- Complete code
https://github.com/CheapMiao/Godot-ThirdPersonController
extends KinematicBody
# ---Object properties---
# Moving speed
export var moveSpeed : float = 10
# Jump speed
export var jumpAcceleration : float = 200
# Falling acceleration
export var fallAcceleration : float = 9.8
# Linear velocity
var linearVelocity : Vector3 = Vector3.ZERO
# Mouse sensitivity
export var mouseSensitivity : float = 0.05
# Maximum mouse movement speed
export var mouseMoveMaxSpeed : float = 10
# Minimum pitch angle
export var cameraMinPitch : float = -45
# Maximum pitch angle
export var cameraMaxPitch : float = 90
# Character turning speed
export var playerRotSpeed : float = 0.2
# Acceleration of a character sliding on a slope
export var slipAcceleration : float = 1
# ---Component reference---
# Mesh
onready var meshes = $Meshes
# Spring arm
onready var springarm = $SpringArm
# video camera
onready var camera = $SpringArm/Camera
# ---Control cache---
# Should the spring arm be rotated
var shouldCameraMove : bool = false
# On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive
var mouseMoveSpeed = Vector2(0,0)
# Acceleration in y direction
var yAcceleration = 0
# ---Control parameters---
# Scaling of acceleration in y direction
# In order to keep fallAcceleration unchanged in 9.8, it is common sense
var yAccelerationScale : float = 10
# ---Events---
func _ready():
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func _unhandled_input(event) -> void:
# If you get the mouse in motion event
if event is InputEventMouseMotion:
# If the displacement of the mouse relative to the last frame is not 0 but Vector2, it means that the mouse moves relative to the last frame
if typeof(event.relative) == TYPE_VECTOR2:
# The camera should be rotated
shouldCameraMove = true
# Gets the amount of mouse movement within a frame
mouseMoveSpeed = event.relative
# If you press the exit key
if Input.is_action_just_released("ui_cancel"):
print("cancel")
# Toggle between mouse hide and dock
if Input.get_mouse_mode() == Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_VISIBLE)
else:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
# ---Custom function---
# Player movement
func playerMove(deltaTime):
# ---Horizontal direction---
# Controls the direction of cache movement
var direction = Vector3.ZERO
# Obtain the front, rear, left and right directions of the camera
# Notice the direction of the xyz coordinate system
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
direction += camera.get_global_transform().basis.x
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
direction -= camera.get_global_transform().basis.x
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_up"):
direction -= camera.get_global_transform().basis.z
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_down"):
direction += camera.get_global_transform().basis.z
# Horizontal movement direction unitization
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
direction = direction.normalized()
# Horizontal linear velocity
linearVelocity = direction * moveSpeed
# ---Vertical direction---
# On the ground, judge whether to jump
if is_on_floor():
# Take off on the ground, jump acceleration
if Input.is_action_pressed("jump"):
yAcceleration = jumpAcceleration
# If there is no take-off on the ground, the downward acceleration is the slope sliding acceleration
else:
yAcceleration = slipAcceleration
# Not on the ground, gravitational acceleration
else:
yAcceleration -= fallAcceleration
# Apply y-direction acceleration
linearVelocity += Vector3.UP * yAcceleration / yAccelerationScale
# Character movement
linearVelocity = move_and_slide(linearVelocity, Vector3.UP)
# Camera rotation
func cameraRotate(deltaTime):
# Rotate the camera if necessary
if shouldCameraMove:
# Has started rotating the camera
shouldCameraMove = false
# Rotating camera
camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.y/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# Clamp
camera.rotation_degrees.x = clamp(camera.rotation_degrees.x,cameraMinPitch,cameraMaxPitch)
# Rotating spring arm
springarm.rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.x/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# Player model rotation
func meshesRotate(deltaTime):
# meshes front direction
var meshesForwardVector = meshes.get_global_transform().basis.z
# The front direction of the spring arm is opposite to the expected front direction due to the setting of the spring arm
var springarmForwardVector = -springarm.get_global_transform().basis.z
# Angle between meshes front direction and spring arm front direction
var angle = meshesForwardVector.angle_to(springarmForwardVector)
# Vector from mesh front direction to spring arm front direction
var deltaVector = springarmForwardVector - meshesForwardVector
# rotate_ The direction in which x increases is counterclockwise
# If the direction from the mesh front to the spring arm front is clockwise, set the angle to negative
if deltaVector.dot(meshes.get_global_transform().basis.x) < 0:
angle = -angle
# Apply character turn speed
angle *= playerRotSpeed
# meshes rotation
meshes.rotate_y(angle)
