Single line notes #;
For multiline comments Multiple # numbers' '' 'and' '' ';
python doesn't need parentheses, but pay attention to indentation and the use of spaces (it's best to separate every operator with spaces)
There are two ways to index characters: start with 0 from left to right and - 1 from right to left.
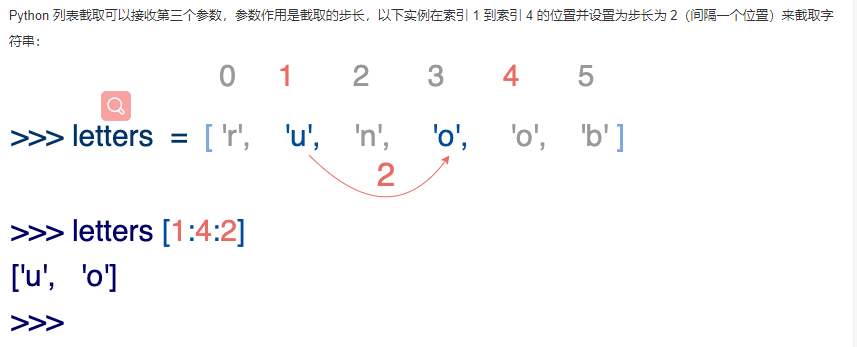
String interception method: Variable [head subscript: tail subscript: step size] What is not written represents the end or the end
+Is the connector of a string * Copy current string
When there are escape characters in the content to be output Add r before to represent the original string
>>> print('\n') # Output blank line
>>> print(r'\n') # Output \ nRead a value input() from the keyboard
x = input("Please enter a value:")
print(x)
Please enter a value:5
5Use when there are multiple python statements on a line; separate
print will wrap automatically Add end = "" "" at the end of the variable No line breaks can be realized End can be replaced with the desired operation
sep="" Settable spacer
File -- file object to write
print("I won't wrap", end="")
print("I", "can't", "Line feed")
print("I", "can't", "Line feed", sep=".")
print("Backspace", end="\b")
output:
I won't wrap. I won't wrap
I.can't.Line feed
retreat
import and from import module or function
Import the whole module in the format: import somemodule
Import a function from a module in the following format: from somemodule import somefunction
Import multiple functions from a module in the following format: from somemodule import firstfunc, secondfunc, thirdfunc
Import all functions in a module in the following format: from somemodule import *
multiline comment
a = b = c = 1 a, b, c = 1, 2, "char"
type(a) You can view the object type of variable a
x = 2.11 print(type(x)) <class 'float'>
isinstance(a,int) Judge whether a is of type int (bool belongs to int)
del x Delete x object
del x,y,z Delete the three objects x, y and Z
x / y Divide to get a floating point number
x // y Divide to get an integer
x % y Division remainder
x ** y Power
x = 7; y = 2 print(x/y) print(x // y) print(x ** y) 3.5 3 49
A list is similar to a numeric value, but its elements support multiple types
list = [ 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'runoob', 70.2 ]
+No. connection list * Copy list
If the third parameter is selected, the value is reversed
Tuples are similar to lists But its elements cannot be modified (can be spliced with +) You can also index
tuple = ( 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'runoob', 70.2 )
tp = (0,) # an element, you need to add a comma after the element
Set Used to test membership and delete duplicate elements
sites = {'Google', 'Taobao', 'Runoob', 'Facebook', 'Zhihu', 'Baidu', 'Runoob'}
# Output auto delete duplicate elements
{'Runoob', 'Facebook', 'Baidu', 'Zhihu', 'Taobao', 'Google'}Creating an empty collection must use (), not {} Such as sites()
# Member test
if 'Runoob' in sites :
print('Runoob In collection')
else :
print('Runoob Not in collection')
# Set can perform set operations
a = set('abracadabra')
b = set('alacazam')
print(a)
print(a - b) # Difference sets of a and b
print(a | b) # Union of a and b
print(a & b) # Intersection of a and b
print(a ^ b) # Elements in a and b that do not exist at the same time
Dictionary Read by key
Mark with {} Is a disordered Keys: Values Collection of
dictionary = {'one': 'aggregate', 'two': 'list', 'three': 'tuple', 'four': 'Dictionaries'}
print(dictionary) # Output full dictionary
print(dictionary['one'], dictionary['two'])
print(dictionary.keys()) # Output all keys
print(dictionary.values()) # Output all values
#output
{'one': 'aggregate', 'two': 'list', 'three': 'tuple', 'four': 'Dictionaries'}
Collection list
dict_keys(['one', 'two', 'three', 'four'])
dict_values(['aggregate', 'list', 'tuple', 'Dictionaries'])Create an empty dictionary with {} Such as dictionary {}
Dictionary keywords cannot be duplicate and must be of immutable type
About functions of type conversion
| int(x [.base]) | Convert x to an integer |
| float(x) | Convert x to an integer |
| complex(real [, imag]) | Create a complex number |
| str(x) | Will object × Convert to string |
| repr(x) | Will object × Convert to expression string |
| eval(str) | Used to evaluate a valid Python expression in a string and return an object |
| tuple(s) | Convert sequence s to a tuple |
| list(s) | Convert sequence s to a list |
| set(s) | Convert to variable set |
| dict(d) | Create a dictionary. d must be a (key, value) tuple sequence. |
| frozenset(s) | Convert to immutable set |
| chr(x) | Converts an integer to a character |
| ord(x) | Converts a character to its integer value |
| hex(x) | Converts an integer to a hexadecimal string |
| oct(x) | Converts an integer to an octal string |