1, New features of HTML5
1.1 new label
- : header label
- : navigation tab
- : content label
- : defines an area of the document
- : sidebar labels
- : tail label
<body>
<header>Header title</header>
<nav>:Navigation tab</nav>
<acticle>:Content label</acticle>
<section>:Define an area of the document</section>
<aside>:Sidebar label</aside>
<footer>:Tail label</footer>
</body>
1.2 new multimedia Tags
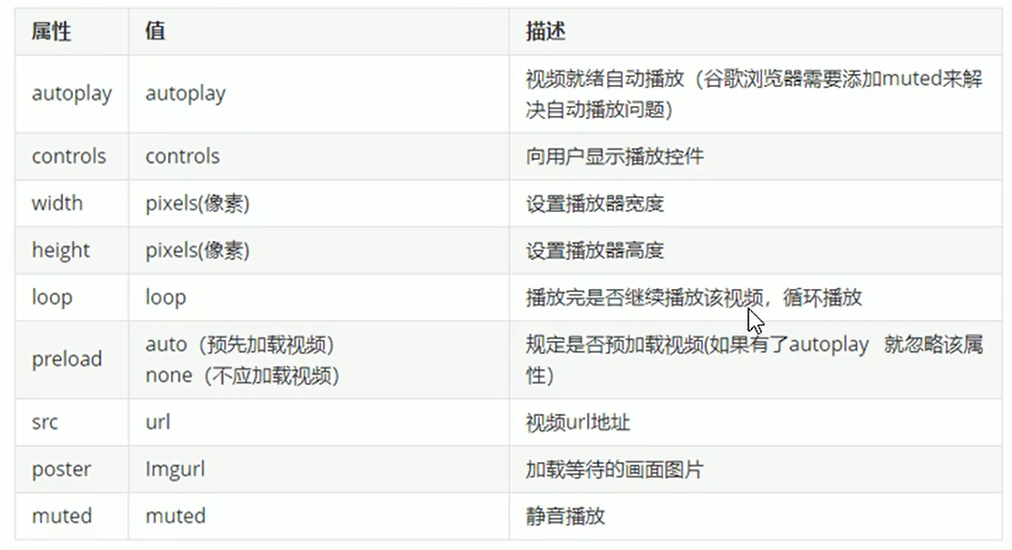
1.1 common attributes of video
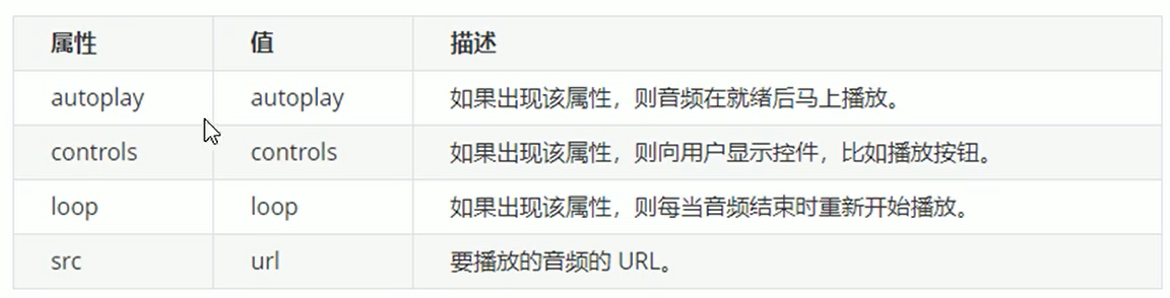
1.2 audio
1.3. New input type in HTML
The written code must be included in the form field

<form action="">
<ul>
<li> Email:<input type="email"> </li>
<li> Website:<input type="url"> </li>
<li> Date:<input type="date"> </li>
<li>Time: <input type="time"> </li>
<li> number:<input type="number"> </li>
<li> phone number:<input type="tel"> </li>
<li> Search:<input type="search"> </li>
<li> Color: <input type="color"> </li>
<li> <input type="submit"> Submit</li>
</ul>
</form>
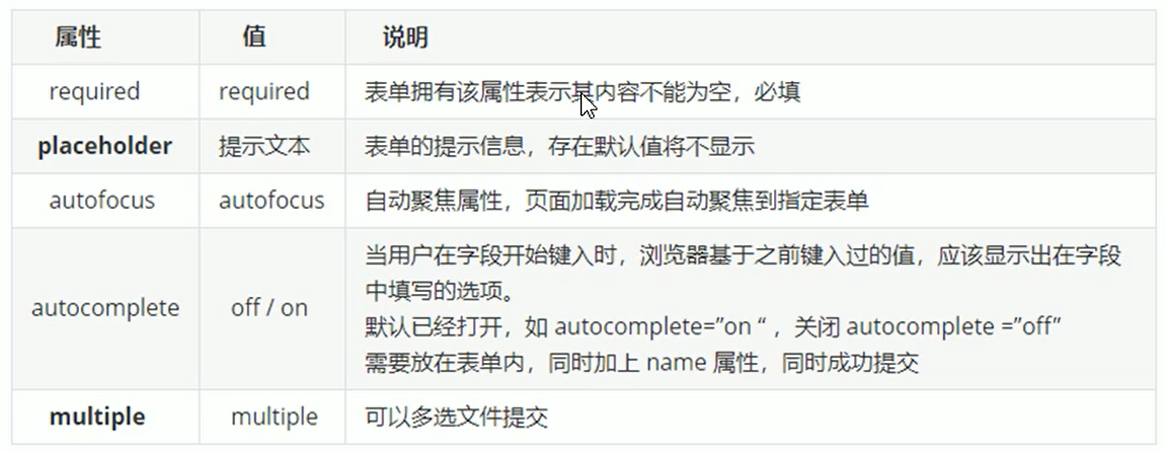
1.4. Add HTML form attributes
2, New CSS features
1. CSS3 new attribute selector (weight 10)

<style>
input[value]{ /* The selected element must be input, but it also has the attribute value */
background-color: pink;
}
input[type=text]{
color: skyblue;
}
div[class^=icon]{ /* Select these elements with div first, then class attribute, and attribute value must start with icon */
color: pink;
}
section[class$=data]{ /* Select those elements that first have a section, then have a class attribute, and the attribute value must be the end of icon */
color: blueviolet;
}
span[class*=z]{ /* Select these elements with span first, then class attribute and attribute value must contain "Z" */
font-weight: 700px;
color: lawngreen;
}
</style>
<body>
<!-- 1,Using attribute selectors can eliminate the need for classes or id selector -->
<!-- <input type="text" value="enter one user name">
<input type="text"> -->
<!-- 2,The attribute selector can also select attributes=Some elements of the value -->
<input type="text" name="" id="">
<input type="password" name="" id="">
<!-- 3,The attribute selector can select some elements at the beginning of the attribute value -->
<div class="icon1">Small icon 1</div>
<div class="icon2">Small icon 2</div>
<div class="icon3">Small icon 3</div>
<div class="icon4">Small icon 4</div>
<div>none of my business</div>
<!-- 4,The attribute selector can select certain elements at the end of the attribute value -->
<section class="icon1-data">I'm bean paste bag</section>
<section class="icon2-data">I'm bean beef bun</section>
<section class="icon3-ico">Who am I</section>
<!-- 5,There are elements in the matching attribute that contain some fields -->
<span class="iconz">Oil duck bean sandbag</span>
<span class="icon">Duck bean beef bun with oil</span>
<span class="iconz">Come on, duck dry rice King</span>
<span class="iconz">never give up</span>
</body>
2. Structure pseudo class selector

