Flume log collection
1, Flume introduction

Logo refers to the transfer of wood (data) from one place (data source) to another place (data destination) through the river channel (channel)

Working with documents
2, Installation configuration of Flume
1. Download and upload to the server
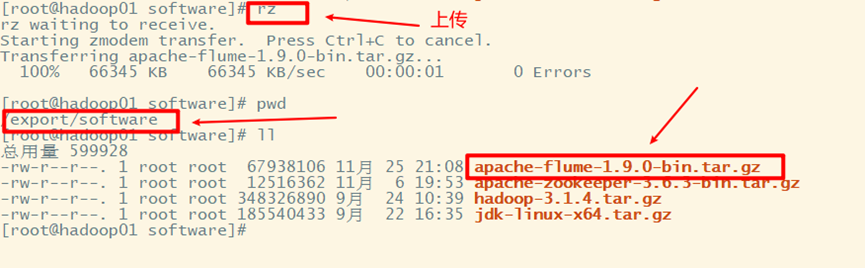
2. Decompression
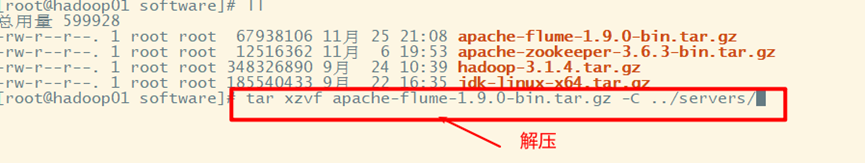
3. Configuration
Copy flume env. From the template sh
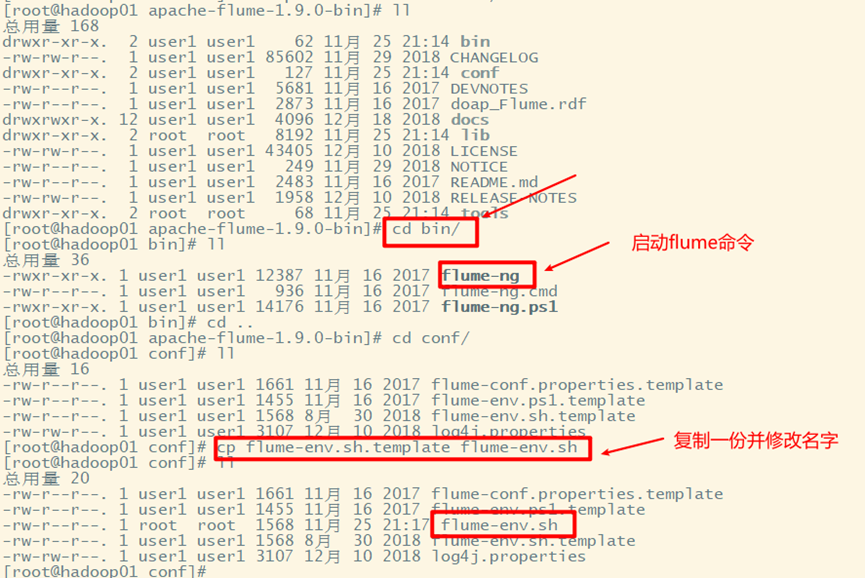
Modify flume env sh
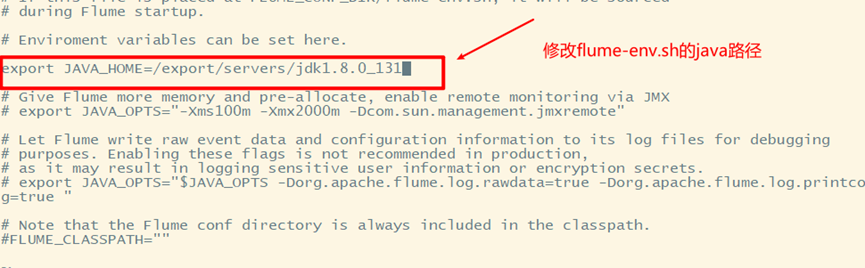
4. Configure environment variables
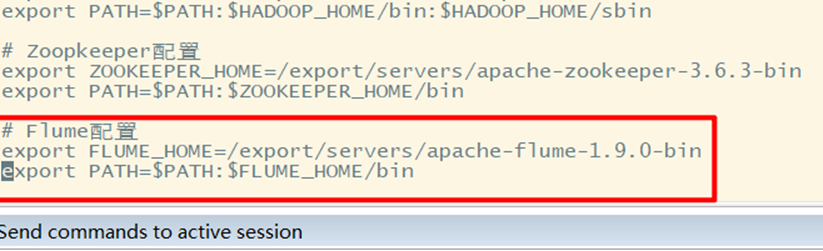
5. Make environmental variables work
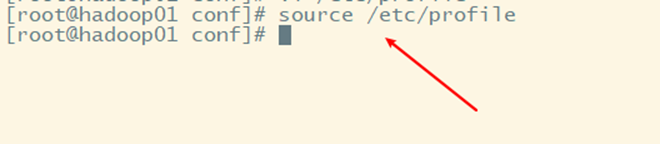
3, Getting started with Flume
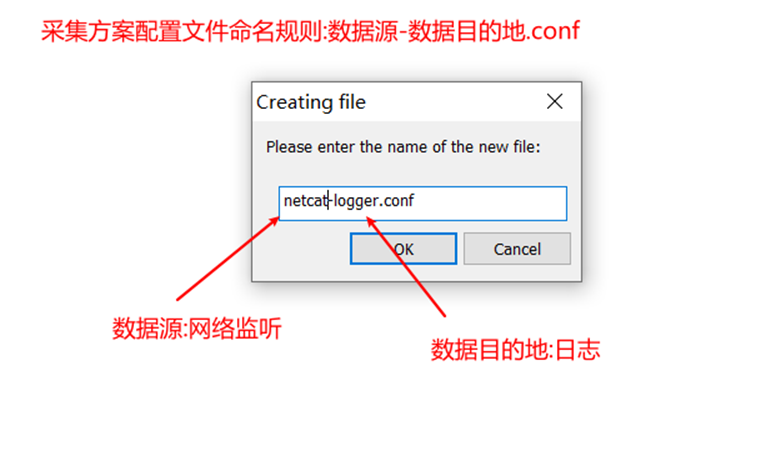
1. Configure acquisition scheme
View official website


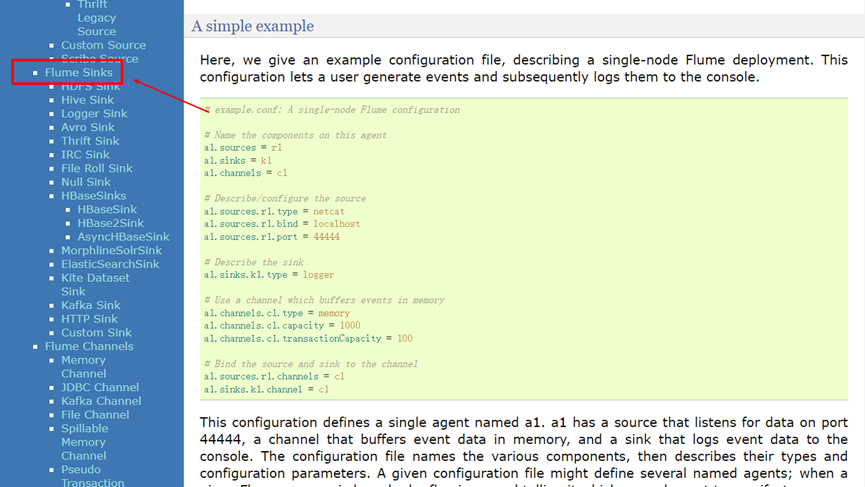
Case: connect and monitor a port, collect data and display
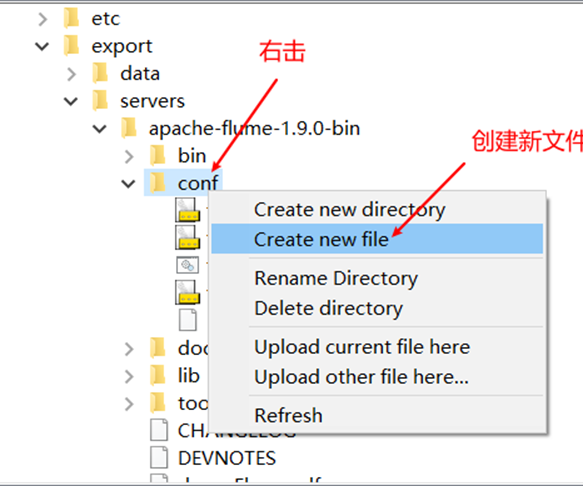
Configure with notepad + +
create a new file
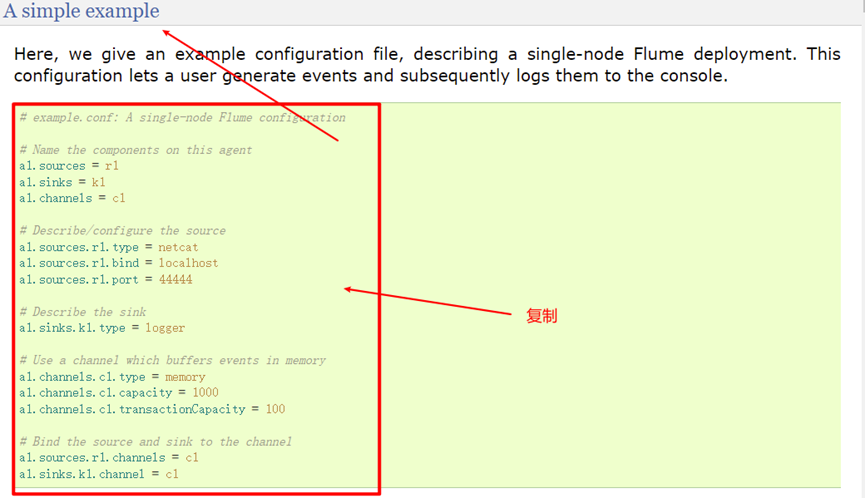
Example of copying the collection configuration of the official website:
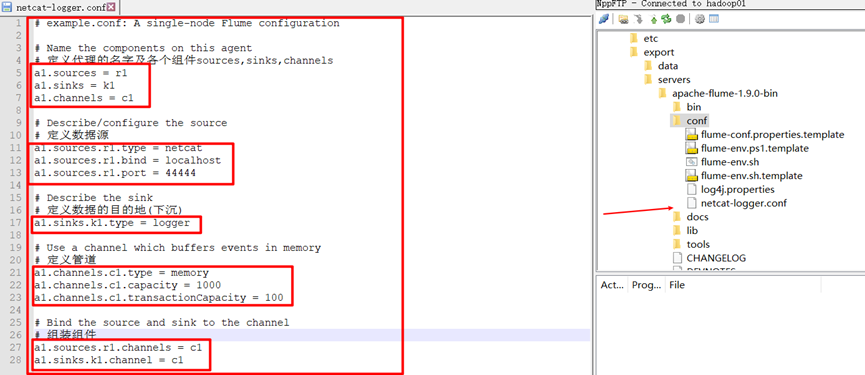
Source code:
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent # Define the name of the agent and the components sources, sinks, and channels a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source # Define data source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Describe the sink # Define the destination of the data (sink) a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # Define pipe a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel # Assembly components a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
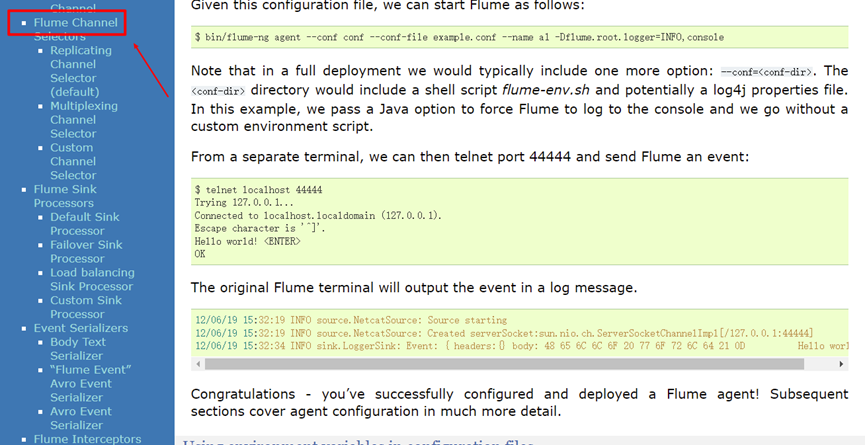
2. Specify a collection scheme to start flume
View official website
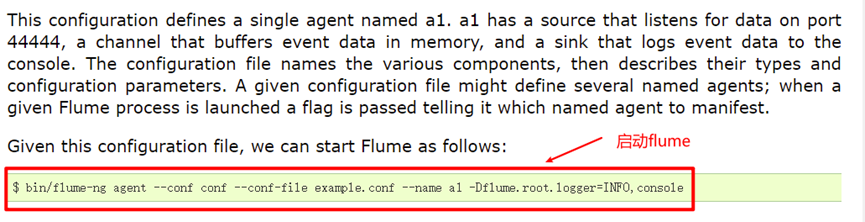
Command details

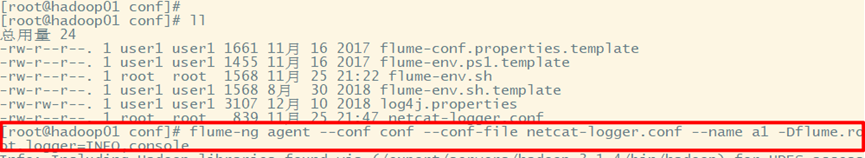
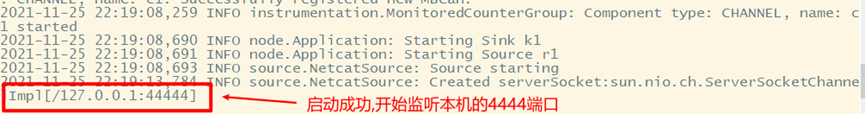
3. Data collection test
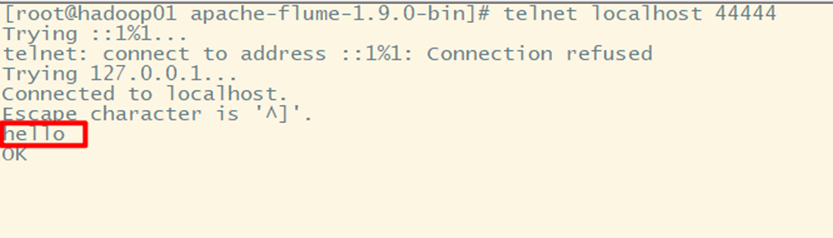
You can use the telnet command to send data to port 444 of this machine
Install telnet first


After installing Telnet, start telnet
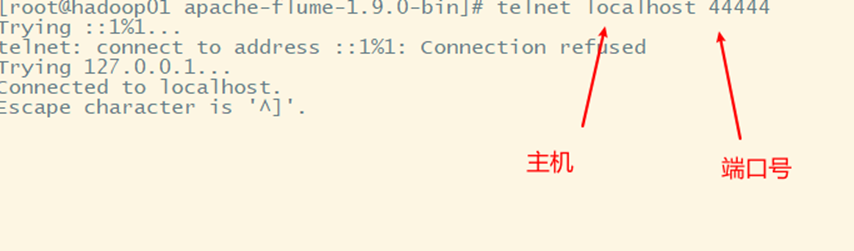
Send data at telnet
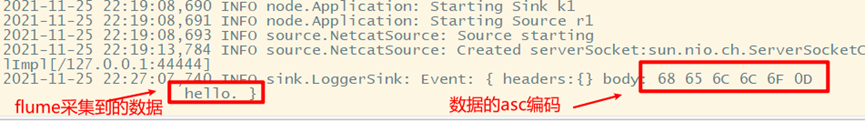
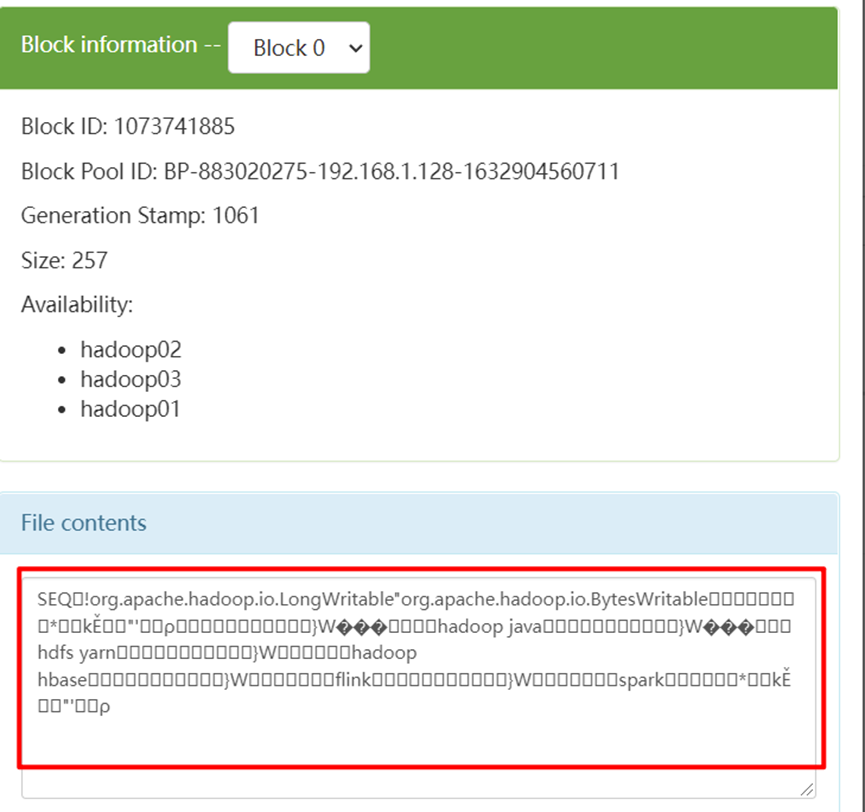
 Data collected after flume is short:
Data collected after flume is short:
4, Case 1: monitor the change of a folder and save the new file collection to hdfs
If a new file is generated in a folder (log folder) under the collection server, the data in the file will be transferred to a folder on hdfs
1. The acquisition scheme needs to determine three parts
Data source: view the official website

Data sinking:
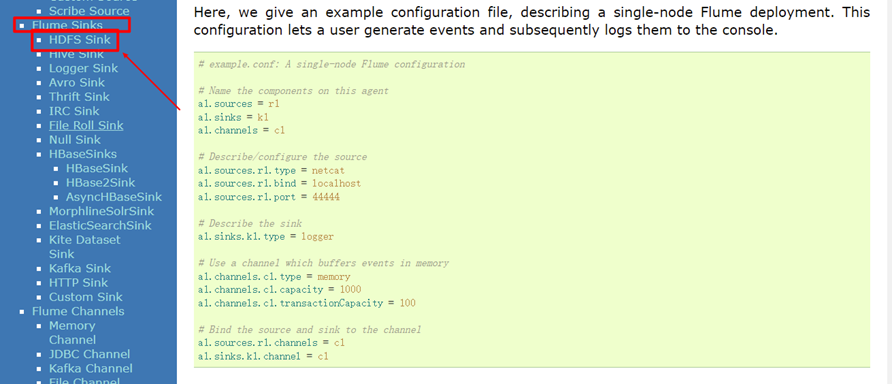
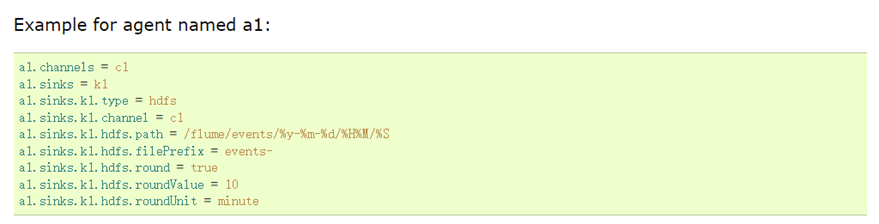
2. Acquisition profile:
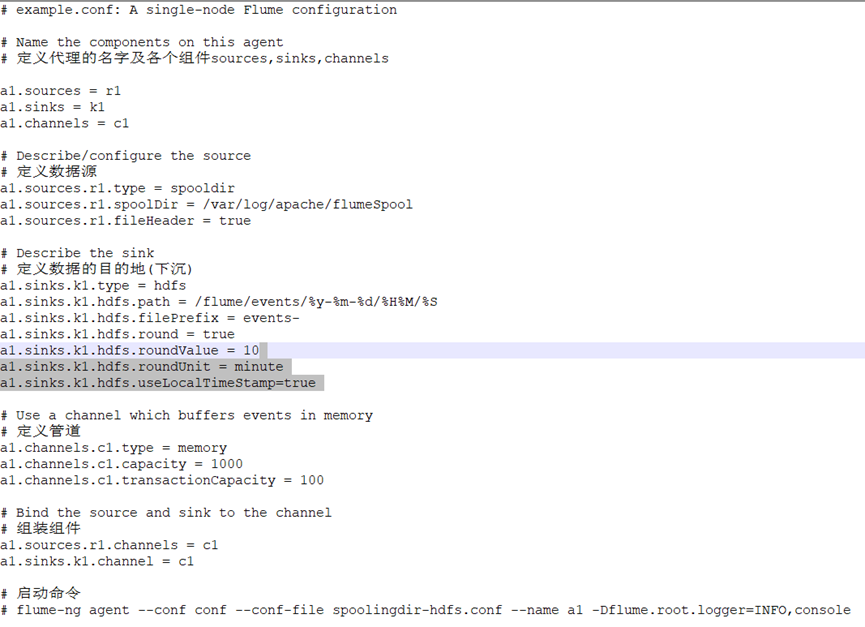
Final profile:
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent # Define the name a1 of the agent and the components sources, sinks, and channels a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source # Define data source a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /var/log/apache/flumeSpool a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true # Describe the sink # Define the destination of the data (sink) a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/events/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events- a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # Define pipe a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel # Assembly components a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 # Start command # flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file conf/spoolingdir-hdfs.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
3. Start flume

4. Test
Flume will detect whether a new file is generated in the / var/log/apache/flumeSpool / folder, upload a file to the folder, and flume will upload the file to the hdfs cluster,
5. An error occurred
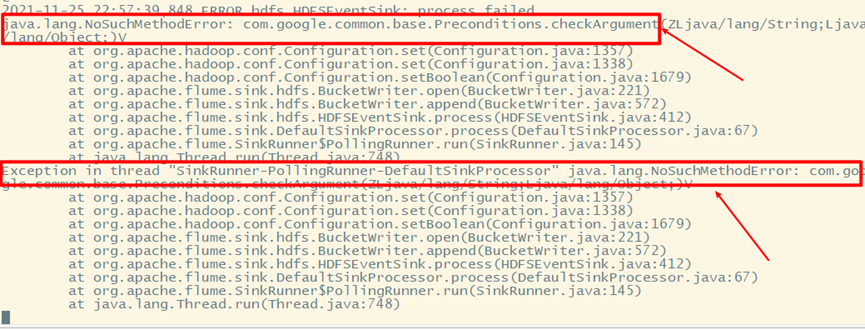
Caused by inconsistent guava versions
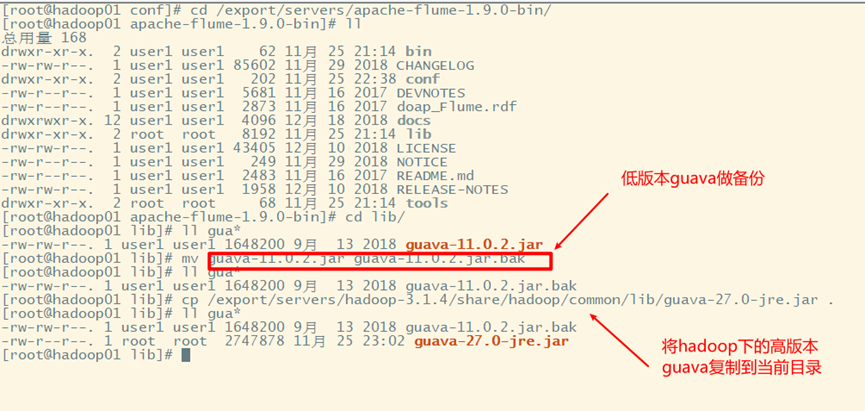
6. Restart flume and upload a file to the log folder to view the results
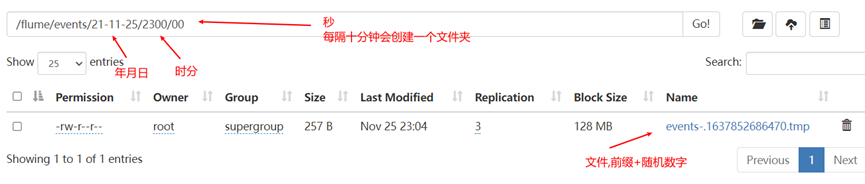
If the file is garbled, it indicates that the collection scheme needs to be improved
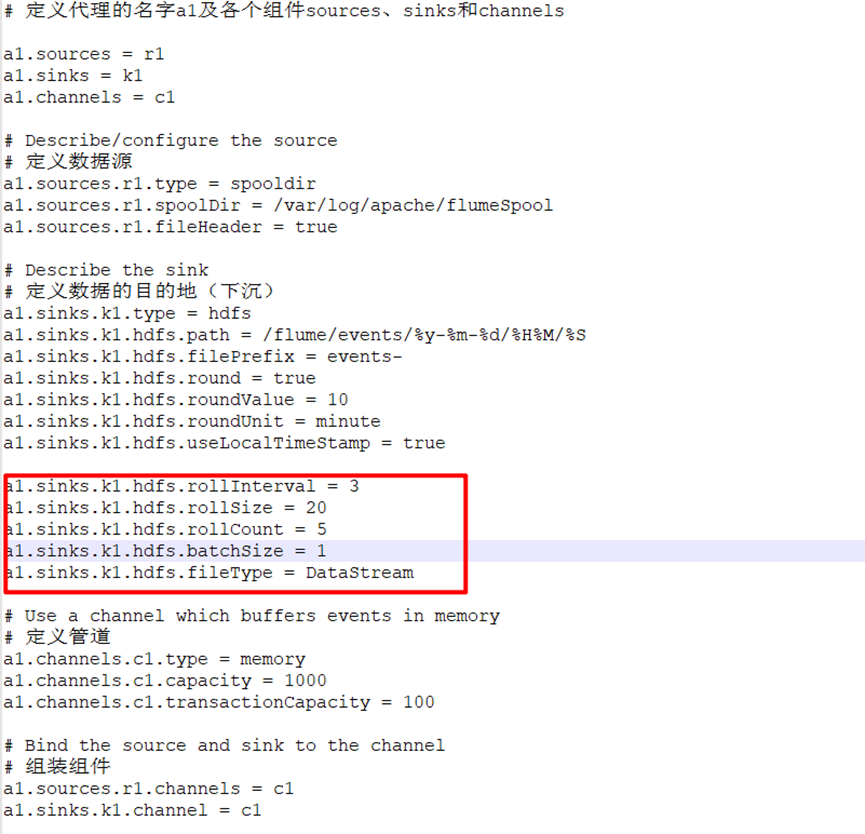
7. Modify the acquisition scheme, restart flume and upload the file test results
