catalogue
1. High precision realization of the n-th power of 2
5. High precision multiplication
6. High precision factorial and
7. High precision calculation sequence and
1. High precision realization of the n-th power of 2
Corresponding link of Niuke website:
N-th power of 2_ Niuke Tiba_ Niuke.com (nowcoder.com)
Title Description:
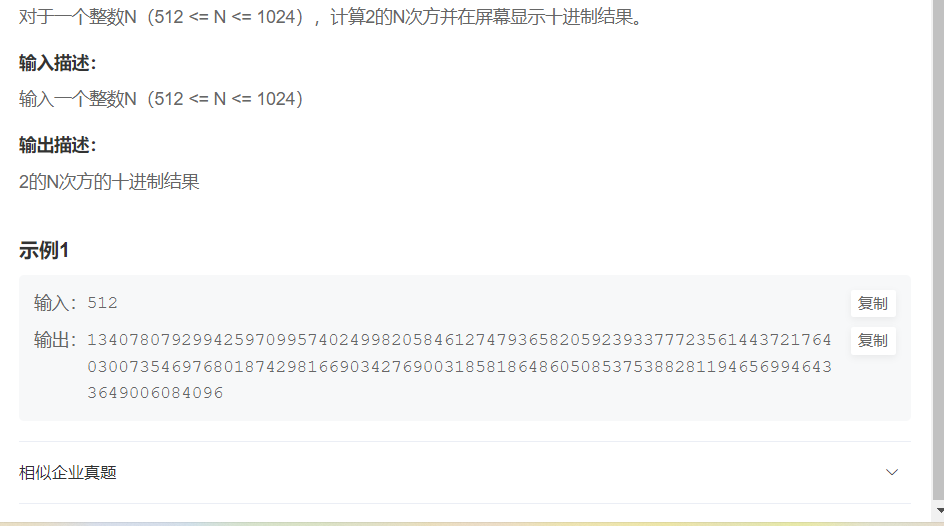
Problem solving ideas:
Due to the large range of N, if we use long long numbers for storage, it will definitely overflow the stack. Therefore, we can only use arrays for simulation, that is, high precision.
1. We set the first position and the second position of the array to 1. The number of the first position represents the length and the number of the second position represents the initial value.
1 1
First time * 2:
1 2
Second * 2:
1 4
Multiply 2 for the third time
1 8
Fourth * 2
116
At this time, we find that the carry occurs when 16 is greater than 10. At this time, we need to take the remainder of 16, and the length is + 1:
2 6 1
Fourth * 2:
2 16 2
Remainder and carry 16:
2 6 3
Repeat the above steps to complete the simulation.
Corresponding code:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int>arr(n);
arr[0]=1;//Represents the current length
arr[1]=1;//Represents the initial value
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int carry=0;//carry
for(int j=1;j<=arr[0];j++){
arr[j]=arr[j]*2+carry;//Add carry
carry=arr[j]/10;//carry
arr[j]%=10;//Surplus
}
if(carry){//If there is carry
arr[++arr[0]]=carry;//Carry is either 0 or 1
}
}
for(int i=arr[0];i>=1;i--){//Inverse output
cout<<arr[i];
}
}2. High precision factorial
Corresponding link of Niuke website:
Factoring an integer_ Niuke Tiba_ Niuke (nowcoder.com)
Title Description:
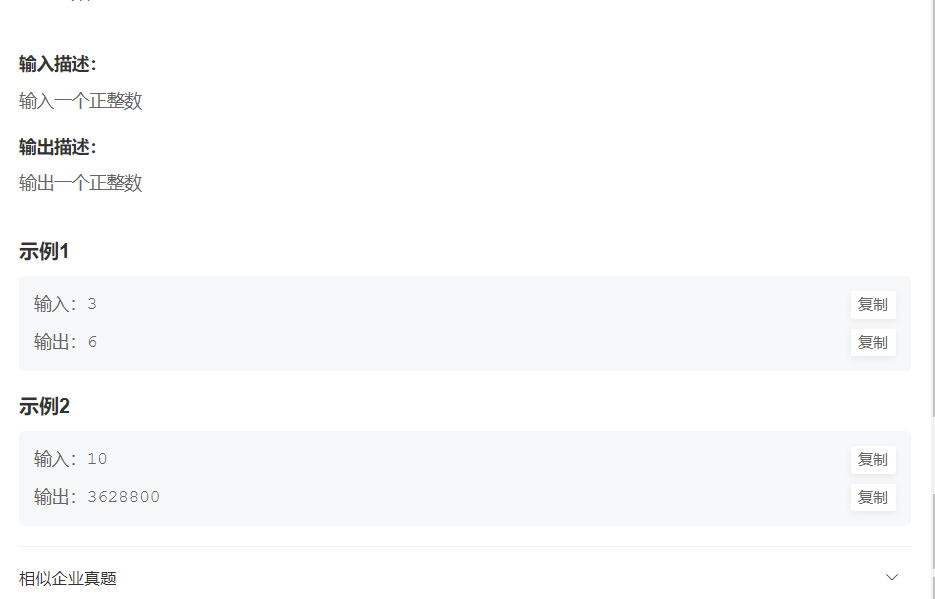
Problem solving ideas:
The idea of this question is basically the same as that of the previous question, except that the number multiplied each time is not 2, but i, and the carry may not be 10, which may be very large. Please see the code for details:
Corresponding code:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int>arr(3*n);
arr[0]=1;
arr[1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int carry=0;//carry
for(int j=1;j<=arr[0];j++){
arr[j]=arr[j]*i+carry;//Every time * i and add carry
