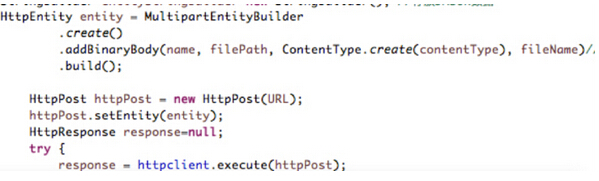
1. MultipartEntityBuilder for File Upload
Prior to HttpCient 4.3, MultipartEntity was the main class for uploading files, but it is no longer recommended for this class. The class that replaces it is MultipartEntityBuilder.
Introduction of MultipartEntityBuilder Class
MultipartEntityBuilder is a class used to create HttpEntity. Its main methods are:
|
Modifiers and types |
Method and description |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addBinaryBody(String name, byte[] b) Adding data to byte arrays in binary form. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addBinaryBody(String name, byte[] b, ContentType contentType, String filename) Adding data to byte arrays in binary form. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addBinaryBody(String name, File file) Add data to the file in binary form. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addBinaryBody(String name, File file, ContentType contentType, String filename) Add data to the file in binary form. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addBinaryBody(String name, InputStream stream) |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addBinaryBody(String name, InputStream stream, ContentType contentType, String filename) Add data to the input stream in binary form. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addPart(String name, ContentBody contentBody) Add data of ContentBody type. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addTextBody(String name, String text) Add text data. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
addTextBody(String name, String text, ContentType contentType) Adds text data to the specified content type. |
|
HttpEntity |
build() Create an HttpEntity. |
|
static MultipartEntityBuilder |
create() Create a MultipartEntityBuilder object. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
setBoundary(String boundary) Set boundaries. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
setCharset(Charset charset) Set the encoding format of the request. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
setLaxMode() |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
setMode(HttpMultipartMode mode) Set mode. |
|
MultipartEntityBuilder |
setStrictMode() |
The main methods are as follows:
The addBinaryBody, addPart, and addTextBody methods are used to add data to be uploaded. From the table above, you can see that the methods used to add data are all key-value types. So on the server side, we can get the corresponding key data by request.getPart("keyname"). You can also get all the data submitted by the client through request.getParts().
1. File, InputStream, byte [] data can be added directly by addBinaryBody method.
2. Only data of Content Body type can be added by addPart method. Subclasses of String, File and InputStream corresponding to Content Body type, such as FileBody, InputStream Body and StringBody, have been provided in the org.apache.http.entity.mime.content package, through which we can convert data of String, File and InputStream type into data of Body type.
3. Through the addTextBody method, we can easily add text data.
3. Implement by HttpCient Upload File Core Code
The Android side needs to be added httpcore-4.3.2.jar,httpmime-4.3.5.jar Two bags. Two bags are indispensable. Here I use the latest version of HTTP Cient, you can from http://hc.apache.org/downloads.cgi Download the required jar package, if the above website can not be opened, you need not worry, I have uploaded the jar package needed in the project to CSDN.< httpcomponents-client-4.3.5-bin.zip > Need friends can download.
3.1 Android-side project core code:
HttpClient client=new DefaultHttpClient();// Open a client HTTP request
HttpPost post = new HttpPost(url);//Create HTTP POST requests
MultipartEntityBuilder builder = MultipartEntityBuilder.create();
builder.setCharset(Charset.forName("uft-8"));//Set the encoding format of the request
builder.setMode(HttpMultipartMode.BROWSER_COMPATIBLE);//Setting Browser Compatibility Mode
int count=0;
for (File file:files) {
builder.addBinaryBody("file"+count, file);
count++;
}
builder.addTextBody("method", params.get("method"));//Setting Request Parameters
builder.addTextBody("fileTypes", params.get("fileTypes"));//Setting Request Parameters
HttpEntity entity = builder.build();// Generating HTTP POST Entities
post.setEntity(entity);//Setting Request Parameters
HttpResponse response = client.execute(post);// Initiate the request and return the response to the request
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()==200) {
return true;
}
return false; Code analysis:
The above code mainly realizes multi-file upload. In order to save files on the server side, the above code sets parameters named fileTypes. FileTypes is a string composed of uploaded file type names, such as ".jpg.png.docx";
3.2 Core code of server-side project:
The server side can get the type of file to be saved by taking a parameter named fileTypes and splitting it into character arrays. Server segment is mainly used in Servlet 3.0 API. The main methods used are:
request.getParameter(");// Gets the String type data added by the client through the addTextBody method.
request.getPart(");// Gets the specified data added by the client through the addBinaryBody, addPart, addTextBody methods, and returns the object of type Part.
3. request.getParts(); // Gets all the data added by the client through the addBinaryBody, addPart, addTextBody methods, and returns the Collection < Part > type object.
part.getName(); // Get the name of the uploaded file, which is the key specified when uploading.
5. part.getSize()// Gets the size of the uploaded file in bytes.
String fileTypes=request.getParameter("fileTypes");//Get all file types uploaded by the client
String[]typeArray=fileTypes.substring(1).split("\\.");//Split the file type string into String arrays
try {
Iterator<Part>iterator=request.getParts().iterator();
int count=0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {//Traverse all files uploaded by the client
if (count>=typeArray.length)break;//Jump out of the loop if you exceed the size of an array of file types
Part part = (Part) iterator.next();
System.out.println("part.getSize()"+part.getSize());//Get the size of the uploaded file
System.out.println("part.getName()"+part.getName());//Get the name of the uploaded file and the key name when adding data
File file=new File("E:\\upload\\"+count+"."+typeArray[count++]);
InputStream inputStream=part.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[]buffer=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while ((len=inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1) {
fos.write(buffer,0, len);
}
inputStream.close();
fos.close();
}
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}Code analysis:
The server side is implemented through a Servlet, which accesses all file types uploaded by the client by calling request.getParameters ("fileTypes"), and then splits the file type string into String arrays. All data uploaded by client through addBinaryBody, addPart and addTextBody are extracted by request.getParts() method, and then files can be saved by traversing the data set.
Because of the prior agreement with the client, the order of adding uploaded files is before adding request parameters, so the number of uploaded files can be determined according to the length of the split file type array. So when the above code traverses beyond the length of the type array, the program jumps out of the loop and no longer saves the files, because the following Part s are parameters, not to be saved. Save the file.
3.3 Program Running Effect Chart:

IV. Project Code
package com.jph.ufh.activity;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.jph.ufh.R;
import com.jph.ufh.service.UploadService;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* Upload files in batches through httpClient
* @author jph
* Date: 2014.10.09
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ArrayList<File>files;
private Map<String, String>params;
Handler mHandler=new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch (msg.what) {
case UploadService.UPLOAD_SUCCESS:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Upload success", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
}
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
files=new ArrayList<File>();
params=new HashMap<String, String>();
}
public void upload(View v) {
files.clear();
params.clear();
File file=new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),"kaola.jpg");
File file2=new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),"test.docx");
File file3=new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),"test.jpg");
files.add(file);
files.add(file2);
files.add(file3);
StringBuffer sbFileTypes=new StringBuffer();
for (File tempFile:files) {
String fileName=tempFile.getName();
sbFileTypes.append(getFileType(fileName));
}
params.put("fileTypes",sbFileTypes.toString());
params.put("method", "upload");
UploadService uploadService=new UploadService(mHandler);
uploadService.uploadFileToServer(params, files);
}
/**
* Get the type of file
* @param fileName : file name
* @return file type
*/
private String getFileType(String fileName) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."), fileName.length());
}
}
package com.jph.ufh.service;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.entity.mime.HttpMultipartMode;
import org.apache.http.entity.mime.MultipartEntityBuilder;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import android.os.Handler;
/**
* Using HttpClient to upload files to support multi-file uploading
* @author jph
* Date:2014.10.09
*/
public class UploadService {
private static String url="http://10.219.57.16:8080/ServerForUpload/ServletForUpload";
// private static String url="http://10.110.6.58:8080/ServerForUpload/ServletForUpload";
public static final int UPLOAD_SUCCESS=0x123;
public static final int UPLOAD_FAIL=0x124;
private Handler handler;
public UploadService(Handler handler) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.handler=handler;
}
/**
* @param params Request parameters, including the method parameters of the request, such as "upload".
* fileTypes requesting upload are as follows: ".jpg.png.docx"
* @param files Collection of files to upload
*/
public void uploadFileToServer(final Map<String, String> params, final ArrayList<File>files) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
if (uploadFiles(url,params,files)) {
handler.sendEmptyMessage(UPLOAD_SUCCESS);//Notify the main thread that the data was sent successfully
}else {
//Failed to send data to server
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
/**
* @param url servlet Address
* @param params The parameters to be passed
* @param files Documents to be uploaded
* @return true if upload success else false
* @throws ClientProtocolException
* @throws IOException
*/
private boolean uploadFiles(String url,Map<String, String>params,ArrayList<File>files) throws ClientProtocolException, IOException {
HttpClient client=new DefaultHttpClient();// Open a client HTTP request
HttpPost post = new HttpPost(url);//Create HTTP POST requests
MultipartEntityBuilder builder = MultipartEntityBuilder.create();
builder.setCharset(Charset.forName("uft-8"));//Set the encoding format of the request
builder.setMode(HttpMultipartMode.BROWSER_COMPATIBLE);//Setting Browser Compatibility Mode
int count=0;
for (File file:files) {
builder.addBinaryBody("file"+count, file);
count++;
}
builder.addTextBody("method", params.get("method"));//Setting Request Parameters
builder.addTextBody("fileTypes", params.get("fileTypes"));//Setting Request Parameters
HttpEntity entity = builder.build();// Generating HTTP POST Entities
post.setEntity(entity);//Setting Request Parameters
HttpResponse response = client.execute(post);// Initiate the request and return the response to the request
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()==200) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}