1, Initial experience of MySQL database
- Basic concepts of database
- Development of database
- Introduction to mainstream database
- MySQL installation method
- Operating MySQL
1. Basic concept of database
Data
- A symbolic record describing something
- Including numbers, words, graphics, images, sounds, archives, etc
- It is stored in a unified format in the form of "record"
surface
- Organize different records together
- Used to store specific data
database
- A collection of tables is a warehouse for storing data
- A collection of interrelated data stored in an organized manner
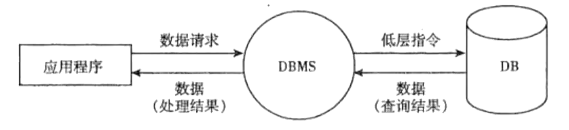
Database management system (DBMS)
- It is a system software to realize the effective organization, management and access of database resources
database system
- It is a man-machine system, which is composed of hardware, OS, database, DBMS, application software and database users
- Users can operate the database through DBMS or application
2. Development history of database system
First generation database
- Since the 1960s, the first generation database system came out
- It is a database system of hierarchical model and mesh model
- It provides strong support for unified management of shared data
Second generation database
- In the early 1970s, the second generation database, relational database, began to appear
- In the early 1980s, IBM's relational database system DB2 came out and began to gradually replace the hierarchical and mesh model database and become the mainstream of the industry
- So far, relational database system still occupies the main position of database application
Third generation database
- Since the 1980s, new database systems adapted to different fields have been emerging
- The object-oriented database system has strong practicability and wide adaptability
- In the late 1990s, a variety of database systems jointly supported the application
- Some new elements have been added to the mainstream database
- For example, Oracle supports the relational object database model
2.1 shortcomings of document management system
-
Writing applications is inconvenient
-
Data redundancy is inevitable
-
Application dependencies
-
Concurrent access to files is not supported
-
Weak connection between data
-
Difficult to represent data by user view
-
No safety control function
-
......
2.2 development stage of database system
-
Embryonic stage: file system
Use disk files to store data
-
Primary stage: first generation database
The database of mesh model and hierarchical model appears
-
Intermediate stage: second generation database
Relational database and structured query language
-
Advanced stage: next generation database
Relational object database
3. Database principle
3.1 data age
- Large amount of data involved
- The data does not disappear with the end of the program
- Data is shared by multiple applications
- big data
3.2 classification of data
-
Structured data: data with fixed format and limited length. For example, the form filled in is structured data, nationality: People's Republic of China, nationality: Han, gender: male, which are all called structured data
-
Unstructured data: there are more and more unstructured data, that is, data with variable length and no fixed format, such as web pages, which are sometimes very long and sometimes disappear in a few words; For example, voice and video are unstructured data
-
Semi structured data: such as data in XML or HTML format
3.3 DBMS database management system
- Database: a database is a collection of data. It is stored on the storage medium in a certain organizational form
- DBMS: system software for managing database. It realizes various functions of database system. It is the core of database system
- DBA: responsible for database planning, design, coordination, maintenance and management
- Application: refers to the application based on database
3.4 advantages of database management system
-
A collection of interrelated data
-
Less data redundancy
-
The program and data are independent of each other
-
Ensure the safety and reliability of data
-
Ensure the correctness of data to the greatest extent
-
Data can be used concurrently and ensure consistency at the same time
-
......
3.5 basic functions of database management system
- Data definition
- data processing
- data security
- Data backup
3.6 architecture of database system
- Stand alone architecture
- Mainframe / terminal architecture
- Master slave architecture (C/S)
- Distributed architecture
3.7 RDBMS relational database
The Relational Database Management System and relational model were first described by Edgar F. Codd, a British computer scientist of IBM in 1969. In 1974, IBM began to develop system R, which is a research project to develop RDBMS prototype.
