Inner class and API, exception
Inner class
- Access characteristics of internal classes
Internal classes can directly access members of external classes, including private classes
An object must be created for an external class to access members of an internal class - The definition location of the class inside the member
In a class, a method is in the same place as a member variable
- External member internal class format
Format: external class name Internal class name object name = external class object Internal class objects;
Example: outer Inner oi = new Outer(). new Inner();
- Recommended usage scheme of inner class of member
For the purpose of designing a class as an internal class, most of them do not want to be accessed by the outside world, so the definition of the internal class should be privatized. After privatization, a method that can be called by the outside world is provided. The internal class object is created and called inside the method.
The biggest difference between c + + internal class and java internal class is that the internal class object of c + + has no pointer to the external class object and cannot access the non static members of the external class object; java's non static internal class object has a pointer to the external class object, which can access the non static members of the external class object.
There are multiple inner classes in java, as well as anonymous inner classes.
Local class (less used)
- **Local internal class definition location**
A local inner class is a class defined in a method
- Local internal class mode
Local internal classes cannot be used directly by the outside world. You need to create objects inside the method and use them
This class can directly access members of external classes or local variables in methods
Anonymous Inner Class
- Premise of anonymous inner class
There is a class or interface, where the class can be concrete or abstract
- Format of anonymous inner class
Format: new class name () {rewrite method} new interface name () {rewrite method}
new Inter()
{
@Override
public void method(){}
}
- The nature of anonymous inner classes
Essence: it is an anonymous object that inherits the class or implements the subclass of the interface
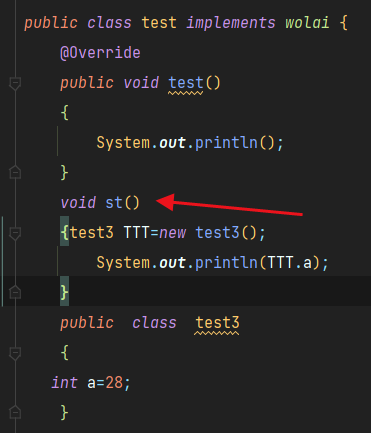
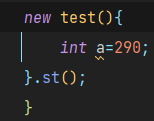
You can call the parent class member method through the anonymous object, and you can also receive the object in a polymorphic way
Anonymous inner classes can be accepted in the form of polymorphism
Inter i = new Inter(){ @Override public void method(){ } }
Anonymous inner classes call methods directly
interface Inter
{ void method(); }
class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args){
new Inter(){
@Override
public void method()
{ System.out.println("I am an anonymous inner class"); }
}.method(); // Direct call method}
}
Use of anonymous inner classes in development
When a method needs a subclass object of an interface or abstract class, we can pass an anonymous inner class to simplify the traditional code
System class
public static void exit(int status)
Terminate the current java virtual machine. Non zero indicates abnormal termination
public static long currentTimeMillis() returns the current time in milliseconds
Basic type packing class
Integer to string:Also available String.valueof String str = Integer.toString(i); String to integer:It can also be used parseInt method int i = Integer.valueOf(str).intValue(); double Type, please see Double method toLowerCase,toUpperCase Convert case
Date class
Date()
Allocate a Date object and initialize it so that it represents the allocated time, in the nearest millisecond.
boolean after(Date when) Tests whether this date is after the specified date. boolean before(Date when) Test whether this date is before the specified date. Object clone() Returns a copy of this object. int compareTo(Date anotherDate) Compare two dates to order. boolean equals(Object obj) Compare the two dates to be equal. static Date from(Instant instant) from Instant Object acquisition Date An example.
case
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy year M month d day");
Date date = new Date();
String format = sdf1.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
2022 January 14
Implementation of date tool class
public class data {
private data() { };
public static String ToString(Date d, String format) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(format);
return sdf.format(d);
}
public static Date todata(String S, String format) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(format);
return sdf.parse(S);
}
}
Calendar Class
static Calendar getInstance() Gets the calendar using the default time zone and locale. static Calendar getInstance(Locale aLocale) Gets the calendar using the default time zone and the specified locale. static Calendar getInstance(TimeZone zone) Gets the calendar using the specified time zone and default locale. static Calendar getInstance(TimeZone zone, Locale aLocale) Gets the calendar with the specified time zone and locale abstract void add(int field, int amount) Add or subtract the specified amount of time from the given calendar field according to the rules of the calendar. boolean after(Object when) return Calendar Indicates whether the specified Object Represents the time after the time of. boolean before(Object when) Return to this Calendar Indicates whether the specified Object Represents the time before the time of.
February day case
public class hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Please enter the year to query:");
Scanner Sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int number=Sc.nextInt();
calendar.set(number,2,1);
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,-1);
System.out.println(number+"In February of"+calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)+"day");
}
}
Please enter the year to query:
2018
2018 There are 28 days in February