preface
Before introducing the text, let's talk about spel
01 what is spel
Spring expression language ("spiel") is a powerful expression language that supports querying and manipulating object graphs at run time.
The language syntax is similar to Unified EL, but provides other functions, most notably method calls and basic string template functions.
In addition, it is not directly bound to Spring, but can be used independently
What functions can 02spel support
- Literal expression
- Boolean and relational operators
- Common expressions
- Class expression
- Access properties, arrays, lists, and mappings
- Method call
- Relational operator
- distribution
- Call constructor
- Bean reference
- Array construction
- Inline list
- Inline Map
- Ternary operator
- variable
- User defined functions
- Set projection
- Set selection
- Template expression
The above spel syntax can be found through the following link
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#expressions-language-ref
03
Basic flow of spel parsing
The shape is shown in the figure below

The general steps are as follows
- Create parser
- Analytical expression
- Construct context
- evaluation
04
Introduction to spel core interface
org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser
Expression parser, whose main function is to convert string expressions into expression objects. Supports parsing templates and standard expression strings
Its default implementation is
org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser
org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext
Spel calculates the "Context" of the expression value. This Context object can contain multiple objects, but there can only be one root object. When the expression contains variables, spel will evaluate the expression according to the value of the variables in the EvaluationContext. You can use setRootObject method to set the root object, setVariable method to register custom variables, and registerFunction to register custom functions.
Its default implementation is
org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext
org.springframework.expression.Expression
Represents an expression. The expression value is obtained according to the context through the getValue method
Its default implementation is
org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpression
05
spel official documents
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#expressions
02
text
Let's give a brief introduction to spel. Let's demonstrate it with a small example.
This small example is mainly realized through AOP+SPEL. The example scenario is: when the product price is greater than 10, put it into the local cache, and print the value of the local cache through the timer
01
Business logic implementation core code
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductMockDao productMockDao;
@Override
@LocalCacheable(key = "#product.id",condition = "#product.price ge 10")
public Product save(Product product) {
return productMockDao.save(product);
}
}02
aop aspect writing
@Component
@Aspect
public class CacheAspect {
@Around("@annotation(localCacheable)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, LocalCacheable localCacheable) throws Throwable{
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature)pjp.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
Object result = pjp.proceed();
String key = pjp.getTarget().getClass().getName() + "_" + method.getName() + "_" + args.length;
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(localCacheable.key())){
key = SpELParserUtils.parse(method,args,localCacheable.key(),String.class);
}
System.out.println("key:"+key);
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(localCacheable.condition())){
boolean condition = SpELParserUtils.parse(method,args,localCacheable.condition(),Boolean.class);
if(condition){
LocalCache.INSTANCE.put(key,result);
}
}else{
LocalCache.INSTANCE.put(key,result);
}
return result;
}
}03
Parsing spel core tool classes
@Slf4j
public final class SpELParserUtils {
private static final String EXPRESSION_PREFIX = "#{";
private static final String EXPRESSION_SUFFIX = "}";
/**
* expression parser
*/
private static ExpressionParser expressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser();
/**
* Parameter name parser, which is used to obtain the parameter name
*/
private static DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
private SpELParserUtils(){}
/**
* Parsing spel expressions
*
* @param method method
* @param args Parameter value
* @param spelExpression expression
* @param clz Type of returned result
* @param defaultResult Default result
* @return The result of executing the spel expression
*/
public static <T> T parse(Method method, Object[] args, String spelExpression, Class<T> clz, T defaultResult) {
String[] params = parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(method);
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
//Setting context variables
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
context.setVariable(params[i], args[i]);
}
T result = getResult(context,spelExpression,clz);
if(Objects.isNull(result)){
return defaultResult;
}
return result;
}
/**
* Parsing spel expressions
*
* @param method method
* @param args Parameter value
* @param spelExpression expression
* @param clz Type of returned result
* @return The result of executing the spel expression
*/
public static <T> T parse(Method method, Object[] args, String spelExpression, Class<T> clz) {
String[] params = parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(method);
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
//Setting context variables
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
context.setVariable(params[i], args[i]);
}
return getResult(context,spelExpression,clz);
}
/**
* Parsing spel expressions
*
* @param param Parameter name
* @param paramValue Parameter value
* @param spelExpression expression
* @param clz Type of returned result
* @return The result of executing the spel expression
*/
public static <T> T parse(String param, Object paramValue, String spelExpression, Class<T> clz) {
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
//Setting context variables
context.setVariable(param, paramValue);
return getResult(context,spelExpression,clz);
}
/**
* Parsing spel expressions
*
* @param param Parameter name
* @param paramValue Parameter value
* @param spelExpression expression
* @param clz Type of returned result
* @param defaultResult Default result
* @return The result of executing the spel expression
*/
public static <T> T parse(String param, Object paramValue,String spelExpression, Class<T> clz, T defaultResult) {
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
//Setting context variables
context.setVariable(param, paramValue);
T result = getResult(context,spelExpression,clz);
if(Objects.isNull(result)){
return defaultResult;
}
return result;
}
/**
* Gets the result of the spel expression
*
* @param context Parser context interface
* @param spelExpression expression
* @param clz Type of returned result
* @return The result of executing the spel expression
*/
private static <T> T getResult(EvaluationContext context,String spelExpression, Class<T> clz){
try {
//Analytical expression
Expression expression = parseExpression(spelExpression);
//Gets the value of the expression
return expression.getValue(context, clz);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(),e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Analytical expression
* @param spelExpression spel expression
* @return
*/
private static Expression parseExpression(String spelExpression){
// If the expression is an #{} expression, you need to pass in the template parser context for parsing
if(spelExpression.startsWith(EXPRESSION_PREFIX) && spelExpression.endsWith(EXPRESSION_SUFFIX)){
return expressionParser.parseExpression(spelExpression,new TemplateParserContext());
}
return expressionParser.parseExpression(spelExpression);
}
}04
Example effect
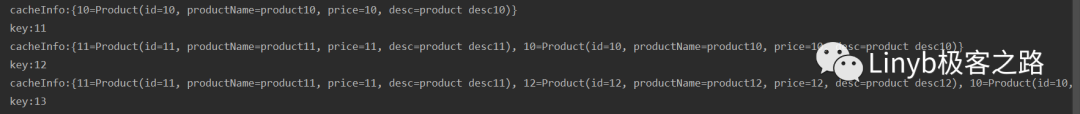
03
summary
Spel can be seen everywhere in spring applications, such as @ cacheable, @ Value, etc. we can also implement functions suitable for our business scenarios through aop+spel
04
demo link
https://github.com/lyb-geek/springboot-learning/tree/master/springboot-aop-spel