# ---Virtual function implementation---
# Fixed frame rate execution
func _physics_process(deltaTime):
playerMove(deltaTime)
cameraRotate(deltaTime)
meshesRotate(deltaTime)
Layout:
- Debug process
Spring arm rotation at the beginning
# Spring arm onready var springArm = $SpringArm func _unhandled_input(event): if event is InputEventMouseMotion: # On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive var mouseMoveLocalDir = event.speed.normalized() # The mouse movement speed on the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system is regarded as the arc length on the ball with the player as the ball center and the spring arm as the radius var mouseMoveArcLength = event.speed.length() # Mouse movement direction in 3D space of world coordinate system var mouseMoveWorldDir = to_global(Vector3(-mouseMoveLocalDir.x,-mouseMoveLocalDir.y,0)) # Player's front direction in three-dimensional space of world coordinate system var playerWorldForwardDir = get_global_transform().basis.z # The rotation axis of the spring arm in the three-dimensional space of the world coordinate system is the cross product of the moving direction of the mouse and the front direction of the player in the three-dimensional space var springArmRotAxis = mouseMoveWorldDir.cross(playerWorldForwardDir) # The rotation angle of the spring arm is equal to the arc length divided by the radius var mouseMoveAngle = mouseMoveArcLength/clamp(springArm.get_hit_length(),1,springArm.spring_length) # Spring arm rotation springArm.global_rotate(springArmRotAxis,mouseMoveAngle)
It runs in a mess, and then I think it may need to be put in_ physics_process, so it's changed to
# Mouse sensitivity var mouseSensitivity = 0.01 # ---Component reference--- # Spring arm onready var springarm = $SpringArm # ---Control cache--- # On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive var mouseMoveLocalDir = Vector2(0,0) # The movement speed of the mouse on the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system is regarded as the arc length on the ball with the player as the center and the spring arm as the radius var mouseMoveArcLength = 0 # ---Input event--- # Get mouse motion status func _unhandled_input(event): if event is InputEventMouseMotion: mouseMoveLocalDir = event.speed.normalized() mouseMoveArcLength = event.speed.length() else: mouseMoveLocalDir = Vector2(0,0) mouseMoveArcLength = 0 # ---Custom function--- # Spring arm rotation func springarmRotate(deltaTime): # Mouse movement direction in 3D space of world coordinate system var mouseMoveWorldDir = to_global(Vector3(-mouseMoveLocalDir.x,-mouseMoveLocalDir.y,0)) # Player's front direction in three-dimensional space of world coordinate system var playerWorldForwardDir = get_global_transform().basis.z # The rotation axis of the spring arm in the three-dimensional space of the world coordinate system is the cross product of the mouse movement direction and the player's front direction in the three-dimensional space, which needs to be unitized var springarmRotAxis = (mouseMoveWorldDir.cross(playerWorldForwardDir)).normalized() # The rotation angle of the spring arm is equal to the arc length divided by the radius var mouseMoveAngle = mouseMoveArcLength/clamp(springarm.get_hit_length(),1,springarm.spring_length) # Physical time interval and mouse sensitivity shall be considered for spring arm rotation springarm.global_rotate(springarmRotAxis,mouseMoveAngle*deltaTime*mouseSensitivity) # ---Virtual function implementation--- # Fixed frame rate execution func _physics_process(deltaTime): springarmRotate(deltaTime) print(mouseMoveArcLength)
When running, the rotation direction is correct, but there will be stroboscopic and still rotating when the mouse is stationary.
At first glance_ unhandled_ InputEventMouseMotion in input has a problem with the speed of mouse movement. Ideally, when the mouse moves_ unhandled_input recognizes InputEventMouseMotion and obtains the mouse speed; When the mouse does not move_ unhandled_input does not recognize InputEventMouseMotion and does not obtain mouse speed
Testing_ unhandled_ Mechanism for obtaining event by input
# ---Input event--- var tmp = null # Get mouse motion status func _unhandled_input(event): tmp = event # ---Virtual function implementation--- # Fixed frame rate execution func _physics_process(deltaTime): print(tmp)
As a result, as long as you slide the mouse in the window, and then keep the mouse still, the printed event is only the last InputEventMouseMotion, that is, only when there is input_ unhandled_input only works
Official documents http://godot.pro/doc/tutorials/inputs/inputevent.html The delivery flow of inputevent is explained in, which means that there is inputevnet_ unhandled_input can work.
Comprehensive:
① When there is input_ unhandled_input only works
② inputevnet_ unhandled_input can work
It can be seen that without input, there is no inputevent
When the mouse is still, there is no input, so when the mouse is still, an inputevent will not be given_ unhandled_input, so I use_ unhandled_ There is a problem with the logic of obtaining the mouse movement speed by input. Only the last recorded mouse movement speed can be obtained.
