[the external chain picture transfer fails. The source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (IMG yrgfthrr-1625790195541)( https://ducafecat.tech/2021/07/09/translation/how-to-handle-401-unauthorised-with-dio-interceptor-flutter/2021-07-08-22-00-27.png )]
Old iron remember to forward, brother old fellow will show more Flutter good text ~ ~ ~
Wechat group ducafecat
Station b https://space.bilibili.com/404904528
original text
https://medium.com/@wmnkrishanmadushanka/how-to-handle-401-unauthorised-with-dio-interceptor-flutter-60398a914406
reference resources
- https://pub.dev/packages/dio/versions/4.0.0
- https://pub.dev/packages/flutter_secure_storage
- https://pub.dev/packages/shared_preferences
text
In this article, I'll explain how to use fluent DIO (4.0.0) for network calls and how to use refresh tokens and access tokens to handle authorization processing 401 in your fluent application.
Before reading this article, I hope you have a basic understanding of mobile application development.
Basic Authentication flow with refresh and access tokens
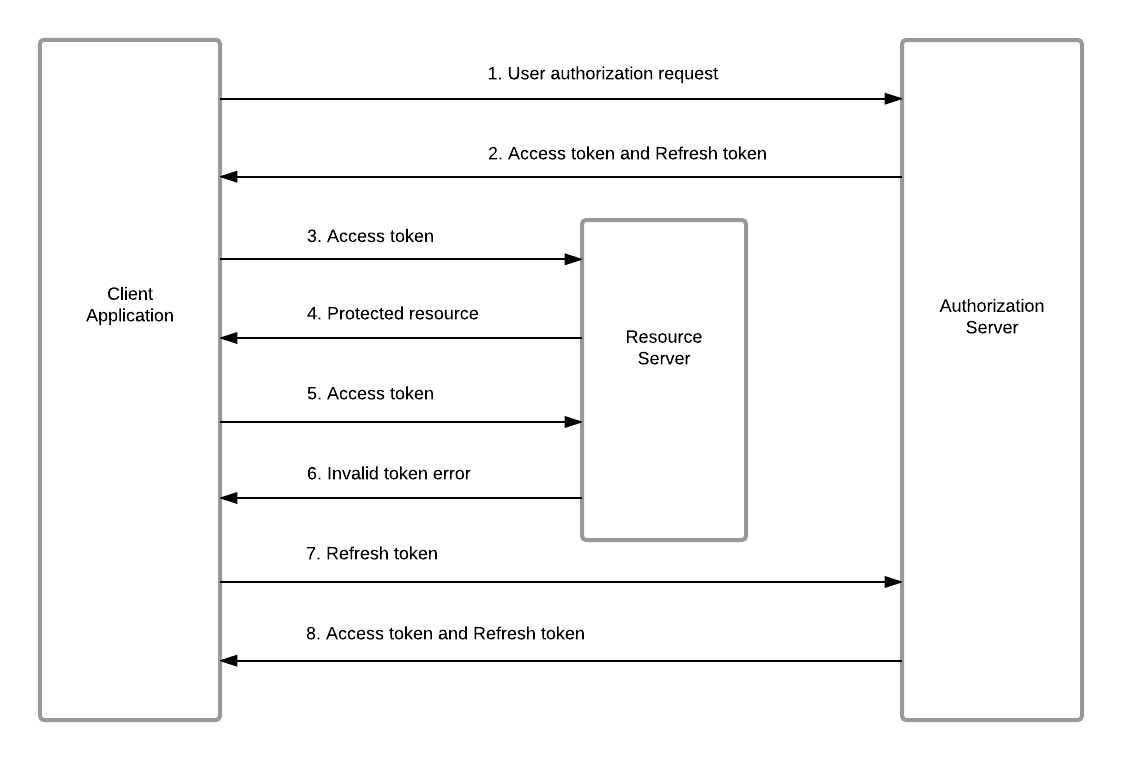
As you can see in the figure above, it is clear what the process is when using refresh and access tokens in the authentication flow. After you log in, you get two tags called refresh and access. This access token expires quickly (the refresh token also expires, but it will take more time than the access token). When you make a request with an expired access token, the status code 401 (unauthorized) will appear in the response. In this case, you must request a new token from the server and issue the previous request again with a valid access token. If the refresh token has also expired, you must instruct the user to log in to the page and force the user to log in again.
