I Introduction to CJSON
1.1 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight text data exchange format, which is easy to read. At the same time, it is also easy for machine analysis and generation. Although JSON is a subset of Javascript, it is a language independent text format and adopts some habits similar to the C language family.
1.2 JSON structure
typedef struct cJSON
{
struct cJSON *next;
struct cJSON *prev;
struct cJSON *child;
int type;
char *valuestring;
int valueint;
double valuedouble;
char *string;
} cJSON;
next and prev : Cjson As a ring with two-way tables, the structure can be connected through next and prev Pointer for table traversal child: Can be cJSON_Array,cJSON_Object Type data type: Type of current item valuestring: Content storage, when the type is cJSON_String and cJSON_Raw valueint: Content storage, integer, can be cJSON_False,cJSON_True data valuedouble: Content store, floating point, when the type is cJSON_Number string: Key name
II Common library functions of CJSON Library
analysis
2.1.cJSON_Parse
JSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value);
Function: serialize a JSON packet according to the structure of the cJSON structure, and open up a memory in the heap to store the cJSON structure
NULL: a pointer to the success of the memory block, and a value returned from the failure
2.2. cJSON_Print
char *cJSON_Print(cJSON *item);
Function: parse cJSON data into JSON string, and open up a memory space of char * in the heap to store JSON string
Return value: a char * pointer is returned successfully, which points to the JSON string in the heap, and NULL is returned in case of failure
2.3 cJSON_PrintUnformatted
And cjson_ The print function is similar. But it is unformatted output.
establish
2.4 cJSON_CreateObject
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateObject(void);
After creating a JSON object, you can add data items such as string or int to this object. Using this function will open up a space in memory through malloc() function, which needs to be released manually after use.
Other creation
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateNull(void); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateTrue(void); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateFalse(void); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateBool(cJSON_bool boolean); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateNumber(double num); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateString(const char *string); /* raw json */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateRaw(const char *raw); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateArray(void); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateObject(void); /* Create a string where valuestring references a string so * it will not be freed by cJSON_Delete */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateStringReference(const char *string); /* Create an object/array that only references it's elements so * they will not be freed by cJSON_Delete */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateObjectReference(const cJSON *child); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateArrayReference(const cJSON *child); /* These utilities create an Array of count items. * The parameter count cannot be greater than the number of elements in the number array, otherwise array access will be out of bounds.*/ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers, int count); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers, int count); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers, int count); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char *const *strings, int count);
add to
2.5 cJSON_AddItemToObject
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);
Function: add an object object item named string to an object object object
2.6 cJSON_AddItemToArray
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
Adding elements to an array
cJSON *array: indicates the array to be added
cJSON *item: array object to add
Other additions
/* Append item to the specified array/object. */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item); /* Use this when string is definitely const (i.e. a literal, or as good as), and will definitely survive the cJSON object. * WARNING: When this function was used, make sure to always check that (item->type & cJSON_StringIsConst) is zero before * writing to `item->string` */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item); /* Append reference to item to the specified array/object. Use this when you want to add an existing cJSON to a new cJSON, but don't want to corrupt your existing cJSON. */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);
delete
2.7 cJSON_Delete() and cJSON_free
After the cjson object is created, the memory needs to be released after processing:
If it is an object in cjson, please use cJSON_Delete()
If not object: cJSON_free() or free()
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_Delete(cJSON *item); CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_free(void *object);
obtain
7.1: cJSON_GetObjectItem
cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string);
Function: get JSON string field value
Return value: a pointer to the structure of cJSON type is returned successfully, and NULL is returned in failure
Other acquisition
7.2: cJSON_GetArraySize
CJSON_PUBLIC(int) cJSON_GetArraySize(const cJSON *array);
Gets the format of the elements in the array and returns
7.3: cJSON_GetArrayItem
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_GetArrayItem(const cJSON *array, int index);
Get the index data element in the array and return
/* Returns the number of items in an array (or object). */ CJSON_PUBLIC(int) cJSON_GetArraySize(const cJSON *array); /* Retrieve item number "index" from array "array". Returns NULL if unsuccessful. */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_GetArrayItem(const cJSON *array, int index); /* Get item "string" from object. Case insensitive. */ CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_GetObjectItem(const cJSON * const object, const char * const string); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON *) cJSON_GetObjectItemCaseSensitive(const cJSON * const object, const char * const string); CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON_bool) cJSON_HasObjectItem(const cJSON *object, const char *string); /* For analysing failed parses. This returns a pointer to the parse error. You'll probably need to look a few chars back to make sense of it. Defined when cJSON_Parse() returns 0. 0 when cJSON_Parse() succeeds. */ CJSON_PUBLIC(const char *) cJSON_GetErrorPtr(void); /* Check item type and return its value */ CJSON_PUBLIC(char *) cJSON_GetStringValue(const cJSON * const item); CJSON_PUBLIC(double) cJSON_GetNumberValue(const cJSON * const ite
Reference link: Introduction to common cJSON library functions
III. installation and use examples of CJSON Library
3.1 cJSON Library Download
git clone https://github.com/DaveGamble/cJSON.git
Then we go to the cJSON folder and see cJSON c and cJSON h. When a c file needs to be called, move the two files to the corresponding c folder

Packaging instances using the cJSON Library
/*********************************************************************************
* Copyright: (C) 2022 hubeiwuhan
* All rights reserved.
*
* Filename: cjsontest.c
* Description: This file
*
* Version: 1.0.0(03/03/22)
* Author: yanp <2405204881@qq.com>
* ChangeLog: 1, Release initial version on "03/03/22 12:49:44"
*
********************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
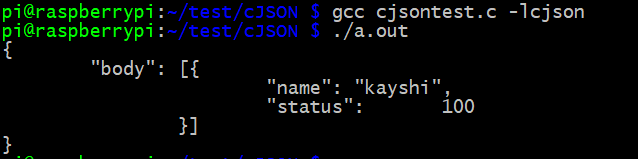
int main()
{
cJSON *root, *js_body, *js_list;
root = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "body", js_body = cJSON_CreateArray());
cJSON_AddItemToArray(js_body, js_list = cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddStringToObject(js_list, "name", "kayshi");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(js_list, "status", 100);
char *s = cJSON_Print(root);
if(s)
{
printf("%s \n", s);
free(s);
}
if(root)
cJSON_Delete(root);
return 0;
}