The most detailed installation tutorial in history
The above tutorials are for extended learning. In fact, they can be installed completely by default; We explain the configuration process in detail
Configure git environment: git config --global
- config: the parameter is used to configure the git environment
- global: long command means to configure the whole git environment
When using git for the first time, you need to set your user name and mailbox, which will be used as the identification of GIT of the current machine. If you use it to download remote warehouses, some warehouses that need login permission will require login. Git logs in by default using the configured mailbox and user name, but will require you to enter the password manually. The user will record the user name and mailbox every time he submits the code
User configuration
- User represents the user
- . Name represents the name of the configuration user
- . email represents the mailbox of the configuration user
Note: username and email should be consistent with those of github, gitlab (or other similar remote warehouses).
#Set user name and password git config --global user.name "Your username" git config --global user.email Your mailbox (no need for double quotes)
#View user name and password git config user.name git config user.email
Note: if you need to modify, repeat the above command, that is, modify in the form of overwrite without configuration. However, when you encounter a remote warehouse requiring login permission, you will be asked to manually enter the user name, mailbox and password. After configuration, it will be displayed in the directory
View other configuration information (git settings list)
git config --list
It can be seen that the configuration has been successful
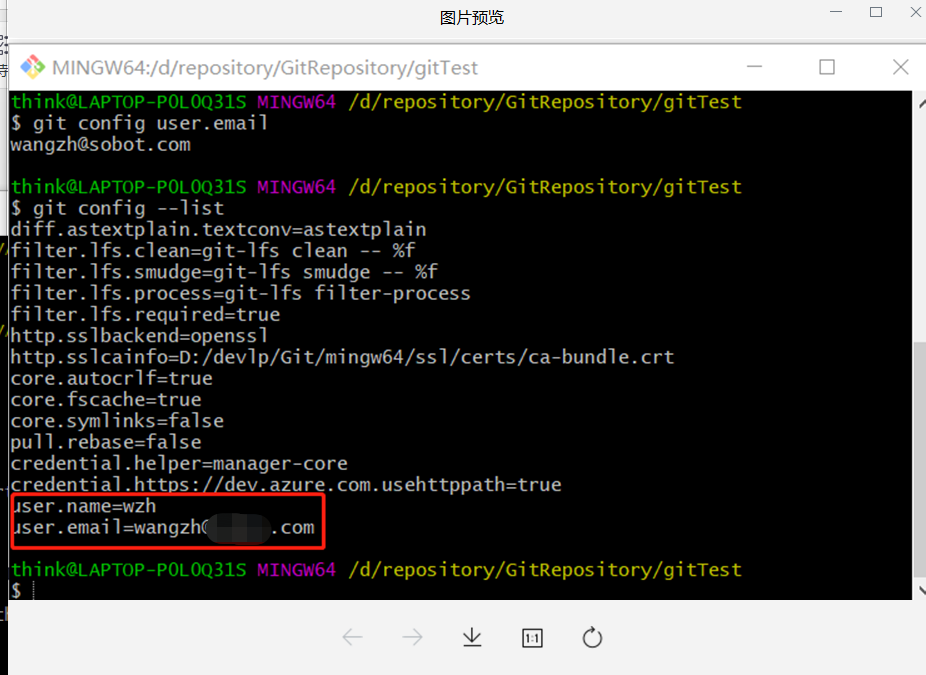
– global means global, that is, the current user is valid. The configuration will appear in ~ / In the gitconfig file, ~ indicates the directory of the current user. For example, mine is
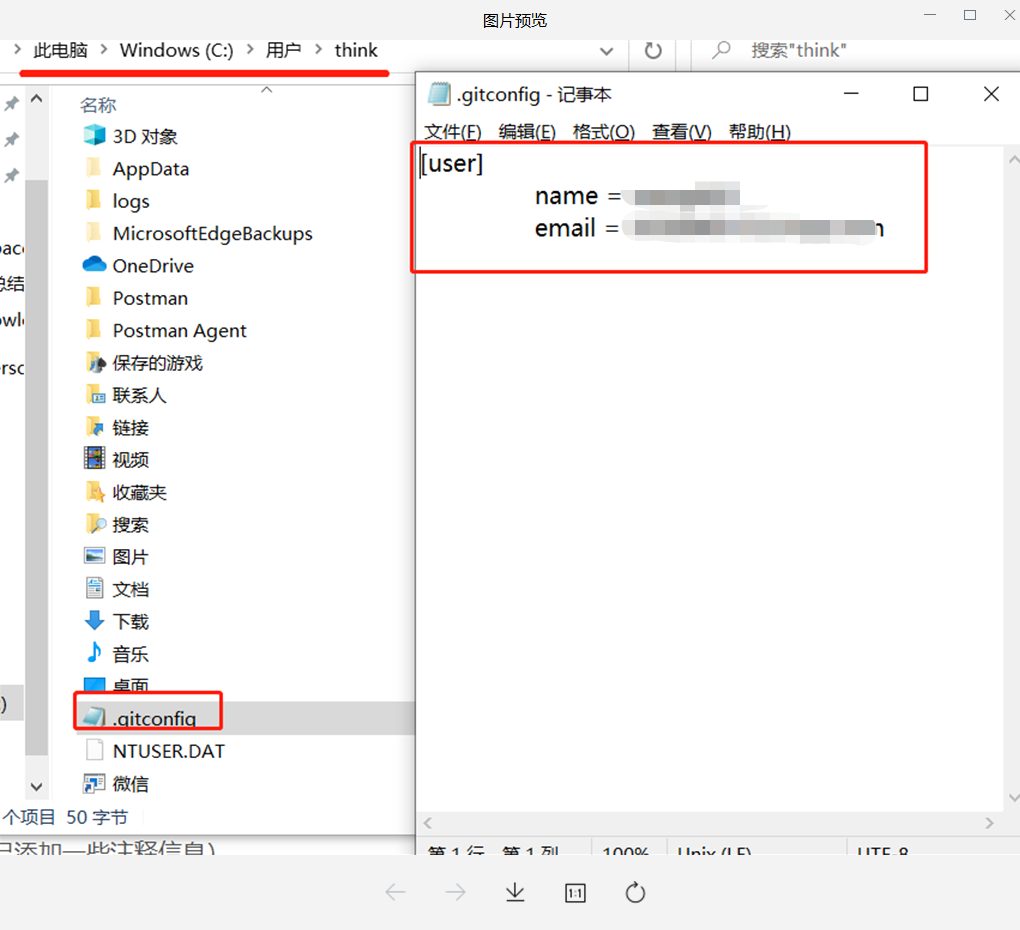
Since there is an overall situation, there must be a local one! Local is not added -- global. Local is only effective for the current warehouse. Its configuration information will be in the root directory of the current warehouse / git/config file