<style>
ul li:first-child{ /* Choose the first child in ul */
background-color: pink;
}
ul li:last-child{ /* Choose the last child in ul */
background-color: skyblue;
}
ul li:nth-child(2){ /* Chose the second child*/
background-color: red;
}
</style>
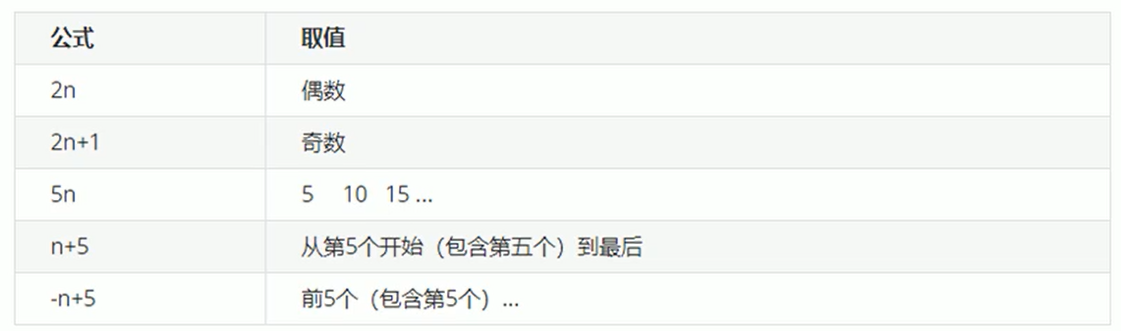
1.1. Nth child (n) select one or more specific child elements of an element
- n can be numbers, keywords and formulas
- If n is a number, it starts with the nth child element, starting with the number 1
- n can also be Keywords: even, odd
<style>
ul li:nth-child(even){ /* 1,Pick out all the even even even children */
background-color: yellow;
}
ul li:nth-child(odd){ /* 1,Pick out all the odd odd odd children */
background-color: greenyellow;
}
/* ol li:nth-child(n){ Starting from 0, add 1 to the back every time. It must be n. It's not difficult. Other letters are equivalent to choosing all children
background-color: pink;
} */
ol li:nth-child(2n){ /* If write 2n equals all even numbers are selected */
background-color: pink;
}
ol li:nth-child(2n+1){ /* If 2n+1 is written, all odd numbers are selected */
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
1.2 difference between nth child and nth of type
-
1.nth- child sorts and selects all children in the parent element (the sequence number is fixed). First find the nth child, and then see if it matches E
-
2. Nth of type sorts and selects the specified child elements in the parent element, matches e first, and then finds the nth child according to E
<style>
/* nth-child And nth of type */
/* nth-child Will sequence all the boxes */
/* When executing, first look at nth child (1), and then go back to the previous div*/
section div:nth-child(1){
background-color: red;
}
/* nth-of-type The boxes of the specified elements are arranged in sequence numbers */
/* When executing, first look at the element specified by div, and then go back to see: nth child (1) which child*/
section div:nth-of-type(1){
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
3. Pseudo element selector (emphasis)
- Pseudo element selectors can help us create new tag elements using CSC without HM tags, thus simplifying the HTM structure.
| Selector | brief introduction |
|---|---|
| ::before | Insert content before the inside of the element |
| ::after | Insert content after the inside of the element |
be careful:
- before and after create an element, but they are inline elements
- The newly created element cannot be found in the document tree, so we call it a pseudo element
- Syntax: element: before
- before and after must have content attribute
- Before creates an element before the parent element content, and after inserts an element after the parent element content
- The pseudo element selector, like the label selector, has a weight of 1
- 1.1 pseudo element selector uses Font Icon
<style>
div{
position: relative;
width: 200px;
height: 35px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
