All content is a video recording of madness teacher's station B
MyBatisPlus Complete Tutorial B-Station Video for Crazy Java
brief introduction
MyBatis-Plus (opens new window) (MP) is an enhancement tool for MyBatis (opens new window). On the basis of MyBatis, only enhancements are made and no changes are made to simplify development and increase efficiency.

(<''<) Very interesting
Mybatis-Plus feature
- Non-intrusive: Enhance without changing, introduce without affecting existing projects, silky smooth
- Low loss: automatic injection of basic CURD at startup, basic lossless performance, direct object-oriented operation, BaseMapper
- Powerful CRUD operations: Built-in generic Mapper, generic Service, most CRUD operations on forms can be achieved with only a few configurations, more powerful conditional constructor, to meet all kinds of usage needs, simple CRUD operations in the future, do not have to write your own!
- Supports Lambda-style calls: through Lambda expressions, it is easy to write various query conditions without worrying about field errors
- Supports auto-generation of primary keys: supports up to four primary key strategies (including distributed unique ID generator-Sequence), can be configured freely, and perfectly solves primary key problems
- Supports ActiveRecord mode: supports ActiveRecord form calls, and entity classes can perform powerful CRUD operations simply by inheriting Model classes
- Support for custom global common operations: support for global common method injection (Write once, use anywhere)
- Built-in code generator: Use code or Maven plug-ins to quickly generate Mapper, Model, Service, Controller layer code, support template engine, and more custom configurations to use (automatically help you generate code)
- Built-in Paging Plug-in: Based on MyBatis physical paging, developers don't need to worry about specific operations. Once the plug-in is configured, writing paging is equivalent to a normal List query
- Paging plug-ins support multiple databases: MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle, DB2, H2, HSQL, SQLite, Postgre, SQLServer and many other databases
- Built-in performance analysis plug-in: can output Sql statements and their execution time, it is recommended to enable this feature when developing tests to quickly pick up slow queries
- Built-in global interception plug-in: provides full table delete, update operation smart analysis blocking, or can customize interception rules to prevent misoperation
Quick Start
Official Links
1. Create a database, create a User table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Full name',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Age',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
2. Insert data
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES (1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'), (2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'), (3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'), (4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'), (5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');
3. Create a SpringBoot project
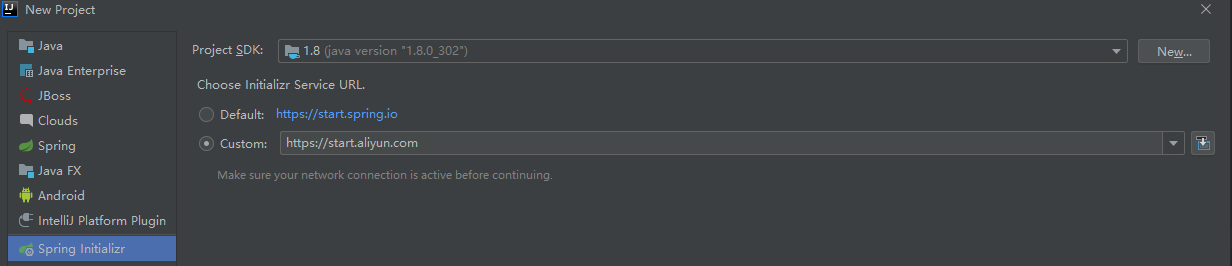
Watch out for this dependency

4. In addition to the old dependencies:
<!-- Database Driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Note the version here!!! -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
Note that the version number of MyBatisPlus here is 3.0 as mad as it is. 5
5. Connect to the database
configuration file
#Database Connection Configuration spring.datasource.username= #Fill in your own spring.datasource.password= #Fill in your own #mysql5 #Mac Note that add secure connection useSSL=false, mybatis_plus Be careful to fill in your own database name spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #Mysql8 8 needs to increase the time zone configuration serverTimezone=GMT%2B8 spring.datasource.username= #Fill in your own spring.datasource.password= #Fill in your own #Mac note that adding a secure connection to the back is false useSSL=false, mybatis_plus Be careful to fill in your own database name spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
6. Write entity classes
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
7. Write mapper interfaces for entity classes
package com.ggqq.mybatisplus.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.ggqq.mybatisplus.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
//Inherit a base interface BaseMapper on the corresponding interface
@Repository //This annotation represents the persistence layer
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
//The generic passed in here is the object of the subsequent CRUD
//All CRUD operations are written without having to configure a bunch of files as before
}
8. Add the @MapperScan annotation to the main startup class
package com.ggqq.mybatisplus;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
//Scan our mapper folder
@MapperScan("com.ggqq.mybatisplus.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class MybatisplusApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisplusApplication.class, args);
}
}
9. Test

package com.ggqq.mybatisplus;
import com.ggqq.mybatisplus.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.ggqq.mybatisplus.pojo.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisplusApplicationTests {
//Inherited BaseMapper, all methods are from the parent class,
// We can also write our own extension methods!
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//Parameter is a wrapper, conditional constructor, we don't need null here
//Query all users
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
10. Results
User(id=1, name=Jone, age=18, email=test1@baomidou.com) User(id=2, name=Jack, age=20, email=test2@baomidou.com) User(id=3, name=Tom, age=28, email=test3@baomidou.com) User(id=4, name=Sandy, age=21, email=test4@baomidou.com) User(id=5, name=Billie, age=24, email=test5@baomidou.com)
Configuration Log
All of our SQLs are invisible and we want to know how they are performing, so configure the log to know
#Configure log-impl:Log implementation mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
Execute the test class again:
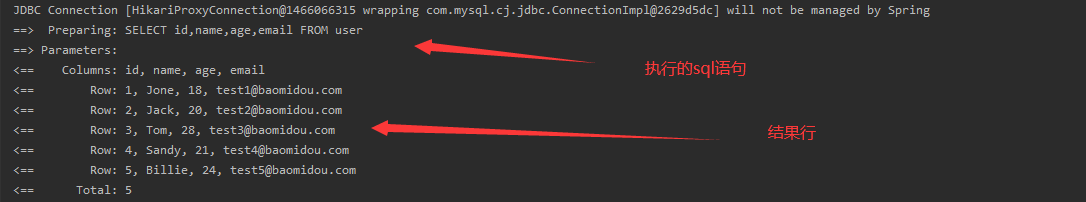
CRUD Extension
Insert
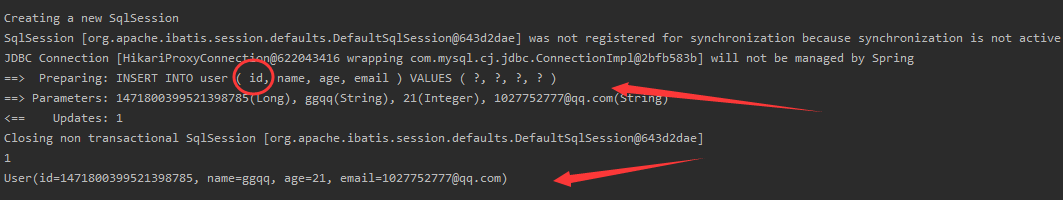
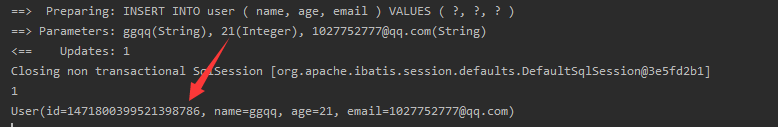
We can see that the sql statement printed in the log has an id, and we insert it without assigning a value to the user object
The insertion just made in the database is accompanied by a series of weird numbers
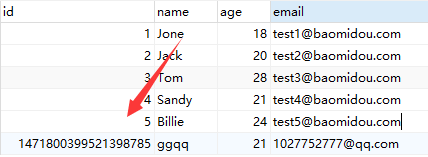
This id is actually the global unique id generated by the MyBatisPlus primary key generation strategy Snowflake algorithm
Distributed System Unique Id Generation: https://www.cnblogs.com/haoxinyue/p/5208136.html
Primary key generation policy:
Configure @TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) on the entity class field Click TableId to see the source code:
package com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation;
public enum IdType {
AUTO(0), //Database id self-increasing
NONE(1), //No primary key set
INPUT(2),//Manual Input
ID_WORKER(3),//Globally unique id
UUID(4),//Globally unique ID UUID
ID_WORKER_STR(5);// ID_WORKER string representation
...
}
Default: ID_WORKER Globally Unique Id (Snowflake algorithm used)
Snowflake algorithm:
snowflake is an open source distributed ID generation algorithm for Twitter, resulting in a long ID. Its core idea is to use 41 bits as milliseconds, 10 bits as machine ID (5 bits are data centers (Beijing, Hong Kong...), 5 bits as machine ID), 12 bits as flow number in milliseconds (meaning 4096 IDs per node per millisecond), and finally one symbol bit, always 0, to ensure almost global uniqueness!
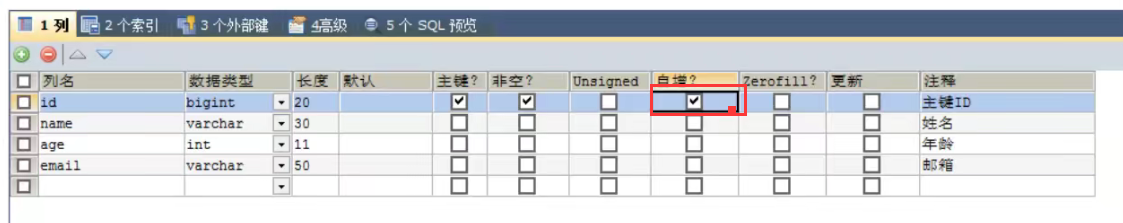
Primary key auto-increment: AUTO requires us to set primary key auto-increment in database tables
1. Configure @TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) on the entity class field
2. Database fields must be self-increasing
You can see that the default id at insertion is id + 1 generated by the last snowflake algorithm
Manual input: INPUT needs to set its own id
For example:
@TableId(type = IdType.INPUT)
private Long id;
//Add values manually when testing methods
user.setId(777L);
Update
@Test//Test Update
public void updateTest(){
User user = new User();
//Automatically stitching dynamic Sql through conditions
user.setId(5L);
user.setName("ggqq");
user.setAge(17);
//Note: updateById, but the parameter is a user
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(i);
}

Auto Fill
Create time, change time! These operations are usually automated and we don't want to update them manually
Alibaba Development Manual: All database tables: gmt_create, gmt_modified needs to be configured! And it needs to be automated
Mode 1: Database level (database modifications are not allowed at work)
1. Add fields to the table: create_ Time, update_ Time (younger brother uses Navicat, check to update according to current timestamp when adding, and manually enter CURRENT_TIMESTAMP in the entry and exit box, if using sqlyog, just like mad teacher)

2. Test the insertion method again, we need to synchronize in the entity class!
private Date createTime; private Date updateTime;
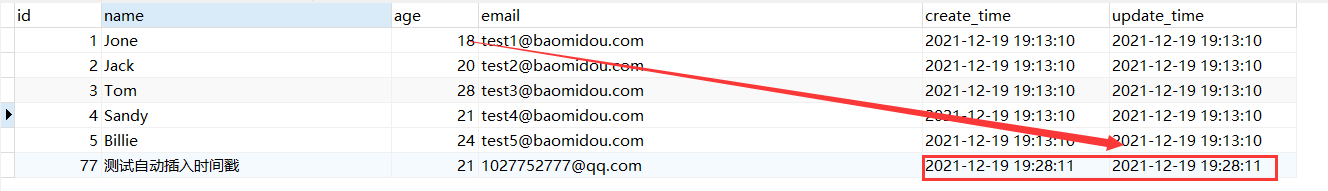
Any insertion during the test will automatically populate the corresponding timestamp
Mode 2: Code level
1. Delete the database field create_time, update_ CRURRENT_of time TIMESTAMP, cancel update based on current timestamp (sqlyog just like mad teacher)

2. Additional annotations are needed on entity class field attributes
//Field Add Fill @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) private Date createTime; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE) private Date updateTime;
3. Write a processor to handle this annotation
Create a new package in the mapper sibling directory
Create class MyMetaObjectHandler
Implement the MetaObjectHandler class:
@Slf4j//Print Log
@Component//Don't forget to add the processor to the Ioc container!
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
//Filling strategy at insert time
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start insert fill......");
// //setFieldValByName(String fieldName, Object fieldVal, MetaObject metaObject)
this.setFieldValByName("createTime",new Date(),metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
//Filling strategy when updating
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("start update fill......");
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}
PS: Note to set the id field to: @TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) and set the field auto-increment
Test code:
@Test//Test Insert
public void testInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("Code test auto-insert timestamp");
user.setAge(21);
user.setEmail("1027752777@qq.com");
int insert = userMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println(insert);
System.out.println(user);
}
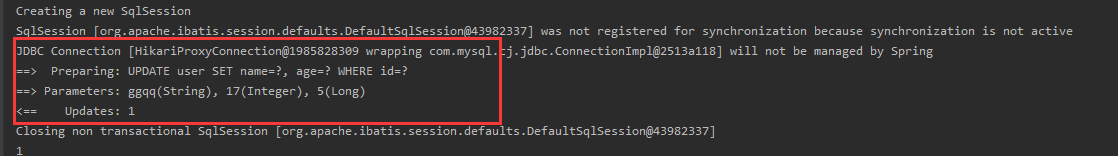
@Test//Test Update
public void updateTest(){
User user = new User();
//Automatically stitching dynamic Sql through conditions
user.setId(78L);//Select IDS already in the table
user.setName("Code test auto-insert timestamp");
user.setAge(17);
//Note: updateById, but the parameter is a user
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println(i);
}
Insert:

To update:
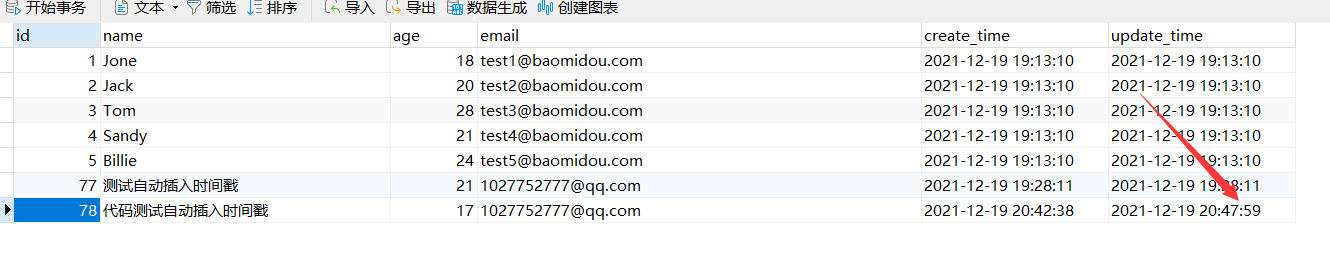
PS: Update the fields that already exist in the note id selection table
Optimistic Lock
During interviews, we are often asked the lock of optimism, the lock of pessimism! This is actually very simple!
Optimistic Lock: The name intentionally is very optimistic, it always thinks there will be no problem, no matter what to do to lock! If there is a problem, update the value again to test the pessimistic lock: the intent is very pessimistic, it always thinks there is always a problem, lock whatever you do! Do it again!
- Let's talk about the Optimistic Lock mechanism here! Optimistic lock implementation:
- Get the current version when the record is taken out
- When updating, bring this version with you
- When performing an update, set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion
- Update fails if version is incorrect
Optimistic lock: 1.Query first to get the version number version = 1 --A update user set name = "ggqq" ,version = version + 1 where id = 2 and version = 1 -- B Threads finish first, at this time version = 2,A Thread update failed update user set name = "ggqq",version = version + 1 where id = 2 and version = 1
Test MP's Optimistic Lock Plugin
1. Add field version to the database
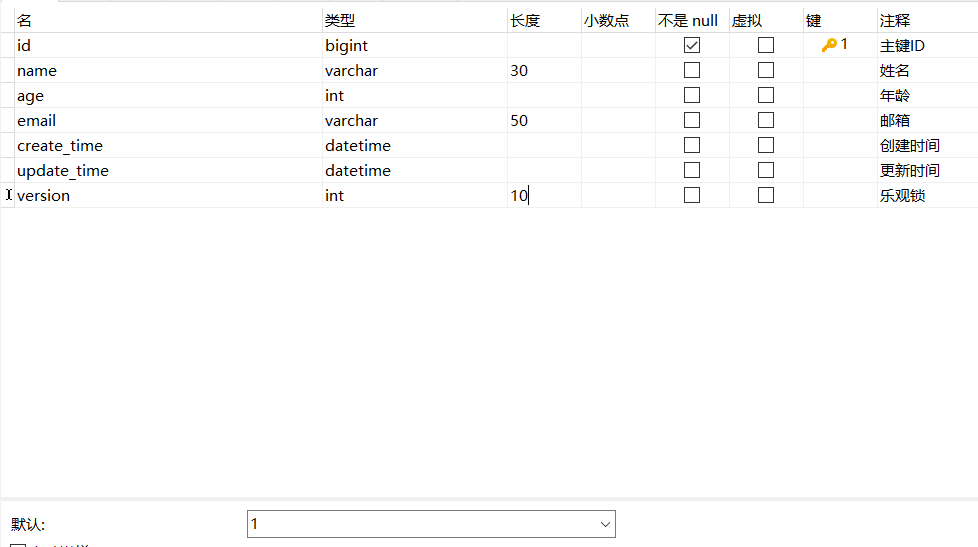
Set default value to 1
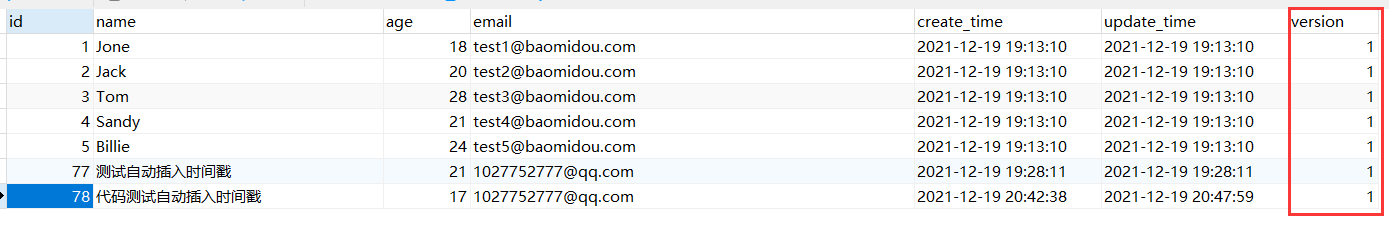
2. Entity class plus version field
@Version//version comment for optimistic locks
private Integer version;
3. Register Components
1. Create packages and configuration classes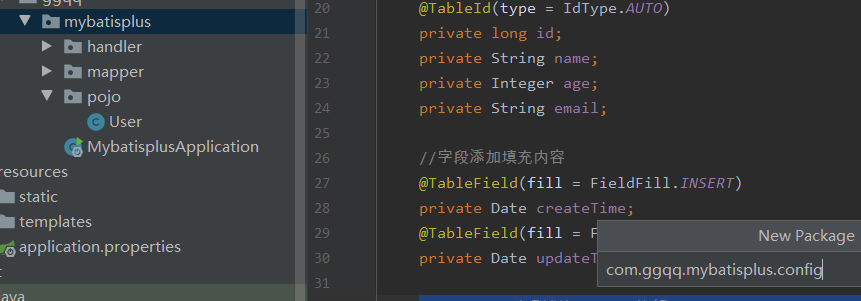

(2) Code:
//Scan our mapper folder
@MapperScan("com.ggqq.mybatisplus.mapper")//Mad teacher used to put this configuration class here for scanning
@EnableTransactionManagement//Automatically manage transactions
@Configuration//Declare Configuration Class
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
//Register Optimistic Lock Plugin
@Bean
public OptimisticLockerInterceptor optimisticLockerInterceptor(){
return new OptimisticLockerInterceptor();
}
}
4. Testing
Success stories
@Test//Single Thread Test Optimistic Lock
public void testOptimisticLocker1(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user.setAge(18);
user.setEmail("10277525777@qq.com");
userMapper.updateById(user);
}

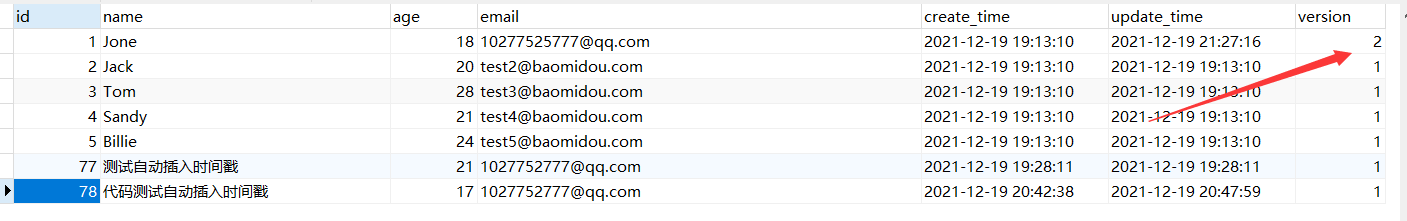
Failure List:
Remember this data

Code:
@Test//Multithreaded test optimistic lock failed
public void testOptimisticLocker2(){
//Thread 1
User user1 = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user1.setAge(1);
user1.setEmail("10277525777@qq.com");
//Simulate another thread and get a copy of the data at the same time
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user2.setAge(2);
user2.setEmail("10277525777@qq.com");
userMapper.updateById(user2);
//Spin lock to try submitting multiple times!
userMapper.updateById(user1);//Overwrite the value of the second thread if there is no optimistic lock
}
Thread 1 can be seen because optimistic lock update failed
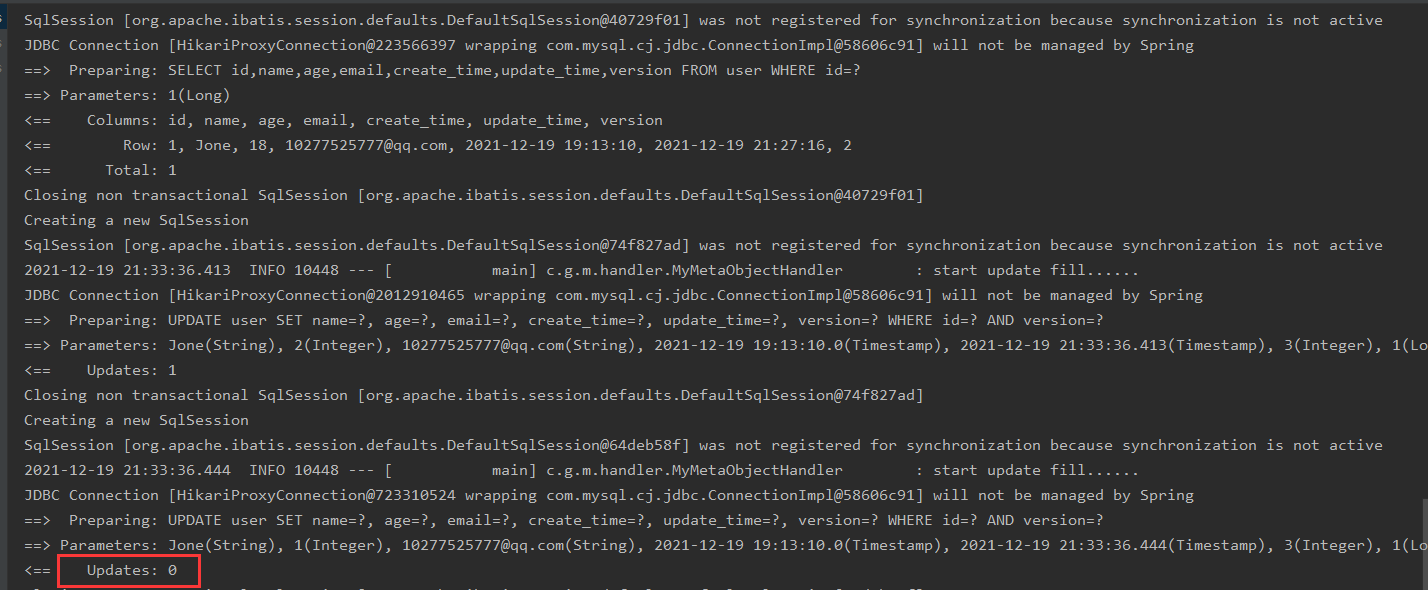
Result:
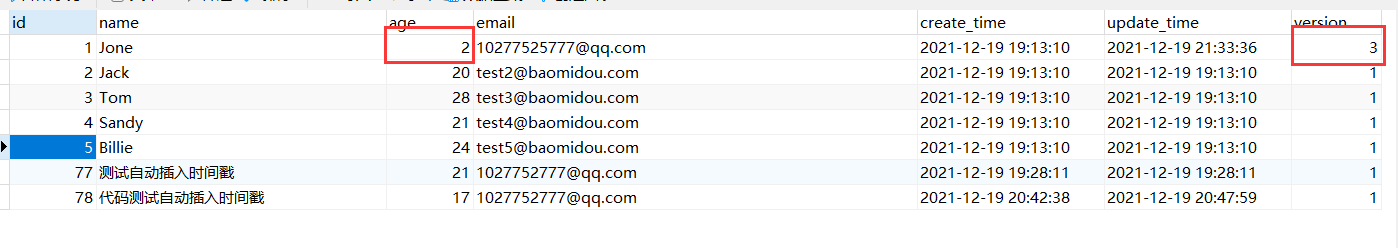
select
(1) Query a single user by id:
@Test//Query a data by id
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println(user);
}

(2) Test batch queries:
@Test
public void testSelectBatchIds(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}

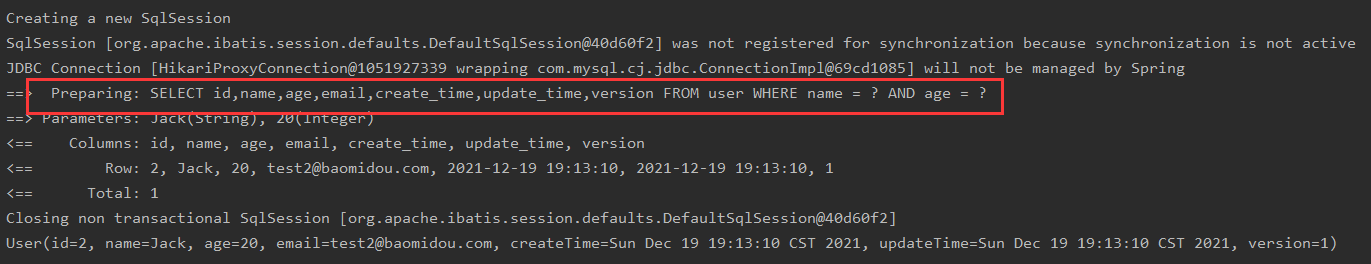
Maps queried conditionally:
@Test
public void testMap(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//Custom Conditions
map.put("name","Jack");
map.put("age",20);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
sql has already written for us
Paging Query
Paging is used a lot on websites!
1. Paging with original limit
2. Page Helper third-party plug-in
3. MP actually has a built-in paging plugin!
How to use
1. Configure Interceptor Components
//jPaginate
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
Test Paging Code:
@Test
public void testPage(){
//Parameter 1, current page
//Parameter 3, page size
Page<User> page = new Page<>(2,3);
userMapper.selectPage(page,null);
page.getRecords().forEach(System.out::print);
}
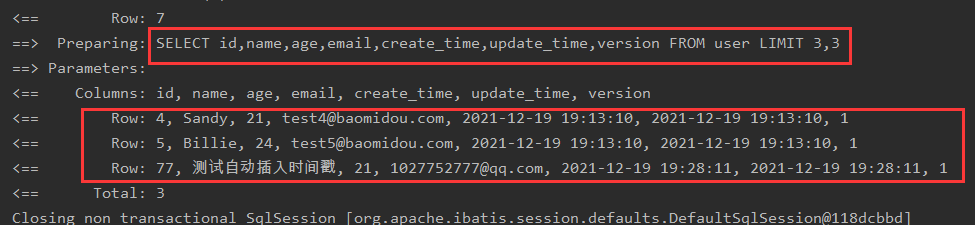
delete
Code:
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
userMapper.deleteById(77L);
}
@Test
public void testDeleteBatchIds(){
//Input a collection
userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(78L,5L));
}
//Conditional Delete
@Test
public void testD(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//key is the column in the table and value is the value to delete the column
map.put("name","Sandy");
userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
}
We will encounter some problems in our work: logical deletion!
Logical Delete
Physical Delete: Remove directly from the database
Logical Delete: Not removed from the database, but invalidated by a variable! Deleted=0 ==> deleted=1
Administrators can view deleted records! Prevent data loss, like a recycle bin!
Test it:
1. Add a deleted field to the data table
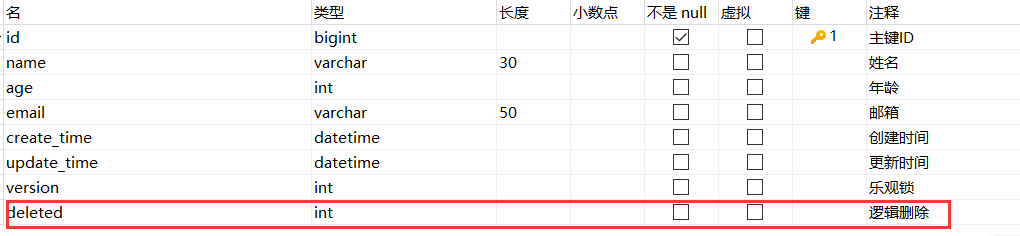
PS: Note to have an initial value of 0
2. Add corresponding attributes to entity classes
@TableLogic//Logically Delete Comments
private Integer deleted;
3. Profile:
//MyBatisPlusConfig
//Logically delete components
@Bean
public ISqlInjector sqlInjector(){
return new LogicSqlInjector();
}
//properties file
#Configuration logic delete 0 delete 1
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0
4. Test Delete:
@Test
public void testDeleteByIdLogic(){
//Logical Delete
userMapper.deleteById(1L);
}
Result:
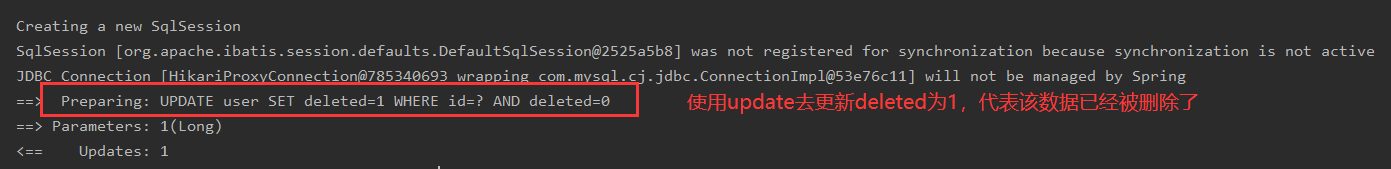

The record is still there, deleted becomes 1
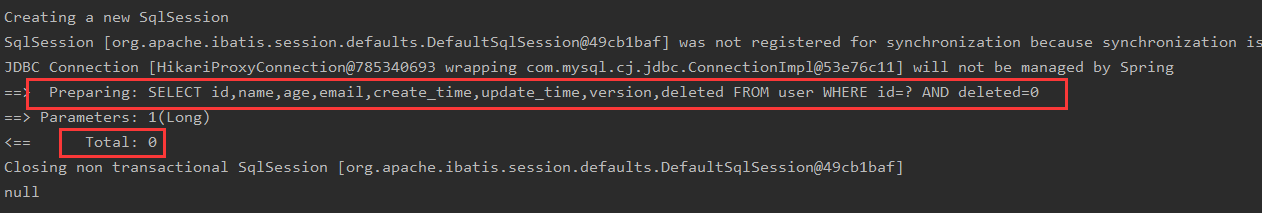
Test the query again for the deleted user and the result is empty:
@Test//Query a data by id
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println(user);
}
Result:
All of the above CRUD operations and their extensions must be mastered! It will greatly improve the efficiency of your work in writing projects!
Performance Analysis Plug-in
In our normal development, we will encounter some slow Sql. Test! druid /.
MP also provides a performance analysis plug-in, if it exceeds this time stop running!
Role: Performance analysis interceptor, which outputs each sql statement and its execution time
Configuration class:
//SQL Execution Efficiency Plug-in
@Bean
@Profile({"dev","test"})//Set up dev development, test environment open to ensure our efficiency
public PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor(){
PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor = new PerformanceInterceptor();
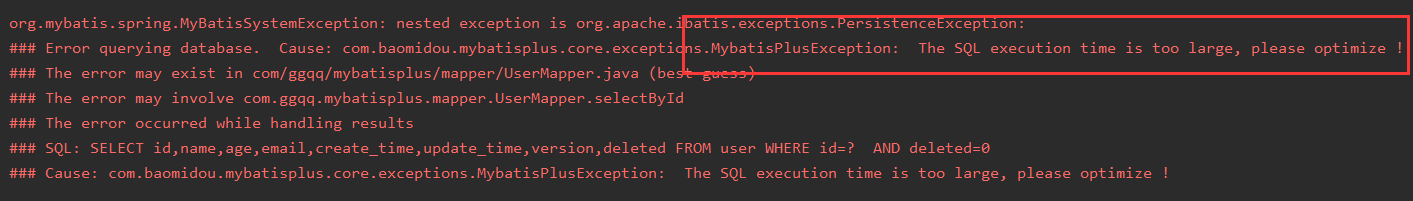
performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(1);//Set sql maximum execution time*ms, if exceeded do not execute
performanceInterceptor.setFormat(true);//Turn on sql formatting
return performanceInterceptor;
}
Configure the environment to be dev or test in SpringBoot!
#Set up development environment spring.profiles.active=dev
Since the maximum execution time of sql is 1ms, almost all queries will time out errors, and the results of executing any test method are as follows:
Modification time is 100ms test, performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(100);
Successful execution:
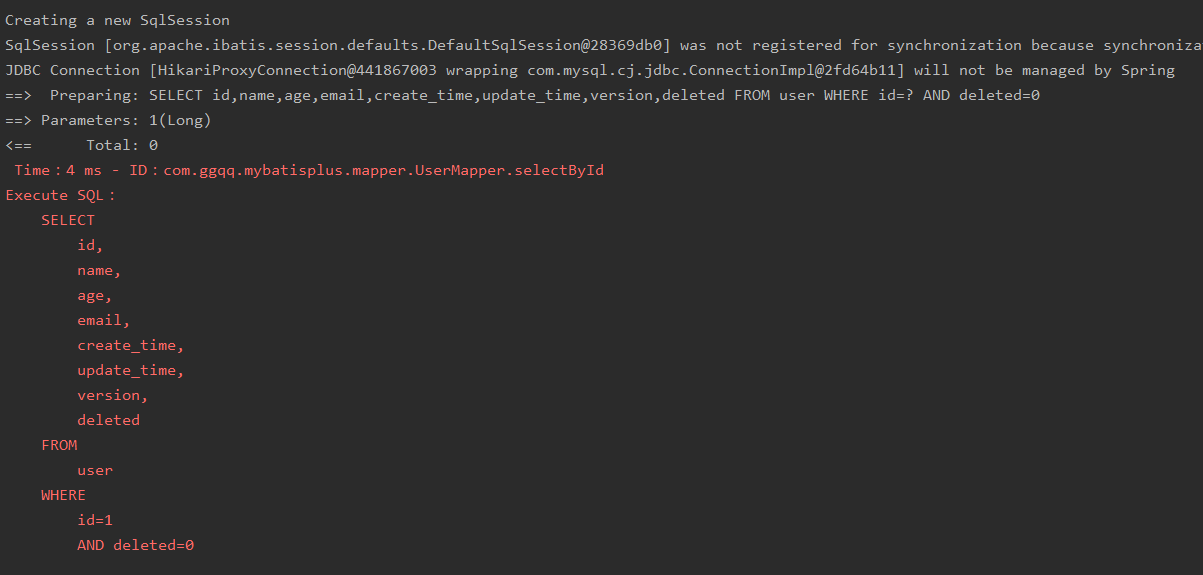
SQL formatting is displayed because of this sentence: performanceInterceptor.setFormat(true)
Conditional constructor
Test code:
@Test
public void test1() {
//Query name is not empty, email is not empty, age is greater than 18 users
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper
.isNotNull("name")
.isNotNull("email")
.ge("age",18);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
public void test2() {
//Query user name=wsk
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("name","jone");
//Use list or map if multiple results occur
User user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
System.out.println(user);
}
@Test
public void test3() {
//Query age for users between 3 and 10
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.between("age", 3, 10);//Interval 3-10
Integer count = userMapper.selectCount(wrapper);//Number of queries count
System.out.println(count);
}
@Test
public void test4() {
//Fuzzy Query
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper
.notLike("name","s") //name NOT LIKE '%s%'
.likeRight("email","com");//email LIKE 'com%'
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = userMapper.selectMaps(wrapper);
maps.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//Inner Query
@Test
public void test5() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//id found in subquery
wrapper.inSql("id","select id from user where id<3"); //id IN (select id from user where id<3)
List<Object> objects = userMapper.selectObjs(wrapper);
objects.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
public void test6() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//Sort descending by id
wrapper.orderByDesc("id");
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
Code generator
AutoGenerator is the code generator for MyBatis-Plus. AutoGenerator can quickly generate code for Entity, Mapper, Mapper XML, Service, Controller and other modules, which greatly improves the development efficiency.
Code:
package com.ggqq.mybatisplus;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.DbType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.FieldFill;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.AutoGenerator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.DataSourceConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.GlobalConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.PackageConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.StrategyConfig;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.po.TableFill;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.rules.DateType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.rules.NamingStrategy;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class AutoCoder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//A code generator object needs to be built
AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator();
//Configuration Policy
//1. Global Configuration
GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig();
//Get Current Directory
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
//Which directory to output
gc.setOutputDir(projectPath+"/src/main/java");
//Set the author name so that each class generated will have
gc.setAuthor("ggqq");
//Whether to open Resource Manager
gc.setOpen(false);
//Whether to overwrite the originally generated
gc.setFileOverride(false);
//I prefix to de-Service
gc.setServiceName("%sService");
//Primary Key Generation Policy
gc.setIdType(IdType.ID_WORKER);
//Date type
gc.setDateType(DateType.ONLY_DATE);
//Setting up swagger documents
gc.setSwagger2(true);
//Drop Configuration to Auto Generator
mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc);
//2. Setting up data sources
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
dsc.setUsername("root");
dsc.setPassword("123456");
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8");
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//Set database type
dsc.setDbType(DbType.MYSQL);
//Drop Data Source into Auto Generator
mpg.setDataSource(dsc);
//3. Configuration of packages
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
//Set module name
pc.setModuleName("daydayup");
//Under which package
pc.setParent("com.ggqq.mybatisplus");
//Set up persistence, mapper, server, and control layers
pc.setEntity("entity");
pc.setMapper("mapper");
pc.setService("service");
pc.setController("controller");
mpg.setPackageInfo(pc);
//4. Policy Configuration
StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig();
//Set the table name to map, you can pass multiple table names
strategy.setInclude("user");
//Table column, name underscore to hump
strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
strategy.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
//Open lombok comment
strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true);
//Configuration Logical Delete
strategy.setLogicDeleteFieldName("deleted");
//Automatic Fill Configuration
TableFill gmtCreate = new TableFill("gmt_create", FieldFill.INSERT);
TableFill gmtUpdate = new TableFill("gmt_update", FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE);
//new a collection holds fill rules
ArrayList<TableFill> tableFills = new ArrayList<>();
tableFills.add(gmtCreate);
tableFills.add(gmtUpdate);
strategy.setTableFillList(tableFills);
//Optimistic Lock Configuration
strategy.setVersionFieldName("version");
//Naming with humps
strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true);
//Set rules related to the control layer url and change the hump style to an underscore, for example: localhost:8080/hello_id_2
strategy.setControllerMappingHyphenStyle(true);
mpg.setStrategy(strategy);
mpg.execute();//implement
}
}
Created successfully:
Note that there is a swagger configuration in the code that sets up entity classes, and related dependencies need to be introduced in advance, or the execution will not succeed:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>