However, the first commercially available RDBMS was Oracle, released in 1979 by relational software (now Oracle)
3.7. 1. Related concepts of relational database
- Relational: a relationship is a two-dimensional table, in which the order of rows and columns in the table is not important
- Row: each row in the table, also known as a record
- Column: each column in the table is called attribute, field and field
- Primary key: PK, used to uniquely determine the field of a record. A table has only one primary key
- domain: the value range of the attribute. For example, gender can only be male and female, and human age can only be 0-150
3.7. 2 common relational databases
-
MySQL (acquired by Oracle): MySQL, MariaDB, Percona Server
-
PostgreSQL: pgsql for short, EnterpriseDB
-
Oracle (Oracle products)
- For all major platforms
- Safe, perfect and complex operation
-
MSSQL
-
DB2 (IBM products)
- For all major platforms
- Large, safe and perfect
-
SQL Server (Microsoft products)
- Windows oriented operating system
- Simple and easy to use
4. Relational database
- Relational database system is a database system based on relational model
- The data structure of the relational model uses a simple and understandable two-dimensional data table
- The relational model can be represented by a simple "entity relationship" (E-R) diagram
- The E-R diagram contains three elements: entity (data object), relationship and attribute
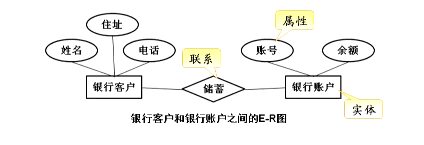
entity
- Also known as instances, they correspond to "events" or "things" that can be distinguished from other objects in the real world
- Such as bank customers, bank accounts, etc
attribute
- An entity has a certain property. An entity can have multiple attributes
- For example, each entity in the "bank customer" entity set has name, address, telephone and other attributes
contact
- The corresponding relationship between entity sets is called relation
- For example, there is a "savings" relationship between bank customers and bank accounts
The collection of all entities and their relationships constitutes a relational database
The storage structure of relational database is two-dimensional table
In each 2D table
- Each line is called a record and is used to describe the information of an object
- Each column is called a field and is used to describe an attribute of an object
5. Non relational database
Non relational databases are also called NoSQL (Not Only SQL)
The stored data is not based on the relational model and does not need a fixed table format
Advantages of non relational database
- The database can be read and written with high concurrency
- Efficient storage and access of massive data
- The database has high scalability and high availability
Common non relational databases: Redis, mongoDB, etc
6. Relational and non relational databases
The difference between the two
relational database
The relational database structure is a two-dimensional database table. Each field (column) in the two-dimensional table is used to describe an attribute of an object,
Each record (row) is used to describe the information (complete information) of an object. Where the relational database is written, it is stored in the hard disk
The read-write system will be subject to IO restrictions or bottlenecks
other
The most typical data structure of relational database is table, which is a data organization composed of two-dimensional tables and their relationships
advantage:
- Easy to maintain: all use table structure with consistent format;
- Easy to use: SQL language is universal and can be used for complex queries;
- Complex operation: it supports SQL and can be used for very complex queries between one table and multiple tables.
Disadvantages:
- Poor reading and writing performance, especially the efficient reading and writing of massive data;
- Fixed watch structure, less flexibility;
- With high concurrent read and write requirements, hard disk I/O is a big bottleneck for traditional relational databases.
Cache acceleration software
Non relational database (NoSQL):
MongoDB, Redis (in memory database / cache database) K-V key value pairs, similar Memcache,K-V key value pairs
Redis memecache comparison:
Same point: store high heat data (run at high speed in memory)
Difference: redis can do persistent storage and store objects
Non relational database is not strictly a database, but a collection of data structured storage methods, which can be document or key value equivalence.
advantage:
- Flexible format: the format for storing data can be key,value, document, picture, etc
The image format is flexible and has a wide range of application scenarios, while the relational database only supports basic types. - Fast speed: nosql can use hard disk or random access memory as the carrier, while relational database can only use hard disk;
- High scalability;
- Low cost: nosql database is easy to deploy and is basically open source software.
Disadvantages:
- sql support is not provided, and the cost of learning and using is high;
- No transaction;
- The data structure is relatively complex, and the complex query is slightly insufficient.