div::after{
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
font-family: "iconfont";
content: "\e6a1";
}
</style>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
1.2 pseudo element selector imitation potato net effect
<style>
.box::before{
content: '';
display: none;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .3);
}
.box:hover::before{
display: block;
}
</style>
1.3 pseudo element selector clear float
<style>
clearfix: after
content: '';
display: block
height: 0;
clear: both;
visibility: hidden;
clearfix:before, .clearfix: after {
content:'';
display: table; /* Converted to block level elements and displayed in one line*/
}
- List item
clearfix:after {
clear: both;
}
</style>
3, CSS3 box model
- In CSS3, you can specify the box model through box sizing. There are two values: content box and border box. In this way, we can
The way the box size is calculated changes
There are two situations: - 1. Box sing: content - the box size is width+ padding+ border (previously the default)
- 2. Box sizing: the size of the border box box is width
- 3. If we change the box model to box sizing; Border box, then padding and border will not support a large box (provided that
padding and border will not exceed width)
3.1 CSS3 filter
- The filter CSS property applies graphical effects such as blur or color offset to the element.
3.2. CSS3 calc function
- calc {} This CSS function allows you to perform some calculations when declaring CSS property values.
<style>
.father{
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.son{
width: calc(100% - 30px); /* Note that there should be a space in the middle */
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="father">
<!-- Our child box is always 30 smaller than the parent box px -->
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
3.3 CSS3 transition (key)
- Transition: the attribute to transition takes time, and when the motion curve starts; (who gives too much to who)
- 1. Attribute: the css attribute you want to change, width, height, background color, and inner and outer margins. If you want all attributes to be
Change transition, just write a name - 2. Time spent: the unit is seconds (the unit must be written), such as 055
- 3. Motion curve: the default is ease (can be omitted)
- 4. When to start: the unit is seconds (the unit must be written). You can set the delay trigger time. The default is 0s (can be omitted)
<style>
div{
/* The transition is written wherever the attribute wants to change */
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
/* transition: The time spent on changing attributes and when the motion curve starts; */
/* transition: width 1s ease 0s; */
/* transition: width .5s, height .5s; Multiple attributes are written together */
/* transition: all 1s; /* If you want multiple attributes to change, write all for the attribute */
}
div:hover{
width: 400px;
height: 500px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>