reference material: http://dblab.xmu.edu.cn/blog/1233/
Note: the experiment of this blog requires a Docker image with Hadoop cluster environment.
Operating environment
Ubuntu20.04
Hadoop3.3.1
JDK8
1. Open three containers with Docker
Node introduction of this test
| Node name | effect |
|---|---|
| master | Master node |
| slave1 | Secondary node |
| slave2 | Secondary node |
Create a container using the image with Hadoop cluster environment, and one terminal is responsible for controlling one container
Master node
sudo docker run -it -h master --name master ubuntu/hadoop
Secondary node 1
sudo docker run -it -h slave1 --name slave1 ubuntu/hadoop
Secondary node 2
sudo docker run -it -h slave2 --name slave2 ubuntu/hadoop
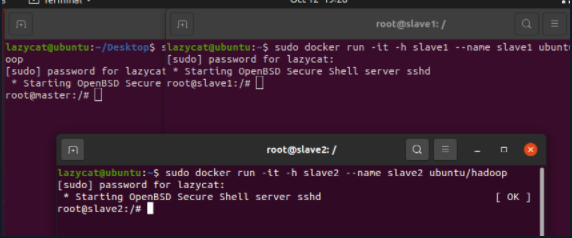
*2. Configure ip mapping test ssh
The following operations need to be performed on three nodes at the same time
hosts needs to be configured every time the container restarts
vim etc/hosts
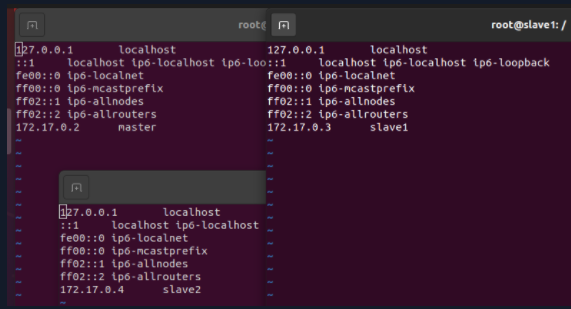
According to the query, the IP information of the three nodes is shown in the following table:
| Node name | Mapped IP |
|---|---|
| master | 172.17.0.2 |
| slave1 | 172.17.0.3 |
| slave2 | 172.17.0.4 |
In order to connect the three nodes to each other, you need to add another two IP addresses to each configuration file, as shown in the figure below
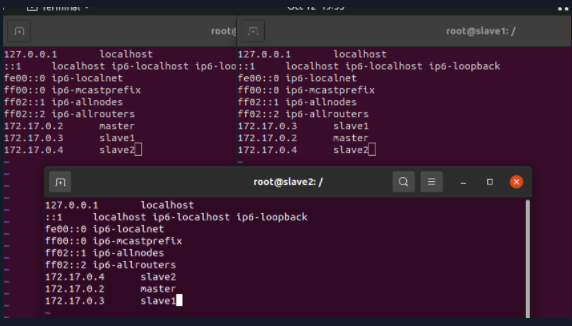
Save and exit after modification
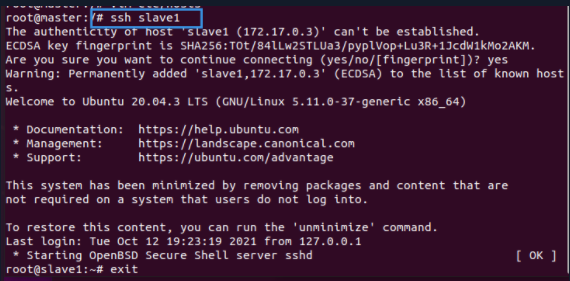
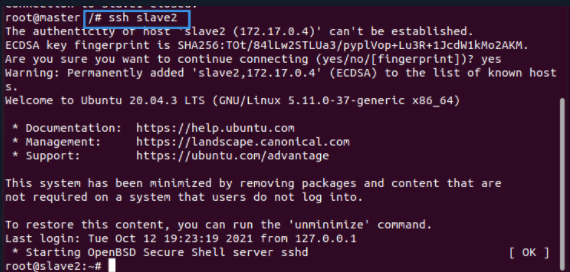
Test SSH
Take the Master node as an example. If it can connect slave1 and slave2, the ssh function is intact (perform the same operation on slave1 and slave2, which is omitted here)
ssh slave1 exit ssh slave2 exit
3. Modify the Hadoop configuration file
The following three configuration files need to be modified to build a Hadoop cluster. Because three nodes have been opened, the strategy adopted here is to modify the configuration file at the master node, and then copy all the configuration files to the corresponding directories of the other two nodes using the cp command. Note: it indicates that the configuration files (workers) of cluster nodes need to be modified separately
The files are in. / etc/hadoop
- hadoop-env.sh configures environment variables related to Hadoop operation, such as setting JDK paths, users of various processes in the cluster, and so on
- core-site.xml sets the hadoop temporary directory and the remote address of HDFS
- hdfs-site.xml for HDFS, name / data node storage location, number of file copies, etc
- mapred-site.xml setting MapReduce parameters
- Configure cluster resource management system parameters with yarn-site.xml
- workers specifies the secondary node in the cluster
When modifying the configuration, only the contents are added, and other contents remain intact.
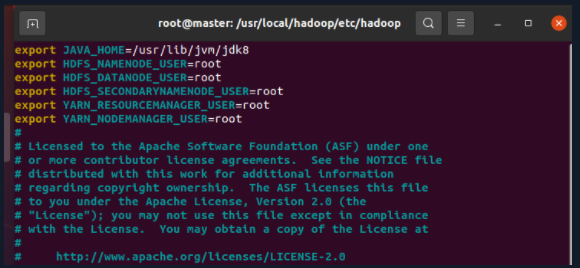
