Install and configure Nginx in Linux Environment
preface
It was the same project some time ago. Because the production environment was configured with nginx with domain name, it was found that the test environment had no domain name and was not installed after returning from the customer's site. Some problems were encountered during installation. Let's talk about how to install nginx and configure domain name in Linux environment
Installation preconditions
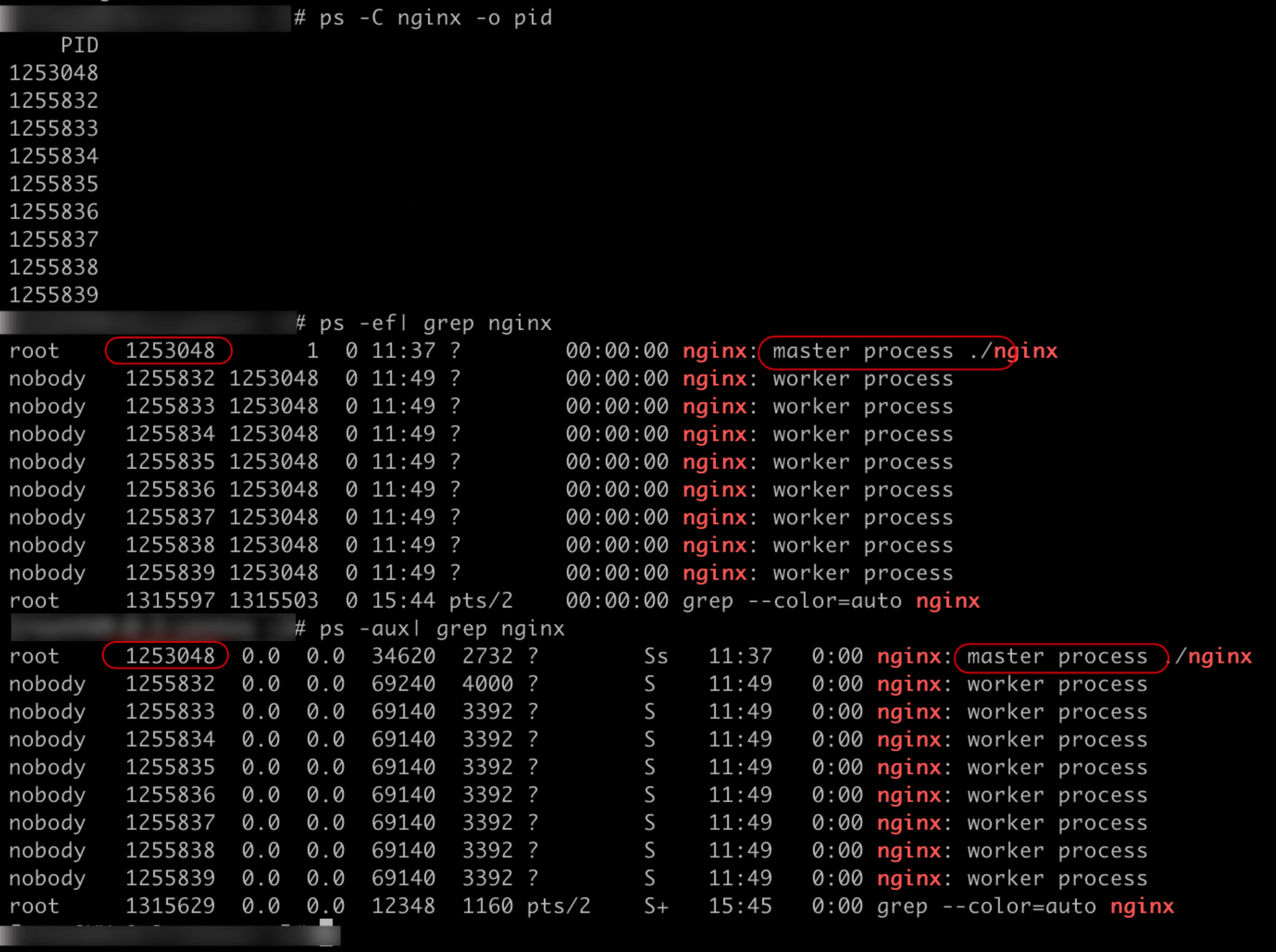
Check whether nginx is installed (if it is installed, skip the following step and stop directly
## Check the default installation path / usr/local/nginx/ cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin ## implement ./nginx -V ##If you want to upgrade the version, you can consider uninstalling and then installing it ## If it is not the default installation path, you can view the nginx path you installed by viewing the process ps -aux | grep nginx # perhaps ps -ef | grep nginx # perhaps whereis nginx
Stop nginx (if not, skip the next step)
# Method 1: go to check the default installation path and stop /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop # Method 2: stop by searching the process of nginx and killing the process # Find the process of nginx ps -ef| grep nginx # or ps -aux| grep nginx ## Force stop nginx kill -9 pid
Completely remove nginx
Find all files with nginx in the root directory
find / -name nginx
Global search often finds out many related files, but the prefixes are basically the same, and the later different parts can be replaced with * for quick deletion
