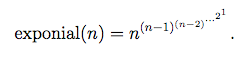I went to it for an exponential cycle section.
After nearly a week's exponential cycle, although I prove that I still can't, I still understand how to use it.
Core thing, power reduction formula: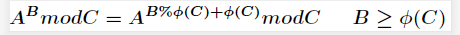
The proof of the mailing mogul: Exponential cyclic section
Then it goes straight to the question.
fzu 1759 Super A^B mod C
The website of fzu seems to have collapsed, so this question is directly edited.
f(0) = 1 and 0^0=1. f(n) = (n%10)^f(n/10) to find f(n)%m.
For the recursive plus exponential cyclic section, f(n)% M = f(n%10)^ f(n/10)% phi(m)+phi(m)% m,
Then f(n/10)%phi(m)=(n/10%10)^f(n/10/10)%phi(m)+phi(phi(m)%phi(m)
A layer of recursion, until n==0, then 0 ^ 0 = 1, return to the current number of mod 1%, and because it is not good to judge whether f(x) is greater than phi(y), so add judgment directly in the fast power.
1 #include<cstdio>
2 typedef long long ll;
3 ll poww(ll a,ll b,ll c){
4 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c;
5 ll ans=1;
6 while(b){
7 if(b&1){
8 ans=ans*a;
9 if(ans>c) ans=ans%c+c;
10 }
11 a=a*a;
12 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c;
13 b>>=1;
14 }
15 return ans;
16 }
17 int euler(int x){
18 int ans=x;
19 for(int i=2;i*i<=x;i++){
20 if(x%i==0){
21 ans-=ans/i;
22 while(x%i==0) x/=i;
23 }
24 }
25 if(x>1) ans-=ans/x;
26 return ans;
27 }
28 ll f(int x,int y){
29 if(x==0) return 1%y;
30 return poww(x%10,f(x/10,euler(y)),y);
31 }
32 int main()
33 {
34 int t,n,m;
35 scanf("%d",&t);
36 while(t--){
37 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
38 printf("%lld\n",f(n,m)%m);
39 }
40 return 0;
41 }
The board fits well and touches the golden tail.
How many n to satisfy the following formula?

First of all, n n!% P = nn!% phi (p) +phi (p)% p, when n < phi (p), we directly set the board to calculate violence, and when n > = phi (p), n!% phi (p) = 0, it is to see how many nphi (p)% p= b, then we can split n into (phi(p)+k), because the index is fixed at this time, (phi(p)+k)phi(p)%p is the same as (phi(p)+k) 1%, there is one. If we have a loop section of length p, we can find out how many results B is contained in the loop section. Another pit is that when p==1, the answer is obviously m+1, and if m=2 is 64-1 power, the answer will go beyond unsigned long, so it will be judged.


1 #include<cstdio>
2 typedef unsigned long long ull;
3 const int N=101108;
4 int phi[N],yu[N];
5 void init(){//Preprocessing Euler Function
6 for(int i=1;i<N;i++) phi[i]=i;
7 for(int i=2;i<N;i+=2)phi[i]/=2;
8 for(int i=3;i<N;i+=2) if(phi[i]==i){
9 for(int j=i;j<N;j+=i) phi[j]=phi[j]/i*(i-1);
10 }
11 }
12 ull poww(ull a,ull b,ull c){
13 ull ans=1;
14 while(b){
15 if(b&1) ans=ans*a%c;
16 a=a*a%c;
17 b>>=1;
18 }
19 return ans;
20 }
21 int main()
22 {
23 init();
24 int t=1,T,b,p,pp;
25 ull m;
26 scanf("%d",&T);
27 while(t<=T){
28 scanf("%d%d%llu",&b,&p,&m);
29 printf("Case #%d: ",t++);
30 if(p==1){
31 if(m==18446744073709551615ull) printf("18446744073709551616\n");
32 else printf("%llu\n",m+1);
33 continue;
34 }
35 pp=phi[p];
36 ull jc=1,ans=0;
37 for(int i=0;i<pp&&i<=m;i++){//Pretreatment n<phi(p)Situation
38 if(i){
39 jc*=1ll*i;
40 if(jc>=pp) jc=jc%pp+pp;
41 }
42 if(poww(i,jc,p)==b) ans++;
43 }
44 if(pp<=m){//Processing Circle Section
45 int num=0,lim;
46 for(int i=0;i<p;i++){
47 yu[i]=poww(pp+i,pp,p);
48 if(yu[i]==b) num++;
49 }
50 ans+=1llu*(m-pp+1)/p*num;
51 lim=(m-pp+1)%p;
52 for(int i=0;i<lim;i++)
53 if(yu[i]==b) ans++;
54 }
55 printf("%llu\n",ans);
56 }
57 return 0;
58 }
The circle of love
Topic: a1= p,
an+1= pan for n >= 1,
bn = an mod m!,
seek
It can be seen that finding a ^ p ^ p ^ p ^ p ^ p ^ p ^ p ^ p ^ p% m!, n p, n tends to be infinite, that is, recursively inserting an exponential loop section, and then incredibly n tends to be infinite, so the x, phi (phi (m)) of mod is shrinking all the time. When p%x=0, it returns a pp%x, and then goes up to several times of 0, which is already. No impact.
Also, the output format is a bit hollow, there is an empty line.


