Heap of data structure (priority queue) c++
What is a pile?
Heap (priority queue) is a "special" queue. The order in which elements are taken out is based on the priority (keyword) size of elements, not the order in which elements enter the queue.
The heap can be regarded as a complete binary tree. You can use either a linked list or an array. But it is more convenient to use array. It uses an array to implement a heap, as shown in the figure below.
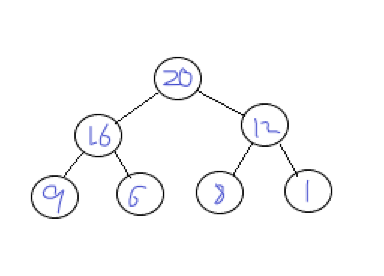
Corresponding array (in the structure with array as storage mode, no data is stored where the index of the array is 0)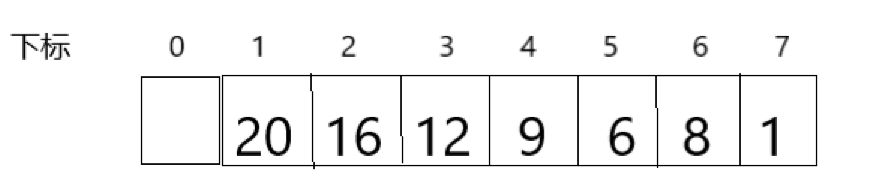
Heap can be divided into two types, one is the largest heap and the other is the smallest heap
Maximum heap: the value of the parent node is larger than its two child nodes (if any).
Minimum heap: the value of the parent node is smaller than its two child nodes (if any).
The following describes the structure and operation of the heap:
In order to cope with different data types, we use template classes here,
template <class T>
class Heap
{
public:
//It is convenient for users to choose whether to create a large pile or a small pile
enum Way
{
GREATER,//large
LESS//Small
};
private:
T *array_heap; //heap
size_t current_size; //Current capacity
size_t max_size; //Maximum capacity
Way flag; //Mark of pile (large pile / small pile)
public:
explicit Heap(const int &Size);
~Heap();
//Output in heap data
void print();
//Is the heap empty
bool empty() const;
//Is the heap full
bool full() const;
//Pile out
T delHeap();
//insert data
void insert(const T &Data, Way way);
//Construction pile
void createHeap(const T *Data_Array, const size_t &Size, Way way = Heap<T>::GREATER);
private:
//less than
bool less(const T &Left, const T &Right);
//greater than
bool greater(const T &Left, const T &Right);
//compare
bool compare(const T &Left, const T &Right, Way way);
//Adjustment reactor
void adjust();
//Adjustment reactor
void adjust(Way way);
public:
T &operator[](const int &location);
};
Next, we give the definition of some functions (out of class implementation)
template <typename T>
Heap<T>::Heap(const int &Size) : max_size(Size), current_size(0), flag(Heap<T>::GREATER)
{
//The requested memory location 0 is not used
this->array_heap = new T[Size + 1];
//Whether the memory request is successful
assert(this->array_heap);
//Initialization data
for (int i = 0; i < Size; ++i)
{
this->array_heap[i] = 0;
}
};
template <typename T>
Heap<T>::~Heap()
{
if (this->array_heap)
{
delete[] this->array_heap;
}
this->array_heap = nullptr;
this->current_size = this->max_size = 0;
}
//Is the heap empty
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::empty() const
{
return (this->current_size == 0);
}
//Is the heap full
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::full() const
{
return (this->current_size == this->max_size + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T &Heap<T>::operator[](const int &Location)
{
return (this->array_heap[Location]);
}
//less than
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::less(const T &Left, const T &Right)
{
return (Left < Right);
}
//greater than
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::greater(const T &Left, const T &Right)
{
return (Left > Right);
}
//compare
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::compare(const T &Left, const T &Right, Heap<T>::Way way)
{
if (way == this->GREATER)
{
return this->greater(Left, Right);
}
else
{
return (this->less(Left, Right));
}
}
//Output in heap data
template <typename T>
void Heap<T>::print()
{
for (auto i = 1; i <= this->current_size; ++i)
{
std::cout << this->array_heap[i] << ' ';
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
Heap construction
We use an array to construct a heap. In order to process multiple data, our construction chooses to accept an array element to initialize our heap (this function is implemented in class)
//Construction pile
void createHeap(const T *Data_Array, const size_t &Size, Way way = Heap<T>::GREATER)
{
this->flag = way; //Identification heap
if (Size > this->max_size)
{
return;
}
for (auto i = 0; i < Size; ++i)
{
this->insert(Data_Array[i], way);
}
}
Heap insertion
You should have noticed that the core operation of our heap construction function is actually insertion,
***Note: * * * when inserting elements into the heap, the nature of the heap cannot be changed.
Insert operation:
Insert the element into the heap. First, we insert the element into the next position of the last element of the array (assuming the subscript is i). Next, we need to adjust the heap.
Let's take a lot of data as an example. Suppose that the data we want to insert is 10, as shown in the figure:
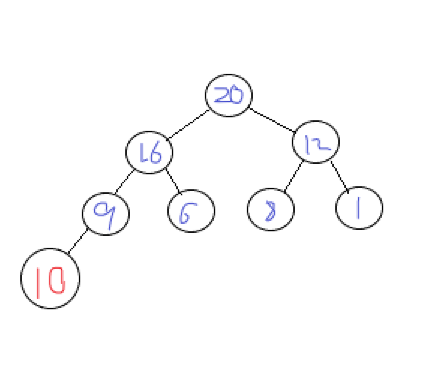
We put 10 at the end of the array. We can see that at this time, 10 > 9, which must have violated the nature of a lot, so we need to adjust it. The adjustment method is to compare 10 with its parent node. If the value is greater than the parent node, we will exchange the node with the parent node, and then continue to compare with its parent node, Until ordered (Note: during the adjustment process, the subscript of the parent node cannot reach zero, i.e. > 1). (the calculation formula of parent node subscript is: parent node subscript = current subscript / 2)
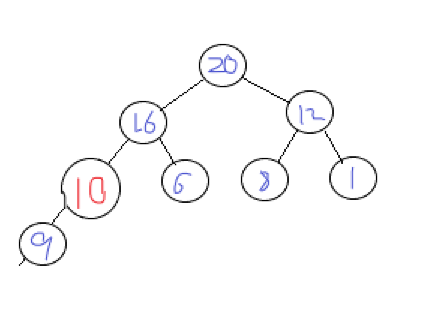
At this time, we find that 10 < 16 (parent node), and the heap is in order, so there is no need to adjust it
Let's look at the code implementation of the insert operation:
//insert data
void insert(const T &Data, Way way)
{
//Is the heap full
if (this->full())
{
return;
}
//Insert data to the end
this->array_heap[++this->current_size] = Data;
//Adjustment reactor
this->adjust(way);
}
The following is the core of the insertion operation, that is, adjusting the heap to make the heap orderly,
//Adjustment reactor
void adjust(Way way)
{
auto curPos = this->current_size; // curPos points to the location of the last node in the heap
auto max = this->array_heap[curPos]; //Save current node data
// Curpos > 1 prevents access to position 0
while (curPos > 1 && this->compare(max, this->array_heap[curPos / 2], way))
{
this->array_heap[curPos] = this->array_heap[curPos / 2]; //Filter down node
curPos = curPos / 2;
}
//Insert original data into
this->array_heap[curPos] = max;
}
Here, in order to improve efficiency, we do not use the way of exchanging two data elements
This way of adjusting the heap is also called downward filtering node
Deletion of heap
The deletion operation is aimed at the opposite top element, that is, the root node. The deletion method we adopt is to remove the root node and put the end node on the original root node, as shown in the figure:
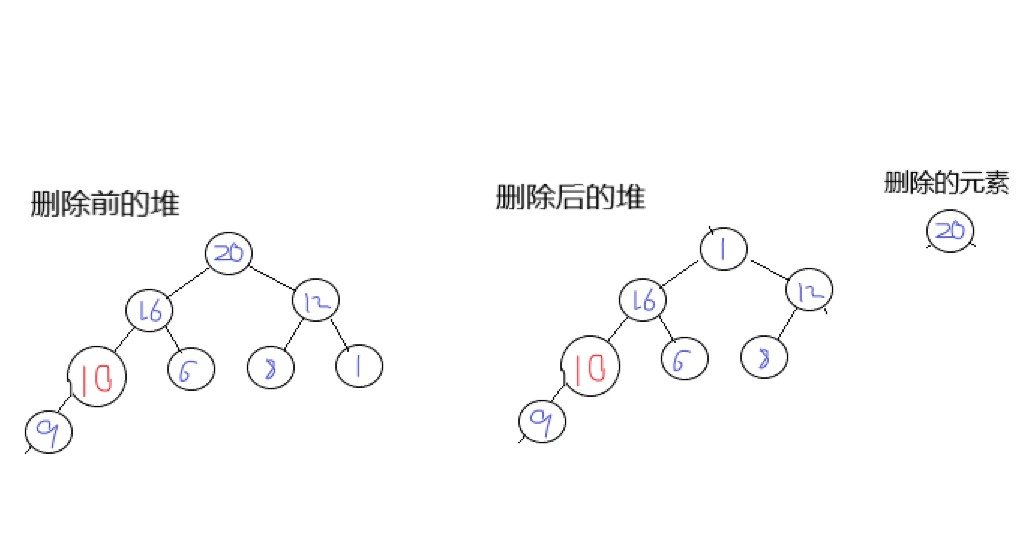
At this time, we find that the value of the root node is significantly smaller than that of its left and right child nodes (1 < 16,1 < 12), which does not meet the nature of a pile. At this time, we need to adjust the of the pile to make it orderly.
At this time, the adjustment method we use is different from that during insertion
This time, we will compare the value of the root node with its child nodes and adjust it downward, that is
Compare the root node with the left and right child nodes, and move the large value upward until the heap is in order (child node subscript = parent node subscript * 2)
As shown in the figure:
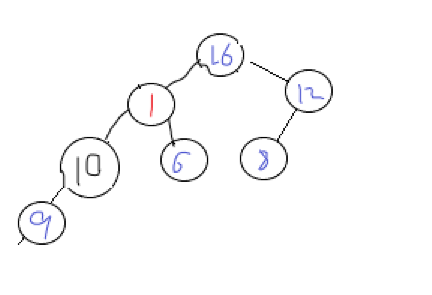
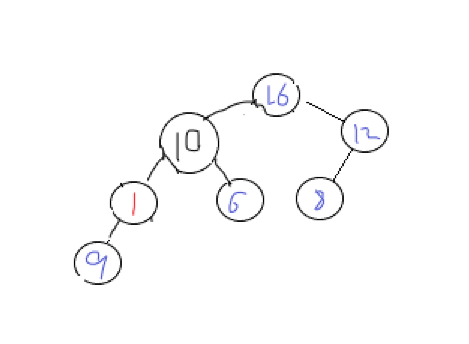
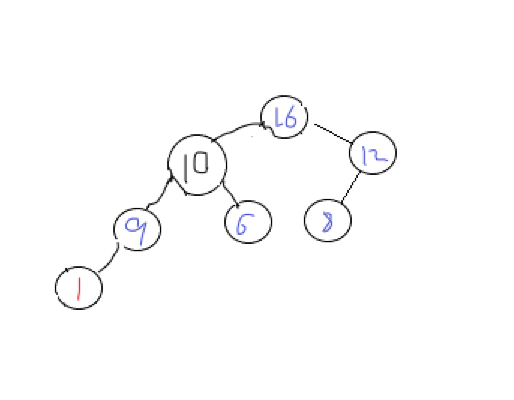
At this time, the heap has been adjusted
Let's look at the code implementation
//Pile out
template <typename T>
T Heap<T>::delHeap()
{
//Determine whether the heap is empty
if(this->empty())
{
return false;
}
//Save root node element
auto item = this->array_heap[1];
//Put the end element on the root node and reduce the size of the heap by one
this->array_heap[1] = this->array_heap[this->current_size--] ;
//Adjustment reactor
this->adjust();
//Returns the root node element
return item;
}
The following is the code implementation of adjusting heap
//Adjustment reactor
template <typename T>
void Heap<T>::adjust()
{
//Record the subscript positions of parent and child nodes
size_t parent, child;
//Save root node element
auto item=this->array_heap[1];
for(parent=1;parent*2<this->current_size;parent=child)
{
child=parent*2;
//Compare left and right node sizes
if(child<this->current_size&&this->compare(this->array_heap[child+1],this->array_heap[child],this->flag))
{
++child;
}
//Filter down node
if(this->compare(this->array_heap[child],item,this->flag))
{
this->array_heap[parent]=this->array_heap[child];
}
}
//insert data
this->array_heap[parent]=item;
}
Let's test:
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {1,3,2,5,4,6,7,9,8,10};
Heap<int> heap1(10);
std::cout<<"Maximum heap"<<std::endl;
//Maximum heap
heap1.createHeap(arr,10,Heap<int>::GREATER);
std::cout<<"In heap element"<<std::endl;
heap1.print();
//delete
heap1.delHeap();
std::cout<<"In heap elements after deletion"<<std::endl;
heap1.print();
//insert
heap1.insert(20,Heap<int>::GREATER);
std::cout<<"In heap elements after insertion"<<std::endl;
heap1.print();
Heap<int>heap2(10);
std::cout<<"Minimum heap"<<std::endl;
//Minimum heap
heap2.createHeap(arr,10,Heap<int>::LESS);
std::cout<<"In heap element"<<std::endl;
heap2.print();
//delete
heap2.delHeap();
std::cout<<"In heap elements after deletion"<<std::endl;
heap2.print();
//insert
heap2.insert(20,Heap<int>::LESS);
std::cout<<"In heap elements after insertion"<<std::endl;
heap2.print();
return 0;
}
This is the output
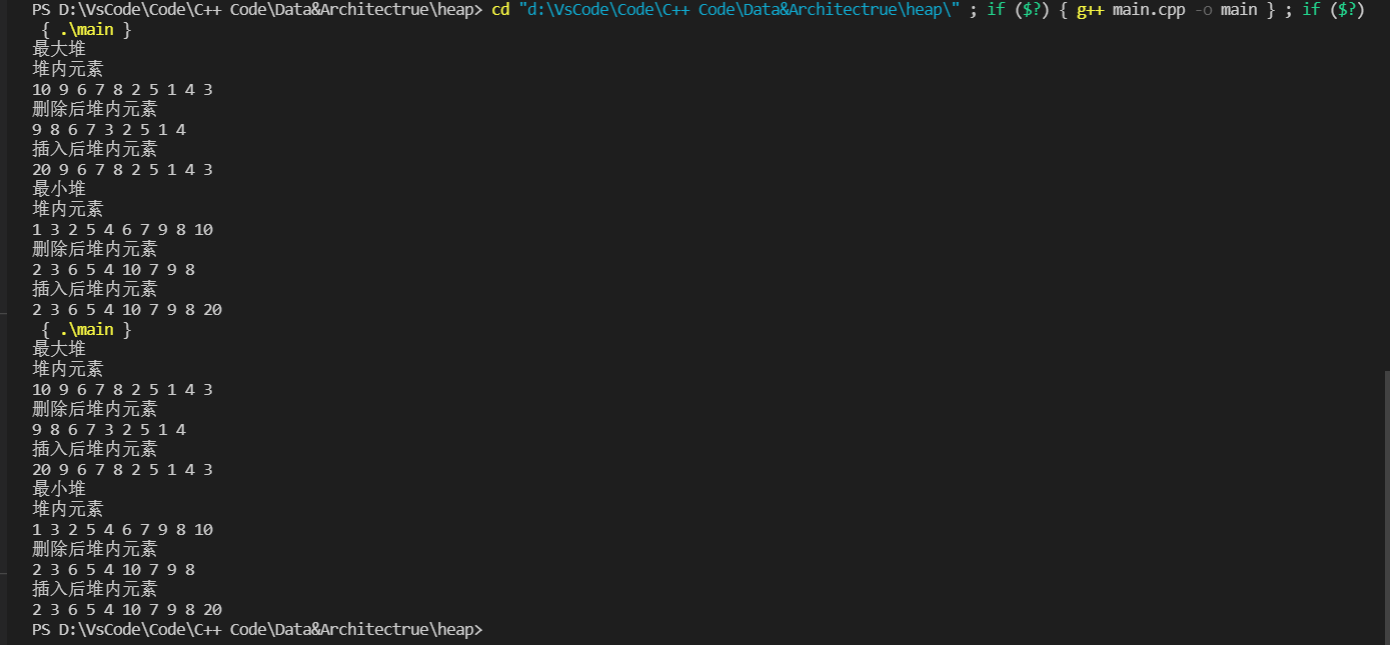
Finally, this is the complete code (sub file)
Header file
#ifndef HEAP_H_
#define HEAP_H_
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
template <class T>
class Heap
{
public:
enum Way
{
GREATER,
LESS
};
private:
T *array_heap; //heap
size_t current_size; //Current capacity
size_t max_size; //Maximum capacity
Way flag; //Representation of heap (large / small heap)
public:
explicit Heap(const int &Size);
~Heap();
//Output in heap data
void print();
//Is the heap empty
bool empty() const;
//Is the heap full
bool full() const;
//Pile out
T delHeap();
//insert data
void insert(const T &Data, Way way)
{
if (this->full())
{
return;
}
//Insert data to the end
this->array_heap[++this->current_size] = Data;
//Adjustment reactor
this->adjust(way);
}
//Construction pile
void createHeap(const T *Data_Array, const size_t &Size, Way way = Heap<T>::GREATER)
{
this->flag = way; //Identification heap
if (Size > this->max_size)
{
return;
}
for (auto i = 0; i < Size; ++i)
{
this->insert(Data_Array[i], way);
}
}
private:
//less than
bool less(const T &Left, const T &Right);
//greater than
bool greater(const T &Left, const T &Right);
//compare
bool compare(const T &Left, const T &Right, Way way);
//Adjustment reactor
void adjust();
//Adjustment reactor
void adjust(Way way)
{
auto curPos = this->current_size; // curPos points to the location of the last node in the heap
auto max = this->array_heap[curPos]; //Save current node data
// Curpos > 1 prevents access to position 0
while (curPos > 1 && this->compare(max, this->array_heap[curPos / 2], way))
{
this->array_heap[curPos] = this->array_heap[curPos / 2]; //Filter down node
curPos = curPos / 2;
}
//Insert original data into
this->array_heap[curPos] = max;
}
public:
T &operator[](const int &location);
};
template <typename T>
Heap<T>::Heap(const int &Size) : max_size(Size), current_size(0), flag(Heap<T>::GREATER)
{
//The requested memory location 0 is not used
this->array_heap = new T[Size + 1];
//Whether the memory request is successful
assert(this->array_heap);
//Initialization data
for (int i = 0; i < Size; ++i)
{
this->array_heap[i] = 0;
}
};
template <typename T>
Heap<T>::~Heap()
{
if (this->array_heap)
{
delete[] this->array_heap;
}
this->array_heap = nullptr;
this->current_size = this->max_size = 0;
}
//Is the heap empty
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::empty() const
{
return (this->current_size == 0);
}
//Is the heap full
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::full() const
{
return (this->current_size == this->max_size + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T &Heap<T>::operator[](const int &Location)
{
return (this->array_heap[Location]);
}
//less than
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::less(const T &Left, const T &Right)
{
return (Left < Right);
}
//greater than
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::greater(const T &Left, const T &Right)
{
return (Left > Right);
}
//compare
template <typename T>
bool Heap<T>::compare(const T &Left, const T &Right, Heap<T>::Way way)
{
if (way == this->GREATER)
{
return this->greater(Left, Right);
}
else
{
return (this->less(Left, Right));
}
}
//Pile out
template <typename T>
T Heap<T>::delHeap()
{
//Determine whether the heap is empty
if(this->empty())
{
return false;
}
//Save root node element
auto item = this->array_heap[1];
//Put the end element on the root node and reduce the size of the heap by one
this->array_heap[1] = this->array_heap[this->current_size--] ;
//Adjustment reactor
this->adjust();
//Returns the root node element
return item;
}
//Adjustment reactor
template <typename T>
void Heap<T>::adjust()
{
//Record the subscript positions of parent and child nodes
size_t parent, child;
//Save root node element
auto item=this->array_heap[1];
for(parent=1;parent*2<this->current_size;parent=child)
{
child=parent*2;
//Compare left and right node sizes
if(child<this->current_size&&this->compare(this->array_heap[child+1],this->array_heap[child],this->flag))
{
++child;
}
//Filter down node
if(this->compare(this->array_heap[child],item,this->flag))
{
this->array_heap[parent]=this->array_heap[child];
}
}
//insert data
this->array_heap[parent]=item;
}
//Output in heap data
template <typename T>
void Heap<T>::print()
{
for (auto i = 1; i <= this->current_size; ++i)
{
std::cout << this->array_heap[i] << ' ';
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
#endif
main file
#include<iostream>
#include "heap.h"
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {1,3,2,5,4,6,7,9,8,10};
Heap<int> heap1(10);
std::cout<<"Maximum heap"<<std::endl;
//Maximum heap
heap1.createHeap(arr,10,Heap<int>::GREATER);
std::cout<<"In heap element"<<std::endl;
heap1.print();
//delete
heap1.delHeap();
std::cout<<"In heap elements after deletion"<<std::endl;
heap1.print();
//insert
heap1.insert(20,Heap<int>::GREATER);
std::cout<<"In heap elements after insertion"<<std::endl;
heap1.print();
Heap<int>heap2(10);
std::cout<<"Minimum heap"<<std::endl;
//Minimum heap
heap2.createHeap(arr,10,Heap<int>::LESS);
std::cout<<"In heap element"<<std::endl;
heap2.print();
//delete
heap2.delHeap();
std::cout<<"In heap elements after deletion"<<std::endl;
heap2.print();
//insert
heap2.insert(20,Heap<int>::LESS);
std::cout<<"In heap elements after insertion"<<std::endl;
heap2.print();
return 0;
}
Well, this is all the contents of the above data structure pile. I hope you like it.
If you like it, please praise it~