Elasticsearch is an open-source distributed RESTful search and analysis engine, which enables you to store, search and analyze a large amount of data quickly and almost in real time, and can solve more and more different application scenarios.
- For example, it is used to search goods in online stores, search users, and search transaction data.
- Business collection and storage
- Report analysis
How to use elasticsearch to store and query data in Springboot? At present, the following methods are more convenient:
- REST Client
- Spring Data
- Spring Data Elasticsearch Repositories
This article will use Spring Data Elasticsearch Repositories to access Elasticsearch.
prepare
You need to build an elasticsearch. The version of elasticsearch is 7.7.0. This elasticsearch is a stand-alone version of elasticsearch, and the production environment should use the cluster version. Execute the following command to install
# Download rpm for elasticsearch wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.7.0-x86_64.rpm wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.7.0-x86_64.rpm.sha512 shasum -a 512 -c elasticsearch-7.7.0-x86_64.rpm.sha512 sudo rpm --install elasticsearch-7.7.0-x86_64.rpm sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service sudo systemctl start elasticsearch.servic
Modify es to other ip access:
cluster.name: "docker-cluster" network.host: 0.0.0.0 # custom config node.name: "node-1" discovery.seed_hosts: ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"] # Enable cross domain access support. The default value is false http.cors.enabled: true # Cross domain access to allowed domain names and addresses, (all domain names are allowed) use regular http.cors.allow-origin: /.*/
Spring boot integrates Elasticsearch
In the pom file of the springboot project, the start of elasticsearch depends on spring boot starter data elasticsearch, as follows:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId> </dependency>
In the springboot configuration file application The properties file fills in the configuration of elasticsearch. The 9300 port used here is the TCP protocol port.
server.port=8500 spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes=127.0.0.1:9300 spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-name=my-application
Similar to most spring boot starter data JPA, entity objects are used to correspond to the storage structure fields of the database. Using @ Document(indexName = "user") annotation, a user index will be created in elasticsearch, and the white name uId field of @ id annotation is the id field of elasticsearch.
@Document(indexName = "user")
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
private String uId;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
//Omit getter setter
}Write an interface UserRepository to inherit ElasticsearchRepository. ElasticsearchRepository contains the basic ability to add, delete, modify and query. Add @ Repository annotation on the interface class and inject it into the spring container.
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<User, String> {
}UserServiceImpl class operates the interface of UserRepository and Elasticsearch.
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public long count() {
return userRepository.count();
}
@Override
public User save(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Override
public void delete(User user) {
userRepository.delete(user);
}
@Override
public Iterable<User> getAll() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public List<User> getByName(String name) {
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
MatchQueryBuilder matchQueryBuilder = new MatchQueryBuilder("name", name);
Iterable<User> iterable = userRepository.search(matchQueryBuilder);
iterable.forEach(e->list.add(e));
return list;
}
@Override
public Page<User> pageQuery(Integer pageNo, Integer pageSize, String kw) {
NativeSearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder()
.withQuery(QueryBuilders.matchPhraseQuery("name", kw))
.withPageable(PageRequest.of(pageNo, pageSize))
.build();
return userRepository.search(searchQuery);
}
}Write a test class, and then call the interface in turn:
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/testInsert")
public void testInsert() {
User user = new User();
user.setuId("1");
user.setName("zhangsna");
user.setAge(101);
user.setAddress("Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province");
userService.save(user);
user.setuId("2");
user.setName("lisi");
user.setAge(32);
user.setAddress("Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province");
userService.save(user);
user.setuId("3");
user.setName("wangwu");
user.setAge(34);
user.setAddress("Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province");
userService.save(user);
}
@GetMapping("/testDelete")
public void testDelete() {
User user = new User();
user.setuId("1");
userService.delete(user);
}
@GetMapping("/testGetAll")
public void testGetAll() {
Iterable<User> iterable = userService.getAll();
iterable.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.toString()));
}
@GetMapping("/testGetByName")
public void testGetByName() {
List<User> list = userService.getByName("lisi");
System.out.println(list);
}
@GetMapping("/testPage")
public void testPage() {
Page<User> page = userService.pageQuery(0, 10, "wangwu");
System.out.println(page.getTotalPages());
System.out.println(page.getNumber());
System.out.println(page.getContent());
}
}kibana display data
First, follow kibana. The installation command is as follows:
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.7.0-x86_64.rpm shasum -a 512 kibana-7.7.0-x86_64.rpm sudo rpm --install kibana-7.7.0-x86_64.rpm //Set kibana to start automatically sudo /bin/systemctl daemon-reload sudo /bin/systemctl enable kibana.service sudo systemctl start kibana.service //Start kibana sudo systemctl stop kibana.service //Stop kibana
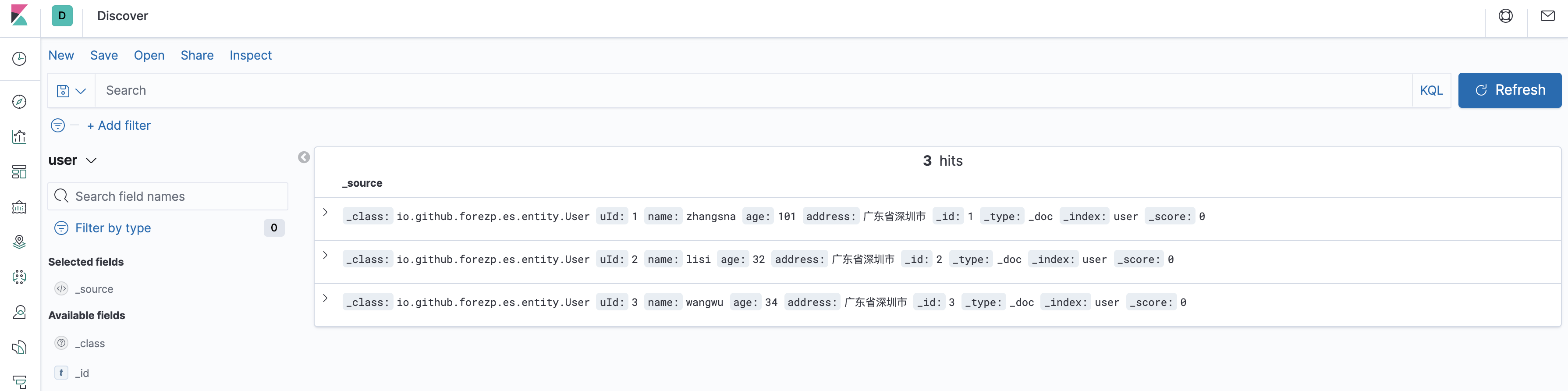
After successful startup, access kibana's address on the browser http://10.10.10.1:5601 , enter kibana's main interface. Then enter the Discover interface. Select the user's index to display the data normally. The data is as follows: