1, Inter thread communication
There are two models of inter thread communication: shared memory {and} message passing. The following methods are implemented based on these two models.
When the thread start() method is called, it is scheduled by the operating system, and the execution order is not fixed.
If you want threads to execute in the required order, you need to communicate between threads.
2, Multithreaded programming steps (medium)
Step 1: create a resource class and create data and operation methods in the resource class;
Step 2: operate the method in the resource class
(1) judgment
(2) work
(3) Notice
Step 3: create multiple threads and call the operation methods of the resource class;
3, Example 1
4, Example 2
Requirements: there are two threads to operate on a variable with an initial value of 0. One thread adds 1 to the current value and the other thread subtracts 1 to the current value. The two threads alternately complete the effect. Inter thread communication is required.
Synchronized implementation:
//The first step is to create a resource class and define properties and operation methods
class Share {
//Initial value
private int number = 0;
//+1
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
//The second step is to judge, work and inform
//1.Judgment: number Whether the value is 0. If not, wait
if (number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
//2.Work: if number If the value is 0, then +1 operation
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
//3.notice
this.notifyAll();
}
//-1
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
//The second step is to judge, work and inform
//1.Judgment: number Whether the value is 1. If not, wait
if (number != 1) {
this.wait();
}
//2.Work: if number If the value is 1, then -1 operation
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
//3.notice
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//The third step is to create multiple threads and call the operation methods of the resource class;
Share share = new Share();
//Create thread
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BB").start();
}
}
5, False awakening problem
1. Modify to four threads
//The first step is to create a resource class and define properties and operation methods
class Share {
//Initial value
private int number = 0;
//+1
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
//The second step is to judge, work and inform
//1.Judgment: number Whether the value is 0. If not, wait
if (number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
//2.Work: if number If the value is 0, then +1 operation
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
//3.notice
this.notifyAll();
}
//-1
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
//The second step is to judge, work and inform
//1.Judgment: number Whether the value is 1. If not, wait
if (number != 1) {
this.wait();
}
//2.Work: if number If the value is 1, then -1 operation
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
//3.notice
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//The third step is to create multiple threads and call the operation methods of the resource class;
Share share = new Share();
//Create thread
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BB").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "CC").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "DD").start();
}
}
2. Operation results
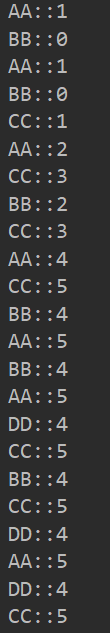
3. Analyze the causes
Changing to 4 or more threads will lead to errors and false wake-up!
Reason: if judgment is used. If the judgment is effective, there will be no problem. Why is the judgment not effective?
Take a look at the wait() method description:
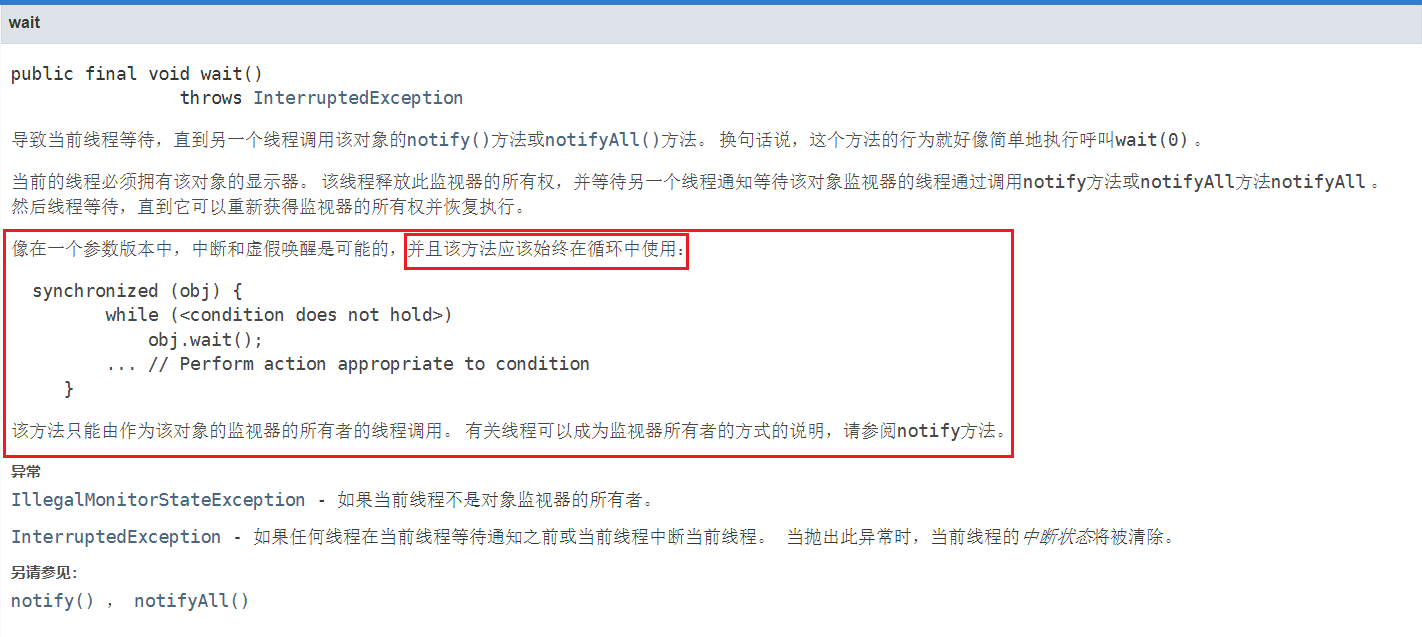
False wake-up:
Schematic diagram:
Normal conditions:
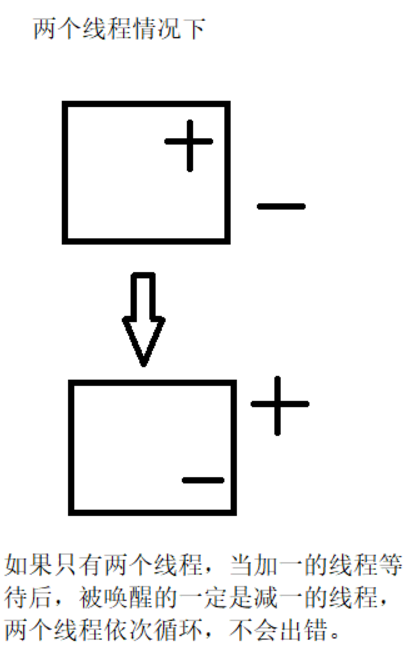
Four threads:
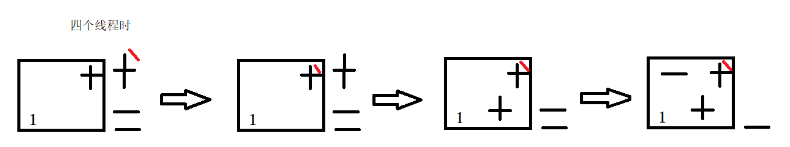
4. Solutions
//The first step is to create a resource class and define properties and operation methods
class Share {
//Initial value
private int number = 0;
//+1
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
//The second step is to judge, work and inform
//1.Judgment: number Whether the value is 0. If not, wait
while (number != 0) {
this.wait(); //Where you sleep, you wake up
}
//2.Work: if number If the value is 0, then +1 operation
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
//3.notice
this.notifyAll();
}
//-1
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
//The second step is to judge, work and inform
//1.Judgment: number Whether the value is 1. If not, wait
while (number != 1) {
this.wait();
}
//2.Work: if number If the value is 1, then -1 operation
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
//3.notice
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//The third step is to create multiple threads and call the operation methods of the resource class;
Share share = new Share();
//Create thread
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BB").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "CC").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "DD").start();
}
}
6, Multithreaded programming steps (Part 2)
Step 1: create a resource class and create data and operation methods in the resource class;
Step 2: operate the method in the resource class
(1) judgment
(2) work
(3) Notice
Step 3: create multiple threads and call the operation methods of the resource class;
Step 4: in order to prevent false awakening, use while judgment;