1 #include<cstdio>
2 typedef long long ll;
3 int p,m,jc[15]={1};
4 int euler(int x){
5 int ans=x;
6 for(int i=2;i*i<=x;i++){
7 if(x%i==0){
8 ans-=ans/i;
9 while(x%i==0) x/=i;
10 }
11 }
12 if(x>1) ans-=ans/x;
13 return ans;
14 }
15 ll poww(ll a,ll b,ll c){
16 ll ans=1;
17 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c;
18 while(b){
19 if(b&1){
20 ans*=a;
21 if(ans>=c) ans=ans%c+c;
22 }
23 a*=a;
24 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c;
25 b>>=1;
26 }
27 return ans;
28 }
29 ll ap(int x){
30 if(p%x==0) return poww(p,p,x);
31 return poww(p,ap(euler(x)),x);
32 }
33 int main()
34 {
35 for(int i=1;i<=12;i++) jc[i]=jc[i-1]*i;
36 int flag=0;
37 while(~scanf("%d%d",&p,&m)){
38 if(flag) printf("\n");
39 flag=1;
40 printf("%lld\n",ap(jc[m])%jc[m]);
41 }
42 return 0;
43 }
apppppppppp
It's also a recursive plus exponential loop section. It's important to note that there are two recursive exits, one is n==1, because the other is the same idea as the previous one, when x%y==0, return an xx-1%y.


1 #include<cstdio>
2 typedef long long ll;
3 int euler(int x){
4 int ans=x;
5 for(int i=2;i*i<=x;i++){
6 if(x%i==0){
7 ans-=ans/i;
8 while(x%i==0) x/=i;
9 }
10 }
11 if(x>1) ans-=ans/x;
12 return ans;
13 }
14 ll poww(ll a,ll b,ll c){
15 ll ans=1;
16 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c;
17 while(b){
18 if(b&1){
19 ans*=a;
20 if(ans>=c) ans=ans%c+c;
21 }
22 a*=a;
23 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c;
24 b>>=1;
25 }
26 return ans;
27 }
28 ll exponial(int x,int y){
29 if(x==1) return 1%y;
30 if(x%y==0) return poww(x,x-1,y);
31 return poww(x,exponial(x-1,euler(y)),y);
32 }
33 int main()
34 {
35 int n,m;
36 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){
37 printf("%lld\n",exponial(n,m)%m);
38 }
39 return 0;
40 }
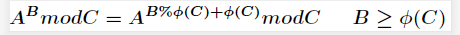
 1 #include<cstdio> 2 typedef long long ll; 3 ll poww(ll a,ll b,ll c){ 4 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c; 5 ll ans=1; 6 while(b){ 7 if(b&1){ 8 ans=ans*a; 9 if(ans>c) ans=ans%c+c; 10 } 11 a=a*a; 12 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c; 13 b>>=1; 14 } 15 return ans; 16 } 17 int euler(int x){ 18 int ans=x; 19 for(int i=2;i*i<=x;i++){ 20 if(x%i==0){ 21 ans-=ans/i; 22 while(x%i==0) x/=i; 23 } 24 } 25 if(x>1) ans-=ans/x; 26 return ans; 27 } 28 ll f(int x,int y){ 29 if(x==0) return 1%y; 30 return poww(x%10,f(x/10,euler(y)),y); 31 } 32 int main() 33 { 34 int t,n,m; 35 scanf("%d",&t); 36 while(t--){ 37 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 38 printf("%lld\n",f(n,m)%m); 39 } 40 return 0; 41 }
1 #include<cstdio> 2 typedef long long ll; 3 ll poww(ll a,ll b,ll c){ 4 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c; 5 ll ans=1; 6 while(b){ 7 if(b&1){ 8 ans=ans*a; 9 if(ans>c) ans=ans%c+c; 10 } 11 a=a*a; 12 if(a>=c) a=a%c+c; 13 b>>=1; 14 } 15 return ans; 16 } 17 int euler(int x){ 18 int ans=x; 19 for(int i=2;i*i<=x;i++){ 20 if(x%i==0){ 21 ans-=ans/i; 22 while(x%i==0) x/=i; 23 } 24 } 25 if(x>1) ans-=ans/x; 26 return ans; 27 } 28 ll f(int x,int y){ 29 if(x==0) return 1%y; 30 return poww(x%10,f(x/10,euler(y)),y); 31 } 32 int main() 33 { 34 int t,n,m; 35 scanf("%d",&t); 36 while(t--){ 37 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 38 printf("%lld\n",f(n,m)%m); 39 } 40 return 0; 41 }