Note: local variables override global variables! It is the same as the variable relationship in the programming language. After installing git, you must configure git at the global level. Later, you need to do local configuration or system level configuration. We divide the levels according to the scope of GIT
-
Execute git config --system: the scope is the largest, the whole computer, no matter which account you log in to, no matter which project
-
Execute git config --global: the scope is medium, which is the user logging in to this computer
-
Execute git config: the scope is minimum, and the value is valid for the current project
We input directly git config,You can see a simple list of commands:
$ git config
usage: git config [<options>]
Config file location
--global use global config file
--system use system config file
--local use repository config file
--worktree use per-worktree config file
-f, --file <file> use given config file
--blob <blob-id> read config from given blob object
Action
--get get value: name [value-regex]
--get-all get all values: key [value-regex]
--get-regexp get values for regexp: name-regex [value-regex]
--get-urlmatch get value specific for the URL: section[.var] URL
--replace-all replace all matching variables: name value [value_regex]
--add add a new variable: name value
--unset remove a variable: name [value-regex]
--unset-all remove all matches: name [value-regex]
--rename-section rename section: old-name new-name
--remove-section remove a section: name
-l, --list list all
-e, --edit open an editor
--get-color find the color configured: slot [default]
--get-colorbool find the color setting: slot [stdout-is-tty]
Type
-t, --type <> value is given this type
--bool value is "true" or "false"
--int value is decimal number
--bool-or-int value is --bool or --int
--path value is a path (file or directory name)
--expiry-date value is an expiry date
Other
-z, --null terminate values with NUL byte
--name-only show variable names only
--includes respect include directives on lookup
--show-origin show origin of config (file, standard input, blob, command line)
--default <value> with --get, use default value when missing entry
(2)git config --help