If a worker wants to do well, he must first sharpen his tools, Minikube
preface
With the development of container technology, more and more enterprises choose to deploy applications using containers. Application deployment is simple, but how to manage a large number of container changes? The operation and maintenance personnel can't operate one container by one.
Speaking of this, you should have thought of it. Is there any tool to manage these containers? Of course, Docker Compose and Kubernetes are the mainstream container choreography technologies at present.
Today, we learn the latter kubernetes to manage containers. Why choose kubernetes? Kubernetes is not just container management, but also has more powerful functions.
Then you may have doubts again. What is the relationship between learning Kubernetes and Minikube?
Haha, the reason is very simple. The Kubernetes environment is complex. Minikube is specially prepared for developers to facilitate debugging. And the installation is very simple and easy to start. After seeing this, I believe you already know what minikube does. Next, I will take you to install minikube and run your first Kubernetes application.
1, Minikube overview
Minikube is a local Kubernetes that focuses on making Kubernetes easy to learn and develop. Minikube supports fast building local Kubernetes clusters on macOS, Linux and Windows.
2, Minikube properties
- Support the latest Kubernetes Version (+ 6 previous minor versions)
- Cross platform (Linux, macOS, Windows)
- Deploy as VM, container, or bare metal
- Multiple container runtime (CRI-O, containerd, docker)
- For fast Image push Docker API endpoint
- Advanced features, such as LoadBalancer , file system mount, and FeatureGates
- For easy installation of the Kubernetes application plug-in unit
3, Minikube function
- Support docker, podman and other container engines
- Mirror cache
- dashboard
- Accessing host resources
- Install extensions
- File system mount
- File synchronization
- NodePort and LoadBalancer are supported
- Support private image source
- Log classification
4, Build your own Minikube
Since the author uses the Windows operating system, the following case will be built on the Windows operating system.
-
Environmental preparation
Here, the author uses Docker. Before installing Kubernetes using Minikube, please ensure that our machine has been correctly installed and started Docker. If Docker is not installed on your operating system, you can refer to another article of mine If a worker wants to do well, he must first use his DockerDesktop
-
Step 1: download the installation package
Here you need to download two installation packages
-
Step 2 install minicube
Find the downloaded installation package minicube installer Exe double click and follow the prompts.
Verify the installation. Enter minicube version on the terminal and see the following information, indicating that the minicube installation is successful
minikube version
Output information
minikube version: v1.19.0 commit: 15cede53bdc5fe242228853e737333b09d4336b5
-
Step 3 install kubectl
Find the downloaded installation package kubectl Exe, add it to the operating system PATH. After adding the PATH, enter kubectl version --client in the terminal and see the following information, indicating that the kubectl environment variable has taken effect
kubectl version --client
Output information
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"21", GitVersion:"v1.21.2", GitCommit:"092fbfbf53427de67cac1e9fa54aaa09a28371d7", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-06-16T12:59:11Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"windows/amd64"}
-
Step 4 use
Minikube is installed successfully. How to use it?
We need to try some minicube commands on the operating system terminal or command line terminal such as PowerShell. How to open the terminal?
Windows opens the shortcut key win+r of the terminal. Enter cmd in the pop-up window and click the OK button to enter the command line terminal, the legendary black window.
Before running Minikube, let's run minikube status.
minikube status
Output information
minikube type: Control Plane host: Stopped kubelet: Stopped apiserver: Stopped kubeconfig: Stopped
Here, don't forget that our goal is to build a mini version of Kubernetes cluster. Therefore, the revolution has not yet succeeded, and we still need follow-up operations.
-
Step 5 start your first Kubernetes cluster
Start the cluster and enter minicube start at the terminal
minikube start
Output information
* Microsoft Windows 10 Home China 10.0.19041 Build 19041 Upper minikube v1.19.0 * Automatic selection docker Drive. Other options: virtualbox, ssh * Starting control plane node minikube in cluster minikube * Pulling base image ... > index.docker.io/kicbase/sta...: 357.67 MiB / 357.67 MiB 100.00% 1.95 MiB ! minikube was unable to download gcr.io/k8s-minikube/kicbase:v0.0.20, but successfully downloaded kicbase/stable:v0.0.20 as a fallback image * Creating docker container (CPUs=2, Memory=3883MB) .../ E0807 17:31:41.808445 25672 kic.go:257] icacls failed applying permissions - err ! This container is having trouble accessing https://k8s.gcr.io * To pull new external images, you may need to configure a proxy: https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/reference/networking/proxy/ * Is Docker 20.10.5 Medium preparation Kubernetes v1.20.2... - Generating certificates and keys ... - Booting up control plane ... - Configuring RBAC rules ... * Verifying Kubernetes components... - Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5 * Enabled addons: storage-provisioner, default-storageclass * Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by defaultVerify the cluster. Enter kubectl cluster info in the terminal and see the following information, indicating that the Kubernetes cluster has been successfully installed
kubectl cluster-info
Output information
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://127.0.0.1:2438 KubeDNS is running at https://127.0.0.1:2438/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'
-
Open dashboard
Start the cluster dashboard and enter minicube dashboard at the terminal
minikube dashboard
Output information
* Opening dashboard ... - Using image kubernetesui/dashboard:v2.1.0 - Using image kubernetesui/metrics-scraper:v1.0.4 * Validating dashboard Operation ... * Launching proxy ... * Validating proxy Health status ... * Opening http://127.0.0.1:11739/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/ in your default browser...
Browser address bar entry http://127.0.0.1:11739/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes -Dashboard / services / http: kubernetes dashboard: / proxy / see the following page to indicate that the dashboard is started successfully
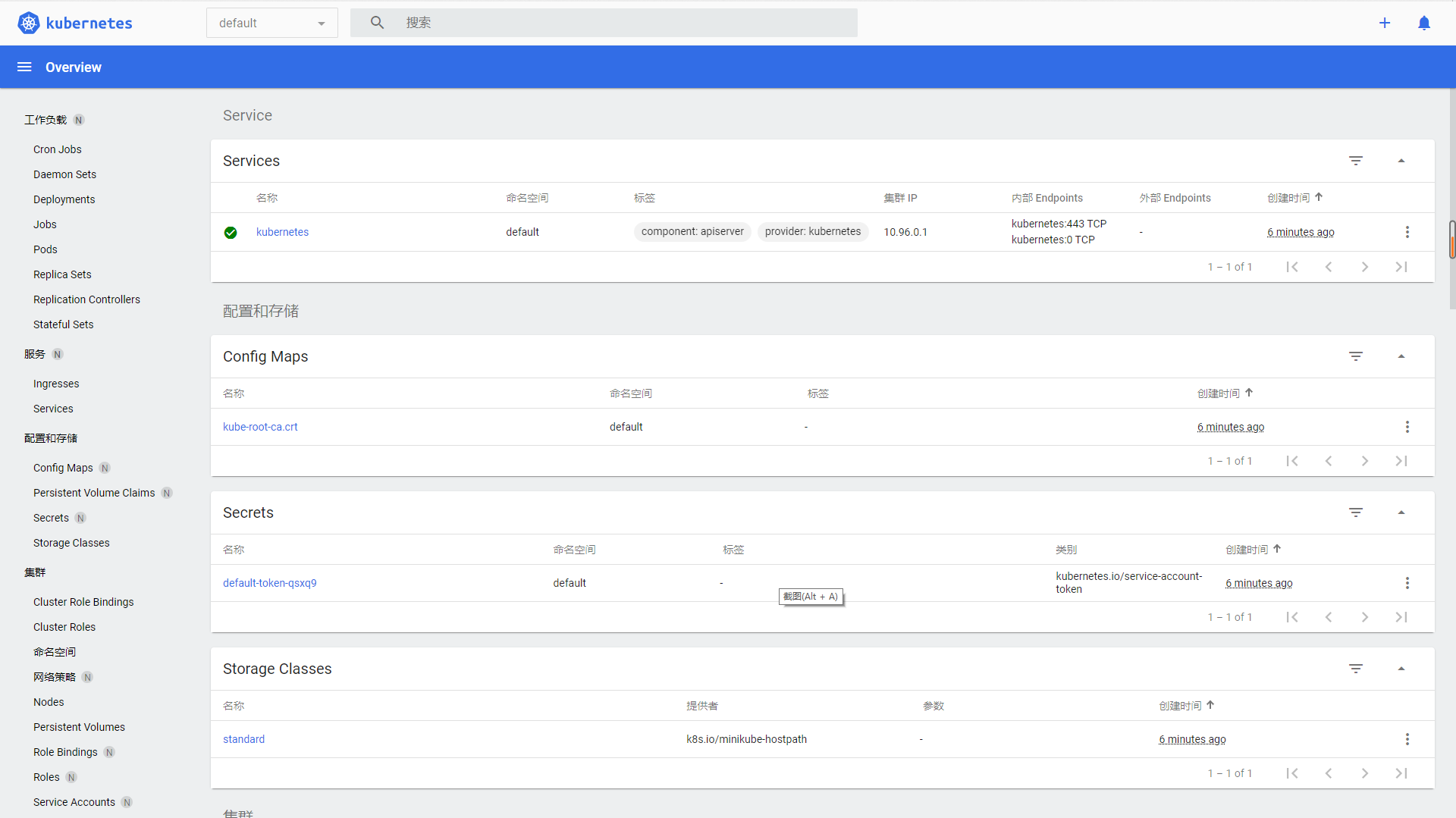
5, Minikube common commands
| command | meaning | remarks |
|---|---|---|
| minikube start | Start cluster | |
| minikube status | View cluster status | |
| minikube dashboard | Access the kubernetes dashboard running in the minicube cluster | |
| minikube pause | Stop the container in the cluster | |
| minikube unpuase | Recovering containers in a cluster | |
| minikube ip | View virtual machine ip | |
| minikube ssh | Log in to the virtual machine | |
| minikube delete | Delete cluster |
summary
The above is the main content of this paper. This paper introduces what is Minikube, why to use Minikube, how to build Minikube and common Minikube commands. The articles later in this column will introduce you to other development tools. Please look forward to (* ^ ▽ ^ *).
statement
The above contents are from the network. If there are errors, please include more.