3.1 hadoop-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk8 export HDFS_NAMENODE_USER=root export HDFS_DATANODE_USER=root export HDFS_SECONDARYNAMENODE_USER=root export YARN_RESOURCEMANAGER_USER=root export YARN_NODEMANAGER_USER=root
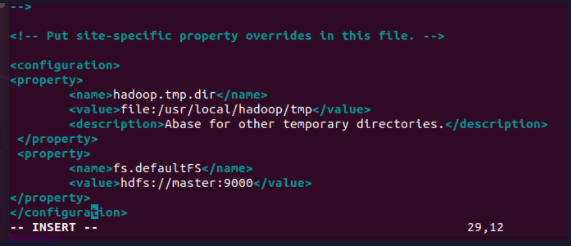
3.2 core-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/tmp</value>
<description>Abase for other temporary directories.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://master:9000</value>
</property>
</configuration>
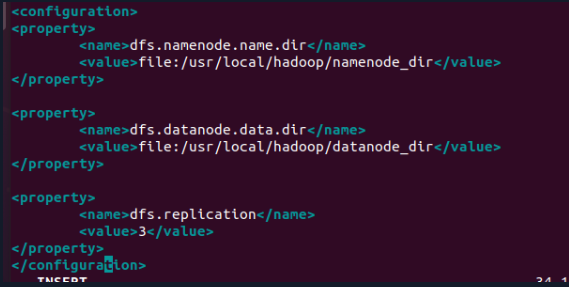
3.3 hdfs-site.xml
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/namenode_dir</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/datanode_dir</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>3</value>
</property>
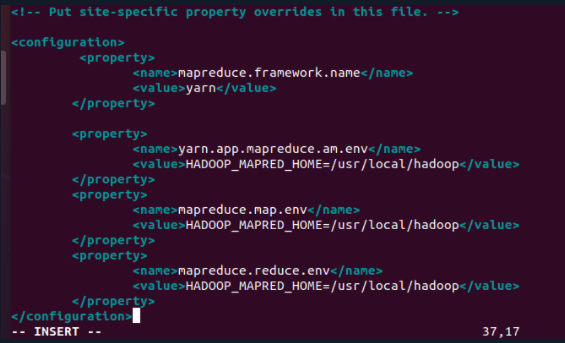
3.4 mapred-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.framework.name</name>
<value>yarn</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop</value>
</property>
</configuration>
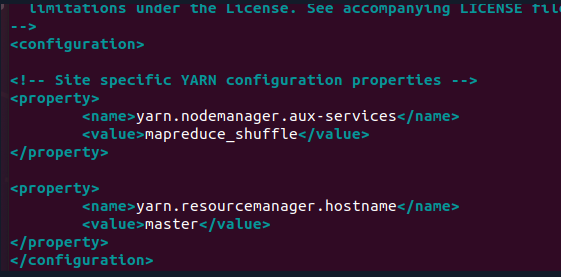
3.5 yarn-site.xml
<configuration>
<!-- Site specific YARN configuration properties -->
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name>
<value>mapreduce_shuffle</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.hostname</name>
<value>master</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Now that the unified configuration file has been modified, you can copy the configuration directory of the master node to other nodes
