1, Introduction
Docker is an open source application container engine; Is a lightweight container technology;
Docker supports compiling software into an image; Then, configure various software in the image and publish the image, so that other users can directly use the image;
The running image is called a container, and the container startup is very fast.

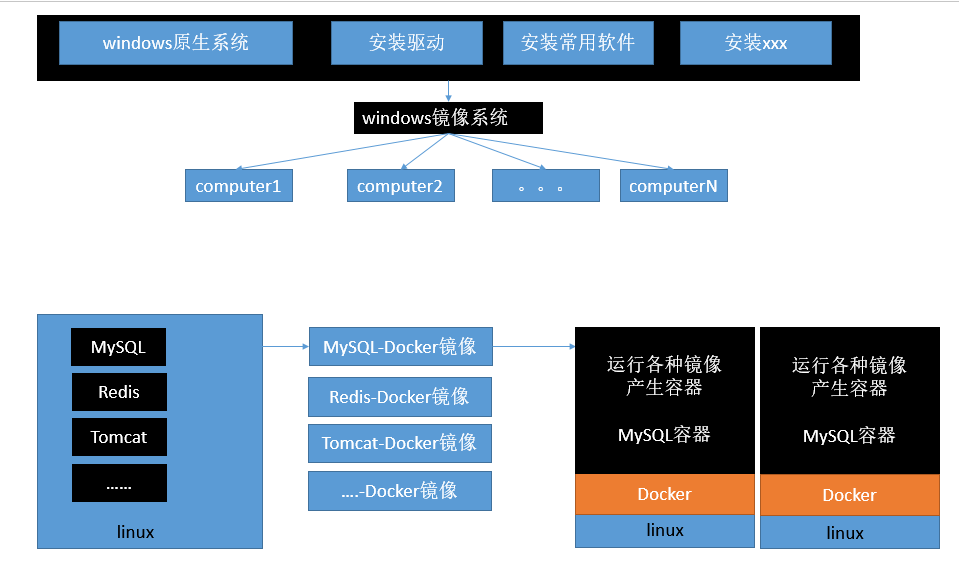
Concept:
- Docker host: the machine on which the docker program is installed (docker is directly installed on the operating system);
- Docker client: connect to the docker host for operation;
- docker repository (Registry): used to store various packaged software images;
- Docker images: images packaged by software; Put it in docker warehouse;
- docker container: the instance after the image is started is called a container; A container is an application or group of applications that run independently
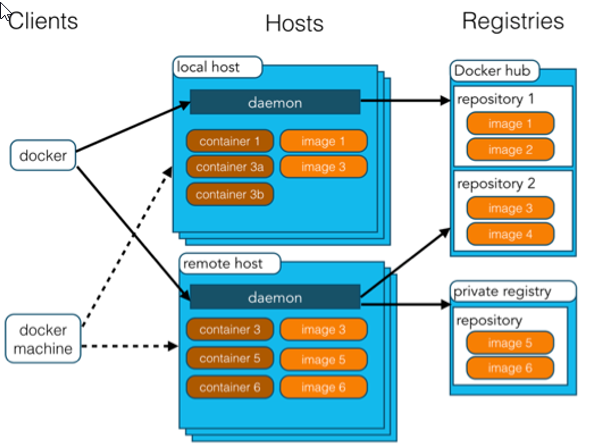
Steps to use Docker:
- Install Docker
- Go to the Docker warehouse to find the corresponding image of the software;
- Run the image using Docker, and the image will generate a Docker container;
- The start and stop of the container is the start and stop of the software;
2, Install Docker
-
Check the kernel version, which must be 3.10 or above
My is the Centos7 and linux 3.10 kernel installed by aliyun. docker officially says it is at least 3.8 or above, and it is recommended to be above 3.10
Log in to the root account and view the kernel version as follows:uname ‐r [root@loaclhost ~]# uname -r 3.10.0-957.21.3.el7.x86_64
-
Install docker
yum install docker
-
Enter y to confirm installation
-
Start docker
systemctl start docker [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start docker [root@localhost ~]# docker ‐v Docker version 1.12.6, build 3e8e77d/1.12.6
-
Boot docker
systemctl enable docker [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable docker Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi‐user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.
-
Stop docker
systemctl stop docker
3, Docker common commands & Operations
1. Mirror operation
| operation | command | explain |
|---|---|---|
| retrieval | docker search keyword eg: dockersearch redis | Often go to the docker hub to retrieve the image details, such as the image TAG |
| Pull | docker pull image name: tag | : tag is optional. Tag indicates the label. Most of them are software versions. The default is latest |
| list | docker images | View all local mirrors |
| delete | docker rmi image-id | Deletes the specified local mirror |
docker official website: https://hub.docker.com/
2. Container operation
Software image (QQ installer) -- running image -- generating a container (running software, running QQ);
1. Search image [root@localhost ~]# docker search tomcat 2. Pull image [root@localhost ~]# docker pull tomcat 3. Boot container based on image docker run ‐‐name mytomcat ‐d tomcat:latest 4. Viewing running containers docker ps 5. Stop the running container docker stop Container id 6. View all containers docker ps ‐a 7. Start container docker start container id 8. Delete a container docker rm container id 9. Start a port mapped tomcat [root@localhost ~]# docker run ‐d ‐p 8888:8080 tomcat ‐d: Background operation ‐p: Map the host's port to one of the container's ports Host port:Port inside container 10. For the sake of demonstration, it is simply closed linux Firewall service firewalld status ;View firewall status service firewalld stop: Turn off firewall 11. Viewing container logs docker logs container‐name/container‐id For more commands, see https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/docker/ You can refer to each mirrored document
4, Sample installation MySQL
1. Pull the image mysql5 seven
docker pull mysql:5.7 #Due to network problems, the pull may fail. Try several more times ~, or configure the alicloud image accelerator
2. Check whether the docker image is downloaded successfully
docker images

3. Create mysql container
docker run --name mysql -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -d mysql:5.7 --name Container name, set to mysql; -p Port mapping. Host port: container port; -v To mount the host directory to the container directory, you need to mount the original data and configuration files; -e Container variables. MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456,Set the password to 123456; -d Run the container in the background and return to the container ID
After installation, MySQL services and storage mounts are all in the container. In case the container goes down once, the content will disappear, so you need to put the data on the host.
# create folder mkdir -p /data/mysql/datadir mkdir /data/mysql/conf.d docker run --name mysql5.7 -p 3320:3306 -v /data/mysql/datadir/:/var/lib/mysql -v /data/mysql/conf.d:/etc/mysql/conf.d # Put the mysql storage path into the new datadir folder and the configuration file into conf.d -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -d mysql:5.7
4. View running status
docker ps

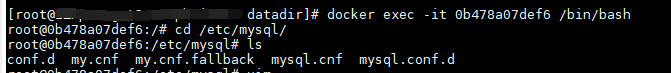
Enter docker:
docker exec -it 0b478a07def6 /bin/bash #/bin/bash: after entering the container, the status is interactive, that is, you can issue commands
5. Remote tool connection test
- If it is an ECS, remember to open the port number
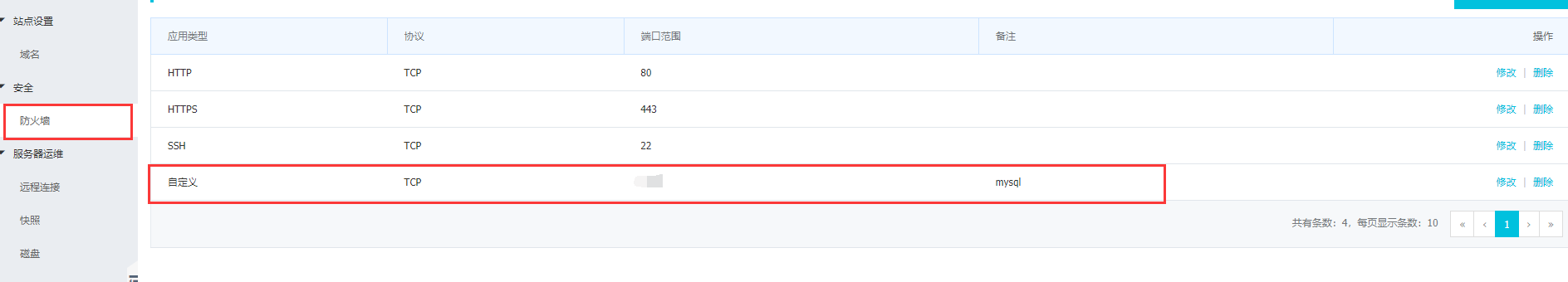
- Turn off firewall or open port for local virtual machine
Firewalld is installed by default in Centos7. If it is not installed, you can use Yum install firewalld firewalld config to install it.
1.Start firewall systemctl start firewalld 2.Disable firewall systemctl stop firewalld 3.Set startup systemctl enable firewalld 4.Stop and disable boot sytemctl disable firewalld 5.service iptables restart firewall-cmd --reload 6.View status systemctl status firewalld perhaps firewall-cmd --state 7.View version firewall-cmd --version 8.view help firewall-cmd --help 9.View area information firewall-cmd --get-active-zones 10.View the area information of the specified interface firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=eth0 11.Reject all packages firewall-cmd --panic-on 12.Cancel reject status firewall-cmd --panic-off 13.Check whether to reject firewall-cmd --query-panic 14.Add interface to area(The default interfaces are public) firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-interface=eth0(Permanent plus --permanent then reload firewall) 15.Set default interface area firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=public(Effective immediately without restart) 16.Update firewall rules firewall-cmd --reload or firewall-cmd --complete-reload(The difference between the two is that the first one does not need to be disconnected firewalld One of the characteristics is dynamic Add a rule. The second one needs to be disconnected, which is similar to restarting the service) 17.View all open ports in the specified area firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports 18.Open the port in the specified area (remember to restart the firewall) firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp(Permanent plus --permanent) –zone Scope –add-port=8080/tcp Add a port in the format:/Communication protocol –permanent #It will take effect permanently. It will become invalid after restart without this parameter
Finally, the connection is successful!!!