... well, although this is understandable
Then I searched again and saw that others had asked this question https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62844337/godot-how-would-i-get-inputeventmousemotion-in-the-process-function Now you can see that the error logic I wrote to obtain the mouse speed is equivalent to input get_ last_ mouse_ speed()
So I changed the rotation script to
# ---Object properties---
# Mouse sensitivity
var mouseSensitivity = 0.01
# ---Component reference---
# Spring arm
onready var springarm = $SpringArm
# Spring arm rotation
func springarmRotate(deltaTime):
# On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive
var mouseMoveLocalDir = Vector2(0,0)
# The mouse movement speed on the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system is regarded as the arc length on the ball with the player as the ball center and the spring arm as the radius
var mouseMoveArcLength = 0
# If the mouse is moving, the last recorded mouse movement speed is obtained
if Input.get_current_cursor_shape() == Input.CURSOR_MOVE:
print("mouse is moving")
mouseMoveLocalDir = Input.get_last_mouse_speed().normalized()
mouseMoveArcLength = Input.get_last_mouse_speed().length()
# Mouse movement direction in 3D space of world coordinate system
var mouseMoveWorldDir = to_global(Vector3(-mouseMoveLocalDir.x,-mouseMoveLocalDir.y,0))
# Player's front direction in three-dimensional space of world coordinate system
var playerWorldForwardDir = get_global_transform().basis.z
# The rotation axis of the spring arm in the three-dimensional space of the world coordinate system is the cross product of the mouse movement direction and the player's front direction in the three-dimensional space, which needs to be unitized
var springarmRotAxis = (mouseMoveWorldDir.cross(playerWorldForwardDir)).normalized()
# The rotation angle of the spring arm is equal to the arc length divided by the radius
var mouseMoveAngle = mouseMoveArcLength/clamp(springarm.get_hit_length(),1,springarm.spring_length)
# The physical time interval and mouse sensitivity should be considered when the spring arm rotates
springarm.global_rotate(springarmRotAxis,mouseMoveAngle*deltaTime*mouseSensitivity)
# ---Virtual function implementation---
# Fixed frame rate execution
func _physics_process(deltaTime):
springarmRotate(deltaTime)
The running result is that it does not rotate at all and does not enter if input at all get_ current_ cursor_ shape() == Input. CURSOR_ MOVE
So I was_ physics_ In process, I tried print(Input.get_current_cursor_shape()), and found that no matter how I move the mouse or click the mouse button, it always prints 0, that is, CURSOR_ARROW
Arrow pattern... I also know it's arrow pattern... Thinking... I don't know what his design is for. It's counter intuitive
Looking at its English meaning, is it possible that I used it wrong? get_current_cursor_shape and get_mouse_mode, one is to obtain the mouse shape, the other is to obtain the mouse state, and always get 0, that is, always move_ MODE_ Visible and CURSOR_ARROW
Although there is no problem, I see cursor in CursorShape_ Move just wanted to use get_current_cursor_shape's... It's invincible
https://github.com/khairul169/3rdperson-godot/issues This wrote a third person controller, but the project can't run anymore
I clicked on the script to control the role. I didn't understand it at the first time. It was a little messy and didn't comment. I didn't read it at all
The other one I found was https://github.com/KevinStirling/ThirdPersonCameraGodot , his writing is really concise and the function is also very correct
extends KinematicBody
export var gravity : int = -12
export var speed : int = 6
export var jump_speed : int = 6
export var air_speed : int = 4
export(float, 0.01, 1) var mouse_sens = 0.05
export(float, -90, 90) var min_camera_angle = -90
export(float, -90, 90) var max_camera_angle = 90
onready var camera : Spatial = $CameraOrbit
var velocity : Vector3 = Vector3()
var jump : bool = false
func _ready():
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func get_input() -> void:
# Handle input and set velocity accordingly
var vy = velocity.y
velocity = Vector3()
var accel = speed if is_on_floor() else air_speed
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_up"):
velocity += -transform.basis.z * accel
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_down"):
velocity += transform.basis.z * accel
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
velocity += transform.basis.x * accel
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
velocity += -transform.basis.x * accel
velocity = velocity.normalized() * speed
velocity.y = vy
jump = false
if Input.is_action_just_pressed("jump"):
jump = true
if Input.is_action_just_pressed("ui_cancel"):
if Input.get_mouse_mode() == Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_VISIBLE)
else:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func _physics_process(delta) -> void :
# Apply velocity calculation to the physics process
velocity.y += gravity * delta
get_input()
velocity = move_and_slide(velocity, Vector3.UP)
if jump and is_on_floor():
velocity.y = jump_speed
func _unhandled_input(event) -> void:
# Translate mouse movement to camera and character model movement
if event is InputEventMouseMotion:
rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouse_sens, event.relative.x/10))
camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouse_sens, event.relative.y/10))
camera.rotation.x = clamp(camera.rotation.x, deg2rad(min_camera_angle), deg2rad(max_camera_angle))
It turns out that it uses_ unhandled_ Event of input relative
I tried to_ unhandled_ Print event in input Relative, I found that he was actually my ideal mouse speed
emmmm... I can't fix it. When I read the document, it said
The mouse position relative to the previous position (position at the last frame).
I didn't think his "position relative to the last frame" could be used to express the speed
I really learned
Then, relative will always return to 0 when the mouse is not moving
What I said earlier:
It can be seen that without input, there is no inputevent
When the mouse is still, there is no input, so when the mouse is still, an inputevent will not be given_ unhandled_input, so I use_ unhandled_ There is a problem with the logic of obtaining the mouse movement speed by input. Only the last recorded mouse movement speed can be obtained.
