introduce
Through a complete example, in gogf/gf Manage logs reasonably in the framework.
What are the usage scenarios?
Log auto scroll Split into multiple log files Log format modification wait
We will use rk-boot To start gogf/gf Microservices of the framework.
Please visit the following address for a complete tutorial:
install
go get github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot/gf
Brief concept
Rk boot uses the following two libraries to manage logs.
- zap Manage log instances
- lumberjack Manage log scrolling
Rk boot defines two log types, which will be described in detail later. Here is a brief introduction.
- ZapLogger: standard log, used to record Error, Info, etc.
- Event logger: JSON or Console format, used to record events, such as RPC requests.
Quick start
In this example, we will try to change the path and format of the zap log.
1. Create boot yaml
---
zapLogger:
- name: zap-log # Required
zap:
encoding: json # Optional, options: console, json
outputPaths: ["logs/zap.log"] # Optional
gf:
- name: greeter
port: 8080
enabled: true2. Create main go
Write a log to the zap log instance.
// Copyright (c) 2021 rookie-ninja
//
// Use of this source code is governed by an Apache-style
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot"
_ "github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot/gf"
)
func main() {
// Create a new boot instance.
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Bootstrap
boot.Bootstrap(context.Background())
// Write zap log
boot.GetZapLoggerEntry("zap-log").GetLogger().Info("This is zap-log")
// Wait for shutdown sig
boot.WaitForShutdownSig(context.Background())
}3. Verification
Folder structure
├── boot.yaml ├── go.mod ├── go.sum ├── logs │ └── zap.log └── main.go
Log output
{"level":"INFO","ts":"2021-10-21T02:10:09.279+0800","msg":"This is zap-log"}Configure EventLogger
In the above example, we configured the zap log. This time, we modify the EventLogger.
1. Create boot yaml
---
eventLogger:
- name: event-log # Required
encoding: json # Optional, options: console, json
outputPaths: ["logs/event.log"] # Optional
gf:
- name: greeter
port: 8080
enabled: true2. Create main go
Write a log to the event log instance.
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-entry/entry"
)
func main() {
// Create a new boot instance.
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Bootstrap
boot.Bootstrap(context.Background())
// Write event log
helper := boot.GetEventLoggerEntry("event-log").GetEventHelper()
event := helper.Start("demo-event")
event.AddPair("key", "value")
helper.Finish(event)
// Wait for shutdown sig
boot.WaitForShutdownSig(context.Background())
}3. Start main go
$ go run main.go
4. Verification
Folder structure
├── boot.yaml ├── go.mod ├── go.sum ├── logs │ └── event.log └── main.go
Log content
{"endTime": "2022-01-18T22:18:44.926+0800", "startTime": "2022-01-18T22:18:44.926+0800", "elapsedNano": 746, "timezone": "CST", "ids": {"eventId":"2aaea6f5-c7ac-4245-ac50-857726f3ede4"}, "app": {"appName":"rk","appVersion":"","entryName":"","entryType":""}, "env": {"arch":"amd64","az":"*","domain":"*","hostname":"lark.local","localIP":"10.8.0.2","os":"darwin","realm":"*","region":"*"}, "payloads": {}, "error": {}, "counters": {}, "pairs": {"key":"value"}, "timing": {}, "remoteAddr": "localhost", "operation": "demo-event", "eventStatus": "Ended", "resCode": "OK"}concept
In the above example, we tried ZapLogger and EventLogger. Next, let's see how rk boot is implemented and used.
framework
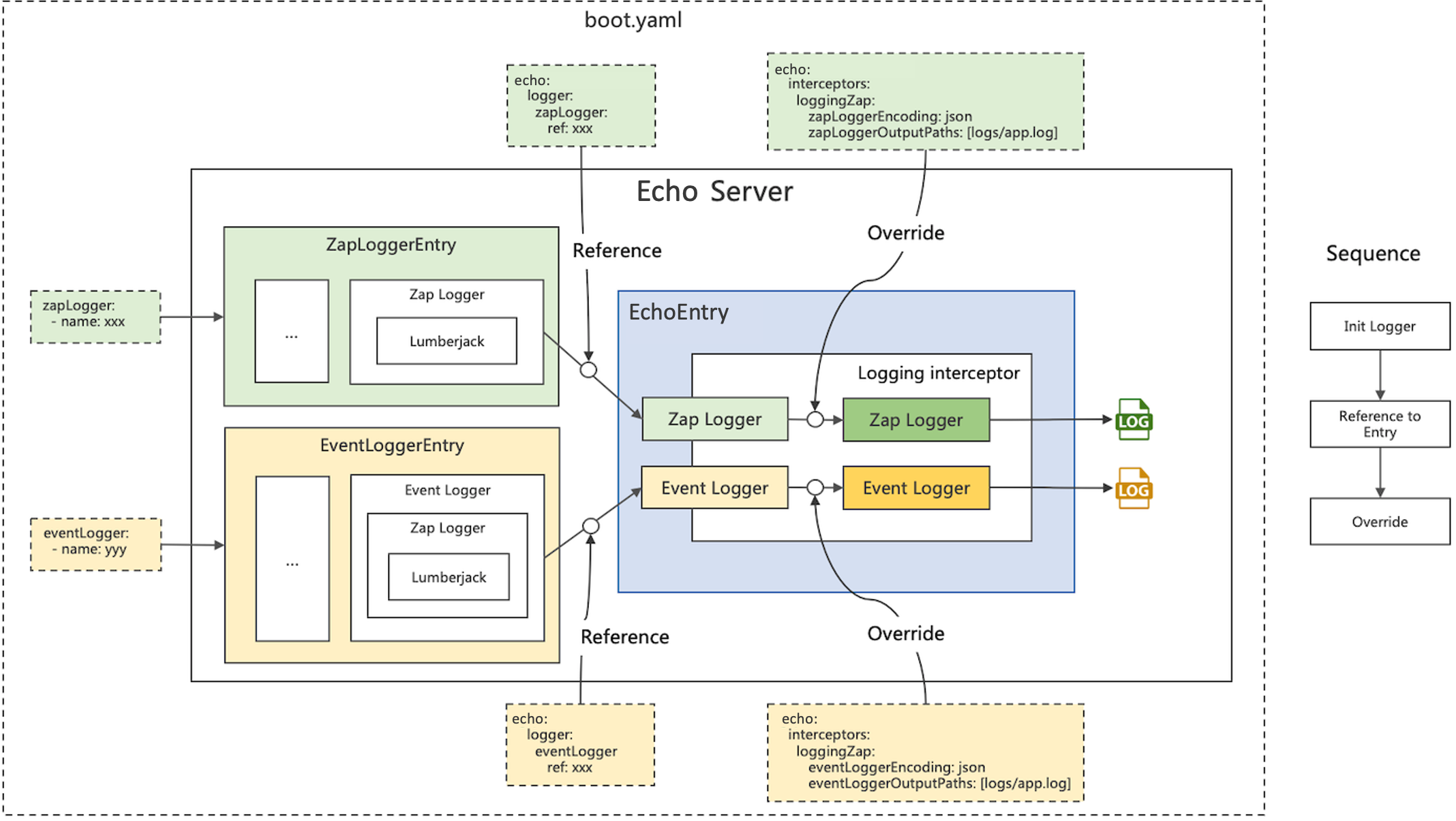
ZapLoggerEntry
ZapLoggerEntry is an encapsulation of zap instances.
// ZapLoggerEntry contains bellow fields.
// 1: EntryName: Name of entry.
// 2: EntryType: Type of entry which is ZapLoggerEntryType.
// 3: EntryDescription: Description of ZapLoggerEntry.
// 4: Logger: zap.Logger which was initialized at the beginning.
// 5: LoggerConfig: zap.Logger config which was initialized at the beginning which is not accessible after initialization..
// 6: LumberjackConfig: lumberjack.Logger which was initialized at the beginning.
type ZapLoggerEntry struct {
EntryName string `yaml:"entryName" json:"entryName"`
EntryType string `yaml:"entryType" json:"entryType"`
EntryDescription string `yaml:"entryDescription" json:"entryDescription"`
Logger *zap.Logger `yaml:"-" json:"-"`
LoggerConfig *zap.Config `yaml:"zapConfig" json:"zapConfig"`
LumberjackConfig *lumberjack.Logger `yaml:"lumberjackConfig" json:"lumberjackConfig"`
}How to boot Configure ZapLoggerEntry in yaml?
ZapLoggerEntry is fully compatible zap and lumberjack YAML structure of.
Users can configure multiple ZapLogger instances according to their needs and access them through name.
Full configuration:
---
zapLogger:
- name: zap-logger # Required
description: "Description of entry" # Optional
zap:
level: info # Optional, default: info, options: [debug, DEBUG, info, INFO, warn, WARN, dpanic, DPANIC, panic, PANIC, fatal, FATAL]
development: true # Optional, default: true
disableCaller: false # Optional, default: false
disableStacktrace: true # Optional, default: true
sampling: # Optional, default: empty map
initial: 0
thereafter: 0
encoding: console # Optional, default: "console", options: [console, json]
encoderConfig:
messageKey: "msg" # Optional, default: "msg"
levelKey: "level" # Optional, default: "level"
timeKey: "ts" # Optional, default: "ts"
nameKey: "logger" # Optional, default: "logger"
callerKey: "caller" # Optional, default: "caller"
functionKey: "" # Optional, default: ""
stacktraceKey: "stacktrace" # Optional, default: "stacktrace"
lineEnding: "\n" # Optional, default: "\n"
levelEncoder: "capitalColor" # Optional, default: "capitalColor", options: [capital, capitalColor, color, lowercase]
timeEncoder: "iso8601" # Optional, default: "iso8601", options: [rfc3339nano, RFC3339Nano, rfc3339, RFC3339, iso8601, ISO8601, millis, nanos]
durationEncoder: "string" # Optional, default: "string", options: [string, nanos, ms]
callerEncoder: "" # Optional, default: ""
nameEncoder: "" # Optional, default: ""
consoleSeparator: "" # Optional, default: ""
outputPaths: [ "stdout" ] # Optional, default: ["stdout"], stdout would be replaced if specified
errorOutputPaths: [ "stderr" ] # Optional, default: ["stderr"], stderr would be replaced if specified
initialFields: # Optional, default: empty map
key: "value"
lumberjack: # Optional
filename: "rkapp-event.log" # Optional, default: It uses <processname>-lumberjack.log in os.TempDir() if empty.
maxsize: 1024 # Optional, default: 1024 (MB)
maxage: 7 # Optional, default: 7 (days)
maxbackups: 3 # Optional, default: 3 (days)
localtime: true # Optional, default: true
compress: true # Optional, default: trueHow to get ZapLogger in code?
Access via name.
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Access entry
boot.GetZapLoggerEntry("zap-logger")
// Access zap logger
boot.GetZapLoggerEntry("zap-logger").GetLogger()
// Access zap logger config
boot.GetZapLoggerEntry("zap-logger").GetLoggerConfig()
// Access lumberjack config
boot.GetZapLoggerEntry("zap-logger").GetLumberjackConfig()EventLoggerEntry
Rk boot treats each RPC request as an Event and uses rk-query Event type in to log.
// EventLoggerEntry contains bellow fields.
// 1: EntryName: Name of entry.
// 2: EntryType: Type of entry which is EventLoggerEntryType.
// 3: EntryDescription: Description of EventLoggerEntry.
// 4: EventFactory: rkquery.EventFactory was initialized at the beginning.
// 5: EventHelper: rkquery.EventHelper was initialized at the beginning.
// 6: LoggerConfig: zap.Config which was initialized at the beginning which is not accessible after initialization.
// 7: LumberjackConfig: lumberjack.Logger which was initialized at the beginning.
type EventLoggerEntry struct {
EntryName string `yaml:"entryName" json:"entryName"`
EntryType string `yaml:"entryType" json:"entryType"`
EntryDescription string `yaml:"entryDescription" json:"entryDescription"`
EventFactory *rkquery.EventFactory `yaml:"-" json:"-"`
EventHelper *rkquery.EventHelper `yaml:"-" json:"-"`
LoggerConfig *zap.Config `yaml:"zapConfig" json:"zapConfig"`
LumberjackConfig *lumberjack.Logger `yaml:"lumberjackConfig" json:"lumberjackConfig"`
}EventLogger field
We can see that the log printed by EventLogger contains fields. Let's introduce these fields.
field | details |
|---|---|
endTime | End time |
startTime | start time |
elapsedNano | Event time overhead (Nanoseconds) |
timezone | time zone |
ids | Contains eventId, requestId and traceId. If the original data interceptor is started, or event As like as two peas, SetRequest () is invoked by the user, the new RequestId will be used, and eventId will be exactly the same as requestId. If the call chain interceptor is started, the traceId will be recorded. |
app | contain appName, appVersion, entryName, entryType. |
env | Including arch, AZ, DOMAIN, hostname, localip, OS, REALM, REGION REALM, REGION, AZ, DOMAIN fields. These fields are from the system environment variables (real, REGION, AZ, DOMAIN). "*" means that the environment variable is empty. |
payloads | Contains RPC related information. |
error | Contains errors. |
counters | Via event Setcounter(). |
pairs | Via event Addpair(). |
timing | Via event Starttimer() and event Endtimer(). |
remoteAddr | RPC remote address. |
operation | RPC name. |
resCode | RPC return code. |
eventStatus | Ended or InProgress |
example
------------------------------------------------------------------------
endTime=2021-11-27T02:30:27.670807+08:00
startTime=2021-11-27T02:30:27.670745+08:00
elapsedNano=62536
timezone=CST
ids={"eventId":"4bd9e16b-2b29-4773-8908-66c860bf6754"}
app={"appName":"gf-demo","appVersion":"master-f948c90","entryName":"greeter","entryType":"GfEntry"}
env={"arch":"amd64","az":"*","domain":"*","hostname":"lark.local","localIP":"10.8.0.6","os":"darwin","realm":"*","region":"*"}
payloads={"apiMethod":"GET","apiPath":"/rk/v1/healthy","apiProtocol":"HTTP/1.1","apiQuery":"","userAgent":"curl/7.64.1"}
error={}
counters={}
pairs={}
timing={}
remoteAddr=localhost:61726
operation=/rk/v1/healthy
resCode=200
eventStatus=Ended
EOEHow to boot Configure EventLoggerEntry in yaml?
EventLoggerEntry will inject the Application name into the Event. The starter will start from go Extract the Application name from the mod file. If there is no go Mod file, the initiator will use the default name.
Users can configure multiple EventLogger instances according to their needs and access them through name.
Full configuration:
---
eventLogger:
- name: event-logger # Required
description: "This is description" # Optional
encoding: console # Optional, default: console, options: console and json
outputPaths: ["stdout"] # Optional
lumberjack: # Optional
filename: "rkapp-event.log" # Optional, default: It uses <processname>-lumberjack.log in os.TempDir() if empty.
maxsize: 1024 # Optional, default: 1024 (MB)
maxage: 7 # Optional, default: 7 (days)
maxbackups: 3 # Optional, default: 3 (days)
localtime: true # Optional, default: true
compress: true # Optional, default: trueHow to get the EventLogger in the code?
Access via name.
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Access entry
boot.GetEventLoggerEntry("event-logger")
// Access event factory
boot.GetEventLoggerEntry("event-logger").GetEventFactory()
// Access event helper
boot.GetEventLoggerEntry("event-logger").GetEventHelper()
// Access lumberjack config
boot.GetEventLoggerEntry("event-logger").GetLumberjackConfig()How to use Event?
Event is an interface that contains several methods. Please refer to: Event
Common methods:
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Get EventHelper to create Event instance
helper := boot.GetEventLoggerEntry("event-log").GetEventHelper()
// Start and finish event
event := helper.Start("demo-event")
helper.Finish(event)
// Add K/V
event.AddPair("key", "value")
// Start and end timer
event.StartTimer("my-timer")
event.EndTimer("my-timer")
// Set counter
event.SetCounter("my-counter", 1)