GMM introduction
Unlike other machine learning models, EM algorithm is an unsupervised learning algorithm, whose input data does not need to be labeled in advance. On the contrary, the algorithm can calculate the maximum likelihood estimation of Gaussian mixture parameters from a given set of samples. It can also get the corresponding annotation value of each sample, similar to kmeans clustering (input sample data, output sample data annotation). In fact, GMM and kmeans are the application of EM algorithm
Please study by yourself. I'm not good at it
Correlation function api
Function api
bool trainEM(InputArray samples, OutputArray logLikelihoods=noArray(), OutputArray labels=noArray(), OutputArray probs=noArray())
Parameter description
- Samples: input samples, a single channel matrix. From this sample, the Gaussian mixture model is estimated.
- logLikelihoods: optional, output a matrix containing the likelihood value of each sample.
- Labels: optional, output the corresponding labels of each sample.
- probs: optional, output a matrix containing the posterior probability of each implicit variable
This function does not input the initialization value of the parameter, because it will automatically execute the kmeans algorithm and initialize the result of kmeans algorithm as the parameter.
The function of trainEM is similar to that of kmeans, which realizes automatic clustering and outputs the corresponding annotation value of each sample. But it has one more function than kmeans, that is, it can also play the role of training classifiers for the prediction of new samples.
This trainEM function actually includes steps E and M. We can also execute the two steps separately. OPENCV3.0 also provides functions to execute separately:
bool trainE(InputArray samples, InputArray means0, InputArray covs0=noArray(), InputArray weights0=noArray(), OutputArray logLikelihoods=noArray(), OutputArray labels=noArray(), OutputArray probs=noArray())
bool trainM(InputArray samples, InputArray probs0, OutputArray logLikelihoods=noArray(), OutputArray labels=noArray(), OutputArray probs=noArray())
Function api
Vec2d predict2(InputArray sample, OutputArray probs) const
Parameter description
-
Sample: sample to be tested
-
probs: as above, an optional output value, including the posterior probability of each implicit variable
-
Return value: returns a Vec2d type number, including the double vector of two elements. The first element is the likelihood pair value of the sample, and the second element is the index value of the maximum possible mixing component.
Code demonstration (settlement)
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <iostream> #include <math.h> using namespace std; using namespace cv; using namespace cv::ml; int main(void) { //create picture Mat img(500,500,CV_8UC3); //Define random number generator RNG rng(12345); //Define 5 colors with a maximum classification of no more than 5 Scalar color_tab[]={ Scalar(0,0,255), Scalar(0,255,0), Scalar(255,0,0), Scalar(0,255,255), Scalar(255,0,255) }; //Define classification, that is, how many classification points of function K value int num_cluster = rng.uniform(2,5); printf("num of num_cluster is %d\n",num_cluster); //How many points are generated for us to test int sample_count = rng.uniform(2,1000); printf("num of sample_count is %d\n",sample_count); Mat points(sample_count,2,CV_32FC1); //The number of samples generated is actually a 2-channel column vector, and the element type is Point2f Mat lables; //What kind of cluster label does each point belong to Mat centers; //Generate random number for(int i=0;i<num_cluster;i++) { Point center; center.x = rng.uniform(0,img.cols); center.y = rng.uniform(0,img.rows); //Get the filled area only get the area no filled value Mat point_chunk = points.rowRange(i*sample_count/num_cluster,i == num_cluster-1 ? sample_count: (i+1)*sample_count/num_cluster); //The Gauss distribution of the random number in the obtained filling area is satisfied (the average value is Scalar(center.x,center.y) equation is Scalar(img.cols*0.05,img.rows*0.05)) rng.fill(point_chunk,RNG::NORMAL,Scalar(center.x,center.y),Scalar(img.cols*0.05,img.rows*0.05)); } //Upset randShuffle(points,1,&rng); Ptr<EM> em_model = EM::create(); //Set K em_model->setClustersNumber(num_cluster); //Set