It's wrong
But that's a little contradictory. The most likely thing is that when there is no input, there will also be inputevent_ unhandled_input, but when the mouse is still, the speed is null, so it can't be printed, which gives me the illusion that there is no event
Brother Kevin Stirling has his own set of calculation logic. I'll follow my calculation logic for the time being
extends KinematicBody
# ---Object properties---
# Moving speed
export var moveSpeed = 10
# Falling acceleration
export var fallAcceleration = 75
# Linear velocity
var linearVelocity = Vector3.ZERO
# Mouse sensitivity
var mouseSensitivity = 0.1
# ---Component reference---
# Spring arm
onready var springarm = $SpringArm
# ---Control cache---
# On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive
var mouseMoveLocalDir = Vector2(0,0)
# The mouse movement speed on the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system is regarded as the arc length on the ball with the player as the ball center and the spring arm as the radius
var mouseMoveArcLength = 0
# ---Events---
func _unhandled_input(event) -> void:
# If you get the mouse in motion event
if event is InputEventMouseMotion:
# If the displacement of the mouse relative to the last frame is not 0 but Vector2, it means that the mouse moves relative to the last frame
if typeof(event.relative) == TYPE_VECTOR2:
# Gets the amount of mouse movement within a frame
mouseMoveLocalDir = event.relative
mouseMoveArcLength = mouseMoveLocalDir.length()
# ---Custom function---
# Player movement
func playerMove(deltaTime):
# Controls the direction of cache movement
var direction = Vector3.ZERO
# Get the movement direction increment before, after, left and right
# Notice the direction of the xyz coordinate system
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
direction.x -= 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
direction.x += 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_up"):
direction.z += 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_down"):
direction.z -= 1
# Unitization of moving direction
# Mesh rotates in the direction of movement
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
direction = direction.normalized()
# If translation is the world coordinate of the parent node, then translation + direction is the point with length of 1 at the moving direction of the parent node
$MeshInstance.look_at(translation + direction, Vector3.UP)
# Horizontal linear velocity
linearVelocity.x = direction.x * moveSpeed
linearVelocity.z = direction.z * moveSpeed
# Vertical velocity
linearVelocity.y -= fallAcceleration * deltaTime
# Moving the character
linearVelocity = move_and_slide(linearVelocity, Vector3.UP)
# Spring arm rotation
func springarmRotate(deltaTime):
# Mouse movement direction in 3D space of world coordinate system
var mouseMoveWorldDir = to_global(Vector3(-mouseMoveLocalDir.x,-mouseMoveLocalDir.y,0))
# Player's front direction in three-dimensional space of world coordinate system
var playerWorldForwardDir = get_global_transform().basis.z
# The rotation axis of the spring arm in the three-dimensional space of the world coordinate system is the cross product of the mouse movement direction and the player's front direction in the three-dimensional space, which needs to be unitized
var springarmRotAxis = (mouseMoveWorldDir.cross(playerWorldForwardDir)).normalized()
# The rotation angle of the spring arm is equal to the arc length divided by the radius
var mouseMoveAngle = mouseMoveArcLength/clamp(springarm.get_hit_length(),1,springarm.spring_length)
# The physical time interval and mouse sensitivity should be considered when the spring arm rotates
springarm.global_rotate(springarmRotAxis,mouseMoveAngle*deltaTime*mouseSensitivity)
# ---Virtual function implementation---
# Fixed frame rate execution
func _physics_process(deltaTime):
playerMove(deltaTime)
springarmRotate(deltaTime)
The result was that
It can be seen that without input, there is no inputevent
When the mouse is still, there is no input, so when the mouse is still, an inputevent will not be given_ unhandled_input, so I use_ unhandled_ There is a problem with the logic of obtaining the mouse movement speed by input. Only the last recorded mouse movement speed can be obtained.
Question of
Curious and strange, that is, my negation of myself is wrong again - what I thought was right?
How do others spin smoothly? Well, others just wrote the mobile logic_ unhandled_ It's just in input
Well, it turns out that others pass_ unhandled_ Input's feature of "when the mouse is still, there is no input". When the mouse is still, it does not call _unhandled_input, and the rotation function does not rotate if it is not called, that is, the effect of "when the mouse is still, it does not rotate"
Grass... Why did I tangle for so long
To unify mobile logic to_ physics_ In process, I change it to:
extends KinematicBody
# ---Object properties---
# Moving speed
export var moveSpeed : float = 10
# Jump speed
export var jumpVelocity : float = 30
# Falling acceleration
export var fallAcceleration : float = 100
# Linear velocity
var linearVelocity : Vector3 = Vector3.ZERO
# Mouse sensitivity
export var mouseSensitivity : float = 1
# ---Component reference---
# Spring arm
onready var springarm = $SpringArm
# ---Control cache---
# Should the spring arm be rotated
var shouldSpringArmMove : bool = false
# On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive
var mouseMoveLocalDir = Vector2(0,0)
# The mouse movement speed on the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system is regarded as the arc length on the ball with the player as the ball center and the spring arm as the radius
var mouseMoveArcLength = 0
# ---Events---
func _ready():
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func get_input() -> void:
# If you press the exit key
if Input.is_action_just_pressed("ui_cancel"):
# Toggle between mouse hide and dock
if Input.get_mouse_mode() == Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_VISIBLE)
else:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func _unhandled_input(event) -> void:
# If you get the mouse in motion event
if event is InputEventMouseMotion:
# If the displacement of the mouse relative to the last frame is not 0 but Vector2, it means that the mouse moves relative to the last frame
if typeof(event.relative) == TYPE_VECTOR2:
# The spring arm should be rotated
shouldSpringArmMove = true
# Gets the amount of mouse movement within a frame
mouseMoveLocalDir = event.relative
mouseMoveArcLength = mouseMoveLocalDir.length()
# ---Custom function---
# Player movement
func playerMove(deltaTime):
# ---Horizontal direction---
# Controls the direction of cache movement
var direction = Vector3.ZERO
# Get the horizontal movement direction increment before, after, left and right
# Notice the direction of the xyz coordinate system
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
direction.x -= 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
direction.x += 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_up"):
direction.z += 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_down"):
direction.z -= 1
# Horizontal movement direction unitization
# Mesh rotates horizontally
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
direction = direction.normalized()
# If translation is the world coordinate of the parent node, then translation + direction is the point with length 1 at the moving direction of the parent node
$MeshInstance.look_at(translation + direction, Vector3.UP)
# Horizontal linear velocity
linearVelocity = direction * moveSpeed
# ---Vertical direction---
# Get vertical movement direction
if Input.is_action_pressed("jump"):
linearVelocity += Vector3.UP * jumpVelocity
# Effect of applied gravity
linearVelocity -= Vector3.UP * fallAcceleration * deltaTime
# Character movement
linearVelocity = move_and_slide(linearVelocity, Vector3.UP)
# Spring arm rotation
func springarmRotate(deltaTime):
# If necessary, rotate the spring arm
if shouldSpringArmMove:
# The spring arm has started to rotate
shouldSpringArmMove = false
# Mouse movement direction in 3D space of world coordinate system
var mouseMoveWorldDir = to_global(Vector3(-mouseMoveLocalDir.x,mouseMoveLocalDir.y,0))
# Player's front direction in three-dimensional space of world coordinate system
var playerWorldForwardDir = get_global_transform().basis.z
# The rotation axis of the spring arm in the three-dimensional space of the world coordinate system is the cross product of the mouse movement direction and the player's front direction in the three-dimensional space, which needs to be unitized
var springarmRotAxis = (mouseMoveWorldDir.cross(playerWorldForwardDir)).normalized()
# The rotation angle of the spring arm is equal to the arc length divided by the radius
var mouseMoveAngle = mouseMoveArcLength/clamp(springarm.get_hit_length(),1,springarm.spring_length)
# The physical time interval and mouse sensitivity should be considered when the spring arm rotates
springarm.global_rotate(springarmRotAxis,mouseMoveAngle*deltaTime*mouseSensitivity)
# ---Virtual function implementation---
# Fixed frame rate execution
func _physics_process(deltaTime):
playerMove(deltaTime)
springarmRotate(deltaTime)
This rotation is probably no problem, but there is another flicker phenomenon

The main reason is that my rotation of the spring arm includes rotation about the x axis. The spring arm can easily be rotated below the horizontal plane, hit the ground, then contract, and then directly enter the interior of the player, so that the player can not be seen; Then turn the spring arm again. Suppose that after the rotation, the spring arm returns to the horizontal plane and returns to the original length, you can see the player again. In this way, it leads to stroboscopic.
The correct approach should be to rotate the camera around the x axis and the spring arm around the y axis
If you say so, you'll still have to rotate alone like him
Directly use event relative. x / 10 and event relative. Y / 10 as a parameter of lerp is not very good for rotation. After all, moving the mouse faster can make event Relative x and y are greater than 10, but it doesn't matter, er, because it uses mouseSensitivity to block the rotation speed of each frame. In this way, if the mouse moves very slowly, the camera rotates slowly; If the mouse rotates very fast, within a certain range, the faster the mouse moves, the faster the rotation speed. However, when the mouse moves faster than a certain value, the rotation speed will not increase. This can prevent confusion caused by excessive force and give a slow and fast body feeling.
After modification:
extends KinematicBody
# ---Object properties---
# Moving speed
export var moveSpeed : float = 10
# Jump speed
export var jumpVelocity : float = 30
# Falling acceleration
export var fallAcceleration : float = 100
# Linear velocity
var linearVelocity : Vector3 = Vector3.ZERO
# Mouse sensitivity
export var mouseSensitivity : float = 0.05
# Maximum mouse movement speed
export var mouseMoveMaxSpeed : float = 10
# ---Component reference---
# Spring arm
onready var springarm = $SpringArm
# video camera
onready var camera = $SpringArm/Camera
# ---Control cache---
# Should the spring arm be rotated
var shouldCameraMove : bool = false
# On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive
var mouseMoveSpeed = Vector2(0,0)
# ---Events---
func _ready():
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func get_input() -> void:
# If you press the exit key
if Input.is_action_just_pressed("ui_cancel"):
# Toggle between mouse hide and dock
if Input.get_mouse_mode() == Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_VISIBLE)
else:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func _unhandled_input(event) -> void:
# If you get the mouse in motion event
if event is InputEventMouseMotion:
# If the displacement of the mouse relative to the last frame is not 0 but Vector2, it means that the mouse moves relative to the last frame
if typeof(event.relative) == TYPE_VECTOR2:
# The camera should be rotated
shouldCameraMove = true
# Gets the amount of mouse movement within a frame
mouseMoveSpeed = event.relative
# ---Custom function---
# Player movement
func playerMove(deltaTime):
# ---Horizontal direction---
# Controls the direction of cache movement
var direction = Vector3.ZERO
# Get the horizontal movement direction increment before, after, left and right
# Notice the direction of the xyz coordinate system
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
direction.x -= 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
direction.x += 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_up"):
direction.z += 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_down"):
direction.z -= 1
# Horizontal movement direction unitization
# Mesh rotates horizontally
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
direction = direction.normalized()
# If translation is the world coordinate of the parent node, then translation + direction is the point with length 1 at the moving direction of the parent node
$MeshInstance.look_at(translation + direction, Vector3.UP)
# Horizontal linear velocity
linearVelocity = direction * moveSpeed
# ---Vertical direction---
# Get vertical movement direction
if Input.is_action_pressed("jump"):
linearVelocity += Vector3.UP * jumpVelocity
# Effect of applied gravity
linearVelocity -= Vector3.UP * fallAcceleration * deltaTime
# Character movement
linearVelocity = move_and_slide(linearVelocity, Vector3.UP)
# Camera rotation
func cameraRotate(deltaTime):
# Rotate the camera if necessary
if shouldCameraMove:
# Has started rotating the camera
shouldCameraMove = false
# Rotating camera
camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.y/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# Rotating spring arm
springarm.rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.x/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# ---Virtual function implementation---
# Fixed frame rate execution
func _physics_process(deltaTime):
playerMove(deltaTime)
cameraRotate(deltaTime)
It still flickers again... This shows that I think the reason for the spring arm is incorrect

This is still the problem of camera rotation. There should still be some discontinuities in the rotation angle, resulting in rendering problems
I saw a tutorial https://godottutorials.pro/third-person-controller-tutorial/ , he rotated the camera to_ In process
So I changed my code to
# ---Virtual function implementation--- # Fixed frame rate execution func _physics_process(deltaTime): playerMove(deltaTime) # Actual frame rate execution func _process(deltaTime): cameraRotate(deltaTime)
There will still be flickering problems
Continuing with the tutorial, I added the reset of the mouse speed variable in the camera rotation function
# Camera rotation func cameraRotate(deltaTime): # Rotate the camera if necessary if shouldCameraMove: # Has started rotating the camera shouldCameraMove = false # Rotating camera camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.y/mouseMoveMaxSpeed)) # Rotating spring arm springarm.rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.x/mouseMoveMaxSpeed)) # Reset camera speed mouseMoveSpeed = Vector2.ZERO
There will still be flickering problems
Besides, there is nothing in this tutorial
In this case, the only difference between me and these smooth controllers is that I want to rotate the spring arm around the Y axis, but they directly rotate the whole character around the Y axis. It is possible that this difference caused me to flicker. In other words, the rotation of the spring arm around the y-axis causes flicker
Test 1 only the camera rotates about the x axis:
# Camera rotation func cameraRotate(deltaTime): # Rotate the camera if necessary if shouldCameraMove: # Has started rotating the camera shouldCameraMove = false # Rotating camera camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.y/mouseMoveMaxSpeed)) # Rotating spring arm # springarm.rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.x/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
Operation results

The camera rotates normally around the x axis
Test 2 only the spring arm rotates about the y-axis
# Camera rotation func cameraRotate(deltaTime): # Rotate the camera if necessary if shouldCameraMove: # Has started rotating the camera shouldCameraMove = false # Rotating camera # camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.y/mouseMoveMaxSpeed)) # Rotating spring arm springarm.rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.x/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
Operation results

It is indeed the rotation of the spring arm around the y-axis that causes the flicker
But I don't want the whole character to rotate around the y axis... It's at an impasse
When I randomly adjusted in the back, I felt that the field of vision was a little bad, so I raised the spring arm
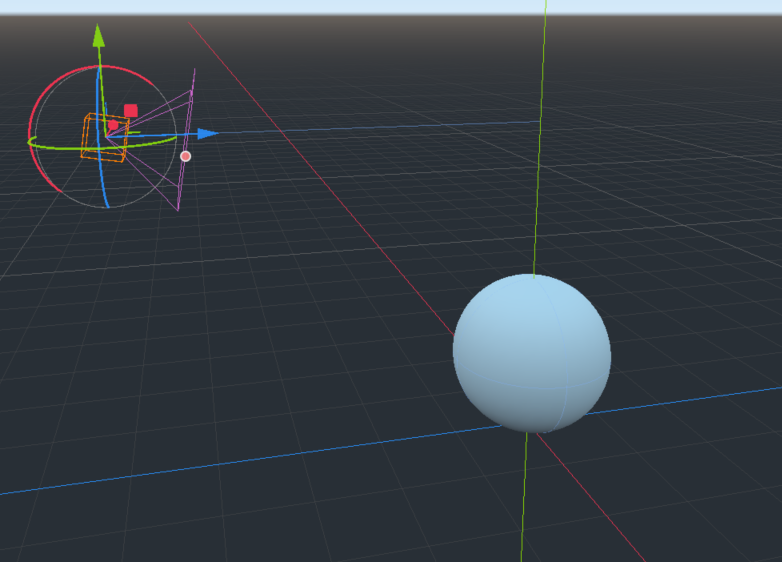
Then magically there was no flicker!
I don't know why
The problem was solved temporarily, so I continued to write
extends KinematicBody
# ---Object properties---
# Moving speed
export var moveSpeed : float = 10
# Jump speed
export var jumpVelocity : float = 30
# Falling acceleration
export var fallAcceleration : float = 100
# Linear velocity
var linearVelocity : Vector3 = Vector3.ZERO
# Mouse sensitivity
export var mouseSensitivity : float = 0.05
# Maximum mouse movement speed
export var mouseMoveMaxSpeed : float = 10
# Minimum pitch angle
export var cameraMinPitch : float = -45
# Maximum pitch angle
export var cameraMaxPitch : float = 90
# Character turning speed
export var playerRotSpeed : float = 0.5
# ---Component reference---
# Mesh
onready var meshes = $Meshes
# Spring arm
onready var springarm = $SpringArm
# video camera
onready var camera = $SpringArm/Camera
# ---Control cache---
# Should the spring arm be rotated
var shouldCameraMove : bool = false
# On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive
var mouseMoveSpeed = Vector2(0,0)
# ---Events---
func _ready():
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func get_input() -> void:
# If you press the exit key
if Input.is_action_pressed("ui_cancel"):
# Toggle between mouse hide and dock
if Input.get_mouse_mode() == Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED:
print("Hi")
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_VISIBLE)
else:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func _unhandled_input(event) -> void:
# If you get the mouse in motion event
if event is InputEventMouseMotion:
# If the displacement of the mouse relative to the last frame is not 0 but Vector2, it means that the mouse moves relative to the last frame
if typeof(event.relative) == TYPE_VECTOR2:
# The camera should be rotated
shouldCameraMove = true
# Gets the amount of mouse movement within a frame
mouseMoveSpeed = event.relative
# ---Custom function---
# Player movement
func playerMove(deltaTime):
# ---Horizontal direction---
# Controls the direction of cache movement
var direction = Vector3.ZERO
# Obtain the front, rear, left and right directions of the camera
# Notice the direction of the xyz coordinate system
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
direction += camera.get_global_transform().basis.x
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
direction -= camera.get_global_transform().basis.x
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_up"):
direction -= camera.get_global_transform().basis.z
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_down"):
direction += camera.get_global_transform().basis.z
# Horizontal movement direction unitization
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
direction = direction.normalized()
# Horizontal linear velocity
linearVelocity = direction * moveSpeed
# ---Vertical direction---
# Get vertical movement direction
if Input.is_action_pressed("jump"):
linearVelocity += Vector3.UP * jumpVelocity
# Effect of applied gravity
linearVelocity -= Vector3.UP * fallAcceleration * deltaTime
# Character movement
linearVelocity = move_and_slide(linearVelocity, Vector3.UP)
# Camera rotation
func cameraRotate(deltaTime):
# Rotate the camera if necessary
if shouldCameraMove:
# Has started rotating the camera
shouldCameraMove = false
# Rotating camera
camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.y/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# Clamp
camera.rotation_degrees.x = clamp(camera.rotation_degrees.x,cameraMinPitch,cameraMaxPitch)
# Rotating spring arm
springarm.rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.x/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# Player rotation
func meshesRotate(deltaTime):
meshes.rotation_degrees.y = lerp(meshes.rotation_degrees.y, springarm.rotation_degrees.y, playerRotSpeed)
# ---Virtual function implementation---
# Fixed frame rate execution
func _physics_process(deltaTime):
playerMove(deltaTime)
cameraRotate(deltaTime)
meshesRotate(deltaTime)
I want the rotation angle of Mesh to follow the rotation angle of the spring arm, but there is a sudden change in the rotation angle of Mesh at a certain angle

Test:
# Player rotation
func meshesRotate(deltaTime):
print("--------")
print(meshes.rotation_degrees.y)
print(springarm.rotation_degrees.y)
meshes.rotation_degrees.y = lerp(meshes.rotation_degrees.y, springarm.rotation_degrees.y, playerRotSpeed)
print(meshes.rotation_degrees.y)
Operation results:
There is a sudden change in the rotation angle of the spring arm in the y direction from - 180 to 180
In this case, the rotation angle in the y direction of the spring arm can not be used directly
It's only rotation increment
Replacement rotation method:
extends KinematicBody
# ---Object properties---
# Moving speed
export var moveSpeed : float = 10
# Jump speed
export var jumpVelocity : float = 30
# Falling acceleration
export var fallAcceleration : float = 100
# Linear velocity
var linearVelocity : Vector3 = Vector3.ZERO
# Mouse sensitivity
export var mouseSensitivity : float = 0.05
# Maximum mouse movement speed
export var mouseMoveMaxSpeed : float = 10
# Minimum pitch angle
export var cameraMinPitch : float = -45
# Maximum pitch angle
export var cameraMaxPitch : float = 90
# Character turning speed
export var playerRotSpeed : float = 0.2
# ---Component reference---
# Mesh
onready var meshes = $Meshes
# Spring arm
onready var springarm = $SpringArm
# video camera
onready var camera = $SpringArm/Camera
# ---Control cache---
# Should the spring arm be rotated
var shouldCameraMove : bool = false
# On the two-dimensional plane of the object coordinate system, the direction of mouse movement up to left is negative, down to right is positive
var mouseMoveSpeed = Vector2(0,0)
# ---Events---
func _ready():
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func get_input() -> void:
# If you press the exit key
if Input.is_action_pressed("ui_cancel"):
# Toggle between mouse hide and dock
if Input.get_mouse_mode() == Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED:
print("Hi")
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_VISIBLE)
else:
Input.set_mouse_mode(Input.MOUSE_MODE_CAPTURED)
func _unhandled_input(event) -> void:
# If you get the mouse in motion event
if event is InputEventMouseMotion:
# If the displacement of the mouse relative to the last frame is not 0 but Vector2, it means that the mouse moves relative to the last frame
if typeof(event.relative) == TYPE_VECTOR2:
# The camera should be rotated
shouldCameraMove = true
# Gets the amount of mouse movement within a frame
mouseMoveSpeed = event.relative
# ---Custom function---
# Player movement
func playerMove(deltaTime):
# ---Horizontal direction---
# Controls the direction of cache movement
var direction = Vector3.ZERO
# Obtain the front, rear, left and right directions of the camera
# Notice the direction of the xyz coordinate system
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
direction += camera.get_global_transform().basis.x
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
direction -= camera.get_global_transform().basis.x
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_up"):
direction -= camera.get_global_transform().basis.z
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_down"):
direction += camera.get_global_transform().basis.z
# Horizontal movement direction unitization
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
direction = direction.normalized()
# Horizontal linear velocity
linearVelocity = direction * moveSpeed
# ---Vertical direction---
# Get vertical movement direction
if Input.is_action_pressed("jump"):
linearVelocity += Vector3.UP * jumpVelocity
# Effect of applied gravity
linearVelocity -= Vector3.UP * fallAcceleration * deltaTime
# Character movement
linearVelocity = move_and_slide(linearVelocity, Vector3.UP)
# Camera rotation
func cameraRotate(deltaTime):
# Rotate the camera if necessary
if shouldCameraMove:
# Has started rotating the camera
shouldCameraMove = false
# Rotating camera
camera.rotate_x(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.y/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# Clamp
camera.rotation_degrees.x = clamp(camera.rotation_degrees.x,cameraMinPitch,cameraMaxPitch)
# Rotating spring arm
springarm.rotate_y(-lerp(0, mouseSensitivity, mouseMoveSpeed.x/mouseMoveMaxSpeed))
# Player model rotation
func meshesRotate(deltaTime):
# meshes front direction
var meshesForwardVector = meshes.get_global_transform().basis.z
# The front direction of the spring arm is opposite to the expected front direction due to the setting of the spring arm
var springarmForwardVector = -springarm.get_global_transform().basis.z
# Angle between meshes front direction and spring arm front direction
var angle = meshesForwardVector.angle_to(springarmForwardVector)
# Vector from mesh front direction to spring arm front direction
var deltaVector = springarmForwardVector - meshesForwardVector
# rotate_ The direction in which x increases is counterclockwise
# If the direction from the mesh front to the spring arm front is clockwise, set the angle to negative
if deltaVector.dot(meshes.get_global_transform().basis.x) < 0:
angle = -angle
# Apply character turn speed
angle *= playerRotSpeed
# meshes rotation
meshes.rotate_y(angle)
# ---Virtual function implementation---
# Fixed frame rate execution
func _physics_process(deltaTime):
playerMove(deltaTime)
cameraRotate(deltaTime)
meshesRotate(deltaTime)
Operation results:

The rotation is really done
But there is still a small problem, that is, he feels that the jump is too fast, because he gives a speed directly
However, the KinematicBody really doesn't have a function for physical simulation, so we still need to implement one by ourselves
Results achieved:

Finally, at least you can see it
http://godot.pro/doc/tutorials/inputs/inputevent.html
Official document inputevent
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48438273/godot-3d-get-forward-vector
Get the front direction of the object
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62844337/godot-how-would-i-get-inputeventmousemotion-in-the-process-function
Method for obtaining inputeventmousemotion
https://github.com/khairul169/3rdperson-godot/issues
An old third person project
https://github.com/KevinStirling/ThirdPersonCameraGodot
A recent third person project
https://godottutorials.pro/third-person-controller-tutorial/
Graphic tutorial for making third person controller
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SIGnJLtgk7w&ab_channel=Zenva
Video tutorial on making a third person controller