Catalog:
- constant
- String+Escape Character+Comment
- Selection Statement
- Loop statement
- array
- Operator
Beginning of text:
Constant:
Constants in C are divided into the following categories:
- Literal Constant
- const-modified constant variable
- Identifier Constant defined by #define
- enumeration constant
int main()
{
//Literal Constant Demo
3.14;//Literal Constant
1000;//Literal Constant
}int main()
{
//const-modified constant variable
const float pai = 3.14; //pai here is a const-modified constant variable
pai = 5.14;//It cannot be modified directly!
printf("%f",pai);
}(At this point, the output is 3.14, pai is modified by const, and the pai value is unchanged)
pai in the example above is called a const-modified constant variable. Const-modified constant variable is only grammatically restricted in C. The variable pai cannot be changed directly, but pai is essentially a variable, so it is called a constant variable.
int main()
{
//#define's demonstration of identifier constants
#define MAX 100
printf("max = %d\n", MAX);
}(The output value is: max = 100)
#include <stdio.h>
int main
{
//Give an example
enum Sex
{
MALE,
FEMALE,
SECRET
};
//MALE,FEMALE,SECRET in parentheses are enumeration constants
//Enumeration Constants Demo
printf("%d\n", MALE);
printf("%d\n", FEMALE);
printf("%d\n", SECRET);
//Note: By default, enumeration constants start at 0 and increment down by 1
}The default for enumeration constants is to start at 0 and increment down by 1, so the output value is:
0
1
2
Be careful!!!
When defining an array, use the following methods to define that c99, PTA, Niukou Passenger Networks are working properly, and errors may occur in other environments.
Understand this: the first line of code states that n is a variable, in which case n is initialized and given an initial value; Arrays need to be defined with constants, so errors will occur!

Character string:
A string of characters caused by double quotation marks is called a String Literal or simply a string.
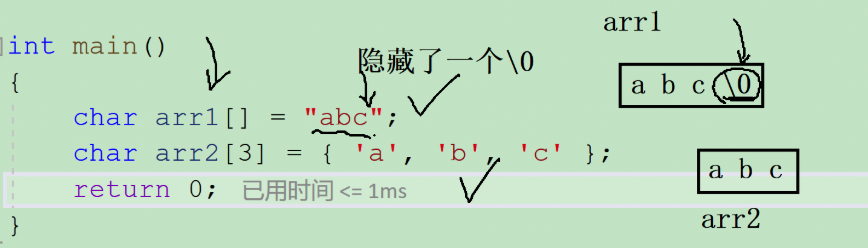
Note: The end flag of the string is an escape character of \0. \0 is the end flag when calculating the length of a string and is not counted as the string content.
Extend knowledge: the difference between strlen and sizeof (focus!!!)
1.strlen is not necessarily related to sizeof;
2.strlen is for string length, only for string length, is a library function, and needs a header file;
3.sizeof calculates the size of variables, arrays, and types in bytes, which are operators
char arr1[]="abc";
char arr2[]={'a','b','c'}; //Output results:
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr1));//4A B C \0 (including \0)
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr2));//3 a b c
printf("%d\n",strlen(arr1));//3A B C \0 (excluding \0)
printf("%d\n",strlen(arr2));//Random value strlen continues to look backwards for'\0'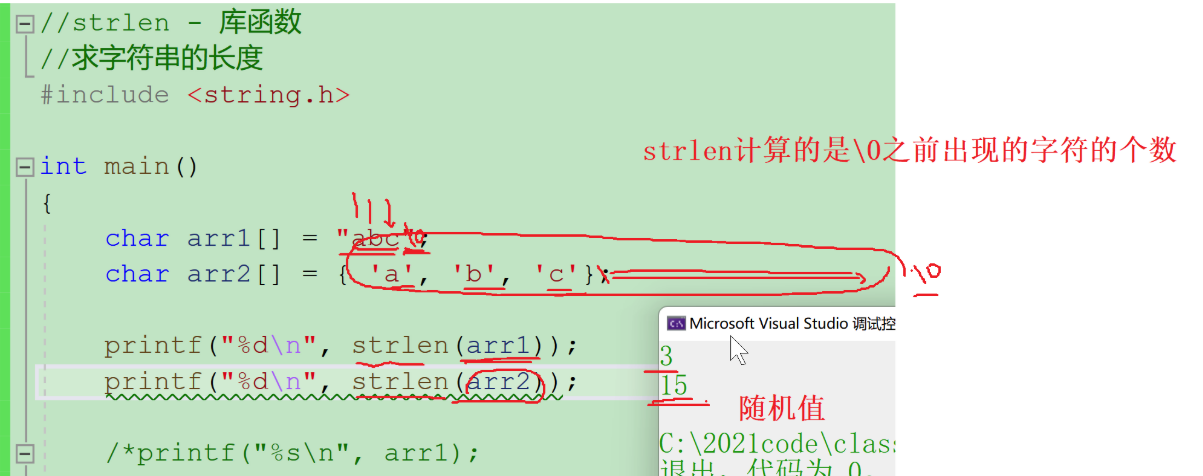
Escape characters:
Escape Character Interpretation
\?: Use when writing consecutive question marks to prevent them from being resolved into three-letter words
\': Used to represent character constants'
\": Double quotation marks used to represent the interior of a string
\: Used to represent a backslash to prevent it from being interpreted as an escape sequence character.