7. Install mysql
Install reference architectures using yum or up2date
MySQL composition
Client program
- mysql: interactive CLI tool
- mysqladmin: manage MySQL LD based on MySQL protocol
- mysqlimport: data import tool
MyISAM management tool for storing wins:
- myisamchk: check MyISAM Library
- myisampack: package MyISAM table, read-only
Server side program
- mysqld_safe
- mysqld
- mysqld_multi instance, instance: mysqld_multi
[root@localhost ~]# yum info mariadb
Installable packages
name : mariadb
framework : x86_64
period : 1
edition : 5.5.68
release : 1.el7
size : 8.8 M
source : base/7/x86_64
brief introduction : A community developed branch of MySQL
website : http://mariadb.org
agreement : GPLv2 with exceptions and LGPLv2 and BSD
describe : MariaDB is a community developed branch of MySQL.
: MariaDB is a multi-user, multi-threaded SQL database server.
: It is a client/server implementation consisting of a server daemon (mysqld)
: and many different client programs and libraries. The base package
: contains the standard MariaDB/MySQL client programs and generic MySQL files.
MySQL cover Sun After the acquisition, we made a transition 6.0 Version, it didn't take long to get offline,Later by Oracle After the acquisition, it finally ushered in a decent 5.6 Version, followed by 5.7,8.0 edition. Due to 6.0 Version number has been used, 7.x The series version is dedicated to NDB Cluster,Therefore, the new version number is from 8.0 Start.
5.5 The version has been eliminated and is not recommended
Install version 5.7 using yum or up2date
[root@localhost ~]#yum install mariadb-server -y [root@localhost ~]#systemctl start mariadb.service [root@localhost ~]#mysql [root@localhost ~]#mysql_secure_installation
Install using Tsinghua source
[root@centos7 ~]#tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mysql.repo <<EOF [mysql] name=mysql5.7 baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/mysql/yum/mysql-5.7-community-el7-x86_64/ gpgcheck=0 EOF [root@centos7 ~]#yum -y install mysql-community-server
Start and view status
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# systemctl start mysqld [root@localhost yum.repos.d]# ss -ntap |grep 3306 [root@localhost yum.repos.d]# mysql -u root -p
mysql command:
mysql [OPTIONS] [database] Command format -A, --no-auto-rehash No completion -u, --user= user name,Default to root -h, --host= Server host,Default to localhost -p, --passowrd= User password,Recommended use-p,The default is blank password -P, --port= Server port -S, --socket= Specify connection socket File path -D, --database= Specify default database -C, --compress Enable compression -e "SQL" implement SQL command -V, --version Display version -v --verbose Show details --print-defaults Gets the default configuration used by the program #Default blank password login mysql -u root -p mysql>use mysql #Switch database mysql> select database(); #View current database mysql>select user(); #View current user mysql>SELECT User,Host,Password FROM user; mysql>system clear #Clear screen mysql> ^DBye #ctrl+d exit mysqladmin command mysqladmin [OPTIONS] command command... #Check whether the mysql service is normal. If it is normal, it will prompt mysqld is alive mysqladmin -u user -p password ping mysqladmin -uroot -p123123 ping #Close the mysql service, but the mysqladmin command cannot be started mysqladmin -uroot -pcentos shutdown #Create database testdb mysqladmin -uroot -pcentos create testdb #Delete database testdb mysqladmin -uroot -pcentos drop testdb #Change root password mysqladmin -uroot -pcentos password 'magedu' #Log scrolling to generate a new file / var / lib / MySQL / MariaDB bin 00000N mysqladmin -uroot -pcentos flush-logs
8. Multiple instances
Multi example introduction
- What is database multi instance
Multiple instances are similar to wechat. The port number is similar to the wechat account, the database is similar to the chat window, and the table is similar to the chat record
MySQL multi instance is to open multiple different service ports (such as 3306, 3307, etc.) on one server and run multiple MySQL service processes at the same time. These service processes listen to different service ports through different sockets to provide services.
Multiple instances may be implemented in different versions of MySQL or in the same version of MySQL
- Benefits of multiple instances
Server resources can be used effectively.
When a single server has surplus resources, it can make full use of the remaining resources to provide more services, and realize the logical isolation of resources to save server resources. For example, the company's server resources are tight, but the databases need to provide services independently as much as possible, and also need master-slave replication and other technologies. Multi instance is the best choice
- Multiple instance disadvantages
There is the problem of resource preemption.
