1, Dialog introduction
Dialog box is the top-level window for brief interaction with users
QDialog is the base class of all dialog windows in QT. QDialog inherits from QWidget. It is a container component and a special QWidget with customized window style.
As a special interactive window, QDialog cannot be embedded in other containers as a subassembly.
2, Dialog type
Dialog box types are divided into modal dialog box and non modal dialog box.
1. Modal dialog
After the modal dialog box is displayed, it cannot interact with the parent window. It is a blocking dialog box, which is called by QDialog::exec() function.
Modal dialog boxes are usually created on the stack.
QDialog dialog(this); dialog.exec();
The modal dialog box is suitable for situations that must depend on user selection, such as message display, file selection, print setting, etc.
2. Modeless dialog box
The modeless dialog box exists independently after it is displayed and can interact with the parent window at the same time. It is a non blocking dialog box, which can be called by QDialog::show() function.
Modeless dialog boxes are generally created on the heap, and QT: wa needs to be specified_ Deleteonclose property to avoid memory leakage.
The modeless dialog box is suitable for special function settings, such as search operation, attribute setting, etc.
QDialog* dialog = new QDialog(this); dialog->setAttribute(Qt::WA_DeleteOnClose); dialog->show();
3. Blend Properties dialog box
The mixed attribute dialog box has the properties of both modal dialog box and non modal dialog box. The generation and destruction of dialog box has the properties of non modal dialog box, and the function has the properties of modal dialog box.
Use the QDialog::setModal() function to create a dialog box for blending properties. In general, creating a dialog box requires specifying the parent component of the dialog box.
QDialog* dialog = new QDialog(this); dialog->setAttribute(Qt::WA_DeleteOnClose); dialog->setModal(true); dialog->show();
3, Return value of dialog box
Only the modal dialog box adopts the return value, and the return value of the modal dialog box is used to represent the interaction result.
The return value of QDialog::exec() function is used as the interaction result.
The void QDialog::done(int i) function closes the dialog box and takes the parameter as the interaction result.
QDialog::Accepted indicates that the user operation is successful
QDialog::Rejected indicates that the user operation failed
If the dialog box runs in modal mode as the main window of the program, the main function of the main program cannot call a.exec() here to avoid entering the message event loop here.
4, Standard dialog box
1. Types of standard dialog boxes
QT provides developers with a variety of reusable dialog types, namely QT standard dialog box. QT standard dialog boxes are all inherited from QDialog class. Common standard dialog box types are as follows:
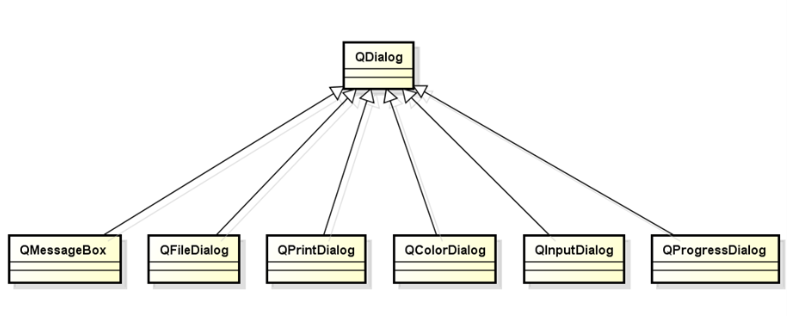
Definition of dialog object
QDialogType dialog(this);
Dialog box property settings
dialog.setPropertyxxxx(value);
if(dialog.exec() == QDialogType::vaule)
{
Type v = dialog.getDialogValue();
}2. Message dialog box QMessageBox
Message dialog boxes are the most commonly used interface elements in applications. The message dialog box is mainly used to prompt users with important information and force users to select.
The message dialog box is used as follows:
A. Create message dialog object
QMessageBox msg(this);
B. Set message dialog properties
msg.setWindowTitle("Warning Message");
msg.setText("Error Massage!");
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox::Information);
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox::Ok | QMessage::Cancel);
if(dialog.exec() == QMessageBox::Ok)
{
//
}C. QMessageBox utility function
QMessageBox defines static member functions, which can be called directly to create message dialog boxes of different styles.
StandardButton information(QWidget * parent, const QString & title,
const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = Ok,
StandardButtondefaultButton = NoButton)
StandardButton question(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString& text,
StandardButtons buttons = Ok,
StandardButtondefaultButton = NoButton)
StandardButton warning(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString& text,
StandardButtons buttons = Ok,
StandardButtondefaultButton = NoButton)
StandardButton critical(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString& text,
StandardButtons buttons = Ok,
StandardButton defaultButton= NoButton)
void about(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text)3. File dialog box QFileDialog
The file dialog box is used to open an external file or store the current content in a specified external file in the application.
The file dialog box is used as follows
A. Create file dialog object
QFileDialog fdialog(this);
B. File dialog properties settings
Open the file settings as follows:
fdialog.setAcceptMode(QFileDialog::AcceptOpen);
//Select to open multiple files. QFileDialog::ExistingFiles
fdialog.setFileMode(QFileDialog::ExistingFile);
if(fdialog.exec() == QFileDialog::Accepted)
{
QStringList s = fdialog.selectedFiles();
for(int i = 0; i < s.count(); i++)
{
qDebug() << s[i];
}
}Save file settings are as follows:
fdialog.setAcceptMode(QFileDialog::AcceptSave);
if(fdialog.exec() == QFileDialog::Accepted)
{
QStringList s = fdialog.selectedFiles();
for(int i = 0; i < s.count(); i++)
{
qDebug() << s[i];
}
}C. File type filter
In the file dialog box, you can define file filters through file suffixes. File filter definition rules are as follows:
Display name (*. Suffix 1) *. Suffix 2... *. Suffix n)
Image(*.jpg *.png)
Text(*.txt)
All(*.*)
fdialog.setFilter("Image(*.png *.jpg)");D. File dialog utility
QFileDialog defines several static member functions to use the file dialog directly.
QString getOpenFileName(QWidget * parent = 0, const QString & caption = QString(),
const QString & dir = QString(),
const QString& filter = QString(),
QString * selectedFilter = 0, Options options = 0)
QStringList getOpenFileNames(QWidget * parent = 0,
const QString& caption = QString(),
const QString & dir = QString(),
const QString & filter = QString(),
QString * selectedFilter = 0, Options options = 0)
QString getSaveFileName(QWidget * parent = 0, const QString & caption = QString(),
const QString & dir = QString(),
const QString& filter = QString(),
QString * selectedFilter = 0, Options options = 0)4. Color dialog QColorDialog
QT also provides a predefined color dialog class QColorDialog. The color dialog box is used as follows:
A. Create color dialog QColorDialog object
QColorDialog cdialog(this);
B. Color dialog property settings
cdialog.setWindowTitle("Color Editer");
//Set initial color
cdialog.setCurrentColor(Qt::red);
if(cdialog.exec() == QColorDialog::Accepted)
{
qDebug() << cdialog.selectedColor();
}C,QColor
QColor is used to represent colors in QT, and multiple color representation methods are supported.
RGB: three color model based on red, green and blue
HSV: hexagonal cone model based on hue, saturation and lightness
CMYK: full color printing color model based on sky blue, magenta, yellow and black
QColor supports conversion between three color models.
QColor color = dlg.selectedColor(); qDebug() << color; qDebug() << color.red(); qDebug() << color.green(); qDebug() << color.blue(); qDebug() << color.hue(); qDebug() << color.saturation(); qDebug() << color.value();
D. QColorDialog utility function
QColorDialog defines static member functions that directly use color dialog boxes.
QColor getColor(const QColor & initial, QWidget * parent,
const QString & title, ColorDialogOptions options = 0)
QColor getColor(const QColor & initial = Qt::white, QWidget * parent = 0)5. Input dialog QInputDialog
QT provides a predefined input dialog class QInputDialog, which is used when temporary data input is required.
The input dialog box can be used as follows:
A. Create input dialog object
QInputDialog idialog(this);
B. Enter dialog box property settings
idialog.setWindowTitle("Enter Data");
idialog.setLabelText("Please Enter a int:");
idialog.setInputMode(QInputDialog::IntInput);
if(idialog.exec() == QInputDialog::Accepted)
{
qDebug() << idialog.intValue();
}C. Input mode of the input dialog box
QInputDialog::TextInput input text string
QInputDialog::IntInput input integer
QInputDialog::DoubleInput input floating point number
D. Practical functions of QInputDialog
QInputDialog defines multiple static member functions, which can be called directly using the input dialog box.
double getDouble(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & label,
double value = 0, double min = -2147483647,
double max = 2147483647, int decimals = 1,
bool * ok = 0, Qt::WindowFlags flags = 0)
int getInt(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & label,
int value = 0, int min = -2147483647, int max = 2147483647,
int step= 1, bool * ok = 0, Qt::WindowFlags flags = 0)
QString getItem(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & label,
const QStringList & items, int current = 0, bool editable = true,
bool *ok = 0, Qt::WindowFlags flags = 0)
QString getText(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & label,
QLineEdit::EchoMode mode = QLineEdit::Normal,
const QString &text = QString(), bool * ok = 0,
Qt::WindowFlags flags = 0)6. Font dialog box QFontDialog
QT provides a predefined font dialog class QFontDialog, which is used to provide dialog box parts for selecting fonts.
The font dialog box is used as follows:
A. Create font dialog object
QFontDialog fdialog(this);
B. Font dialog box property settings
fdialog.setWindowTitle("Select Font");
fdialog.setCurrentFont(QFont("Courier New", 10, QFont::Bold));
if(fdialog.exec() == QFontDialog::Accepted)
{
qDebug() << fdialog.selectedFont();
}C. QFontDialog utility function
QFontDialog defines a static member function, which can be called directly. You can use the font dialog box to select a font.
QFont getFont(bool * ok, const QFont & initial, QWidget * parent,
const QString & title, FontDialogOptions options)
QFont getFont(bool * ok, const QFont & initial, QWidget * parent,
const char * name)
QFont getFont(bool * ok, QWidget * parent, const char * name)
QFont getFont(bool * ok, const QFont & initial, QWidget * parent,
const QString & title)
QFont getFont(bool * ok, const QFont & initial, QWidget * parent = 0)
QFont getFont(bool * ok, QWidget * parent = 0)7. Progress dialog qpprogressdialog
QT provides a predefined progress dialog class qpprogressdialog, which is used to display progress information and occasions where users need to wait.
The progress dialog box is used as follows:
A. Create progress dialog object
QProgressDialog pdialog(this);
B. Progress dialog property settings
pdialog.setWindowTitle("Progress.....");
pdialog.setLabelText("The application having done at ....");
pdialog.setMaximum(100);
pdialog.setMinimum(0);
pdialog.setValue(30);
pdialog.exec();8. Print dialog QPrintDialog
QT provides a predefined Print dialog class QPrintDialog, which is used to set print related parameter information.
The printing dialog box is used as follows:
A. Create print dialog object
QPrintDialog prdialog(this);
B. Print dialog box property settings
prdialog.setWindowTitle("Setting the Printer");
if(prdialog.exec() == QPrintDialog::Accepted)
{
QPrinter *p = prdialog.printer();
QTextDocument td;
td.setPlainText("Hello world!");
p->setOutputFileName("d:\\hello.pdf");
td.print(p);
}C. QPrinter class
QPrinter class in QT is the package of printing equipment and its parameters. It encapsulates the driver interface of printing equipment in the system and uses different printing equipment in the system in the same way.
V. data transfer between forms
There are three ways to transfer data between QT forms: signal slot mechanism, public function interface and global variable.
1. QT signal slot transmission
Define the signal with parameters in the form class of sending data and send the signal; Define the slot function of receiving data in the form of receiving data; Connect the signal of sending data with the slot function of receiving data.