Dio class
class DioUtil {
static Dio _instance;//method for getting dio instance Dio getInstance() {
if (_instance == null) {
_instance = createDioInstance();
}
return _instance;
}
Dio createDioInstance() {
var dio = Dio();// adding interceptor dio.interceptors.clear();
dio.interceptors.add(InterceptorsWrapper(onRequest: (options, handler) {
return handler.next(options);
}, onResponse: (response, handler) {
if (response != null) {
return handler.next(response);
} else {
return null;
}
}, onError: (DioError e, handler) async {
if (e.response != null) {
if (e.response.statusCode == 401) {//catch the 401 here
dio.interceptors.requestLock.lock();
dio.interceptors.responseLock.lock();
RequestOptions requestOptions = e.requestOptions;
await refreshToken();
Repository repository = Repository();
var accessToken = await repository.readData("accessToken");
final opts = new Options(method: requestOptions.method);
dio.options.headers["Authorization"] = "Bearer " + accessToken;
dio.options.headers["Accept"] = "*/*";
dio.interceptors.requestLock.unlock();
dio.interceptors.responseLock.unlock();
final response = await dio.request(requestOptions.path,
options: opts,
cancelToken: requestOptions.cancelToken,
onReceiveProgress: requestOptions.onReceiveProgress,
data: requestOptions.data,
queryParameters: requestOptions.queryParameters);
if (response != null) {
handler.resolve(response);
} else {
return null;
}
} else {
handler.next(e);
}
}
}));
return dio;
}
static refreshToken() async {
Response response;
Repository repository = Repository();
var dio = Dio();
final Uri apiUrl = Uri.parse(BASE_PATH + "auth/reIssueAccessToken");
var refreshToken = await repository.readData("refreshToken");
dio.options.headers["Authorization"] = "Bearer " + refreshToken;
try {
response = await dio.postUri(apiUrl);
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
LoginResponse loginResponse =
LoginResponse.fromJson(jsonDecode(response.toString()));
repository.addValue('accessToken', loginResponse.data.accessToken);
repository.addValue('refreshToken', loginResponse.data.refreshToken);
} else {
print(response.toString()); //TODO: logout
}
} catch (e) {
print(e.toString()); //TODO: logout
}
}
}
The above is the complete course, and I will explain the most important part.
Mainly, as you can see in the creatediinstance method, you must add an interceptor to capture 401. 401 occurs when error: (DioError e, handler) async {} is called. So your heart
- Check the error code(401),
- Get new access token get a new access token
await refreshToken();
The above code calls the refreshToken method and stores the new refresh and access token in the repository. (for repositories, you can use secure storage or shared preferences)
- Copy the previous request and set a new access token
RequestOptions requestOptions = e.requestOptions;
Repository repository = Repository();
var accessToken = await repository.readData("accessToken");
final opts = new Options(method: requestOptions.method);
dio.options.headers["Authorization"] = "Bearer " + accessToken;
dio.options.headers["Accept"] = "*/*";
- Make the previous call again
final response = await dio.request(requestOptions.path,
options: opts,
cancelToken: requestOptions.cancelToken,
onReceiveProgress: requestOptions.onReceiveProgress,
data: requestOptions.data,
queryParameters: requestOptions.queryParameters);
Once you receive a reply, call
handler.resolve(response);
The response will then be sent to the location where you called the api, as shown below.
var dio = DioUtil().getInstance();
final String apiUrl = (BASE_PATH + "payments/addNewPayment/");
var accessToken = await repository.readData("accessToken");
dio.options.headers["Authorization"] = "Bearer " + accessToken;
dio.options.headers["Accept"] = "*/*";//response will be assigned to response variable
response = await dio.post(apiUrl, data: event.paymentRequest.toJson());
Thats all. happy coding 😃
© Cat brother
https://ducafecat.tech/
https://github.com/ducafecat
Previous period
Open Source
GetX Quick Start
https://github.com/ducafecat/getx_quick_start
News client
https://github.com/ducafecat/flutter_learn_news
Translation of strapi manual
https://getstrapi.cn
Wechat discussion group ducafecat
Series collection
translation
https://ducafecat.tech/categories/%E8%AF%91%E6%96%87/
Open source project
https://ducafecat.tech/categories/%E5%BC%80%E6%BA%90/
Basics of Dart programming language
https://space.bilibili.com/404904528/channel/detail?cid=111585
Introduction to Flutter zero Foundation
https://space.bilibili.com/404904528/channel/detail?cid=123470
Flutter actual combat news client from scratch
https://space.bilibili.com/404904528/channel/detail?cid=106755
Fluent component development
https://space.bilibili.com/404904528/channel/detail?cid=144262
Flutter Bloc
https://space.bilibili.com/404904528/channel/detail?cid=177519
Flutter Getx4
https://space.bilibili.com/404904528/channel/detail?cid=177514
Docker Yapi
https://space.bilibili.com/404904528/channel/detail?cid=130578