covariance matrix type em_model->setCovarianceMatrixType(EM::COV_MAT_SPHERICAL); //Convergence condition em_model->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS + TermCriteria::COUNT,100,0.1)); //train em_model->trainEM(points,noArray(),lables,noArray()); // classify every image pixels Mat sample(1, 2, CV_32FC1); for (int row = 0; row < img.rows; row++) { for (int col = 0; col < img.cols; col++) { sample.at<float>(0) = (float)col; sample.at<float>(1) = (float)row; //int response = cvRound(em_model->predict2(sample, noArray())[1]); Vec2d predict = em_model->predict2(sample, noArray()); // Prophesy int response = cvRound(predict[1]); // response is the current classification given Scalar c = color_tab[response]; circle(img, Point(col, row), 1, c*0.75, -1); } } // draw the clusters for (int i = 0; i < sample_count; i++) { Point p(cvRound(points.at<float>(i, 0)), cvRound(points.at<float>(i, 1))); circle(img, p, 1, color_tab[lables.at<int>(i)], -1); } imshow("GMM-EM Demo", img); waitKey(0); destroyAllWindows(); return 0; }
Effect demonstration
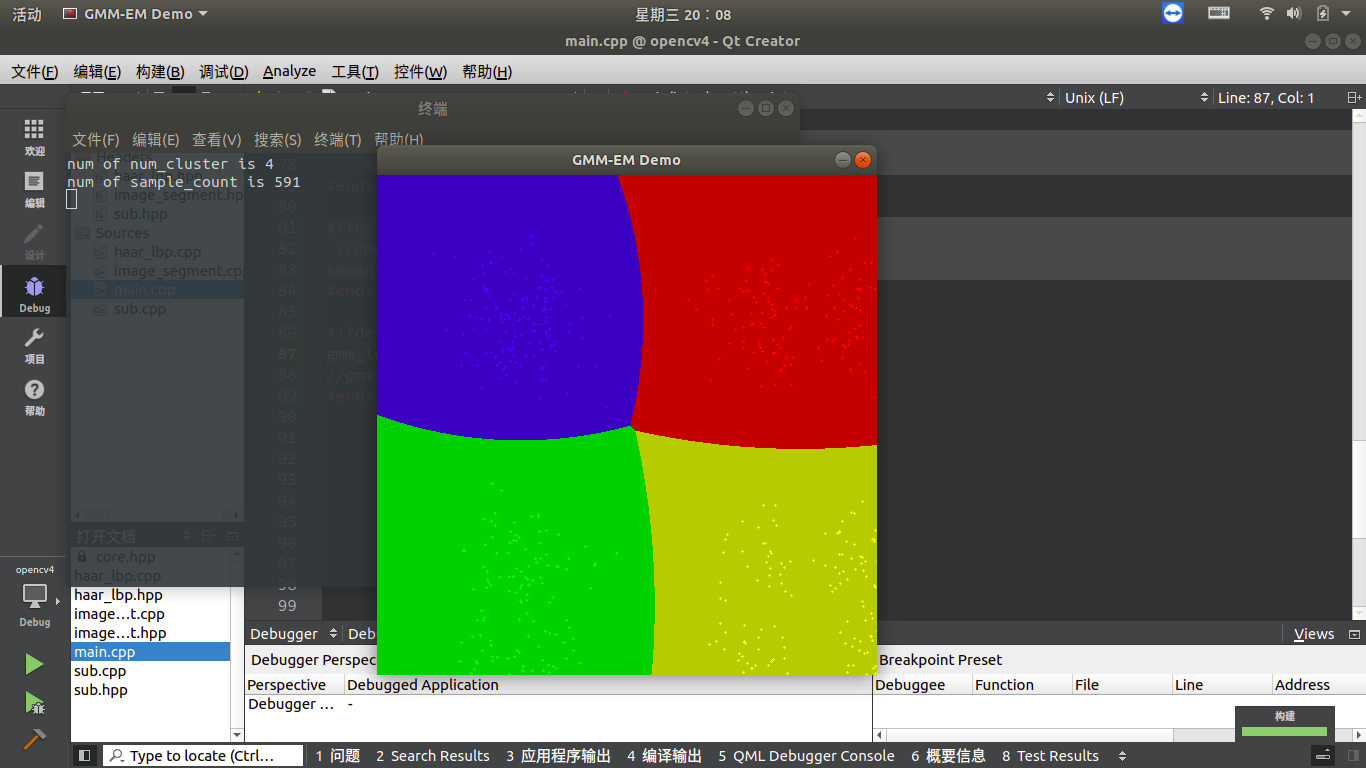
–
Code demonstration (picture segmentation)
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <iostream> #include <math.h> using namespace std; using namespace cv; using namespace cv::ml; #define PIC_PATH "/work/opencv_pic/" #define PIC_NAME "kmeans.jpeg" int main(void) { Mat src; //Get the complete picture path and name string pic = string(PIC_PATH)+string(PIC_NAME); //Print picture path cout << "pic path is :"<<pic<<endl; //Read pictures src = imread(pic); //Judge whether the picture exists if(src.empty()) { cout<<"pic is not exist!!!!"<<endl; return -1; } //display picture namedWindow("src pic",WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); imshow("src pic",src); //Define 5 colors with a maximum classification of no more than 5 Scalar color_tab[]={ Scalar(0,0,255), Scalar(0,255,0), Scalar(255,0,0), Scalar(0,255,255), Scalar(255,0,255) }; int width = src.cols; int height = src.rows; int dims = src.channels(); int nsamples = width*height; Mat points(nsamples, dims, CV_64FC1); Mat labels; Mat result = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3); //Define classification, that is, how many classification points of function K value int num_cluster = 3; printf("num of num_cluster is %d\n",num_cluster); // Image RGB pixel data to sample data int index = 0; for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) { for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) { index = row*width + col; Vec3b rgb = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col); points.at<double>(index, 0) = static_cast<int>(rgb[0]); points.at<double>(index, 1) = static_cast<int>(rgb[1]); points.at<double>(index, 2) = static_cast<int>(rgb[2]); } } // EM Cluster Train Ptr<EM> em_model = EM::create(); //Partition number em_model->setClustersNumber(num_cluster); //Set covariance matrix type em_model->setCovarianceMatrixType(EM::COV_MAT_SPHERICAL); //Set convergence conditions em_model->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS + TermCriteria::COUNT, 100, 0.1)); //Store the probability partition to labs EM according to the sample training em_model->trainEM(points, noArray(), labels, noArray()); // Mark color and display for each pixel Mat sample(1, dims, CV_64FC1);// int r = 0, g = 0, b = 0; //Put each pixel in the sample for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) { for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) { index = row*width + col; //Get the color of each channel b = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[0]; g = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[1]; r = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[2]; //Put pixels in sample data sample.at<double>(0, 0) = static_cast<double>(b); sample.at<double>(0, 1) = static_cast<double>(g); sample.at<double>(0, 2) = static_cast<double>(r); //Rounding int response = cvRound(em_model->predict2(sample, noArray())[1]); Scalar c = color_tab[response]; result.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[0] = c[0]; result.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[1] = c[1]; result.at<Vec3b>(row, col)[2] = c[2]; } } imshow("EM-Segmentation", result); waitKey(0); destroyAllWindows(); return 0; }
Effect demonstration