\a: warning character, beep
\b: Backspace character
\f: Paper feed note
\n: Line break
\r: Enter
\t: Horizontal tabs
\v: Vertical tab
\ddd:ddd represents one to three octal digits. For example: X
\xdd:dd represents two hexadecimal digits. For example: \x30
/What does the program output?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", strlen("abcdef"));
// In the following line of code, \t\ is parsed into an escape character//output result: 14 (Error prone!!!)
printf("%d\n", strlen("c:\test\628\test.c"));
return 0;
}Note:
1. Unnecessary code in the code can be deleted or commented out
2. Some of the code is difficult to understand, so add a comment
(When writing code, it's best to comment on it appropriately to make it more readable and convenient for others and yourself! It's also a good code style! I hope your friends will notice this.)
There are two styles of notes:
1.C Language Style Comments /*xxxxx*/
Defect: Comments cannot be nested
2.C++ style comment //xxxxxxx
One or more lines can be commented on
#include <stdio.h>
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x+y;
}
/*C Language Style Notes
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x-y;
}
*/
int main()
{
//C++ Comment Style
//int a = 10;
//Call the Add function to complete the addition
printf("%d\n", Add(1, 2));
return 0;
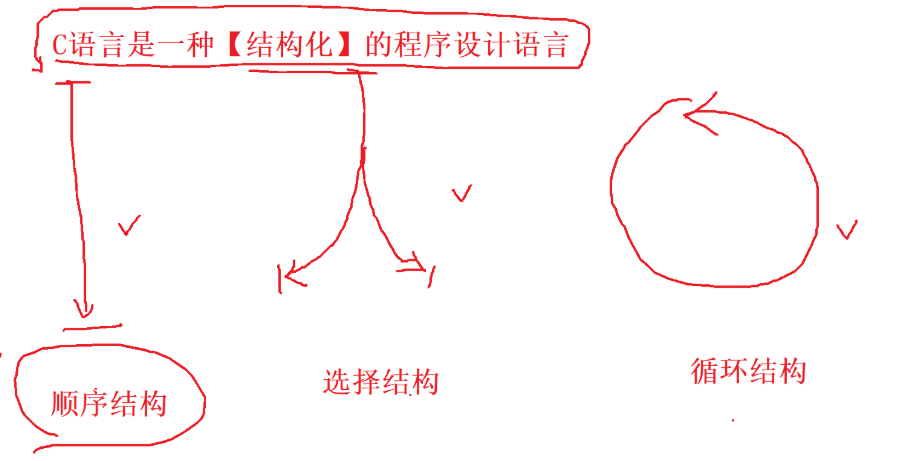
}Selection statement:
if statement
switch Statements
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int coding = 0;
printf("Will you try to type the code? (Select 1 or 0):>");
scanf("%d", &coding);
if(coding == 1)
{
prinf("You'll be fine offer\n");
}
else
{
printf("Eat the bitterness of life\n");
}
return 0;(So, friends choose 1 or 0, haha, I helped you choose 1, duck-feeding!)

Loop statement:
the while statement
for statement
Do... the while statement
//Instances of a while loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Learning Programming\n");
int line = 0;
while(line<=20000)
{
line++;
printf("I want to keep working hard on the code\n");
}
if(line>20000)
printf("good offer\n");
return 0;
}Array:
Definition of an array: a collection of elements of the same type
Definition of the array:
int arr[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};// Define an integer array with up to 10 elements
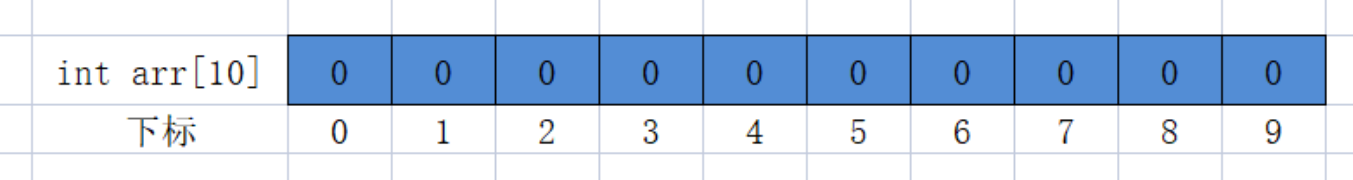
Subscripts to arrays:
Language C specifies that each element of an array has a subscript, which starts with 0.
Arrays can be accessed through subscripts.
For example:
int arr[10] = {0};
//If the array has 10 elements, the subscript range is 0-9
Use of arrays:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int arr[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
for(i=0; i<10; i++)//i starts with 0 because array subscripts start with 0
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");//Output result: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
return 0;
}Operator:
arithmetic operator
+ - * / %
Shift operators
>> <<
Bitwise operators
& ^ |
Assignment operator
= += -= *= /= &= ^= |= >>= <<=
unary operator
! Logical Inverse Operations
- Negative values
++ Positive Value
& Get Address
The type length (in bytes) of the sizeof operand
~ Bitwise inversion of a number
-- Front and rear--
+++ Front and Back++.
** Indirect access operator (dereference operator)
(Type) Cast type
Relational Operators
>
>=
<
<=
!= Used to test "inequality"
== Used to test equality
Logical Operator
&& Logic and
|| Logical or
Conditional Operator
exp1 ? exp2 : exp3
Comma expression
exp1, exp2, exp3, ...expN
Subscript references, function calls, and structure members
[] () . ->
(Get a general overview first, followed by a detailed description in the blog, don't have to memorize by heart, you can gradually remember by reading and writing the code)
This is the first time to share this issue. I hope your friends and friends will support us a lot! Thank!