rm -rf /usr/local/sbin/nginx rm -rf /usr/local/nginx rm -rf /usr/src/nginx-1.11.1 rm -rf /var/spool/mail/nginx
If Nginx startup is set, the following steps may be required
chkconfig nginx off rm -rf /etc/init.d/nginx
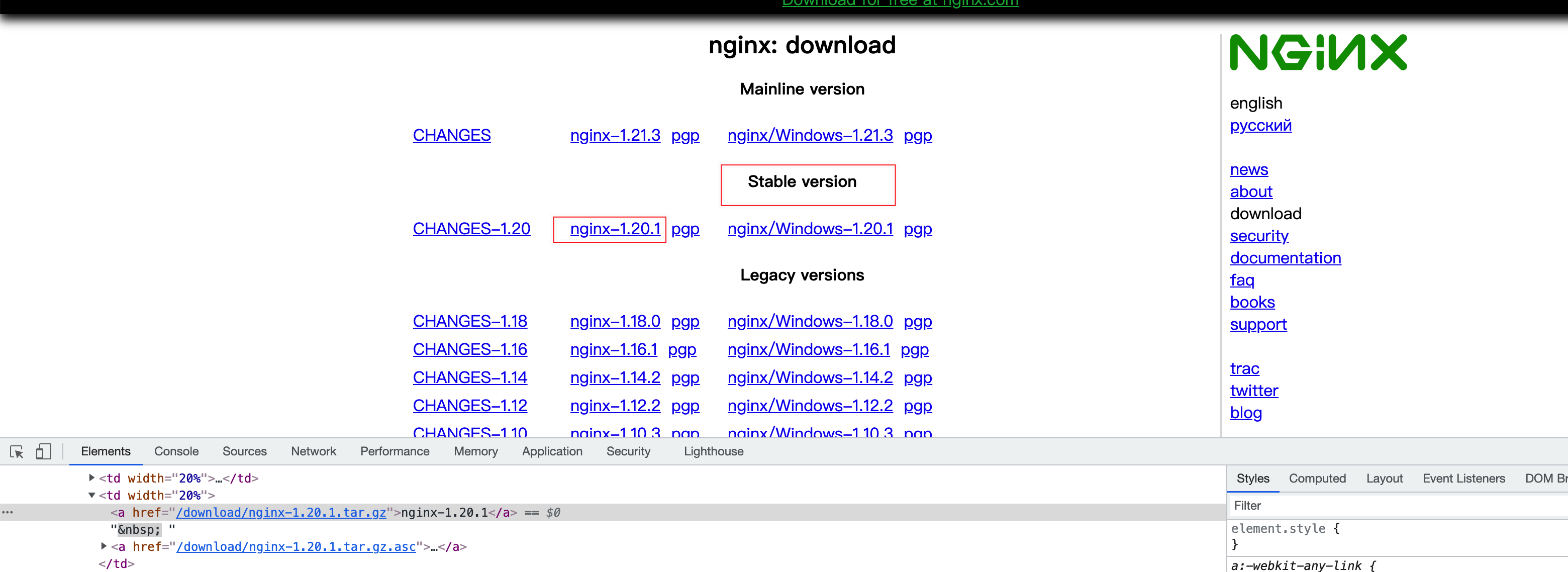
Installation package download
http://nginx.org/en/download.html
Click here to jump
It is recommended to download the stable version
Formal installation of nginx
Install software libraries that nginx depends on
yum install -y gcc openssl openssl-devel zlib zlib-devel pcre-devel
Upload the nginx package just downloaded from the official website to the server and unzip it (it is recommended to put it in the home directory)
tar -zxvf file name
Enter the extracted nginx folder and execute the following commands in sequence
./configure make make install
If the following error occurs during installation
src/os/unix/ngx_user.c:26:7: error: 'struct crypt_data' does not have the name 'current_sal'
It indicates that the version of nginx is too low or the Linux version is too high. You can try to reduce the Linux version or download the high version of nginx
Start / stop / restart nginx
Enter / usr/local/nginx/sbin
# start-up ./nginx # restart ./nginx -s reload # Stop mode I ./nginx -s stop # Stop mode 2 pkill -9 nginx # For stop mode 3, refer to the method of checking the process number of nginx above kill -9 Process number
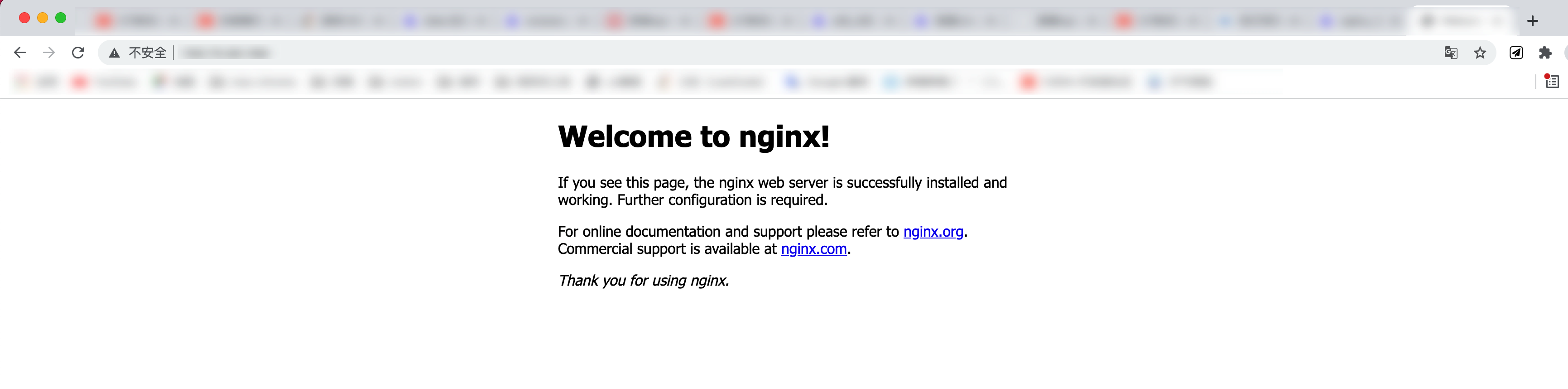
Verify that the installation was successful
If there are no changes after installation, nginx listens to port 80 by default
For browser access, if nginx does not have another listening port, it also accesses port 80
Therefore, enter the external network access IP of the server to verify

nginx configuration details
Default config configuration
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
nginx file structure
... #Global block
events { #events block
...
}
http #http block
{
... #http global block
server #server block
{
... #server global block
location [PATTERN] #location block
{
...
}
location [PATTERN]
{
...
}
}
server
{
...
}
... #http global block
}
1. Global block: configure the instructions that affect the global of nginx, generally including the user group running the nginx server, the pid storage path of nginx process, the log storage path, the introduction of configuration file, the number of worker process es allowed to be generated, etc.
2. events block: configure the network connections that affect the nginx server or users. There is the maximum number of connections per process, which event driven model is selected to process connection requests, whether multiple network connections are allowed to be accepted at the same time, and start the serialization of multiple network connections.
3. http block: it can nest multiple server s, configure most functions such as proxy, cache, log definition and configuration of third-party modules, such as file introduction, MIME type definition, log customization, whether to use sendfile to transfer files, connection timeout, number of single connection requests, etc.