carry=arr[j]/10;//carry
arr[j]%=10;
}
while(carry){//Until the carry is 0
arr[++arr[0]]=carry%10;//The carry can be large, more than 10
carry/=10;
}
}
for(int i=arr[0];i>=1;i--){//Reverse order output
cout<<arr[i];
}
}3. High precision addition
High precision addition bloggers have written it before, so I won't write it here.
Corresponding link:
4. High precision subtraction
Corresponding OJ link:
P2142 high precision subtraction - Luogu | new ecology of Computer Science Education (luogu.com.cn)
Title Description:
There is a little difference between subtraction and addition with high precision. If the first number is less than the second number, a negative number will appear. Therefore, we default that the first number is relatively large. If the first number is small, it will be exchanged. According to the subtraction rules of primary school, if it is not enough, borrow forward. Please see the code for details
Corresponding code:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s1,s2;
cin>>s1>>s2;
if(s1.size()<s2.size()||(s1.size()==s2.size()&&s1<s2)){
//The first number is less than the second
s1.swap(s2);
cout<<"-";
}
vector<int>a(s1.size()+1);
vector<int>b(s1.size()+1);
vector<int>c(s1.size()+1);
for(int i=0;i<s1.size();i++){
a[s1.size()-i]=s1[i]-'0';
}
for(int i=0;i<s2.size();i++){
b[s2.size()-i]=s2[i]-'0';
}
for(int i=1;i<=s1.size();i++){
if(a[i]<b[i]){//Insufficient subtraction forward borrowing
a[i+1]--;
a[i]+=10;
}
c[i]=a[i]-b[i];
}
int len=s1.size();
while(c[len]==0&&len>1){//Eliminate leading 0
len--;
}
for(int i=len;i>=1;i--){
cout<<c[i];
}
}5. High precision multiplication
In fact, the sum of high-precision multiplication is the calculation method in simulating our primary school:
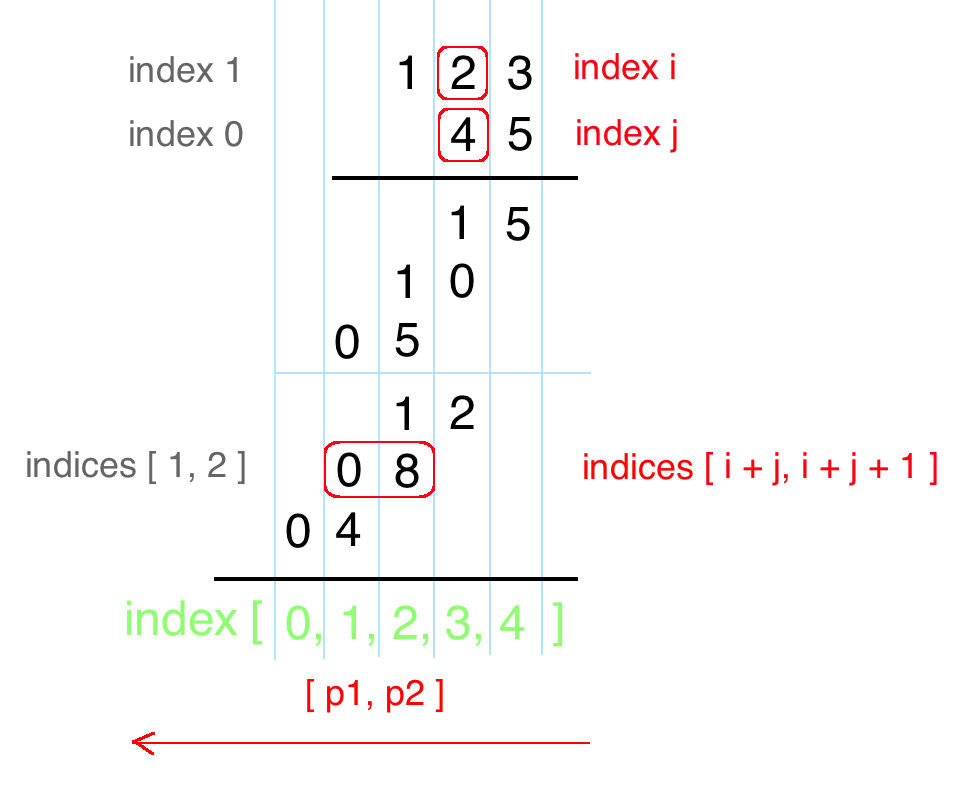
Corresponding code:
class Solution {
public:
string multiply(string num1, string num2) {
int n1=num1.size();
int n2=num2.size();
string res(n1+n2,'0');
for(int i=n2-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=n1-1;j>=0;j--){
int tmp=(res[i+j+1]-'0')+(num1[j]-'0')*(num2[i]-'0');
res[i+j+1]=tmp%10+'0';//Current bit
res[i+j]+=tmp/10; //The previous bit plus carry, res[i+j] has been initialized to '0', and the int type is automatically converted to char, so '0' is not added here
}
}
//Remove leading zeros in the first place
for(int i=0;i<n1+n2;i++){
if(res[i]!='0')
return res.substr(i);
}
return "0";
}
};
6. High precision factorial and
Corresponding OJ link:
Problem solving ideas:
The problem-solving ideas are divided into two parts:
1. Factorial calculation
2. Calculation and
See the code for solving the problem
Corresponding code:
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void fact(int n,vector<int>&tmp) {
int carry = 0;//carry
for (int j = 1; j <= tmp[0]; j++) {
tmp[j] = tmp[j] * n + carry;
carry = tmp[j] / 10;
tmp[j] %= 10;
}
while (carry) {
tmp[++tmp[0]] = carry % 10;
carry /= 10;
}
}
void add(vector<int>&sum,vector<int>&tmp) {
if (sum[0] < tmp[0]) {
sum[0] = tmp[0];
}
int carry = 0;//carry
for (int i = 1; i <= sum[0]; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i] + carry + tmp[i];
carry = sum[i] / 10;
sum[i] %= 10;
}
if (carry) {
sum[++sum[0]] = carry;
}
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>sum(2 * n);
sum[0] = 1;//Represents the length;
vector<int>tmp(2 * n);
tmp[0] = 1;//Representative length
tmp[1] = 1;//Represents the initial value
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact(i,tmp);
add(sum, tmp);
}
for (int i = sum[0]; i >= 1; i--) {
cout << sum[i];
}
return 0;
}7. High precision calculation sequence and
Corresponding OJ link:
Title details - sum of 7-38 series - enhanced version (20 points) (pintia.cn)
Title Description:
Given A number A (1 ≤ A ≤ 9) and A non negative integer n (0 ≤ n ≤ 100000), find the sum of the sequence S=A+AA+AAA + * + AA * A (n A). For example, when A=1 and N=3, S=1+11+111=123.
Enter the number A and the nonnegative integer N.
Output the value of the sum S of its N-term sequence.
1 3
123
Old fellow can draw a picture on paper.
Corresponding code:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,A;
cin>>A>>n;
if(n==0){
cout<<0;
return 0;
}
long long carry=0;//carry
vector<int>arr(5*n);
int high=0;
int i;
for( i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i]=((n-i)*A+carry)%10;//Take the remaining 10;
carry=((n-i)*A+carry)/10;//Calculate carry
high=i;//Record the highest bit
}
if(carry){//See if there is carry
arr[i]=carry;
high=i;//Modify the highest bit
}
for(int j=high;j>=0;j--){
cout<<arr[j];
}
}