Simple use of Swagger2
1. Dependencies needed to import Swagger2
<!--Add to Swagger rely on --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.8.0</version> </dependency> <!--Add to Swagger-UI rely on --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.8.0</version> </dependency>
- Keep versions as consistent as possible
2. Configuring Swagger2
- Create a new Swagger2Config class
package com.yonyou.config; import io.swagger.annotations.Api; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport; import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder; import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors; import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors; import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo; import springfox.documentation.service.Contact; import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType; import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket; import springfox.documentation.swagger.web.UiConfiguration; import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2; @Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class Swagger2Config extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { @Override public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { registry.addResourceHandler("/swagger-ui.html") .addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/"); registry.addResourceHandler("webjars/**") .addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"); } @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .select() //Scanned controller Package .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.yonyou.controller")) .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withClassAnnotation(Api.class)) .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(ApiOperation.class)) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() .title("test API") .description("Test System Interface Document Description") .contact(new Contact("Liu Lusheng", "", "312885991@qq.com")) .version("1.0") .build(); } @Bean UiConfiguration uiConfig() { return new UiConfiguration(null, "list", "alpha", "schema", UiConfiguration.Constants.DEFAULT_SUBMIT_METHODS, false, true, 60000L); } }
3. Writing Test Class FileController
@Api(value = "File Operation API", tags = "File Upload and Download") @RestController @RequestMapping("/file") public class FileController { //Location of file storage private final String location = "D:/upload/"; @ApiOperation(value = "File Download", notes = "File Download") @GetMapping("/download") public Result downLoadFile(@ApiParam(value = "Fill in files to download") String fileName, HttpServletResponse response){ File file = new File(location, fileName); if(file.exists()){ response.setContentType("application/force-download"); response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;fileName=" + fileName); FileInputStream input = null; try{ input = new FileInputStream(file); ServletOutputStream out = response.getOutputStream(); int real; byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; while((real=input.read(bytes))!=-1){ out.write(bytes, 0, real); } return Result.success(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); return Result.error("File Download Exception"); } } return Result.error("File requested for download is empty"); } @ApiOperation(value = "File Upload", notes= "File Upload") @PostMapping("/upload") public Result upLoadFile(@ApiParam(value = "Select Files to Upload",required = true) MultipartFile file){ if (file.isEmpty()){ return Result.error("Please do not upload empty files"); } String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename(); long size = file.getSize(); //Console Prints File Information System.out.println(fileName+"-->"+size); //Stitch into new file names int index = fileName.lastIndexOf("."); String suffix = fileName.substring(index); String name = Date.valueOf(LocalDate.now())+suffix; //Indicate file upload location File dest = new File(location, name); //Determine whether the file parent directory exists if(!dest.getParentFile().exists()){ dest.getParentFile().mkdir(); } try { //write file file.transferTo(dest); return Result.success(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return Result.error("File upload failed"); } } }