Declaration signal:
signals: void sendData(QString);
Sending signal (with parameter content):
emit sendData(lineEdit->text());
Define slot function (with parameter content):
private slots: void receiveData(QString data);
Connecting signal and slot:
connect(sender,SIGNAL(sendData(QString)),receiver,SLOT(receiveData(QString)));
2. Public function interface transfer
Using the public member function interface, you can call the member functions of classes outside different classes to return the required data.
3. Global variable transfer
Global variables can be defined in one file and used after being declared in other files to realize data sharing and transmission.
6, Login dialog instance
The login dialog box is a common part of the application.
1. Login dialog demand analysis
Login dialog box demand analysis:
A. As reusable software components
B. Get user name and password
C. Random code verification
2. Schema of login dialog box
Design and architecture of login dialog box
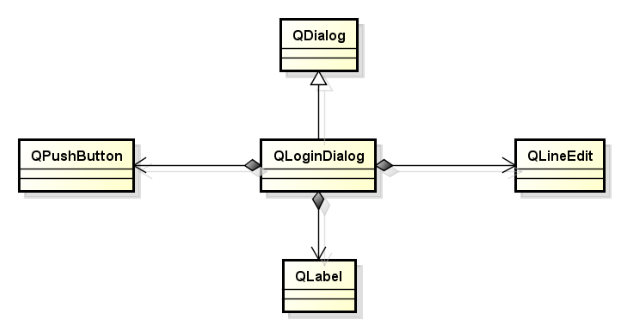
Data is transferred between dialog boxes through member variables and member functions, user data is saved in private member variables, and data is transferred through public member functions.
3. Login dialog class design
#ifndef QLOGINDIALOG_H
#define QLOGINDIALOG_H
#include <QDialog>
#include <QLineEdit>
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QLabel>
class QLoginDialog: public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
private:
QLabel UserLabel;
QLabel PwdLabel;
QLineEdit UserEdit;
QLineEdit PwdEdit;
QPushButton B_Login;
QPushButton B_Cancel;
QString m_user;
QString m_pwd;
public:
QLoginDialog(QWidget *parent);
QString getUser();
QString getPwd();
~QLoginDialog();
private slots:
void Login();
void Cancel();
};
#endif // QLOGINDIALOG_H
Implementation file:
#include "QLoginDialog.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QMessageBox>
QLoginDialog::QLoginDialog(QWidget *parent)
:QDialog(parent, Qt::WindowCloseButtonHint), UserLabel(this),
PwdLabel(this),
UserEdit(this), PwdEdit(this), B_Login(this),B_Cancel(this)
{
UserLabel.setText("User ID:");
UserLabel.move(50, 50);
UserLabel.resize(60, 30);
UserEdit.move(110, 50);
UserEdit.resize(200, 30);
PwdLabel.setText("Password:");
PwdLabel.move(50, 100);
PwdLabel.resize(60,30);
PwdEdit.move(110, 100);
PwdEdit.resize(200, 30);
PwdEdit.setEchoMode(QLineEdit::Password);
B_Login.setText("Login");
B_Login.move(110, 150);
B_Login.resize(80, 30);
B_Cancel.setText("Cancel");
B_Cancel.move(230, 150);
B_Cancel.resize(80, 30);
setWindowTitle("Login Window");
setFixedSize(400, 300);
connect(&B_Login, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(Login()));
connect(&B_Cancel, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(Cancel()));
}
QString QLoginDialog::getUser()
{
return m_user;
}
QString QLoginDialog::getPwd()
{
return m_pwd;
}
void QLoginDialog::Login()
{
qDebug() << "login";
m_user = UserEdit.text().trimmed();
m_pwd = PwdEdit.text();
if(!(m_user.isEmpty() || m_pwd.isEmpty()))
{
done(Accepted);
}
else
{
QMessageBox mb(this);
mb.setWindowTitle("Warning Message");
mb.setIcon(QMessageBox ::Warning);
mb.setText("User or PassWord can't empty! \nPlease check your username or password!");
mb.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox::Ok);
mb.exec();
}
}
void QLoginDialog::Cancel()
{
qDebug() << "cancel";
done(Rejected);
}
QLoginDialog::~QLoginDialog()
{
}