For example, when the concurrency of a database instance is very high or the SQL query is slow, the whole instance will consume a lot of CPU, disk I/O and other resources, resulting in the decline of the service quality of other database instances on the server. Therefore, the specific requirements should be determined according to their actual situation.
9. Basic operation
SQL classification
- database: database
- Table: table, row: row, column: column
- Index: index
- view: view
- Stored procedures: procedure
- Storage function: function
- Trigger: trigger
- Event scheduler: event scheduler, task scheduler
- User: user
- Permission: privilege
SQL language specification
-
In the database system, SQL statements are not case sensitive. It is recommended to use uppercase
-
SQL statements can be written in a single line or multiple lines, with ";" by default ending
-
Keywords cannot span multiple lines or abbreviations
-
Use spaces and TAB indents to improve the readability of statements
-
Clauses are usually located on separate lines to facilitate editing and improve readability
Database objects and naming
Components (objects) of the database:
Database, table, index, view, user, stored procedure, function, trigger, event scheduler, etc
Naming rules:
It must start with a letter, and the following can include letters, numbers and three special characters (# $)
Do not use the reserved word of MySQL. tabble select show databases
SQL statement classification
- DDL: Data Definition Language
CREATE,DROP,ALTER
- DML: Data Manipulation Language
INSERT,DELETE,UPDATE
Software development: CRUD
- DQL: Data Query Language
SELECT
- DCL: Data Control Language
GRANT,REVOKE
- TCL: Transaction Control Language
COMMIT,ROLLBACK,SAVEPOINT
#DDL: Data Definition Language CREATE,DROP,ALTER #DML: Data Manipulation Language INSERT,DELETE,UPDATE #DQL: Data Query Language SELECT #DCL: Data Control Language GRANT,REVOKE,COMMIT,ROLLBACK SELECT * #SELECT Clause FROM products #FROM clause WHERE price>666 #WHERE clause
10. View help information
mysql> help create Many help items for your request exist. To make a more specific request, please type 'help <item>', where <item> is one of the following topics: CREATE DATABASE CREATE EVENT CREATE FUNCTION CREATE FUNCTION UDF CREATE INDEX CREATE LOGFILE GROUP CREATE PROCEDURE CREATE SERVER CREATE TABLE CREATE TABLESPACE CREATE TRIGGER CREATE USER CREATE VIEW SHOW SHOW CREATE DATABASE SHOW CREATE EVENT SHOW CREATE FUNCTION SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE SHOW CREATE TABLE SHOW CREATE USER SPATIAL
11. View supported character sets
show charset; #View supported character sets Default Latin text utf8 | UTF-8 Unicode #Castrated version utf8mb4 | UTF-8 Unicode #Real version Our compilation and installation have been modified
mysql> show databases; #View current database mysql> use mysql; #Using mysql tables
12. Management database
1. Create database
CREATE DATABASE|SCHEMA [IF NOT EXISTS] 'DB_NAME' CHARACTER SET 'character set name' COLLATE 'collate name'; MySQL root@localhost:(none)> create database db1; Query OK, 1 row affected Time: 0.002s MySQL root@localhost:(none)> show create database db1; +----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+ | Database | Create Database | +----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+ | db1 | CREATE DATABASE "db1" /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */ | +----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set Time: 0.018s MySQL root@localhost:(none)> create database db2 charset=utf8; Query OK, 1 row affected Time: 0.001s
2. Modify database
ALTER DATABASE DB_NAME character set utf8;
3. Delete database
DROP DATABASE|SCHEMA [IF EXISTS] 'DB_NAME'; MySQL root@localhost:(none)> drop database db1; You're about to run a destructive command. Do you want to proceed? (y/n): y Your call! Query OK, 0 rows affected Time: 0.005s MySQL root@localhost:(none)> show databases;
4. View database list
SHOW DATABASES; MySQL root@localhost:(none)> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | bbs | | db2 | | db3 | | kgc | | mysql | | performance_schema | | school | | sys | +--------------------+ 9 rows in set Time: 0.010s
5. Data type
Data type:
What does the data look like
How much space is needed to store data
data type
System built-in data type
User defined data type
MySQL * * * * supports multiple built-in data types
value type
Date / time type
String (character) type
Data type reference link
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/data-types.html
