress().toString(); String method = req.getMethod();
For example, I want to get the Contact field
Contact contact = (Contact) req.getHeader("Contact");
Similarly, the key is to go in through the eclipse point and see the source code for this Request
Finally, the MAVEN POM dependency of the JAVA SIP protocol is given:
<!-- SPI Agreement related packages --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.sip</groupId> <artifactId>jain-sip-api</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.sip</groupId> <artifactId>jain-sip-ri</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency>