Authorization: Grant and withdrawal
grant
GRANT <jurisdiction>[,<jurisdiction>]...
ON <object type> <Object name>[,<object type> <Object name>]...
TO <user>[,<user>]...
[WITH GRANT OPTION];
The with grant option clause is used to:
Users with grant option can continue to grant permissions
Users without this clause cannot continue to pass permissions.
[Example 4.1] Put query Student Table permissions granted to users U1
GRANT SELECT
ON TABLE Student
TO U1;

SQL server has some differences in t-sql syntax
GRANT SELECT ON Student TO U1;
Put right Student Table and Course All permissions on the table are granted to the user U2 and U3
Grant all PRIVILIGES on Student,course to u2,u3;
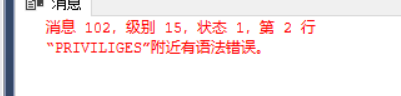
This is because on the one hand, T-SQL does not need (can not have) privileges, on the other hand, T-SQL needs to be given permissions separately, and multiple permissions cannot be given at one time.
Grant all PRIVILEGES on Student to u2,u3; Grant all on SC to u2,u3;

Put query Student The authority to form and modify student numbers is granted to users U4
GRANT UPDATE(Sno), SELECT ON Student TO U4
Set your watch SC of INSERT Permission granting U5 And allow him to grant this permission to other users
GRANT INSERT
ON TABLE SC
TO U5
WITH GRANT OPTION;
The reason for this is the with grant option clause
If you log in with u5 user at this time, you can grant other users the insert permission of SC table through this user, but if there is no tag sentence, you can't. when I do the experiment, I have all permissions because I use the root account.
take back
REVOKE <jurisdiction>[,<jurisdiction>]...
ON <object type> <Object name>[,<object type><Object name>]...
FROM <user>[,<user>]...[CASCADE | RESTRICT];
Put users U4 Withdrawal of permission to modify student ID
REVOKE UPDATE(Sno) ON Student FROM U4;
Recall all user statements SC Query permissions for
REVOKE SELECT ON SC FROM PUBLIC;
Put users U5 yes SC Tabular INSERT Permission withdrawal
REVOKE INSERT ON SC FROM U5 CASCADE ;
Will user U5 of INSERT Should be used when permission is withdrawn CASCADE,Otherwise, the statement is rejected Strange times, this time T-SQl Support again casade Yes In recovery u5 All permissions from u5 The permissions of users who have obtained permissions here will also be withdrawn
Database role
A role is a collection of permissions. You can create a role for a group of users with the same permissions.
Role creation:
CREATE ROLE <Role name>
Authorize roles:
GRANT <jurisdiction>[,<jurisdiction>]... ON <object type>Object name TO <role>[,<role>]...
Grant a role to another role or user
GRANT <Role 1>[,<Role 2>]... TO <Role 3>[,<User 1>]... [WITH ADMIN OPTION]
This statement grants a role to a user or to another role
The grantor is the creator of the role or has the ADMIN OPTION on the role
If WITH ADMIN OPTION is specified, the role or user who obtains certain permission can also grant this permission to other roles
Here is to distinguish roles from users. I don't know why I think roles feel like views.
Withdrawal of role permissions
REVOKE <jurisdiction>[,<jurisdiction>]... ON <object type> <Object name> FROM <role>[,<role>]...
Of course, the premise of this operation is that you have the permission to operate this role. For example, you are his creator or get his permission through some methods
Create a role R1
CREATE ROLE R1;
Then use GRANT Statement to make the role R1 have Student Tabular SELECT,UPDATE,INSERT jurisdiction
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT
ON Student
TO R1;
Grant this role to U1,U2. Give them a role R1 All permissions contained
GRANT R1
TO U1,U2;
There's a mistake here!
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'R1','U1' EXEC sp_addrolemember 'R1','U2'
Here is another small tips
Withdraw all permissions of U1 at one time:
REVOKE R1
FROM U1;

Do this:
EXEC sp_droprolemember 'R1','Wang Ping'
Permission modification of role
GRANT DELETE
ON Student
TO R1;
At this time, R1 is also authorized to modify
To revoke a permission, use revoke
I have to say that during this experiment, t-sql's own characteristics emerge one after another.. It reminds me that when playing games in the past, different versions are also different. You need to have a clear mind to skillfully use different sql languages.