4. Visit http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html address to view
- Result:
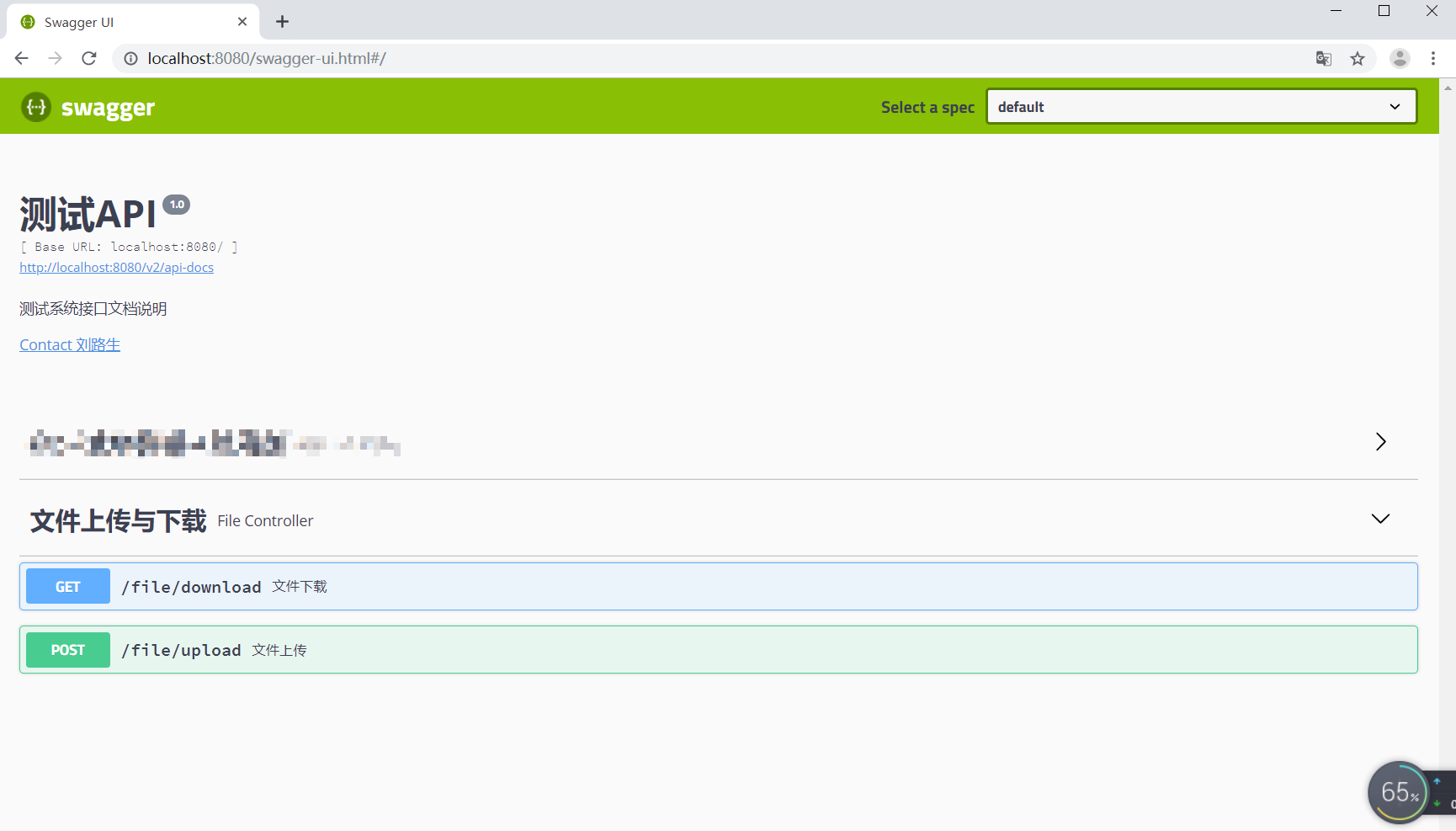
5. Common Notes for swagger2
-
@Api: Used on the requested class to illustrate its role
@Api: Used on the requested class to illustrate its role tags="Explain the role of this class" value="This parameter doesn't make sense, so no configuration is required" -
@ApiOperation: Used in the requested method to illustrate the effect of the method
@ApiOperation: "Used in the requested method to illustrate the role of the method" value="Explain the role of the method" notes="Note description of the method"Example:
@ApiOperation(value="User registration",notes="Mobile phone number, password are required, age is required, but must be a number") -
@ApiParam: Used on requested parameters to describe them
@ApiParam:"Explain the parameters used on the request" value:"Explain the parameters" required:"Is the parameter required to pass"Example:
public Result upLoadFile(@ApiParam(value = "Select Files to Upload",required = true) MultipartFile file) -
@ApiImplicitParams: Used on request methods with a set of parameter descriptions
@ApiImplicitParams: Used on request methods with a set of parameter descriptions @ApiImplicitParam: Used in the @ApiImplicitParams comment to specify configuration information for a request parameter Name: parameter name value: explanation and explanation of parameters in Chinese characters required: whether the parameter must be passed paramType: Where to place the parameter Header --> Get Request Parameters: @RequestHeader .query --> Get Request Parameters: @RequestParam .path (for restful interface)-->Get request parameters: @PathVariable body (not commonly used) form (not commonly used) DataType: Parameter type, default String, other value dataType="Integer" defaultValue: The default value of the parameterExample:
@ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name="mobile",value="Cell-phone number",required=true,paramType="form"), @ApiImplicitParam(name="password",value="Password",required=true,paramType="form"), @ApiImplicitParam(name="age",value="Age",required=true,paramType="form",dataType="Integer") }) -
@ApiResponses: Method used for requests to represent a set of responses
@ApiResponses: Method used for requests to represent a set of responses @ApiResponse: Used in @ApiResponses to convey an incorrect response message code: a number, such as 400 message: information, such as "request parameters not filled in" response: class that throws an exceptionExample:
@ApiOperation(value = "select1 request",notes = "Multiple parameters, multiple query parameter types") @ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code=400,message="Request parameters not filled in"), @ApiResponse(code=404,message="Request path is missing or page Jump path is incorrect") }) -
@ApiModel: Used on response classes to represent information that returns response data
@ApiModel: Used on response classes to represent information that returns response data (This is typically used when post s are created using scenes like @RequestBody, When a request parameter cannot be described with the @ApiImplicitParam annotation) @ApiModelProperty: Used on attributes to describe attributes of response classesExample:
import java.io.Serializable; @ApiModel(description= "Return Response Data") public class RestMessage implements Serializable{ @ApiModelProperty(value = "Success or not") private boolean success=true; @ApiModelProperty(value = "Return Object") private Object data; @ApiModelProperty(value = "error number") private Integer errCode; @ApiModelProperty(value = "error message") private String message; /* getter/setter */ }