Linked list
Linked list concept
Linked list: a storage structure of data. A linked list contains several nodes. Each node contains at least one data field and one pointer field, and the pointer field points to the next node.
Node: the storage image of the data element, which is composed of the data field storing the data element and the pointer field storing the address of the subsequent node.
Features: use a group of arbitrary storage units to store the data elements of the linear table. This group of storage units can be continuous or discontinuous. This means that these data elements can exist anywhere in memory that is not occupied.
Differences among header node, header pointer and first element node:
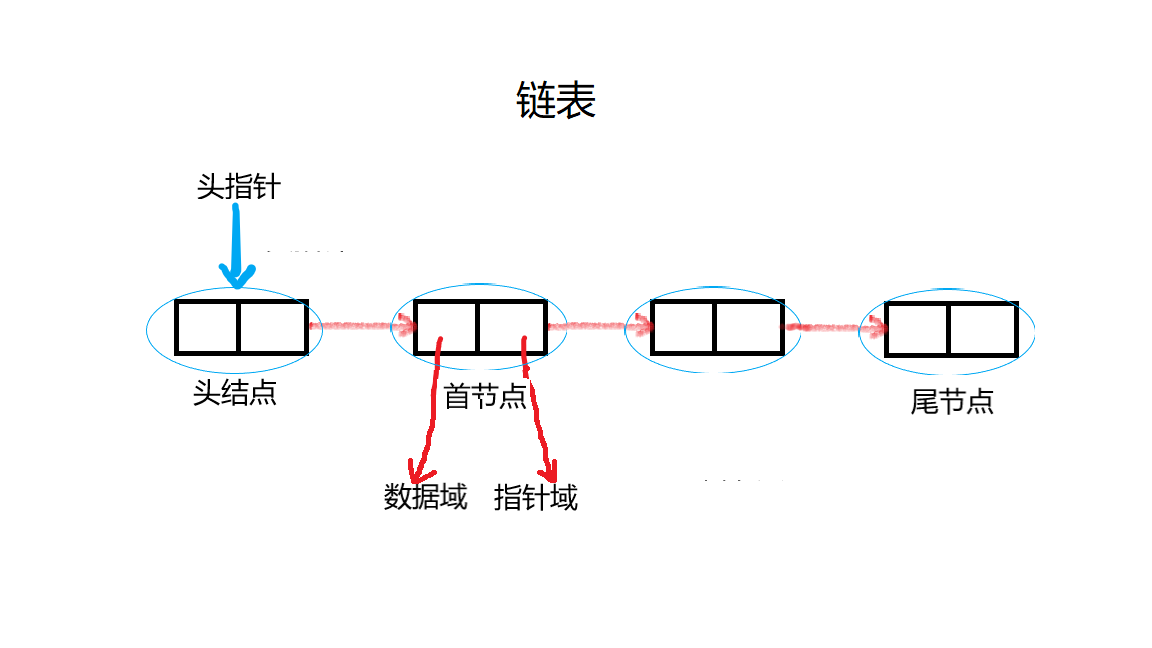
- Head node: a node set before the first element node of the single linked list. The data field can not store any information, and the pointer field points to the node of the first element of the single linked list. The head node is not a necessary element of the linked list
- Header pointer: pointer to the first node of the single linked list. If the single linked list has a header node, the header pointer points to the header node. If the single linked list has no header node, the header pointer points to the first primitive node. The head pointer cannot be null. The head pointer is a necessary element of the linked list.
- First element node: the first node with data elements in the single linked list. If the single linked list has a head node, the first node is the next node of the head node. If the single linked list has no head node, the first node is the first node of the single linked list
Basic operation of linked list:
- Get linked list length
- Determine whether the linked list is empty
- Traversal linked list
- Find element
- Add element
- Delete element
Implementation of single linked list
//Define node classes
class Node
{
constructor(data)
{
this.data = data //Data field of node (data member)
this.next = null //Pointer field of node (pointer member)
}
}
//Define one-way linked list class
class SingleLinked
{
constructor()
{
this.size = 0 //Record the number of nodes in the linked list
this.head = new Node('head') //Is the head pointer of the linked list, which records the starting address of the linked list
this.currentNode = '' //Used to record the current node
}
//Get the length of the linked list
getLength()
{
return this.size
}
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
isEmpty()
{
return this.size===0
}
//Traverse the linked list: do not repeatedly access each node in the linked list
displayList()
{
var list = ''
var currentNode = this.head //Pointer to the head of the linked list
while(currentNode) //If the current node is not empty
{
list += currentNode.data
currentNode = currentNode.next //Make the pointer point to the next node of the current node
if(currentNode)
{
list += '->'
}
}
console.log(list)
}
//Get the last node of the linked list
findLast()
{
var currNode = this.head
while(currNode.next)
{
currNode = currNode.next
}
return currNode
}
//Add elements at the end of the single linked list
appendNode(element)
{
var currNode = this.findLast() //Find the last node of the linked list
var newNode = new Node(element) //Create a new node
currNode.next = newNode
newNode.next = null
this.size++ //Linked list length + 1
}
//Delete a node
delete(element)
{
var currNode = this.head
while(currNode.next.data!=element)
{
currNode = currNode.next
}
currNode.next = currNode.next.next
this.size--
}
}
- Note: when inserting elements in the middle of the single linked list, pay attention to the order of connecting nodes
Implementation of bidirectional linked list
//Define a node class
class Node
{
constructor(data)
{
this.data = data
this.next = null
this.previous = null
}
}
//DNode Class
class DoubleLinked
{
constructor()
{
this.size = 0
this.head = new Node('head')
this.currentCode = '' //Current node pointer
}
//Get linked list length
getLength()
{
return this.size
}
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
isEmpty()
{
return this.size===0
}
//Show current node
showNode()
{
console.log(this.currentNode.data)
}
//ergodic
displayList()
{
var str = ''
var currentNode = this.head
while(currentNode)
{
str += currentNode.data
currentNode = currentNode.next
if(currentNode)
{
str += '-->'
}
}
return str
}
//Traverse the linked list in reverse order
lastDisplay()
{
var str = ''
var currentNode = this.findLast()
while(currentNode)
{
str += currentNode.data
currentNode = currentNode.previous
if(currentNode)
{
str += '-->'
}
}
return str
}
//Find an element
findNode(data)
{
var currentNode = this.head
while(currentNode && (currentNode.data != data))
{
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode
}
//Insert node after data
insertNode(data,element)
{
var currentNode = this.findNode(data)
//If data does not exist
if(!currentNode)
{
return
}
var newNode = new Node(element)
newNode.previous = currentNode
newNode.next = currentNode.next
currentNode.next.previous = newNode
currentNode.next = newNode
this.size++
}
//Get last node
findLast()
{
var currentNode = this.head
while(currentNode.next)
{
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
return currentNode
}
//Add node at tail
appendNode(data)
{
var currentNode = this.findLast()
var newNode = new Node(data)
currentNode.next = newNode
newNode.next = null
newNode.previous = currentNode
this.size++
}
//Delete a node
deleteNode(data)
{
var currentNode = this.findNode(data)
if(currentNode.next == null) //If the deleted node is the last node
{
currentNode.previous.next = null
}
else
{
currentNode.previous.next = currentNode.next
currentNode.next.previous = currentNode.previous
}
this.size--
}
}
- Note: the order of connecting nodes during single linked list insertion
- First connect the predecessor and successor of the new node, then connect the predecessor of the subsequent node, and finally connect the successor of the previous node
newNode.previous = currentNode newNode.next = currentNode.next currentNode.next.previous = newNode currentNode.next = newNode