Starting at: Getting started with java | operator
java entry series, from scratch!!!
operator
1. Overview
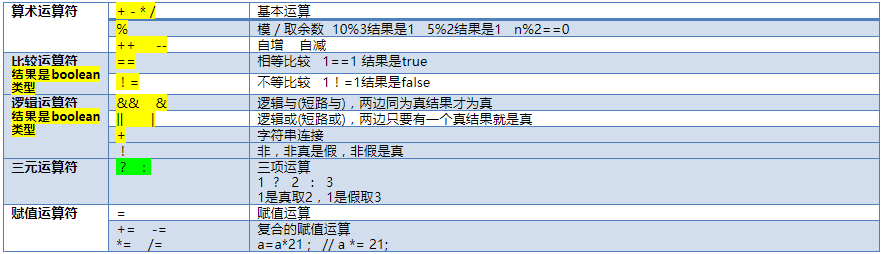
Logical operator: the result is a boolean type
&-- yes and (single and)
1 & 2 want to get the final result to be true, the requirement for 1 and 2 is: both must be true
&&-- yes and (double and / short circuit and)
1 & & 2, efficient, when the result of 1 is false, 2 will be short circuited
|-- yes or
1 | 2 if you want the final result to be true, the requirements for 1 and 2 are: 1 or 2 can be true
||-- yes or (double or / short or)
1 | 2, efficient, when the result of 1 is true, 2 will be short circuited
2. Exercise 1: leap year
Enter the year number to determine if it is a leap year.
Two conditions:
1. Divisible by 4, and not divisible by 100
2. Divisible by 400
package cn.qile.basic; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test4_RunNian { public static void main(String[] args) { //1. Receive the year number entered by the user System.out.print("Please enter the year:"); int year = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); //2. Judge whether year is a normal year or a leap year String desc = "Weekday";//Set the default value as the year of the year //If (judging condition) {code satisfying the condition} // 1. Divisible by 4, and not divisible by 100 if (year % 4 == 0) { //Divisible by 4 if (year % 100 != 0) { //Cannot be divisible by 100 desc = "leap year"; //Change desc to leap year } } // 2. Divisible by 400 if (year % 400 == 0) { desc = "leap year"; //Change desc to leap year } // System.out.println("2000 is a leap year"); //+Concatenate string System.out.println(year + "Year is" + desc); } }
Simplified code
Through the relationship of | - yes or (double or / short or)
-- 1 | 2, efficient, when the result of 1 is true, 2 will be short circuited
//If ((small judgment condition 1 & & small judgment condition 2) | big judgment condition 2) {change desc value to leap year} if(( year%4==0 && year%100 != 0 ) || year%400 == 0 ){ desc="leap year"; }
3. Exercise 2: increase and decrease
package cn.qile.basic; //Test auto increment + + auto decrement-- public class Test5_ZiZeng { public static void main(String[] args) { //Symbol before, change before use //Symbols are used first and then changed int a = 1; System.out.println(a++);//1 int b = 1; System.out.println(++b);//2 System.out.println(++b+a+b++);//8,3+2+3 //TODO self reduction int m = 1; System.out.println(m--);//1 int n = 1; System.out.println(--n);//0 System.out.println(--m-n-m--);//0,-1-0-(-1) } }
4. Ternary operation
package cn.qile.basic; import java.util.Scanner; //Ternary operator public class Test6_Max { public static void main(String[] args) { //The big value of two numbers int a = 10; int b = 6; //Three yuan 1? 2: 3 //The final result is 2 or 3. It depends on the result of 1. If 1 is established, 2 will be obtained. If 1 is not established, 3 will be obtained int max = a > b ? a : b ; System.out.println(max); //Receive the three numbers entered by the keyboard, and take out the maximum value System.out.print("Please enter m ="); int m = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.print("Please enter n ="); int n = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.print("Please enter o ="); int o = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); //1. Define the maximum value of variable record, take the ratio of m and n, and submit the result to the variable for saving int result = m > n ? m : n; //2. Take the ratio of result and o, and the maximum value will be given to maxValue for saving // result = result > o ? result : o ; int maxValue = result > o ? result : o ; System.out.println(maxValue); //TODO optimization //Take the ratio of m to n? The ratio of m to o: the ratio of n to o int result2 = m > n ? (m > o ? m : o ) : (n > o ? n : o ); System.out.println(result2); } }