4. server block: configure the relevant parameters of the virtual host. There can be multiple servers in one http.
5. location block: configure the routing of requests and the processing of various pages.
Example explanation
Let's write a simulation case
########### Each instruction must end with a semicolon.#################
#user administrator administrators; #Configure users or groups. The default is nobody.
#worker_processes 2; #The number of processes allowed to be generated. The default is 1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #Specify the storage address of nginx process running files
error_log log/error.log debug; #Set the log path and level. This setting can be put into the global block, http block and server block. The level is: debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #Set the network connection serialization to prevent group panic. The default is on
multi_accept on; #Set whether a process accepts multiple network connections at the same time. The default is off
#use epoll; #Event driven model, select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #The maximum number of connections is 512 by default
}
http {
include mime.types; #File extension and file type mapping table
default_type application/octet-stream; #The default file type is text/plain
#access_log off; #Cancel service log
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #Custom format
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined is the default value for log format
sendfile on; #sendfile mode is allowed to transfer files. The default is off. It can be in http block, server block and location block.
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #The number of transfers per call of each process cannot be greater than the set value. The default value is 0, that is, there is no upper limit.
keepalive_timeout 65; #The connection timeout, which is 75s by default, can be set in http, server and location blocks.
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:6208;
server 192.168.134.174:9909 backup; #Hot standby
}
upstream rstsvr {
server 127.0.0.1:9905 weight=10; #Weight 10 Visit the website 30 times, and the service has been visited 10 times
server 192.168.134.174:38080 weight=20; #Weight 20 Visit the website 30 times, and this service has been visited 20 times
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; # error page
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #Maximum number of single connection requests.
listen 4545; #The default listening port is 80
server_name 127.0.0.1; #Listening address or domain name
location ~*^.+$ { #Request url filtering, regular matching, ~ is case sensitive, ~ * is case insensitive.
#root path; #root directory
#index vv.txt; #Set default page
proxy_pass http://Mysvr; # request to go to the list of servers defined by mysvr
deny 127.0.0.1; #Rejected ip
allow 192.168.134.176; #Allowed ip
}
location ^~/rstsvr { #Request url filtering, regular matching, ~ is case sensitive, ~ * is case insensitive.
#root path; #root directory
#index vv.txt; #Set default page
proxy_pass http://Rstsvr; # request to go to the list of servers defined by rstsvr
deny 127.0.0.1; #Rejected ip
allow 192.168.134.176; #Allowed ip
}
}
}
The above is the basic configuration of nginx. You should pay attention to the following points
1. Basic configuration
1.
r
e
m
o
t
e
a
d
d
r
And
remote_addr and
remotea ddr and http_x_forwarded_for are used to record the ip address of the client;
2.
r
e
m
o
t
e
u
s
e
r
:
use
come
remember
record
passenger
household
end
use
household
name
call
;
3.
remote_user: used to record the client user name; 3
remoteu # ser: used to record the client user name; 3.time_local: used to record the access time and time zone;
4.
r
e
q
u
e
s
t
:
use
come
remember
record
please
seek
of
u
r
l
And
h
t
t
p
Assist
Discuss
;
5.
Request: the url and http protocol used to record the request; 5
Request: used to record the url and http protocol of the request; 5.status: used to record the request status; success is 200;
6.
b
o
d
y
b
y
t
e
s
s
e
n
t
:
remember
record
hair
give
to
passenger
household
end
writing
piece
main
body
within
Allow
large
Small
;
7.
body_bytes_s ent: records the size of the body content of the file sent to the client; 7
bodyb # ytess # ent: records the size of the body content of the file sent to the client; 7.http_referer: used to record the link accessed from that page;
8.$http_user_agent: record the relevant information of the client browser;
2. Group startling phenomenon
When a network connection arrives, multiple sleeping processes are awakened by colleagues, but only one process can get the link, which will affect the system performance.
3. Each instruction must end with a semicolon.
Xiao Qi also added configuration while groping, and there will be specific cases to supplement later
Share a sentence I particularly like: every day is a new day. Of course, luck is good, but I'd like to make no difference. In this way, when luck comes, you will be ready———— Hemingway's the old man and the sea