3.6 workers
This configuration file is responsible for setting the slave nodes of the Hadoop cluster
3.6 copying configuration files
scp -rq /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop root@slave1:/usr/local/hadoop/etc/ scp -rq /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop root@slave2:/usr/local/hadoop/etc/
3.7 check whether the configuration file is copied successfully
Check at slave1 and slave2 nodes respectively
cat /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml
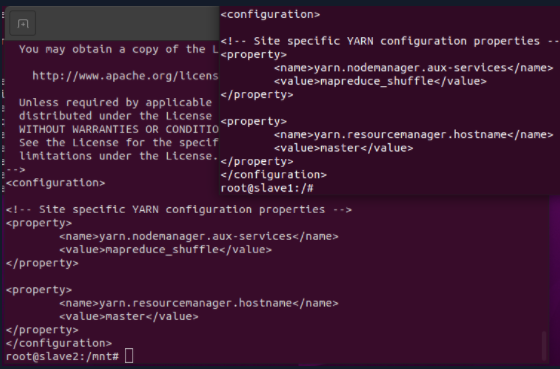
If the configuration information appears, the copy is successful
4. Start Hadoop cluster
4.1 Master node initialization name
This operation is only performed when the cluster is started for the first time, and then the cluster is started again without initialization, otherwise an error will occur
cd /usr/local/hadoop bin/hdfs namenode -format
4.2 start the cluster at the Master node
cd /usr/local/hadoop sbin/start-all.sh
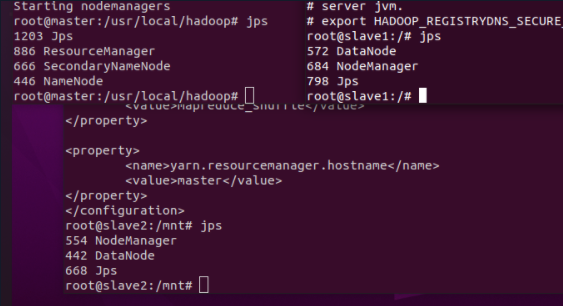
4.3 JPS query results
Enter the jps command at the three nodes to query the current process
If the startup is normal, the process of each node is as follows:
| Node name | Number of processes | Process name |
|---|---|---|
| master | 4 | Jps,ResourceManager,SecondaryNameNode,NameNode |
| slave1 | 3 | Jps,DataNode,NodeManager |
| slave2 | 3 | Jps,Datanode,NodeManager |
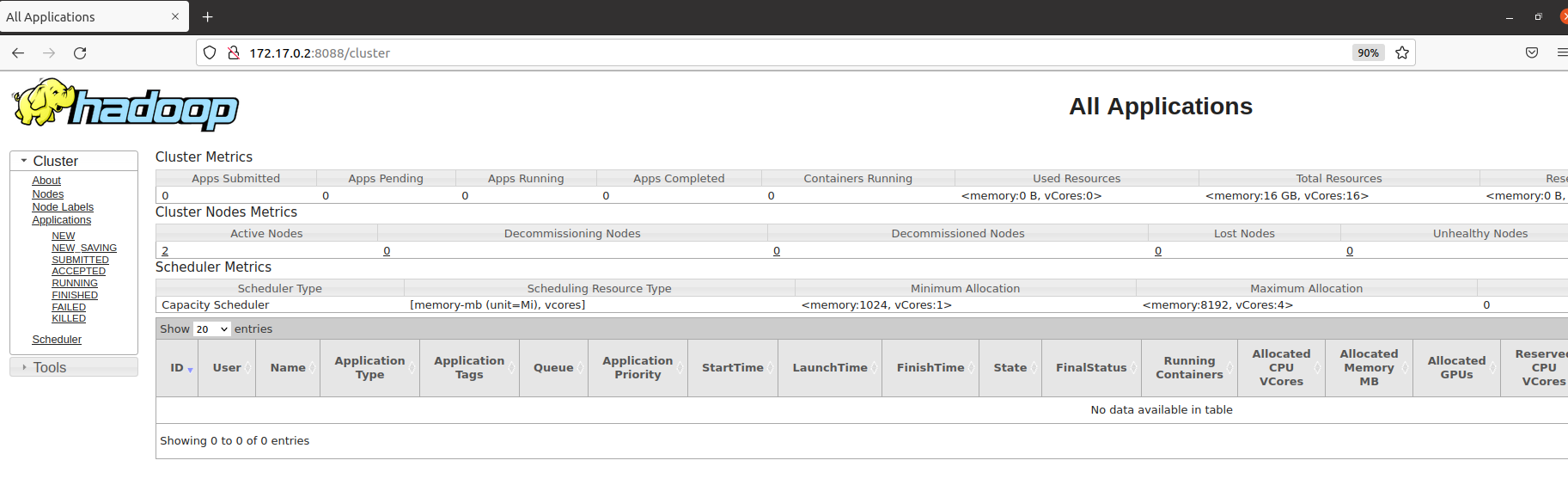
4.4 accessing clusters through the Web
URL: masterIp:8088/cluster
My address here is http://172.17.0.2:8088/cluster
5. Run distributed instances
The following operations are performed on the Master node
5.1 create user directory in HDFS
cd /usr/local/hadoop/bin ./hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/hadoop/input ./hdfs dfs -ls /user/hadoop
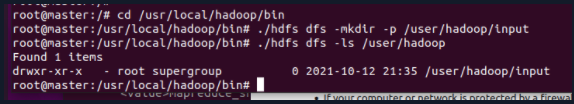
5.2 upload local hadoop configuration files to HDFS
cd /usr/local/hadoop/bin ./hdfs dfs -put /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/*.xml /user/hadoop/input ./hdfs dfs -ls /user/hadoop/input
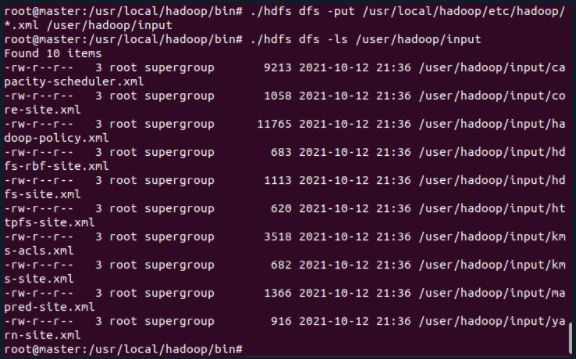
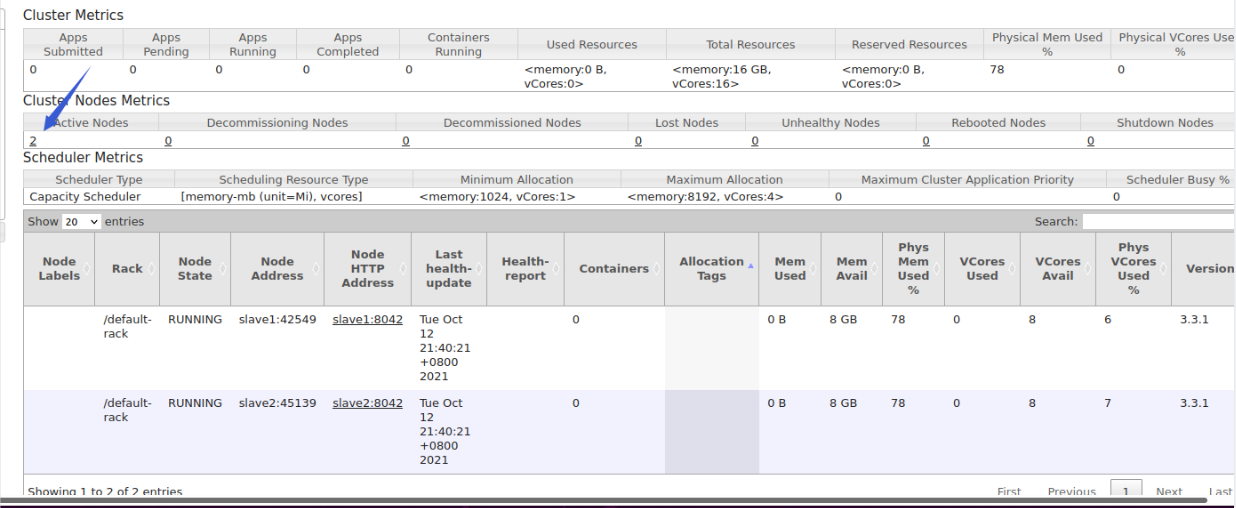
After uploading, the cluster status can be queried externally through the web
http://172.17.0.2:8088/cluster/nodes
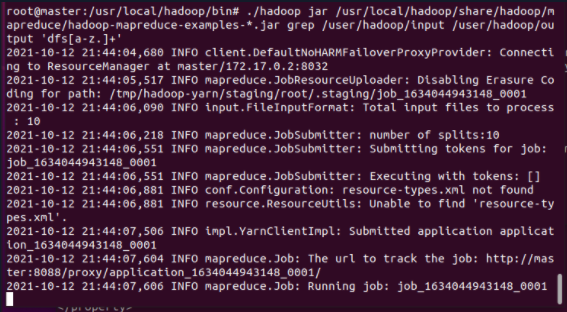
5.3 running MapReduce job
cd /usr/local/hadoop/bin ./hadoop jar /usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-*.jar grep /user/hadoop/input /user/hadoop/output 'dfs[a-z.]+'
5.4 query results
cd /usr/local/hadoop/bin ./hdfs dfs -cat /user/hadoop/output/*
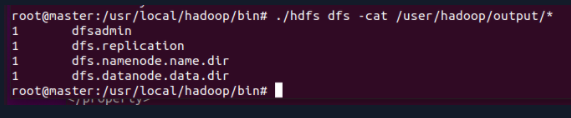
So far, if the above result appears, it indicates that the execution is successful!
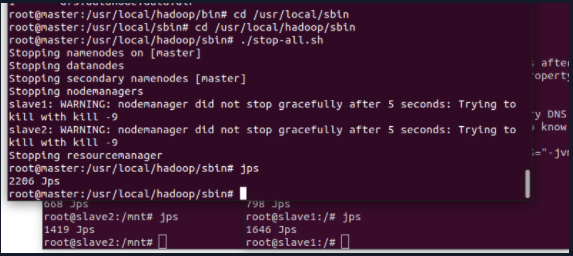
6. Shut down the cluster
The following operations only need to be performed on the Master node
cd /usr/local/hadoop/sbin ./stop-all.sh