Choosing the right data type is very important for high performance. There are three principles:
-
Smaller is usually better, and try to use the smallest data type that can store data correctly
-
Simple is good, simple data type operations usually require less CPU cycles
-
Try to avoid NULL, including NULL columns, which is more difficult to optimize MySQL
Integer type
tinyint(m) 1 byte range (- 128 ~ 127)
smallint(m) 2-byte range (- 32768 ~ 32767)
mediumint(m) 3-byte range (- 8388608 ~ 8388607)
int(m) 4-byte range (- 2147483648 ~ 2147483647)
bigint(m) 8-byte range (± 9.22 * 10 to the 18th power)
For the above data types, if the modifier unsigned is added, the maximum value is doubled
For example, the value range of tinyint unsigned is (0 ~ 255)
Floating point * * (float and double) * * * *, approximate**
float(m,d) single precision floating point 8-bit precision (4 bytes) m total number, D decimal places, note: the decimal point does not occupy the total number
double(m,d) double precision floating point 16 bit precision (8 bytes) m total number, D decimal places, note: the decimal point does not occupy the total number
Let a field be defined as float(6,3). If a number of 123.45678 is inserted, the actual number stored in the database is 123.457, but the total number is
Actual, i.e. 6 digits
Fixed point number
The exact value stored in the database is decimal
The format decimal(m,d) represents a maximum of M digits, including D decimals, and the decimal point is not included in the length
For example, DECIMAL(6,2) can store 6 digits in total, the last 2 digits are decimals, and the maximum value of the field is 9999.99 (the decimal point is not included in the length)
Parameter m < 65 is the total number, d < 30 and d < m is the decimal place
MySQL5.0 and later packages and saves numbers into a binary string (9 numbers every 4 bytes).
For example: decimal(18,9) will store 9 digits on both sides of the decimal point, and a total of 9 bytes will be used: among them, 4 digits are used for the 9 digits before the decimal point
Byte, the 9 digits after the decimal point use 4 bytes, and the decimal point itself accounts for 1 byte
Floating point types usually use less space than decimal when storing the same range of values. float uses 4 bytes to store. double occupancy
8 bytes
Because of the extra space and computational overhead, you should try to calculate decimals accurately only
String (char,varchar,text)
char(n) fixed length, up to 255 characters. Note that it is not a byte
varchar(n) variable length, up to 65535 characters
tinytext variable length, up to 255 characters
Textvariable length, up to 65535 characters
mediumtext variable length, up to the 24th power of 2 - 1 character
longtext variable length, up to the 32nd power of 2 - 1 character
BINARY(M) fixed length, can store binary or characters, and the length is 0-M bytes
VARBINARY(M) variable length, can store binary or characters, and the allowable length is 0-M bytes
Built in type: ENUM enumeration, SET collection
Comparison between char and varchar * * * *:
reference resources: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/char.html
CREATE DATABASE school; USE school; CREATE TABLE ky15 (id int NOT NULL,name char(10) NOT NULL,score decimal(5,2),passwd char(48) DEFAULT'', PRIMARY KEY (id)); DESC zzz;
For example: decimal(18,9) will store 9 digits on both sides of the decimal point, and a total of 9 bytes will be used: among them, 4 digits are used for the 9 digits before the decimal point
Byte, the 9 digits after the decimal point use 4 bytes, and the decimal point itself accounts for 1 byte
Floating point types usually use less space than decimal when storing the same range of values. float uses 4 bytes to store. double occupancy
8 bytes
Because of the extra space and computational overhead, you should try to calculate decimals accurately only
String (char,varchar,text)
char(n) fixed length, up to 255 characters. Note that it is not a byte
varchar(n) variable length, up to 65535 characters
tinytext variable length, up to 255 characters
Textvariable length, up to 65535 characters
mediumtext variable length, up to the 24th power of 2 - 1 character
longtext variable length, up to the 32nd power of 2 - 1 character
BINARY(M) fixed length, can store binary or characters, and the length is 0-M bytes
VARBINARY(M) variable length, can store binary or characters, and the allowable length is 0-M bytes
Built in type: ENUM enumeration, SET collection
Comparison between char and varchar * * * *:
reference resources: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/char.html