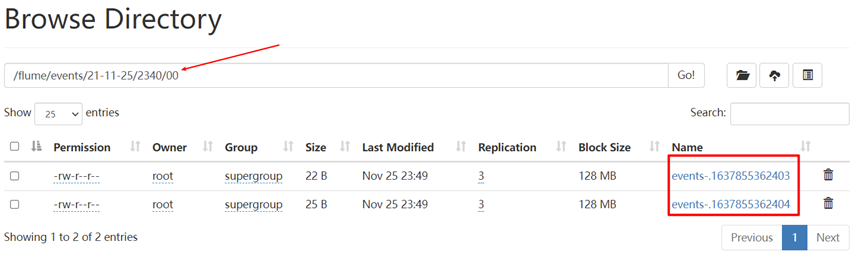
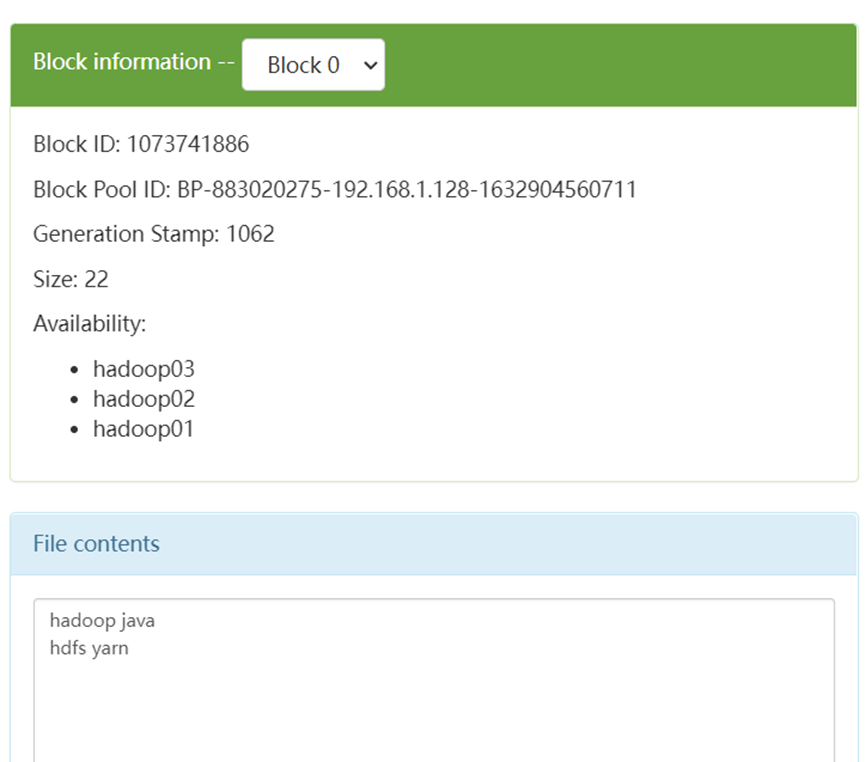
There's no garbled code
5, Case 2: monitor the change of a file and store the changed content on hdfs
1. Acquisition scheme
data source
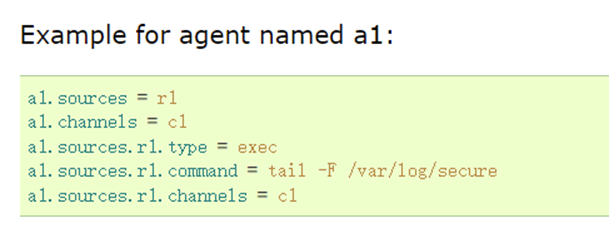
Do not modify the data
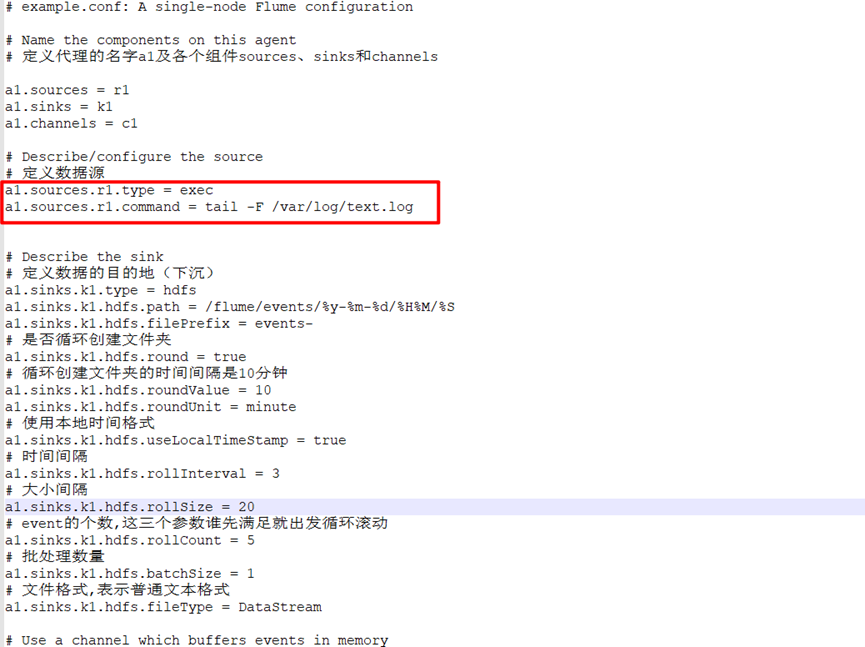
Configuration code:
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent # Define the name a1 of the agent and the components sources, sinks, and channels a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source # Define data source a1.sources.r1.type = exec a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /var/log/text.log # Describe the sink # Define the destination of the data (sink) a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/events/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events- # Create folder circularly a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true # The time interval for circular folder creation is 10 minutes a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute # Use local time format a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true # time interval a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 3 # Size interval a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 20 # The number of event s. Whoever satisfies these three parameters first will start the loop scrolling a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 5 # Batch quantity a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 1 # File format, representing normal text format a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # Define pipe a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel # Assembly components a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 # Start command # flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file conf/exec-hdfs.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
2. Test acquisition function
Simulation scenario
First write a shell script to continuously output the current date to the monitoring file / var / log / test Log, the file that simulates the server log

3. Clone another session and view the new content

4. Start flume

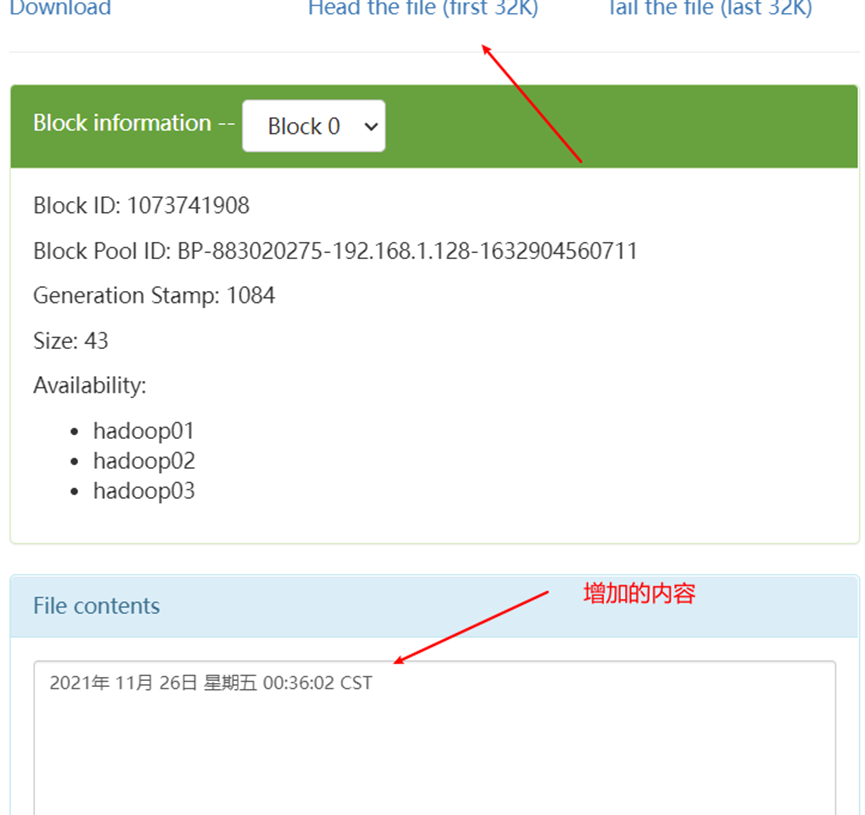
5. View the results on HDFS
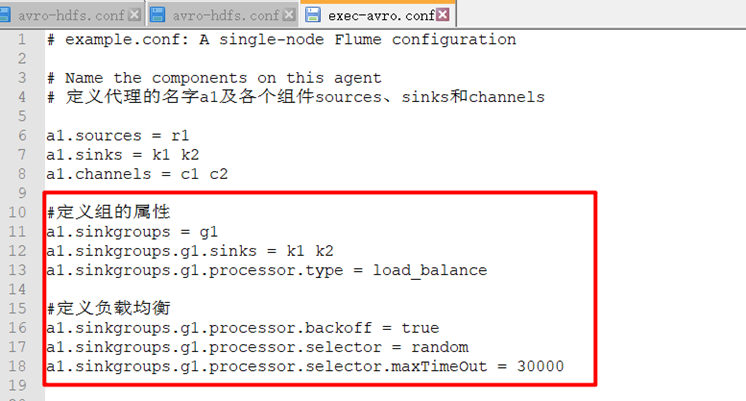
6, Flume's reliability assurance - load balancing
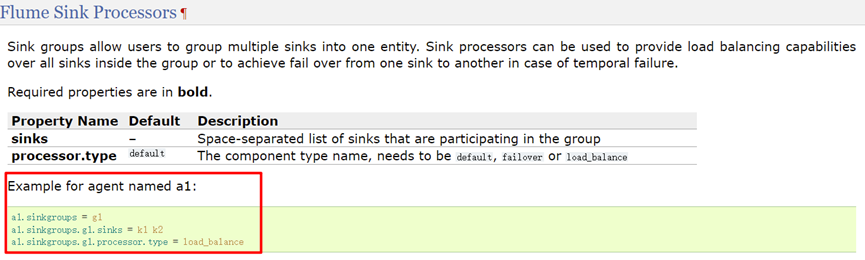
The configured acquisition scheme is to receive the subsequent required data through the only Sink as the receiver, but the current Sink failure or large amount of data collection requests may occur. At this time, a single Sink configuration may not guarantee the reliability of Flume development. Therefore, Flume provides Flume Sink Processors to solve the above problems.
The sink processor allows you to define Sink groups and group multiple sinks into one entity. The sink processor can provide load balancing functions for services through multiple sinks in the group.
1. Build and configure flume cluster
flume cluster of three servers: Hadoop 01, Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03
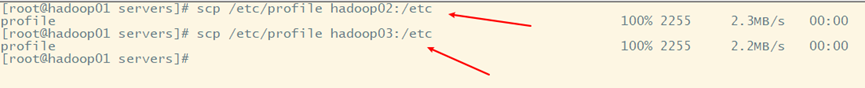
1) Distribute the flume file on Hadoop 01 to Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03


2) Distributing environment variable profiles
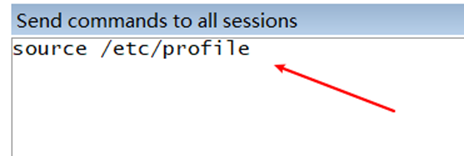
3) Make environment variables work
2. Configure acquisition scheme
1) View an example of an official document
2) Configure the first level acquisition scheme on Hadoop 01
Two level configuration scheme
Avro

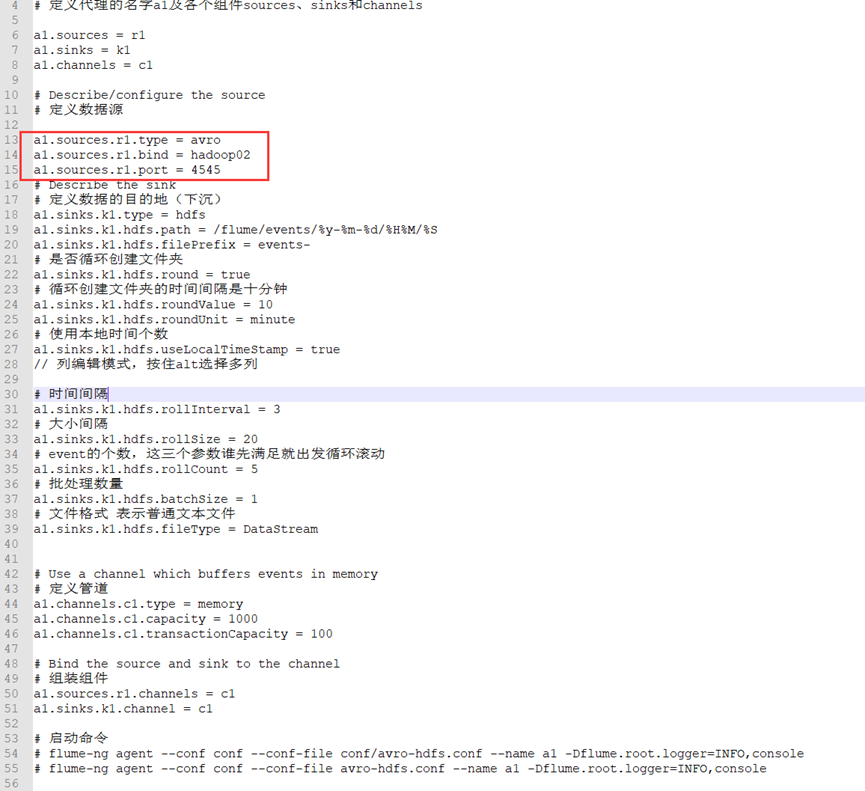
code:
3) Configure the second level scheme on Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03
Hadoop02:
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent # Define the name a1 of the agent and the components sources, sinks, and channels a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 c2 #Define the properties of the group a1.sinkgroups = g1 a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance #Define load balancing a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = random a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector.maxTimeOut = 30000 # Describe/configure the source # Define data source a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r1.type = exec a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /var/log/test1.log # Describe the sink # Define destination 1 of data (sinking) a1.sinks.k1.type = avro a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop02 a1.sinks.k1.port = 4545 # Define Destination 2 of data (sinking) a1.sinks.k2.type = avro a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop03 a1.sinks.k2.port = 4545 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # Define pipe a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Start command # flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file conf/exec-avro.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console # flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file exec-avro.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
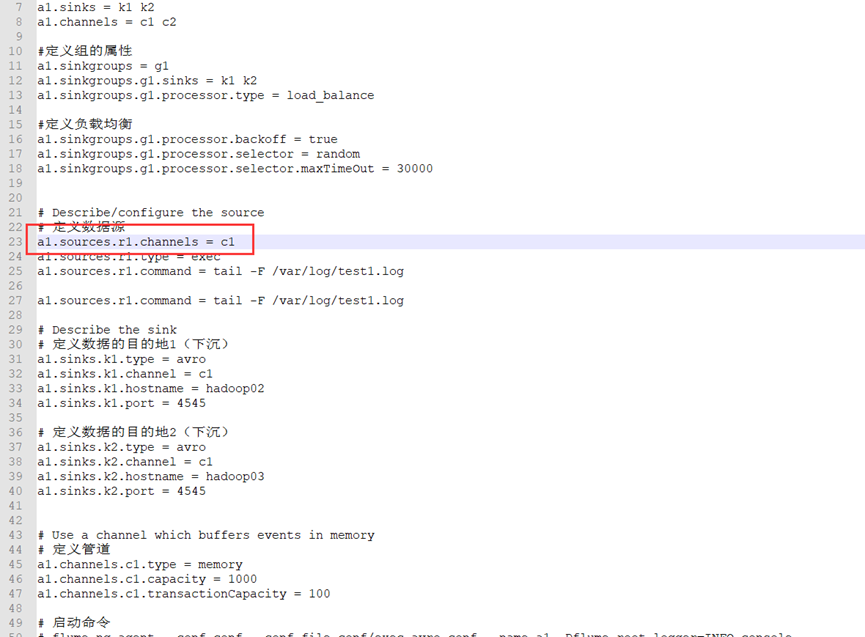
code:
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent # Define the name a1 of the agent and the components sources, sinks, and channels a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source # Define data source a1.sources.r1.type = avro a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop02 a1.sources.r1.port = 4545 # Describe the sink # Define the destination of the data (sink) a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/events/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events- # Create folder circularly a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true # The time interval for circular folder creation is ten minutes a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute # Number of local time used a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true // In column editing mode, press and hold alt to select multiple columns # time interval a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 3 # Size interval a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 20 # The number of event s. Whoever satisfies these three parameters first will start the loop scrolling a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 5 # Batch quantity a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 1 # The file format represents a plain text file a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # Define pipe a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel # Assembly components a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 # Start command # flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file conf/avro-hdfs.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console # flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file avro-hdfs.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
Hadoop03:
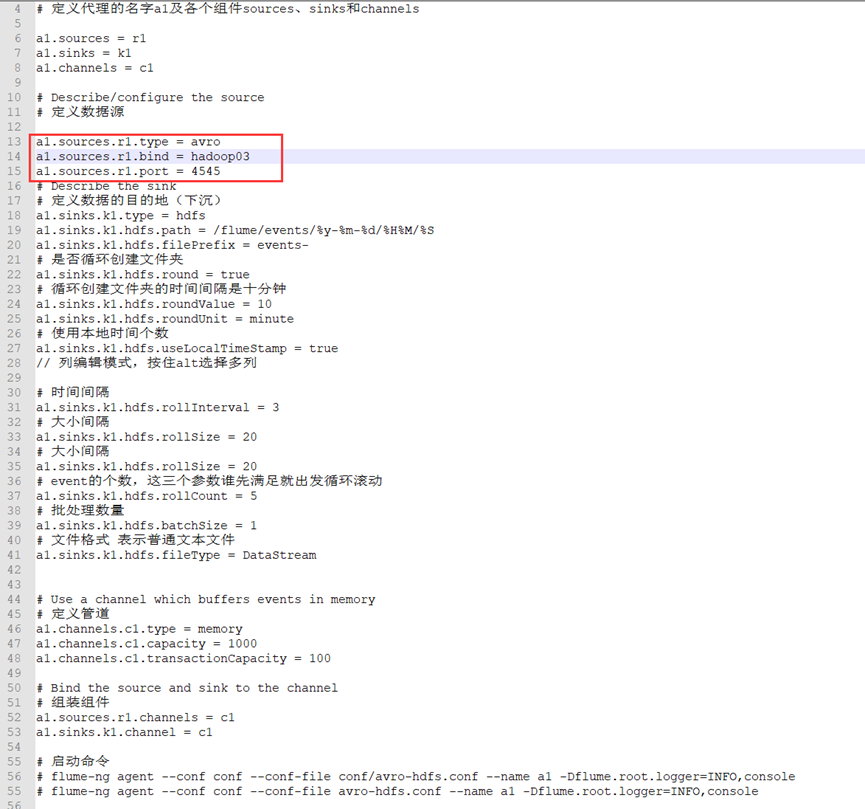
3. Start flume
1) flume on Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03
Start flume from the last level
Hadoop02:
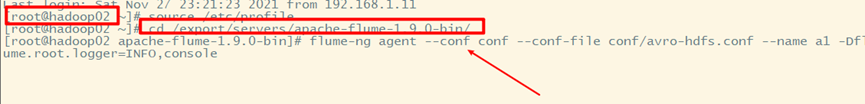
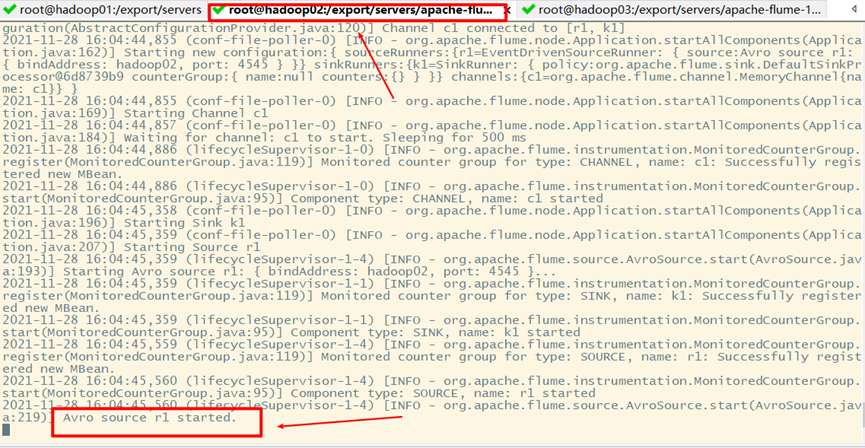
Hadoop03:
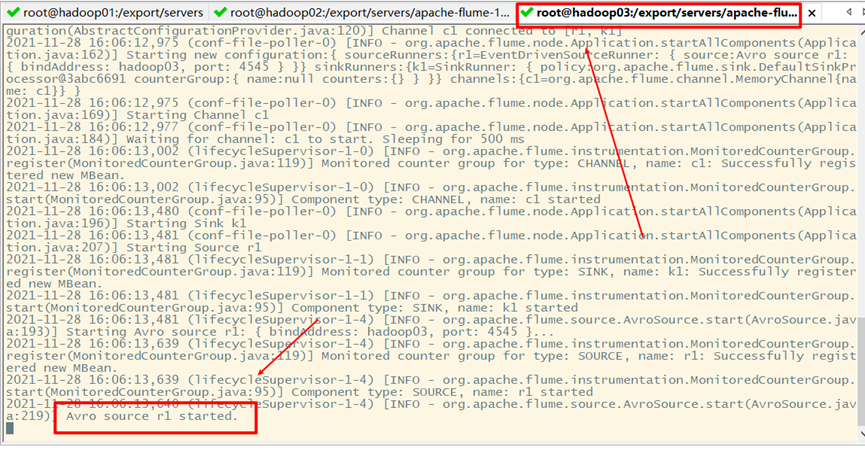
2) Start flume on Hadoop 01
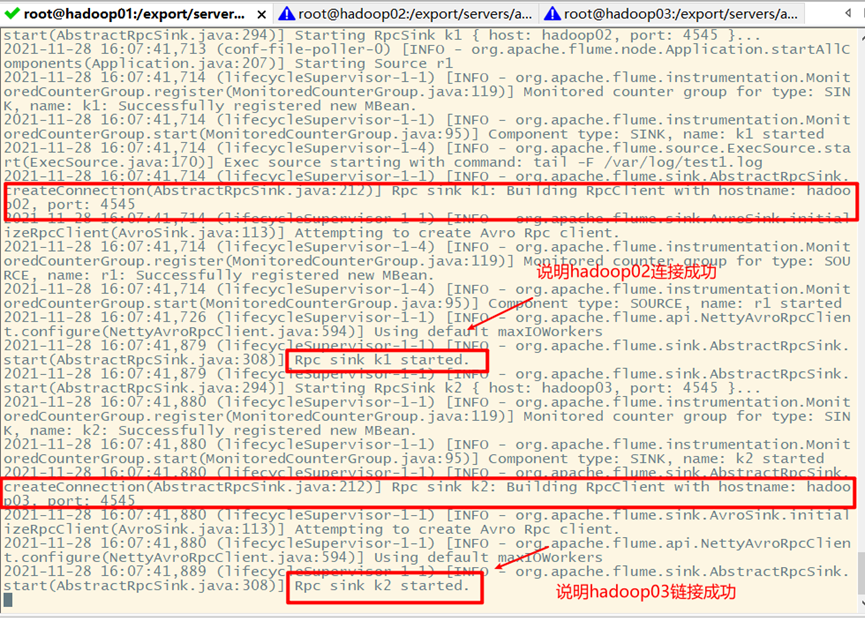
At the same time, it also prompts that the connection is successful on Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03
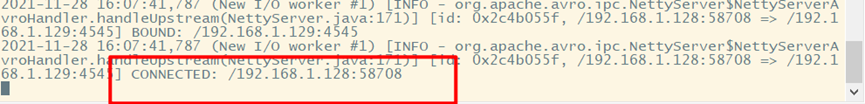
4. Load balancing test
Clone a session of Hadoop 01, write a script and run it
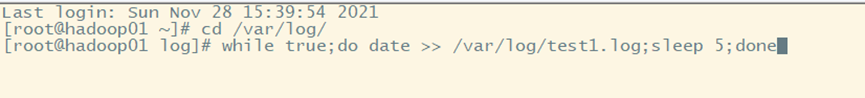
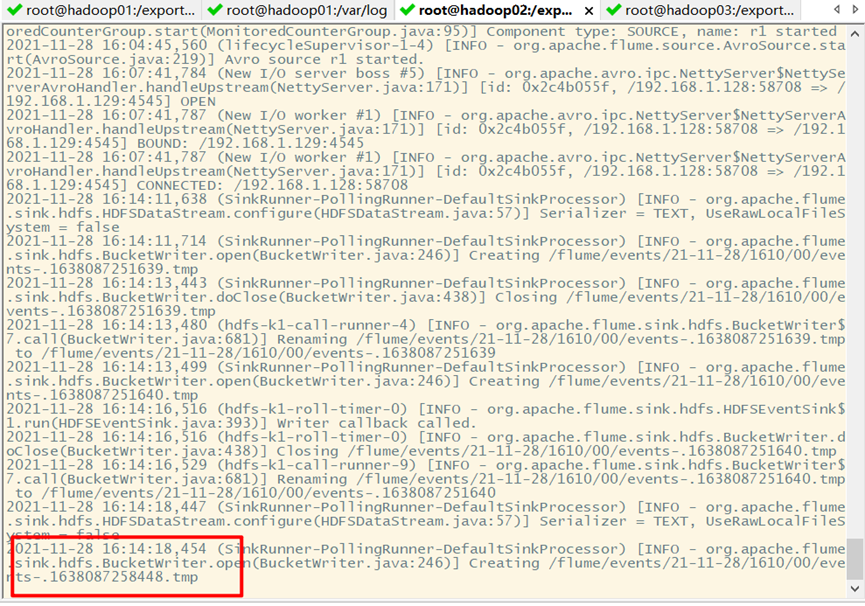
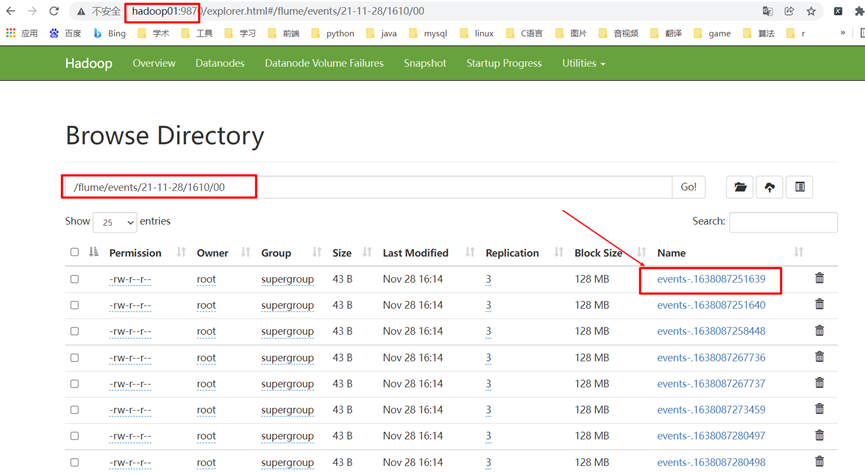
5. View results
Hadoop02:
Hadoop03:
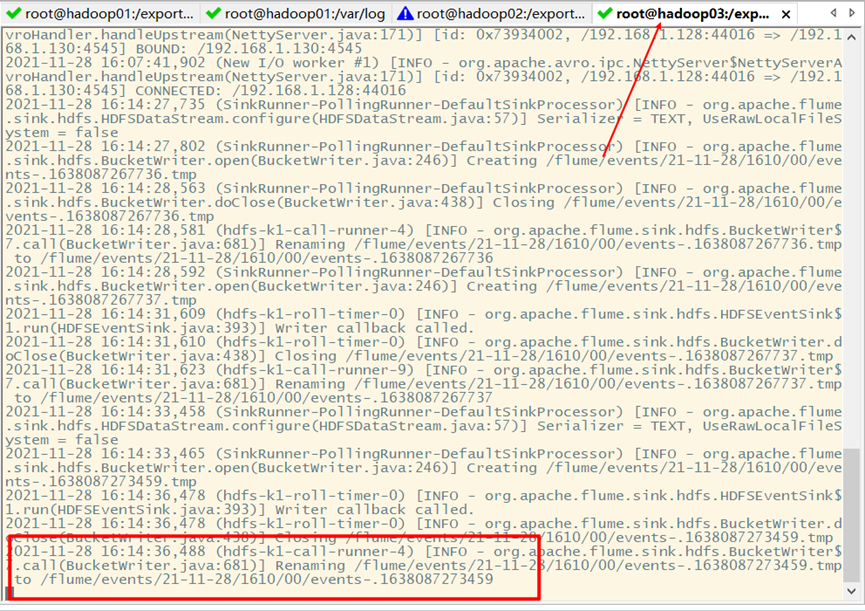
On Hadoop cluster:
7, Flume's reliability assurance - fault recovery

1. Configure acquisition scheme
Only part of the first level acquisition scheme needs to be changed
Change to fault recovery:
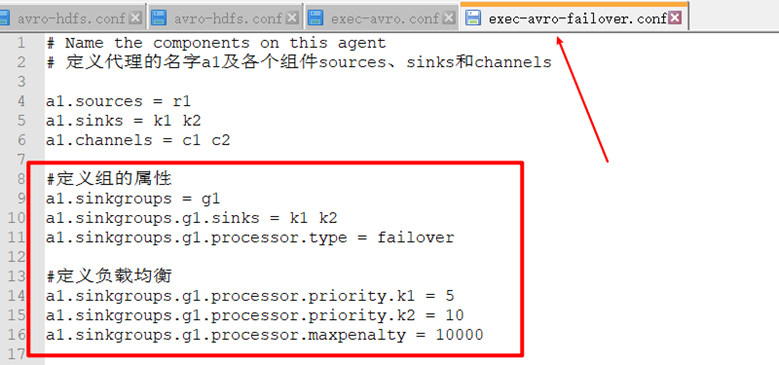
The second level acquisition scheme does not need to be modified
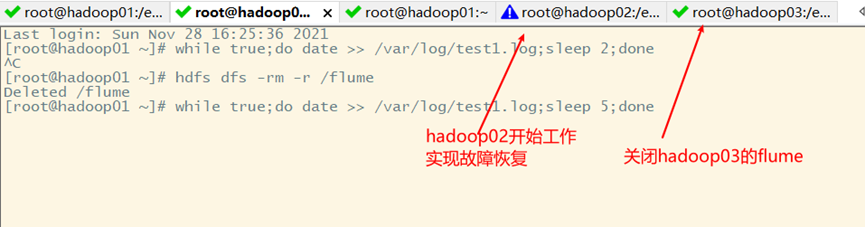
2. Start flume
Start flume from the last level
Restart the test script
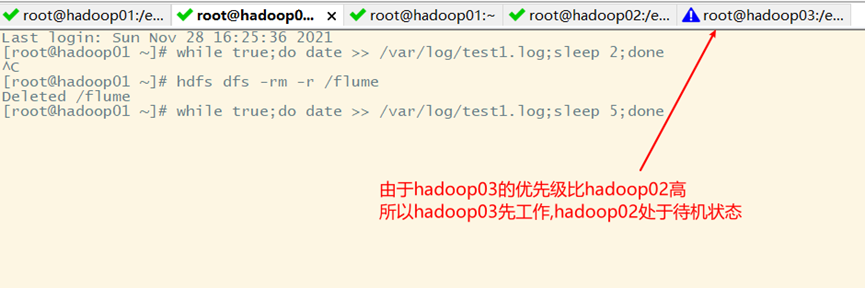
3. Fault recovery
Turn off the flume of Hadoop 03 and wait for ten seconds (timeout, defined in the acquisition scheme)
8, Flume interceptor
1. Scenario:
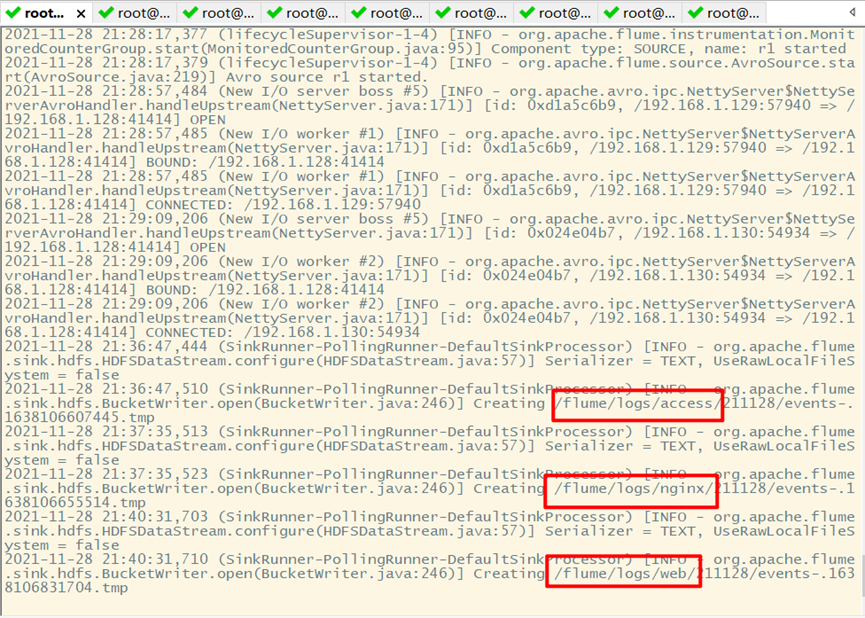
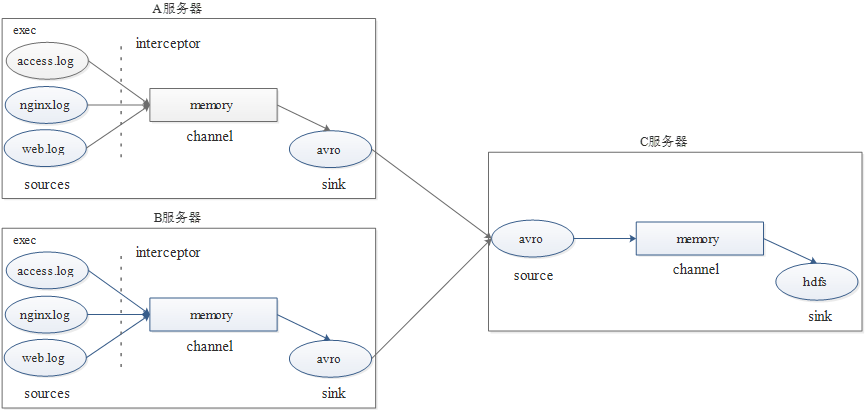
In the actual application scenario, two servers A and B generate log data in real time. The log type is mainly access log,nginx.log and web log. Now you need to access the log data generated by servers A and B log,nginx.log and web Log is collected and summarized on server C, and uniformly collected and uploaded to HDFS file system for saving. The files storing log data in HDFS must be classified and counted according to the following requirements (20180723 represents the current date of collecting log data):
/source/logs/access/20180723/**
/source/logs/nginx/20180723/**
/source/logs/web/20180723/**
2. Flow chart of log data collection
3. Configuration files of Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent # Define the name a1 of the agent and the components sources, sinks, and channels a1.sources = r1 r2 r3 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source # Define r1 data source a1.sources.r1.type = exec a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /var/log/access.log # Define interceptor r1 a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = static a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.key = type a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.value = access # Define r2 data sources a1.sources.r2.type = exec a1.sources.r2.command = tail -F /var/log/nginx.log # Define interceptor r2 a1.sources.r2.interceptors = i2 a1.sources.r2.interceptors.i2.type = static a1.sources.r2.interceptors.i2.key = type a1.sources.r2.interceptors.i2.value = nginx # Define r3 data sources a1.sources.r3.type = exec a1.sources.r3.command = tail -F /var/log/web.log # Define interceptor r3 a1.sources.r3.interceptors = i3 a1.sources.r3.interceptors.i3.type = static a1.sources.r3.interceptors.i3.key = type a1.sources.r3.interceptors.i3.value = web # Describe the sink # Define the destination of the data (sink) a1.sinks.k1.type = avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop01 a1.sinks.k1.port = 41414 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # Define pipe a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel # Assembly components a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r2.channels = c1 a1.sources.r3.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 # Start command # flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file conf/exec-avro.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
4. Collection scheme configuration file on Hadoop 01
# Name the components on this agent
# Define the name a1 of the agent and the components sources, sinks, and channels
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
# Define data source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop01
a1.sources.r1.port = 41414
#Define interceptor
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = timestamp
# Describe the sink
# Define the destination of the data (sink)
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/logs/%{type}/%y%m%d
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events-
# Create folder circularly
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
# The time interval for circular folder creation is ten minutes
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
# Number of local time used
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
// In column editing mode, press and hold alt to select multiple columns
# time interval
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 0
# Size interval
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 10485760
# The number of event s. Whoever satisfies these three parameters first will start the loop scrolling
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
# Batch quantity
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 10
# The file format represents a plain text file
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat = Text
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.threadsPoolSize=10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.callTimeout=30000
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
# Define pipe
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
# Assembly components
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
# Start command
# flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file conf/avro-hdfs.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
5. Start flume
Start flume on Hadoop 01 first
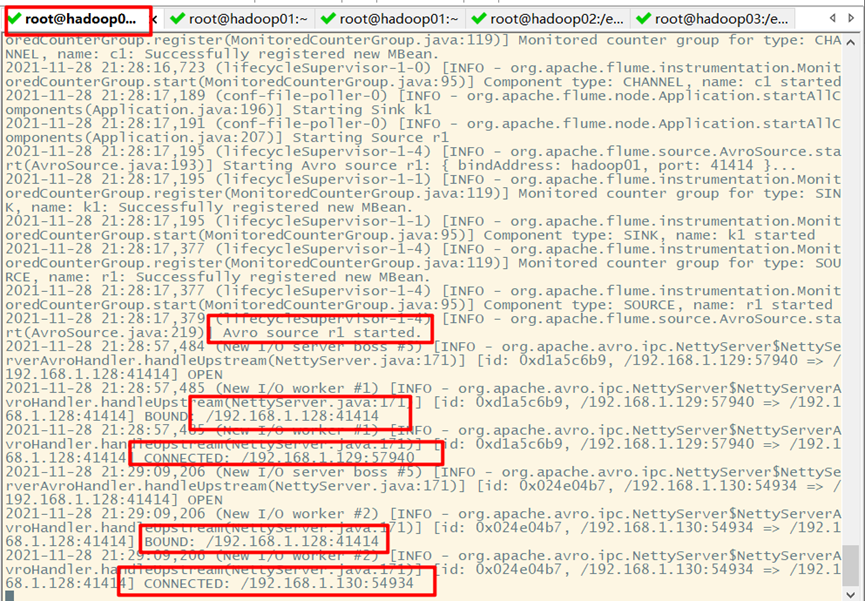
Restart flume on Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03
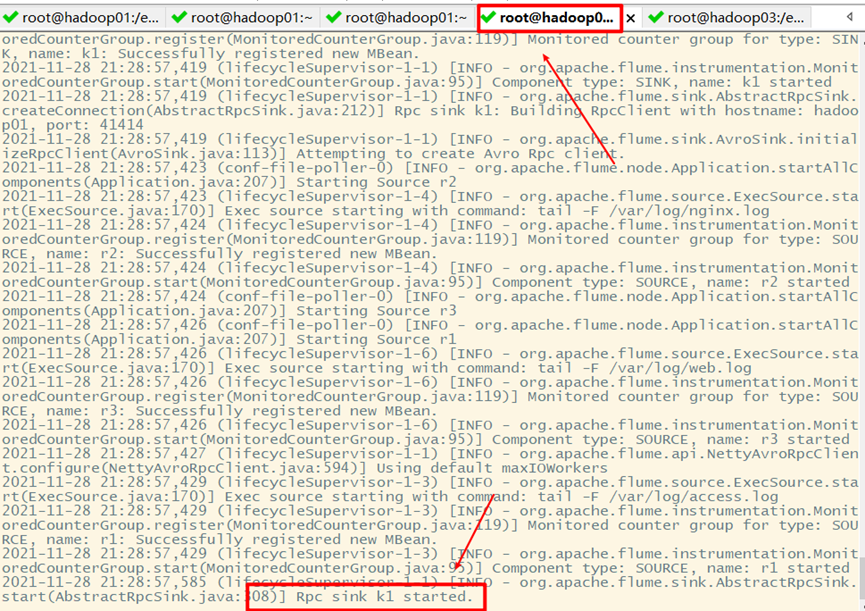
6. Test effect
Clone three sessions on Hadoop 02 and Hadoop 03, and execute the following three scripts to generate production log data
while true;do echo "access log ......" >> /var/log/access.log;sleep 5;done



result: