PHB:Per Hop Behavior
Describe the next forwarding action of messages with the same priority. The value of each priority will correspond to the corresponding phb behavior, such as be, AF, EF, etc
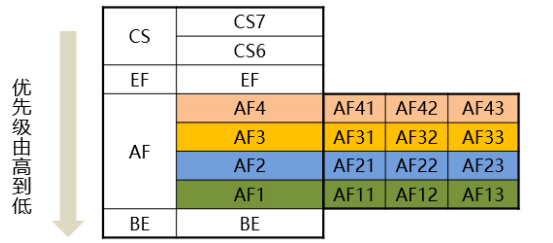
There are four types of PHB: CS EF AF BE
BE: do your best without quality assurance. The default PHB behavior value is 0, corresponding to ipp=0
AF: ensure forwarding bandwidth and controllable delay. It is applicable to 4 types of video and voice. Each type has 3 levels. AF11 12 13 corresponds to IPP = 1, AF 21 22 23 corresponds to IPP = 2, AF 31 32 33 corresponds to ipp=3, AF41 42 43 corresponds to ipp=4
EF: accelerated forwarding, low delay, low jitter, low packet loss rate, time delay sensitivity value is 46, corresponding to ipp=5
CS: used for compatibility with ipp. The first three bits are not 0, and the last three bits are 0, corresponding to ipp=1
AF has suffixes such as af11, af21, CS has CS6, CS7, etc., while BE and EF do not have suffixes. This is because BE and EF only correspond to unique DSCP values, and CS and AF correspond to multiple DSCP values
Each 802.1p priority, dscp priority and exp priority will correspond to a service level by default, which is phb
Each color and service level corresponds to a queue index
phb generally corresponds to the priority of simple flow classification message, which is obtained according to the trust mode of the interface. Its priority is mapped to the internal priority (Class 3 8021p exp dscp) and corresponds to 8 priority queues respectively
be queue0
af1 queue1
af2 queue2
af3 queue3
af4 queue4
ef queue5
cs6 queue6
cs7 queue7
The switch has 8 phb behaviors corresponding to 8 software queues. Use 8021p inbound XX phb and other commands to modify the phb in the diffiv domain of the switch
1 switch
1.1 use drop profile to manage the correspondence between color and discard policy
[Huawei]dis drop-profile all Drop-profile[0]: default Color Low-limit High-limit Discard-percentage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Green 100 100 100 Yellow 100 100 100 Red 100 100 100 Non-tcp 100 100 100 -----------------------------------------------------------------
1.2 using local pre queue map to manage the correspondence between queue and phb
[Huawei]dis qos local-precedence-queue-map Current configurations of mapping between local-precedence and queue: local-precedence value: be queue index: 0 local-precedence value: af1 queue index: 1 local-precedence value: af2 queue index: 2 local-precedence value: af3 queue index: 3 local-precedence value: af4 queue index: 4 local-precedence value: ef queue index: 5 local-precedence value: cs6 queue index: 6 local-precedence value: cs7 queue index: 7
1.3 use diffiv to manage the correspondence between phb and color corresponding to external priority
[Huawei]dis diffserv domain all diffserv domain name:default 8021p-inbound 0 phb be green 8021p-inbound 1 phb af1 green 8021p-inbound 2 phb af2 green 8021p-inbound 3 phb af3 green 8021p-inbound 4 phb af4 green 8021p-inbound 5 phb ef green 8021p-inbound 6 phb cs6 green 8021p-inbound 7 phb cs7 green 8021p-outbound be green map 0 8021p-outbound be yellow map 0 8021p-outbound be red map 0 8021p-outbound af1 green map 1 ......
2 router
2.1 using QoS map profile to manage the mapping relationship between external priority and cos
<r4>dis qos map-table Input Dot1p LP ------------------- 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 Input Dot1p Dot1p ------------------- 0 0
2.2 use drop profile to manage the mapping relationship between external priority and discard policy (congestion avoidance)
<r4>dis drop-profile d1 Drop-profile[1]: d1 IP-Precedence Low-limit High-limit Discard-percentage ----------------------------------------------------------------- 0(routine) 30 100 10 1(priority) 30 100 10 2(immediate) 30 100 10 3(flash) 30 100 10 4(flash-override) 30 100 10 5(critical) 30 100 10 6(internet) 30 100 10 7(network) 30 100 10 ----------------------------------------------------------------- [r4-drop-profile-d1]dis drop-profile d1 Drop-profile[1]: d1 DSCP Low-limit High-limit Discard-percentage ----------------------------------------------------------------- 0(default) 30 100 10 1 30 100 10 2 30 100 10 3 30 100 10 4 30 100 10 5 30 100 10 6 30 100 10 7 30 100 10 8(cs1) 30 100 10 9 30 100 10 10(af11) 30 100 10 11 30 100 10 12(af12) 30 100 10 13 30 100 10 14(af13) 30 100 10 15 30 100 10 16(cs2) 30 100 10 17 30 100 10 18(af21) 30 100 10 ............ ............ 46(ef) 30 100 10 47 30 100 10 48(cs6) 30 100 10 49 30 100 10 50 30 100 10 51 30 100 10 52 30 100 10 53 30 100 10 54 30 100 10 55 30 100 10 56(cs7) 30 100 10
3 how does DSCP correspond to ip preference, exp, 8021p, etc?
VLAN frame: 802.1Q (PRI)
MPLS message: Label (EXP)
IP message: ToS (IPP, DSCP)
IP precedence: 3bit, range 0 ~ 7
DSCP: 6bit, range 0 ~ 63
3.1 rule 1 (CS): used to correspond to ipp
When the last 3bit is 0, the first 3bit is mapped with IPP. DSCP is called CS
Example: CS X = DSCP X*8 = IPP X = 802.1p X = EXP X
DSCP: 1 0 1 0 0 0 DSCP 40 CS5
IPP : 1 0 0 IPP 5
3.2 rule 2 (AF, ensure forwarding)
The first value of AF corresponds to the value of IPP (X represents priority), and the second value of AF corresponds to the last 3 bits of DSCP (Y represents packet loss rate)
Example: AF XY = DSCP X*8 + Y*2 = IPP X = 802.1p X = EXP X
AF12
0 0 1 1 0 0
- 2
3.3 rule 3 (BE)
BE = DSCP 0 = IPP 0 = 802.1p 0 = EXP 0
3.4 Rule 4 (EF, fast forwarding)
EF = DSCP 46 = IPP,802.1p,EXP 0
The first 3 bits of the to field are IPP, followed by D (delay), T (throughput) and R (reliability) bits. The more bits 1 in the last three positions, the higher the discard probability. In addition, C bits represent the transmission overhead.
3.5 cross reference table (i.e. priority mapping relationship by default)
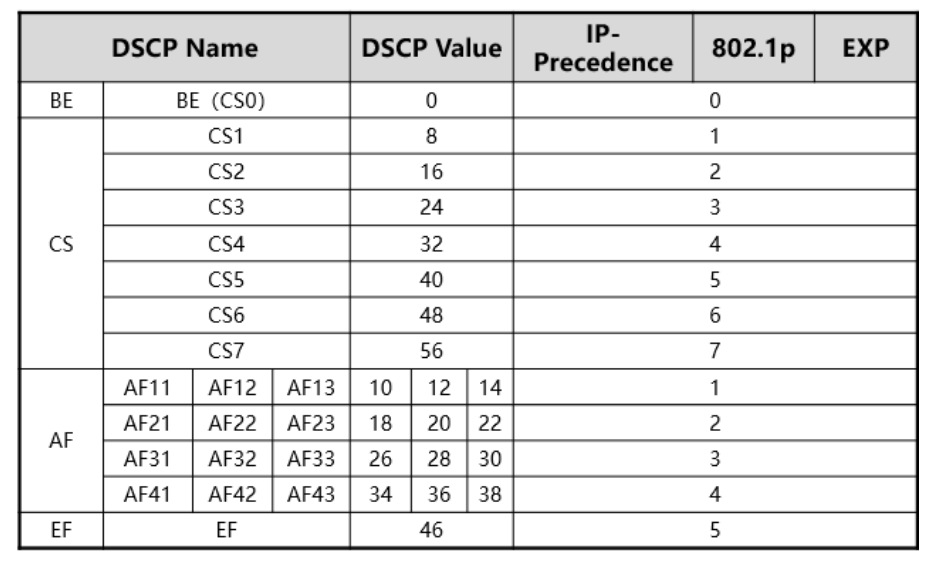
The lp value of the router can correspond to the phb behavior of the switch
You can modify the value of local precedence through remark, which corresponds to af1-af4